A method for evaluating the exposure risk of tobacco-specific nitrosamines to animals
A technology based on exposure risk and animal body, applied in the field of carcinogen exposure risk assessment, can solve problems such as inability to quantify the potential exposure risk of TSNAs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
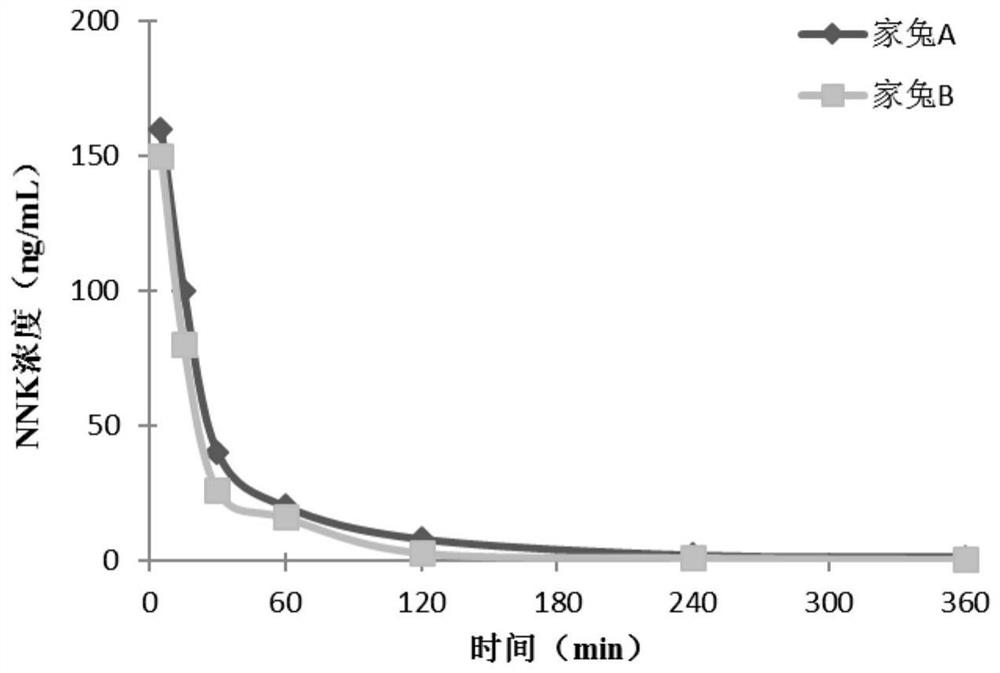
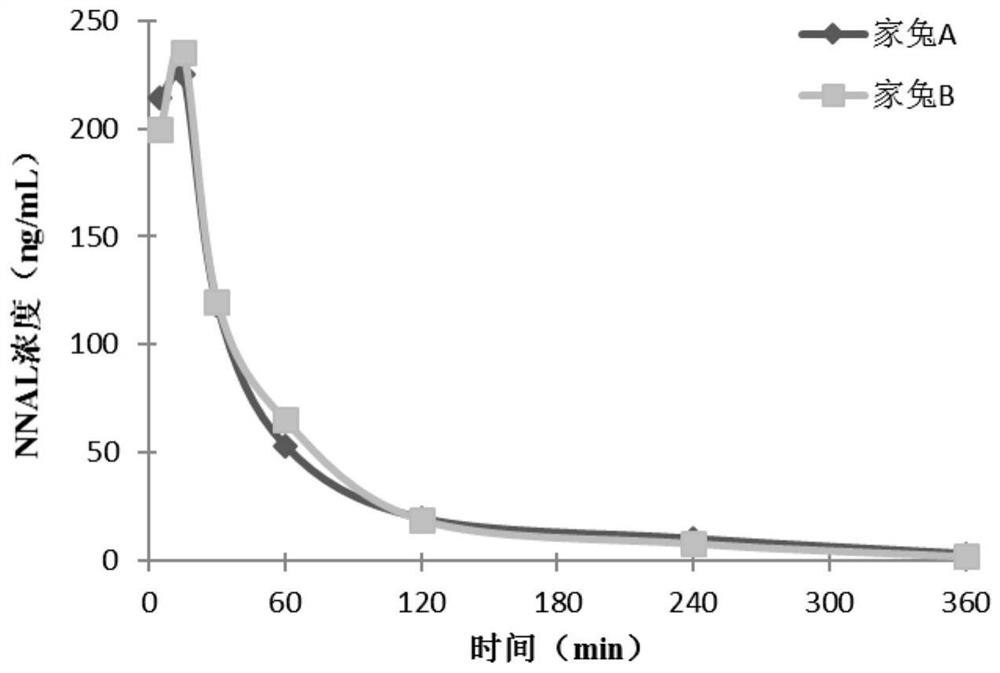
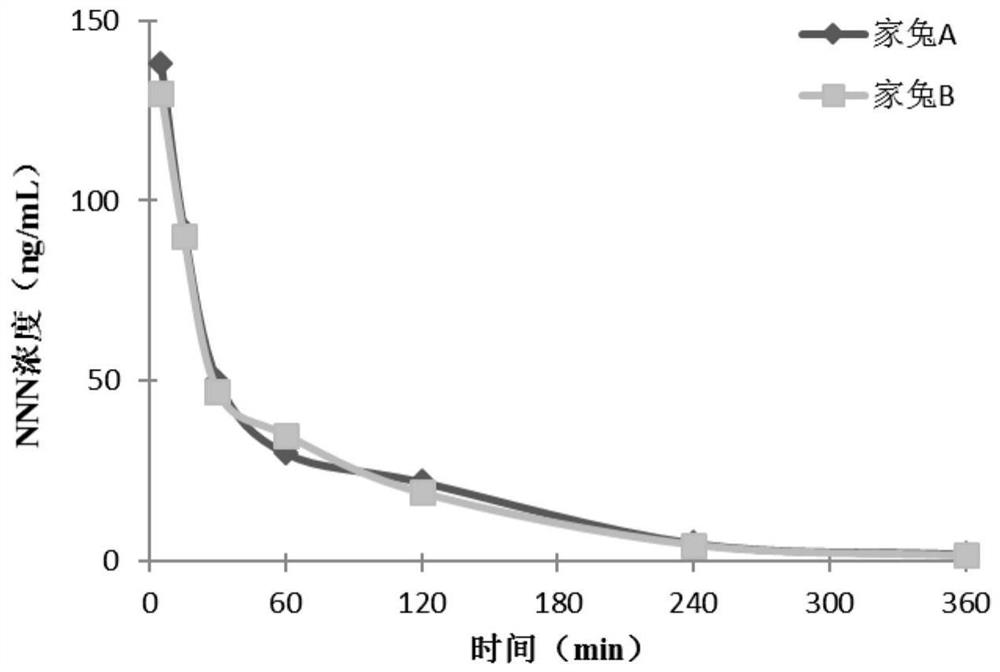
[0032] The present invention mainly uses a certain dose of representative TSNAs (NNK, NNAL, NNN, NAB) solution to expose animal models, and uses high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to measure the direct metabolites of TSNAs in blood and the indirect metabolites in liver tissue , on the basis of obtaining the relative amount of TSNAs and their metabolites entering the systemic circulation, according to the ratio of the total amount of α-hydroxylation metabolic pathway products in the blood to the relative amount of TSNAs entering the systemic circulation (α-hydroxylation coefficient) and the main metabolic organ The production of representative DNA adducts within the body was used to assess the degree of α-hydroxylation in different individuals after exposure to TSNAs.
[0033] On the one hand, this method uses the ratio of direct metabolites in the blood to reflect the average degree of α-hydroxylation metabolism of TSNAs in the body; The degree of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com