Pedestrian re-identification method based on human skeleton key point detection and unequal partition
A pedestrian re-identification and key point technology, applied in the field of pedestrian re-identification, can solve the problems of poor model generalization ability, high false detection rate, and uncorresponding human body area division
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
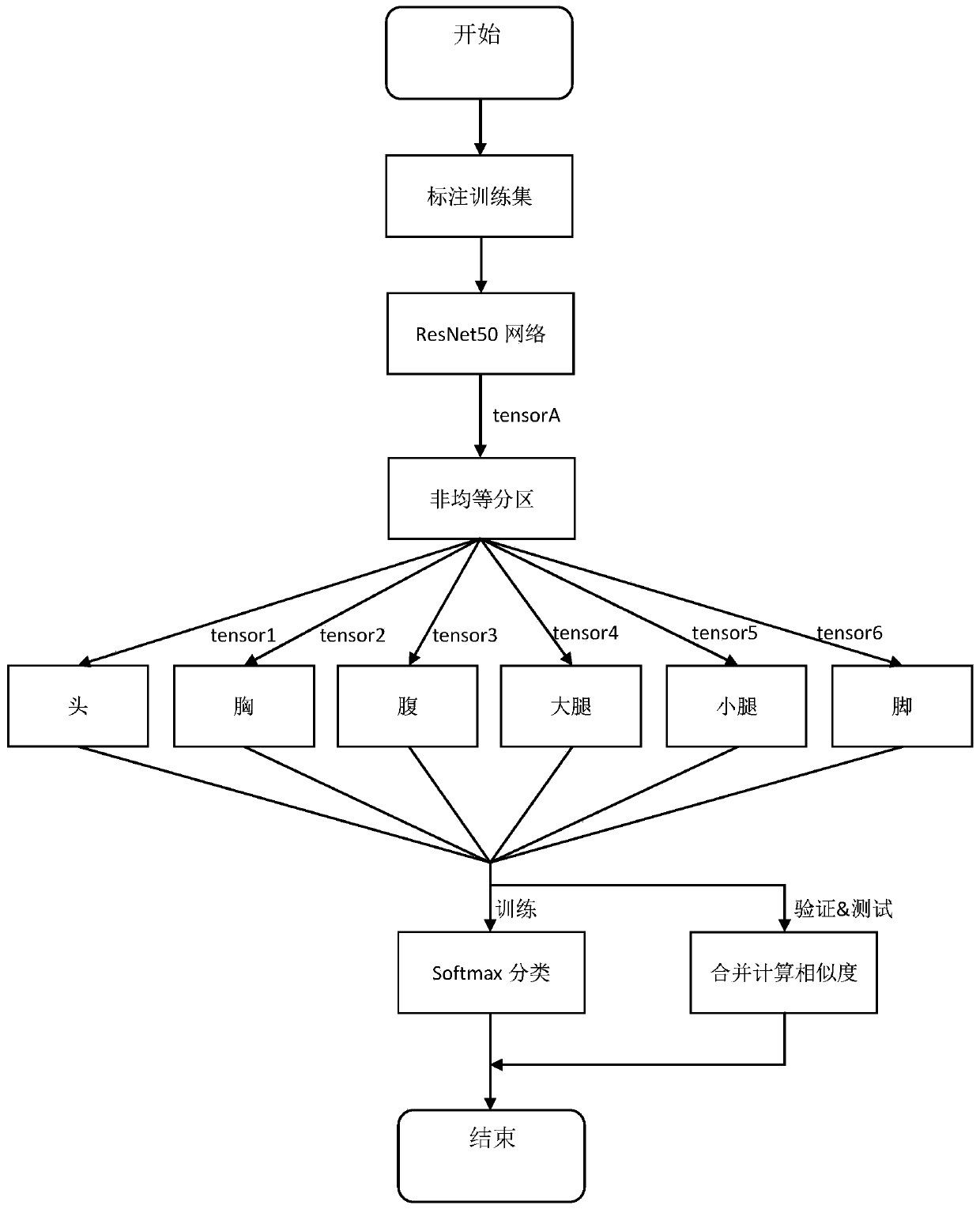
[0064] A pedestrian re-identification method based on human skeleton key point detection and non-equal partition, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0065] (1) Prepare the pedestrian data set, which refers to a large number of pedestrian images in different scenes and with different scales; divide the pedestrian data set into a training set, a verification set and a test set, and use the LabelImg image labeling tool to label the training set;
[0066] (2) Send the marked pictures in step (1) to the ResNet50 network to obtain tensor A representing the characteristics of the human body;
[0067] (3) According to the relative invariance of the human skeleton area, the tensor A is non-uniformly partitioned according to the key points of the human skeleton, and tensor1-1, tensor1-2, tensor1-3, tensor1-4, tensor1-5, tensor1-6 are obtained, respectively Characterize the head, chest, abdomen, thighs, calves, feet of the human body;
[0068] (4) Connect tensor1...
Embodiment 2
[0076] A method for re-identifying pedestrians based on human skeleton key point detection and unequal partitioning according to Embodiment 1, characterized in that:
[0077] In step (1), if Figure 5As shown, using the LabelImg image annotation tool to annotate the training set refers to: download and install the LabelImg image annotation tool, use the built-in drawing rectangle function in the LabelImg image annotation tool, and frame the location of pedestrians and each pedestrian in the pedestrian image key points of the human skeleton. In the pedestrian dataset, the training set accounts for 70%, the validation set accounts for 10%, and the test set accounts for 20%.
[0078] Step (2), such as Image 6 As shown, the steps are as follows: Send the picture marked with the LabelImg picture labeling tool to the input layer of the ResNet50 network in the form of pixels, and after the 50-layer convolution of the ResNet50 network, discard the downsampling of the last block in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com