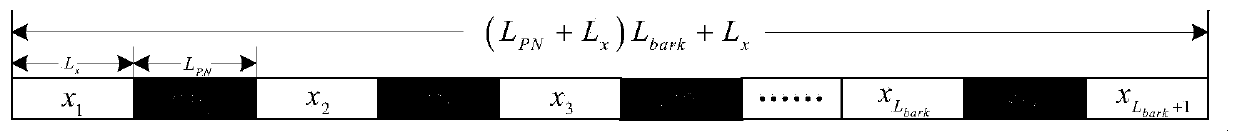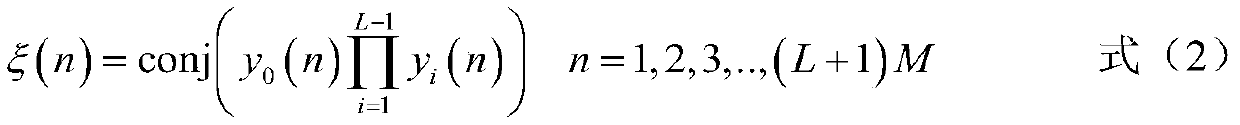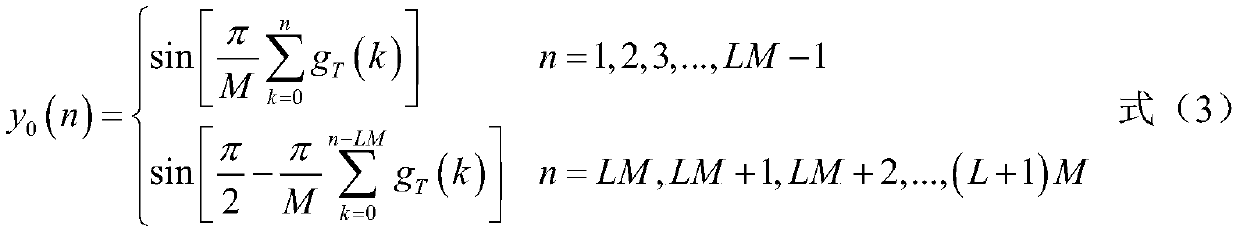A low-complexity GMSK demodulation timing synchronization method in burst communication
A low-complexity, timing synchronization technology, used in synchronization devices, FM carrier systems, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as reducing data reliability, having threshold effects, and weak anti-noise ability, eliminating accumulated errors and realizing The effect of simple architecture and improved robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
[0043] The specific steps of a low-complexity GMSK demodulation timing synchronization method in burst communication are as follows:
[0044] Step 1: The receiving end in communication continuously receives the zero-IF sequence S after AD sampling; the initial value of the flag bit Flag is set to 0. Such as figure 1 As shown, the data frame of this communication system consists of the original information sequence according to the length L bark Each bit value of the Barker code is equally spaced into L bark Pseudo-random synchronization sequence PN a Obtained, the values of a are 0 and 1, which correspond to 0 and 1 of the Barker codeword. All synchronization sequences PN a The length is L PN , by the pseudorandom synchronization sequence PN a The length of each separated information sequence is L x .
[0045] Matched filtering. Compute the filtered output seque...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap