Methods of generating hepatic macrophages and uses thereof
A technology for macrophages and hepatocytes, applied in the field of deriving and maintaining hepatic macrophages, which can solve the problems of human Kupffer cells source limitation and inability to expand
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Example 1--Optimization of culture conditions for the differentiation of hPSC-KC
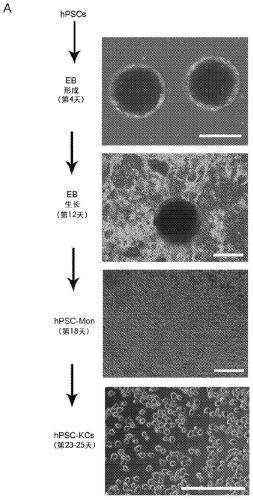
[0092] hPSC-derived monocytes (hPSC-Mon) were differentiated from iPSC-IMR90 according to the method described by Wilgenburg et al. Preliminary results showed that embryoid bodies (EBs) could be formed and maintained in culture under serum-free and feeder-free conditions ( figure 1 A). EBs adhere within 2 weeks, and monocytes can be generated in about 18 days of culture. These monocytes can be harvested weekly from the supernatant of the differentiation culture.
[0093] hPSC-Mon were harvested from the supernatant and differentiated into hepatic macrophages (hPSC-KC) ( figure 1 A). hPSC-Mac used as a control to analyze non-hepatic macrophages Similarities and differences between hepatic macrophages (KC). The results showed that hPSC-Mon could differentiate into adherent hPSC-KC ( figure 1 A).
[0094] To differentiate hPSC-Mon into hPSC-KC, hPSC-Mon were treated with medium cont...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Example 2--marker expression of hPSC-KC
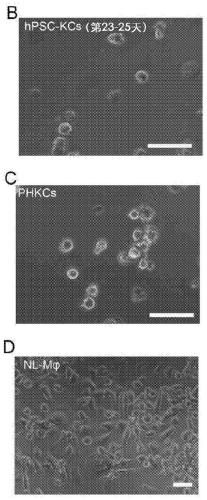
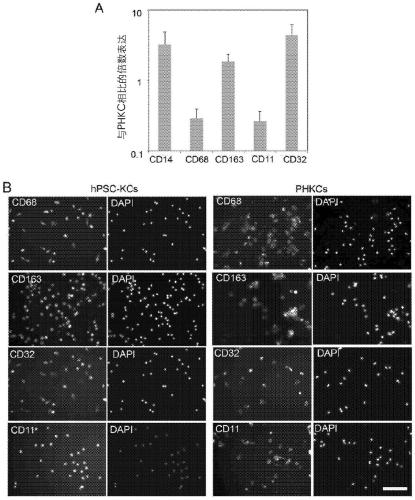
[0097] After generating hPSC-KCs, cells were analyzed for marker expression by gene expression and immunostaining. F4 / 80 has been documented as a representative marker for mouse Kupffer cells but not for human cells. More recently, the combination of CD14 and the classification of CD32, CD68 and CD11 subsets of Kupffer cells has been used to define Kupffer cells in humans. Furthermore, CD163 has been used as a marker of activated macrophages. Therefore, the expression of these markers in hPSC-Mac and hPSC-KC was examined by gene expression studies. The results showed that hPSC-KC expressed CD14, CD163 and CD32 at levels comparable to PHKC ( figure 2 A). CD68 and CD11 expression in hPSC-KC was about 30% of that in PHKC. Marker expression was confirmed by immunostaining ( figure 2 B).
Embodiment 3-
[0098] Example 3--The cytokines produced by hPSC-KC after activation are similar to PHKC but with different
[0099] To activate hPSC-KCs to examine cytokine production, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was added to the medium during the last 16 hours of culture. Media were collected at the end of the incubation period and analyzed for morphological changes and cytokine production upon LPS activation. The results showed that LPS activation in and hPSC-KC induced typical morphological changes from round to flattened and spread cells ( image 3 A). Importantly, the fold induction in hPSC-KC was in the same range as that of PHKC (25-fold) ( image 3 B). IL-6 production in primary human hepatocytes (PHH) was below detectable levels. The fold increase in TNF4α production in hPSC-KC (33-fold) was similar to that in PHKC (35-fold) ( image 3 C). TNF4α production in PHH following LPS activation was below detectable levels. Compared with PHKC and hPSC-KC, produced much higher leve...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com