Method and system for the behavior-based authentication of a user
A user-behavioral technology, applied in the fields of digital data authentication, character and pattern recognition, unauthorized/fraudulent phone call prevention, etc., can solve the problem of low security, fingerprint sensor can no longer identify users, and users are difficult to remember. Living and other issues to achieve the effect of improving safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0120] Mutually corresponding components of the following embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals.
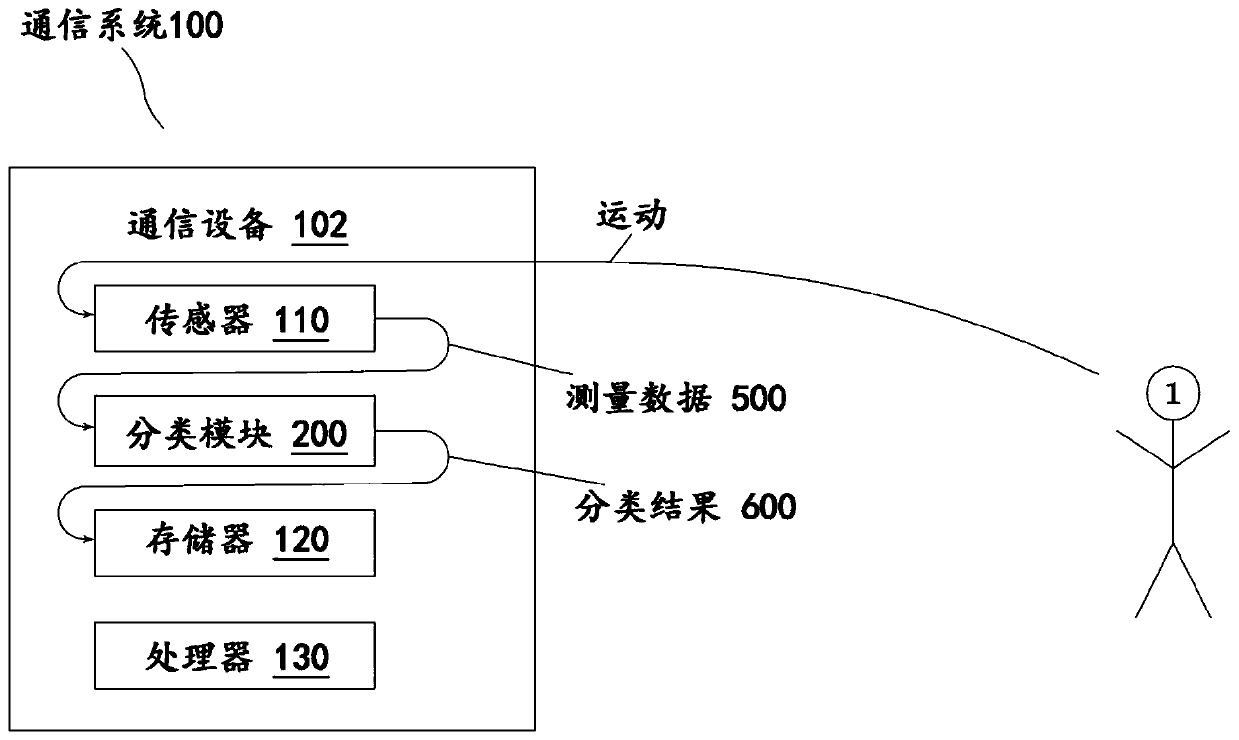
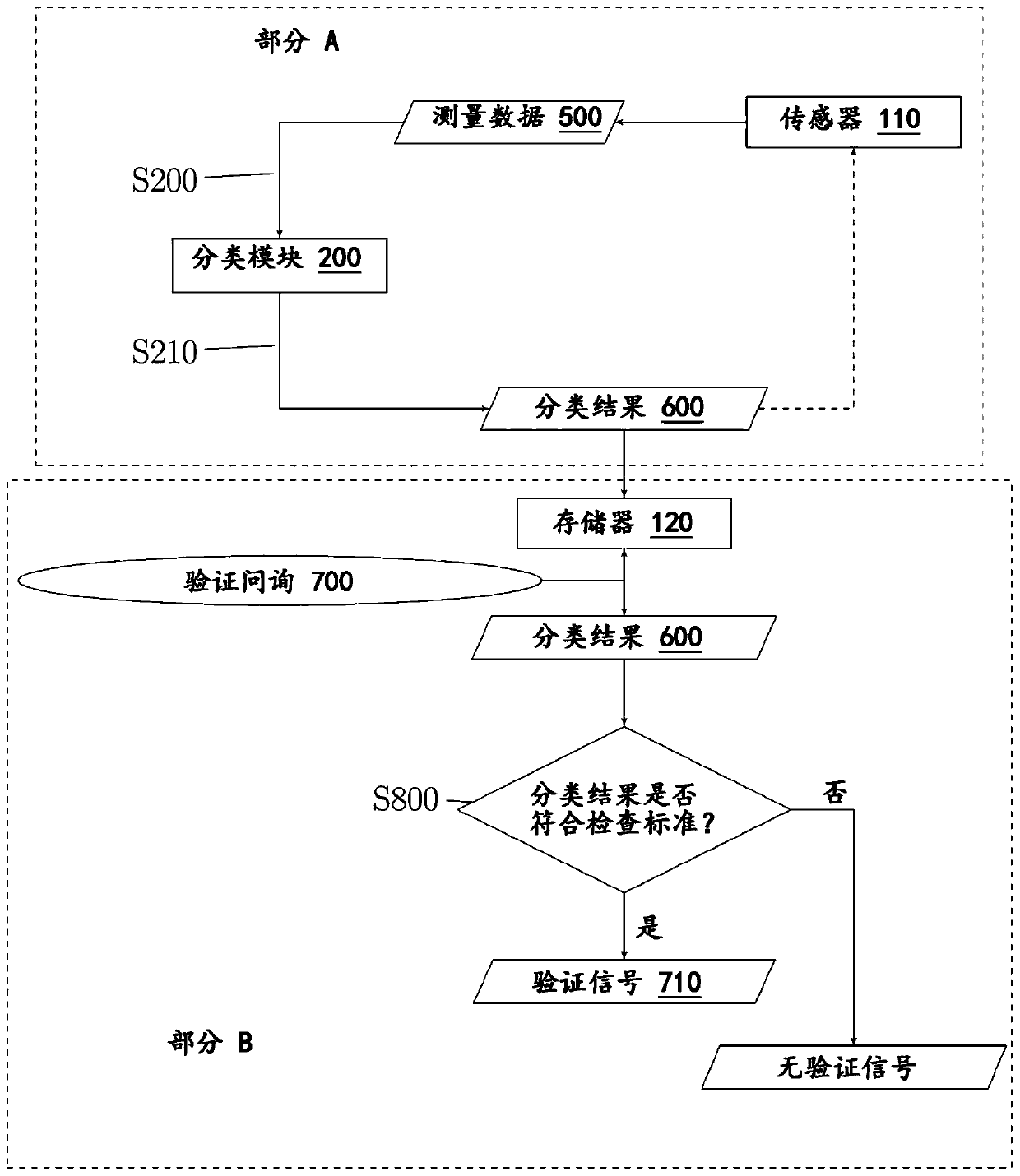
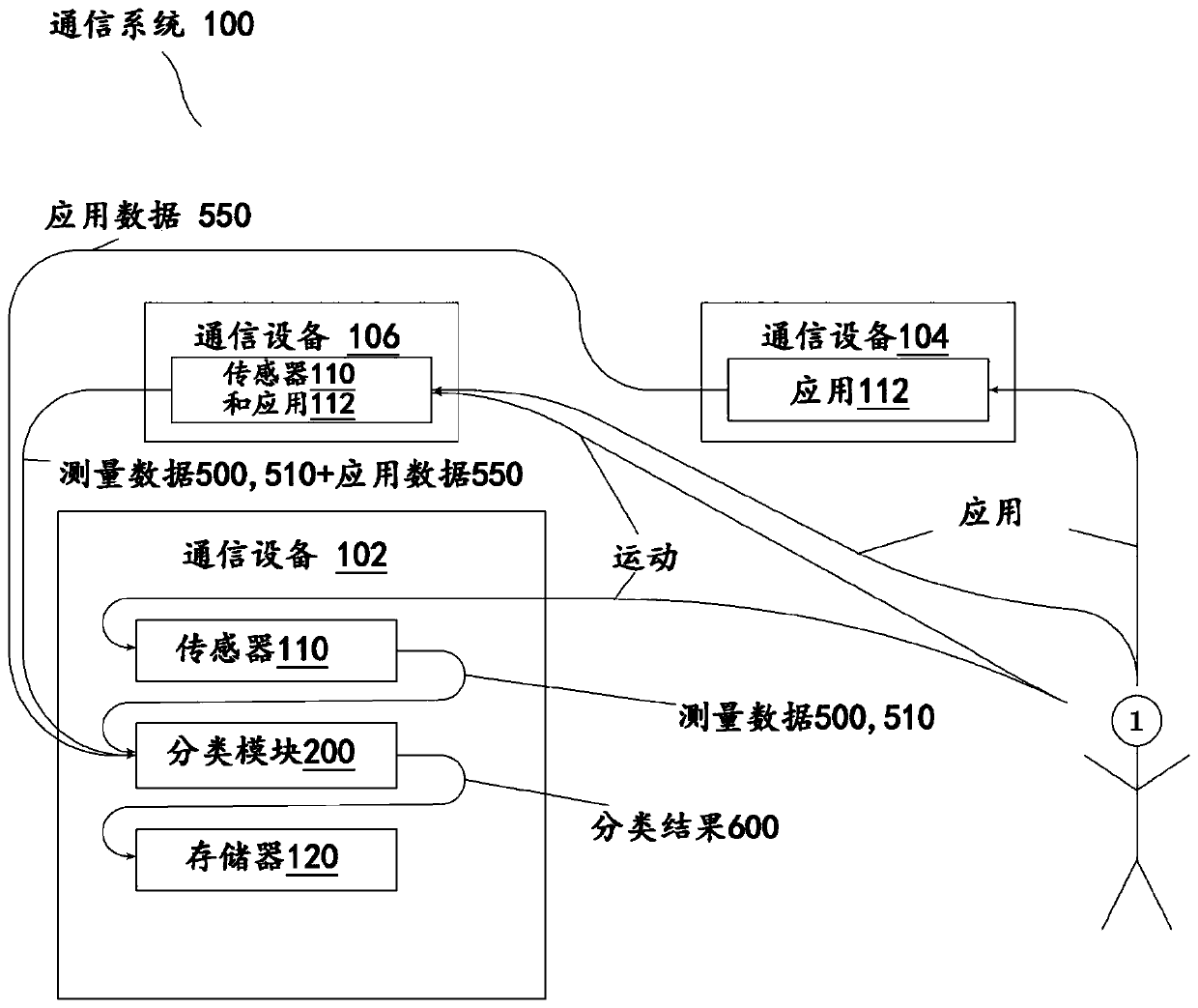
[0121] figure 1 The schematic structure of an embodiment of a mobile portable communication system 100 is shown, which is carried by the user 1 . In this embodiment, the mobile portable communication system has a single mobile portable communication device 102 . The mobile portable communication device 102 is adapted to perform a method for behavior-based authentication of the user 1 with respect to the mobile portable communication system 100 . The mobile portable communication device 102 has a sensor 110 which is suitable for measuring gross motor movements of the user 1 as measurement data 500 . Furthermore, the mobile portable communication device 102 has a large motion classification module 200 adapted to process the measurement data 500 of the sensor 110 . The mobile portable communication device 102 also has a memory 120 in which the measurement data 50...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com