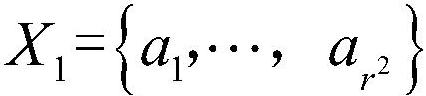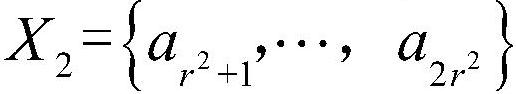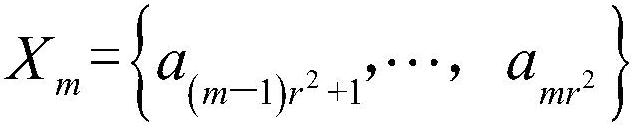A No-Third-Party Quantum Information Equality Comparison Method Based on Permutation Operation
A technology of permutation operation and quantum information, which is applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as complex implementation, low efficiency, and difficulty in protocol implementation, and achieve the effect of overcoming information leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0055] The third-party quantum information equality comparison method based on the replacement operation provided by the present invention, its specific implementation method is as follows:
[0056] Let |S|=r N , and the set S is as follows:
[0057] S={a (1,...,1,1) ,...,a (1,…,1,r) , a (1,...,2,1) ,...,a (1,...,2,r) ,...,a (r,…,r,1) ,...,a (r,…,r,r)}
[0058] Among them, S is an N-order array set, each element in S is taken from the set {0,1}, and both N and r are positive integers.
[0059] The following defines a special permutation operation on the set S
[0060]
[0061] Among them, k i ≤r, i=1,...,N, Wherein, l=1, 2, ..., r. The permutation operation π induces a new permutation operation τ,
[0062]
[0063] The set S here is essentially a set composed of multi-index arrays. In a quantum system, the permutation and transformation of the position of quantum particles can be realized through specific quantum exchange gates. This application provides...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com