Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on vibration signal analysis
A vibration signal, rolling bearing technology, applied in the testing of mechanical components, testing of machine/structural components, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of low fault recognition rate and difficulty in extracting fault features of rolling bearings, and achieve the effect of good fault recognition ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
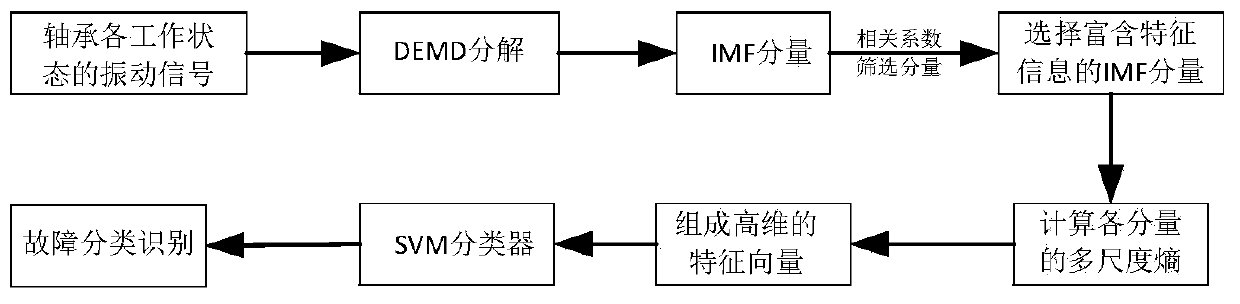
[0033] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, a rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on vibration signals, the specific steps are as follows:
[0034] Step1: Acquire the vibration signals of the rolling bearing in four working states: normal, inner ring fault, outer ring fault and rolling element fault;
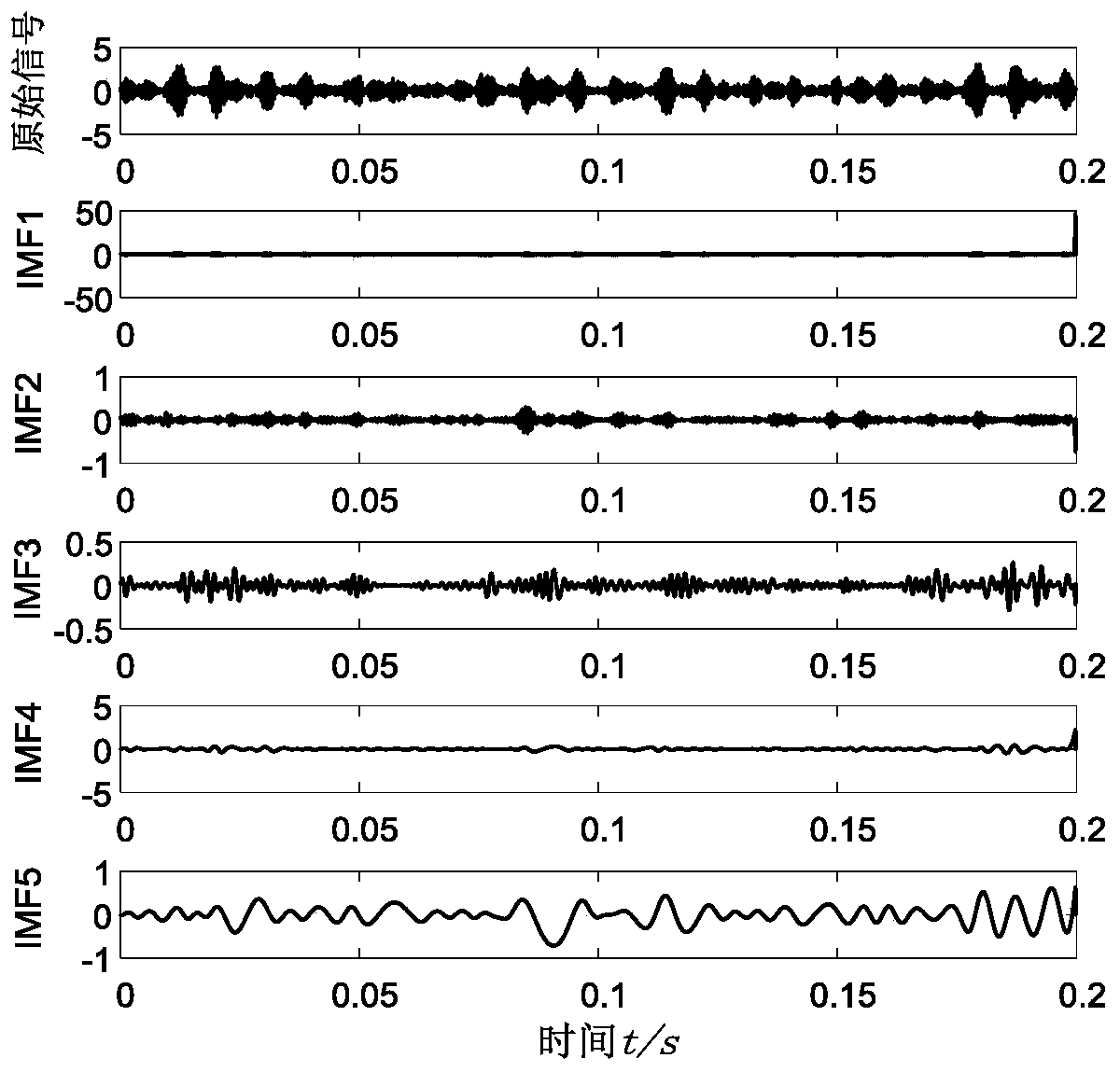
[0035] Step2: Differential Empirical Mode Decomposition (DEMD) decomposition is performed on the vibration signal in each working state and several IMF components with physical meaning are obtained;
[0036] Step3: Calculate the correlation coefficient between the IMF component and the original vibration signal;
[0037] Step4: Select the IMF component with a large correlation coefficient, because the IMF component with a large correlation coefficient is the principal component containing fault characteristic information;
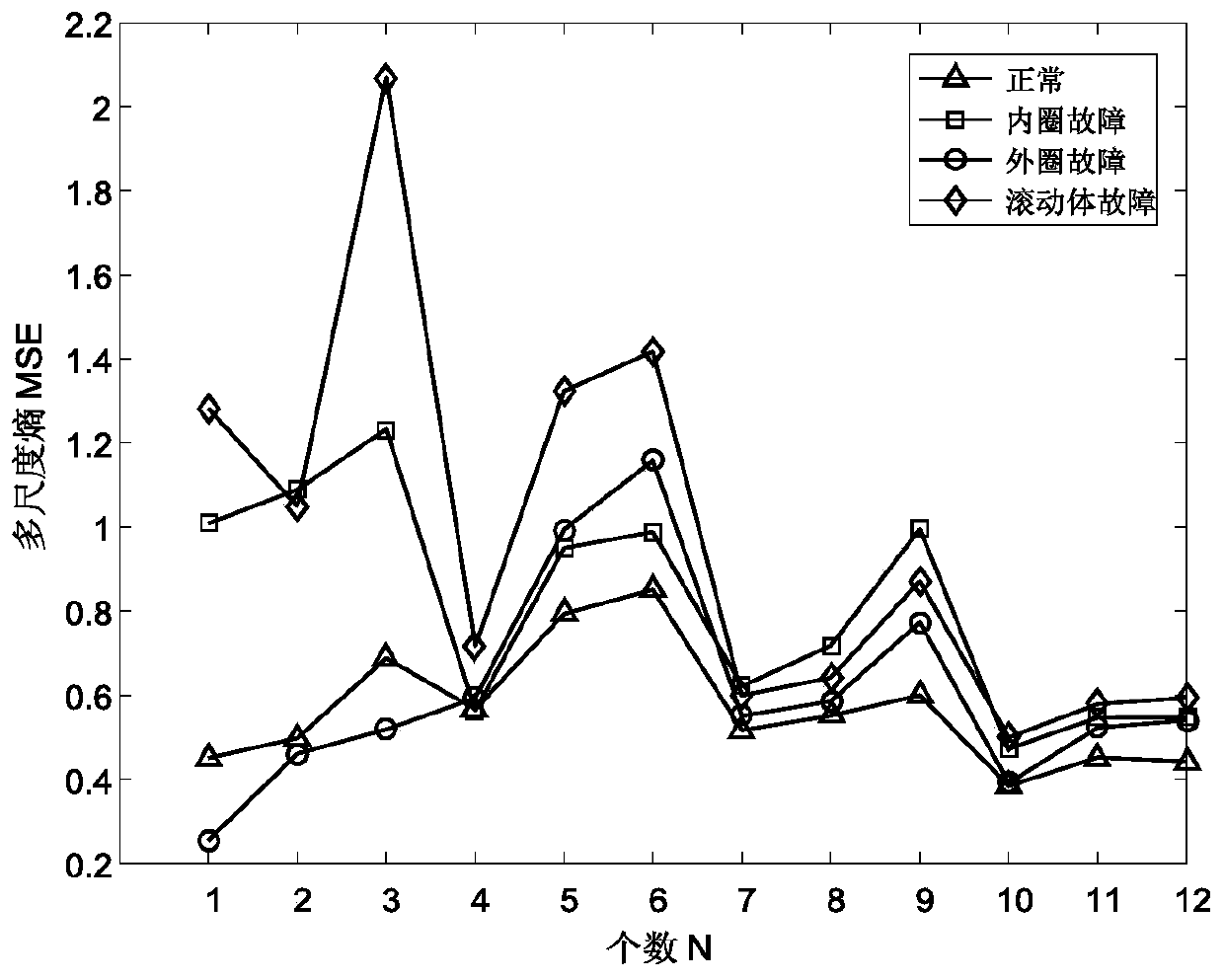
[0038] Step5: Calculate the multi-scale entropy of each IMF component after screening;
[0039] Step6: Constitute the obtained multi-scale entropy...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: In this embodiment, the fault of the rolling bearing is diagnosed by the method described in the following engineering test, and the specific experiment is as follows:
[0041] Step 1. The experimental data comes from the data of the Electrical Engineering Laboratory of Case Western Reserve University in the United States. The bearing model is 6205-2RS JEM SKF, the load is 2.237kW, and the rotation frequency is 1730r·min -1, the sampling frequency is 12kHz. In order to simulate bearing damage and failure, cracks are artificially added on the inner and outer rings of the bearing and on the rolling body respectively. The crack diameter is 0.1778mm and the crack depth is 0.2794mm.
[0042] Step 2. Collect 4 different types of vibration signals of rolling bearings (normal, rolling element fault, inner ring fault, outer ring fault) at a fixed sampling frequency. The length of the data is 2400, and 50 sets of data are collected for each state as a total sample ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3: In order to study the influence of different training sample numbers on the rolling bearing fault identification results, select the above-mentioned Case Western Reserve University rolling bearing vibration number under the four states of a total of 50 * 4 groups, in normal state, inner ring fault, outer ring fault 10, 20, 30, and 40 sets of data are randomly selected from the rolling element fault sample data as training sample data, and the remaining sample data are used as test samples. Table 2 shows when the classification is correct under different numbers of training samples. From the table we can see that when the training data is 30 groups, the diagnostic accuracy of the proposed method can reach 96.25%. When the number of training samples increases, the established classification model is more accurate and the recognition degree is higher, but after a certain number of samples are increased, the correct rate of fault identification will be reduced...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Crack depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com