Speaker recognition method based on dictionary learning and low rank matrix decomposition
A speaker recognition, low-rank matrix technology, applied in the field of speaker recognition, can solve the problems of the decline of dictionary recognition ability and the difficulty of guaranteeing the stability of the algorithm, and achieve the effect of strong recognition and improved recognition.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] Attached below Figure 1-3 The technical scheme of the present invention is described in further detail:
[0041] This embodiment proposes a speaker recognition method based on dictionary learning and low-rank matrix decomposition, including the following steps:
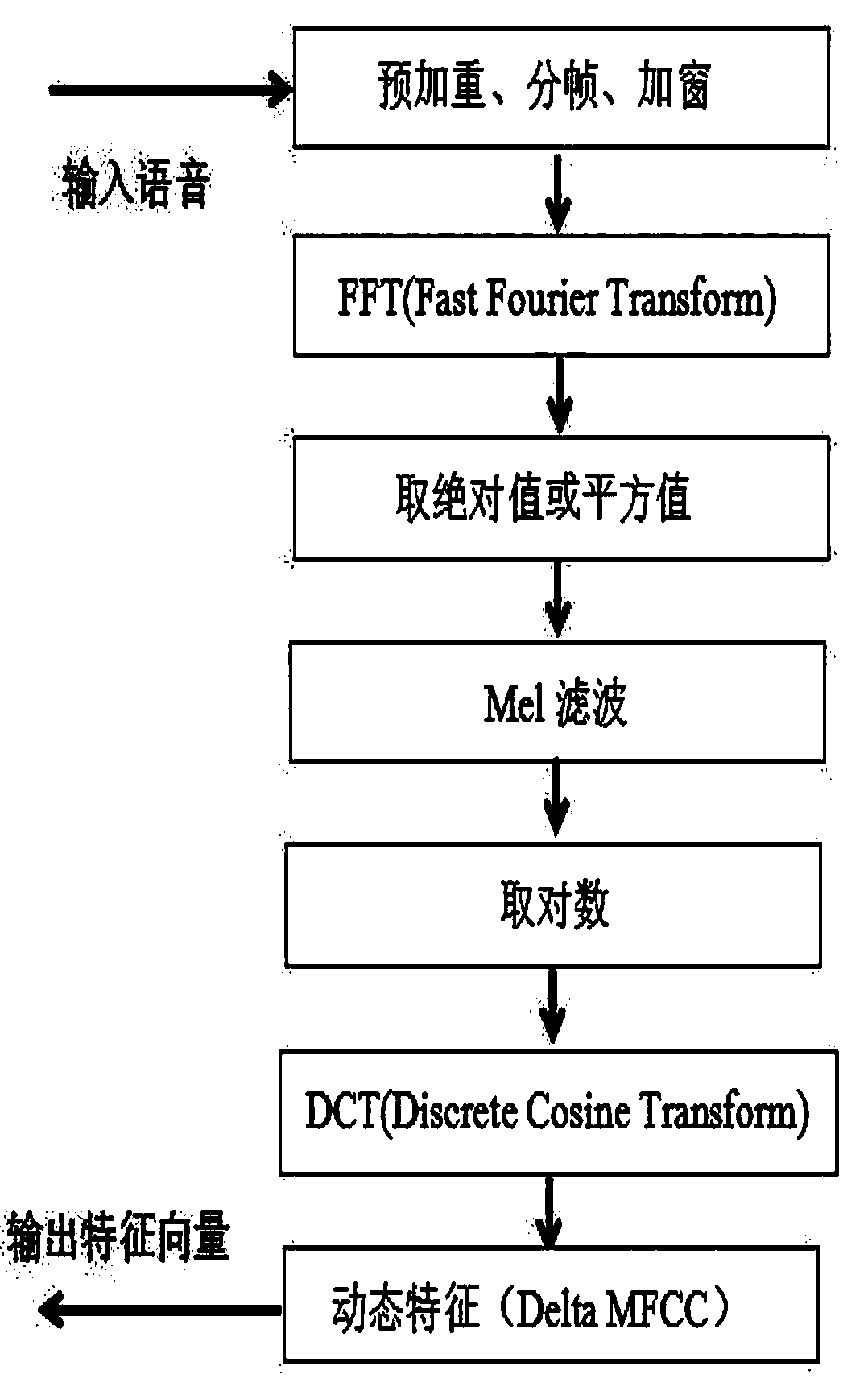
[0042] Step 1, perform pre-emphasis, framing, windowing, endpoint detection and other processing on the speaker audio;
[0043] Step 2, extract the MFCC features corresponding to each speaker's sentence, and train the GMM-UBM model;
[0044] Step 3, estimate the global difference space matrix T and the global difference space factor w by joint factor analysis (JFA);
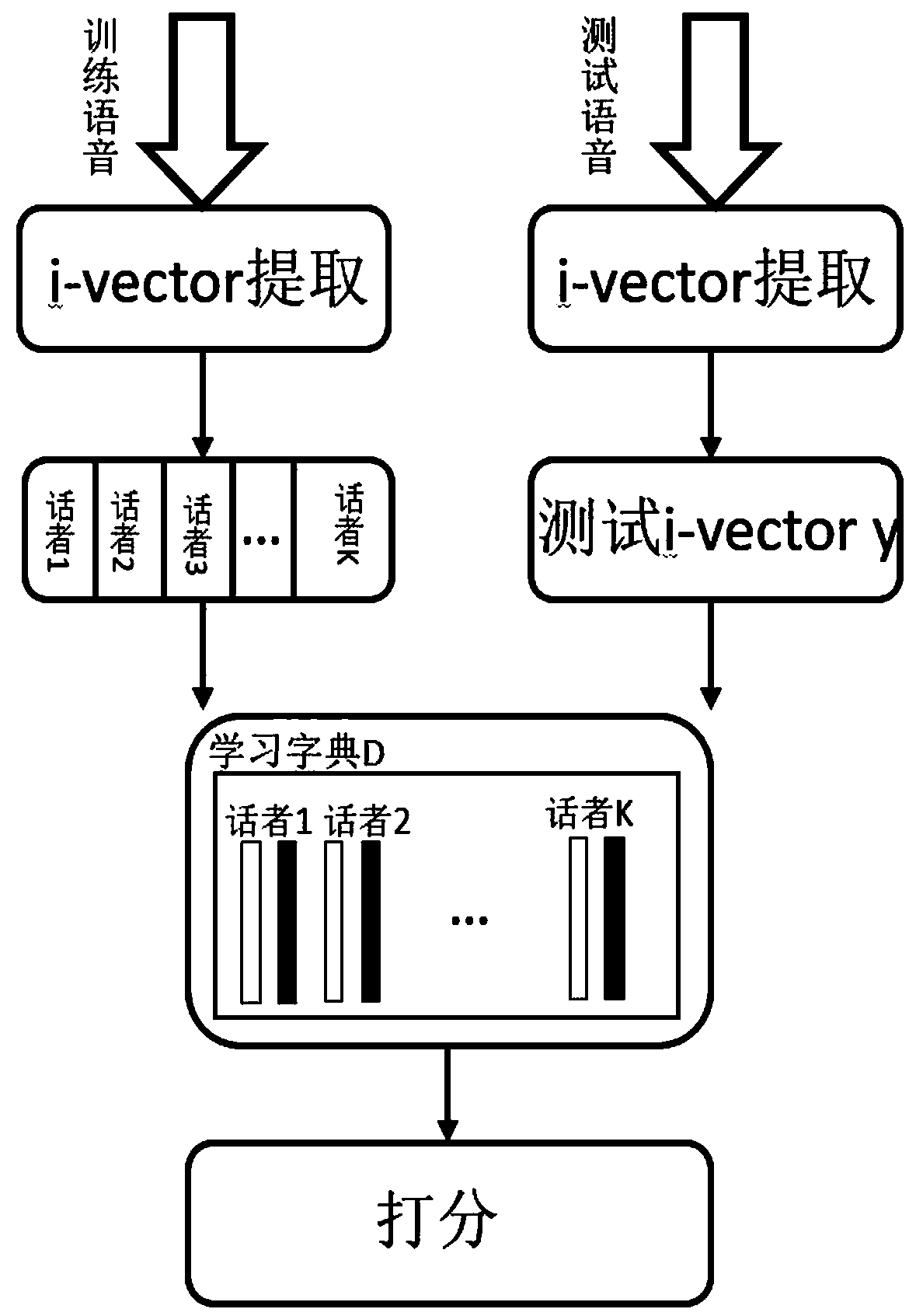
[0045] Step 4, get the i-vector corresponding to each speaker sentence;
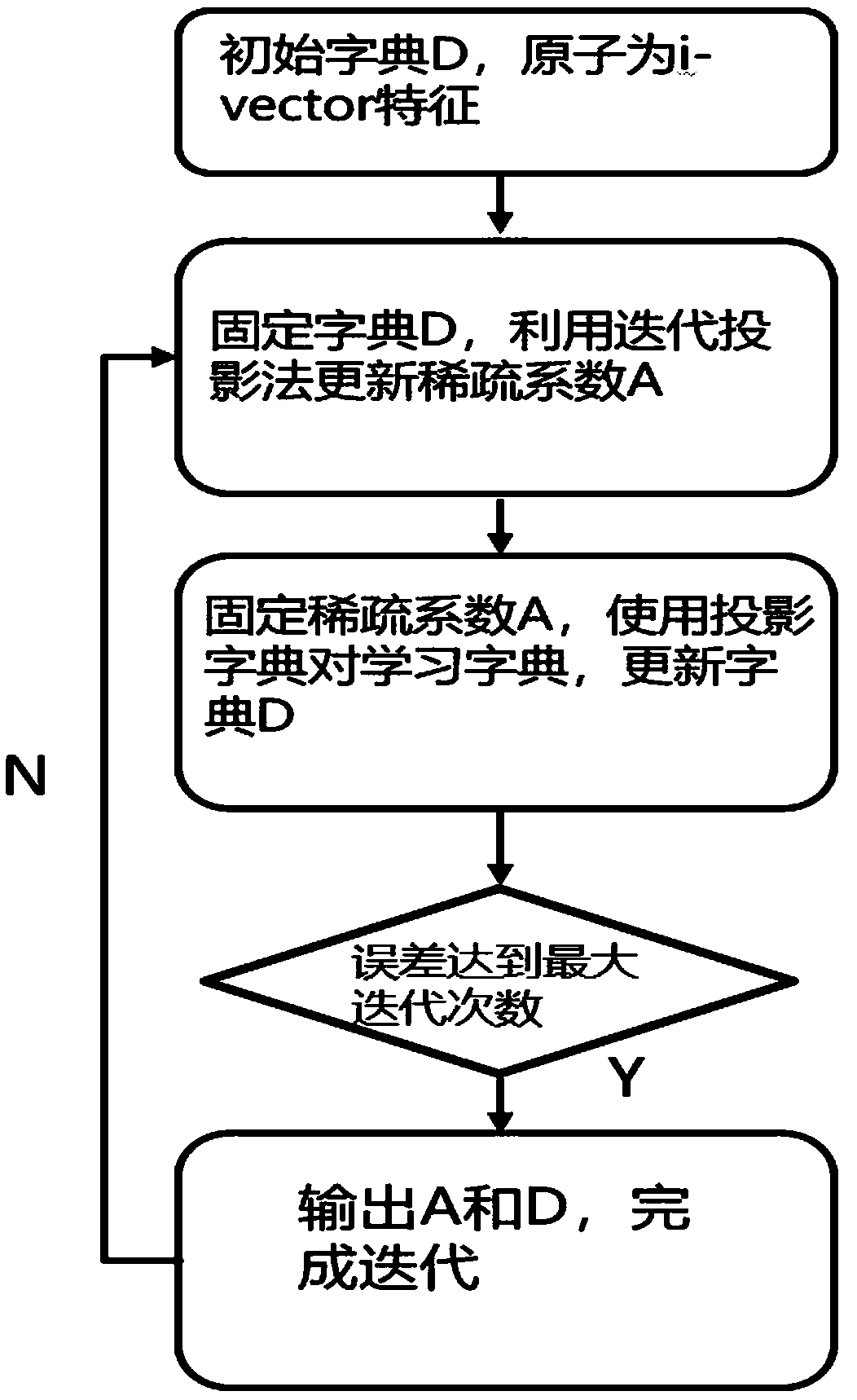
[0046] Step 5, extract the M-dimensional i-vector from the training set and generate a feature matrix, generate a discrimination dictionary according to the training set and test set, and the obtained dictionary will be used as the i-vector back-end processing and scoring ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com