A method for automatic traceability of groundwater pollutants on site
A technology for pollutants and groundwater, applied in surface/boundary effects, instruments, analytical materials, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of calculation, limited promotion, and inability to fully satisfy the traceability model, and achieve the effect of weakening adverse effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] A method for automatic traceability of groundwater pollutants on site, comprising the following steps:
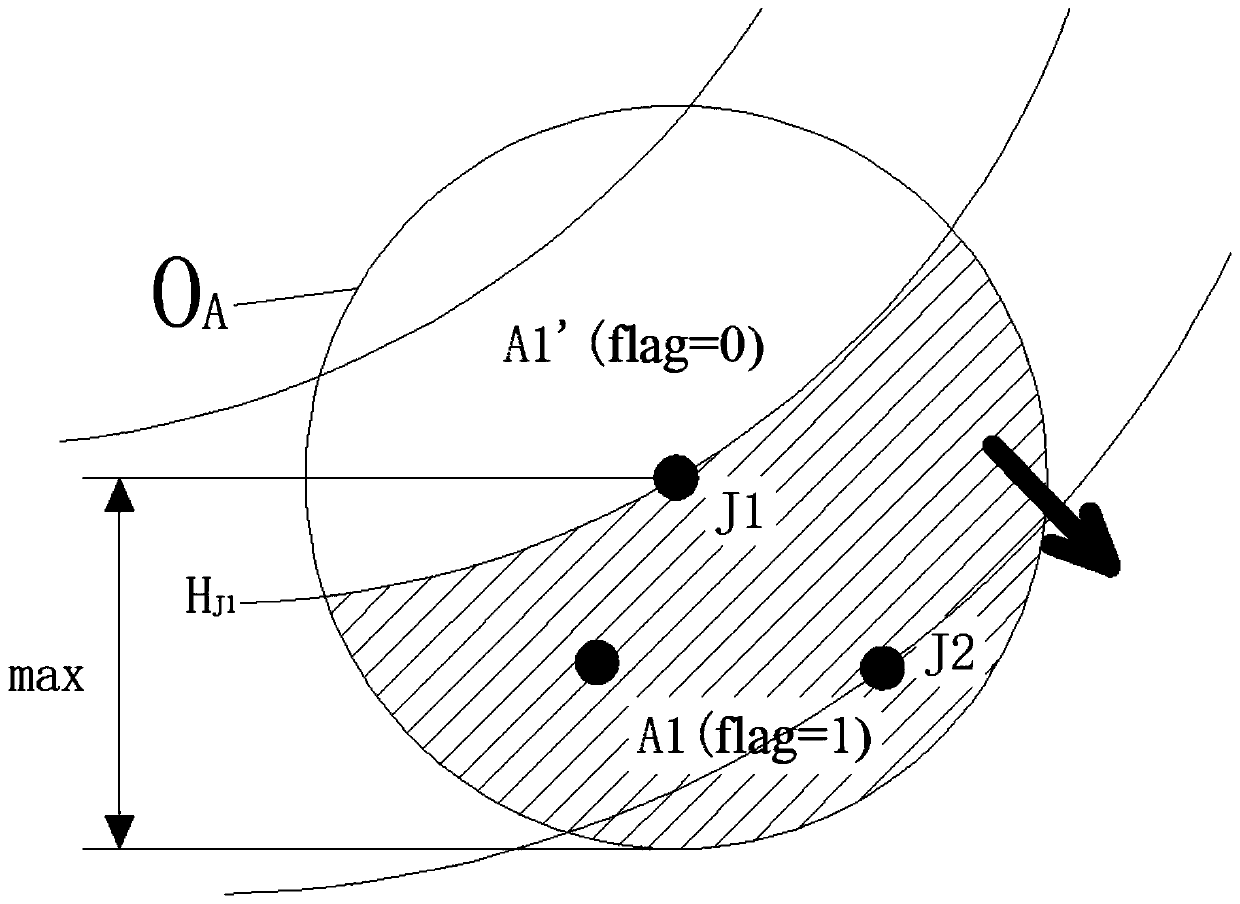
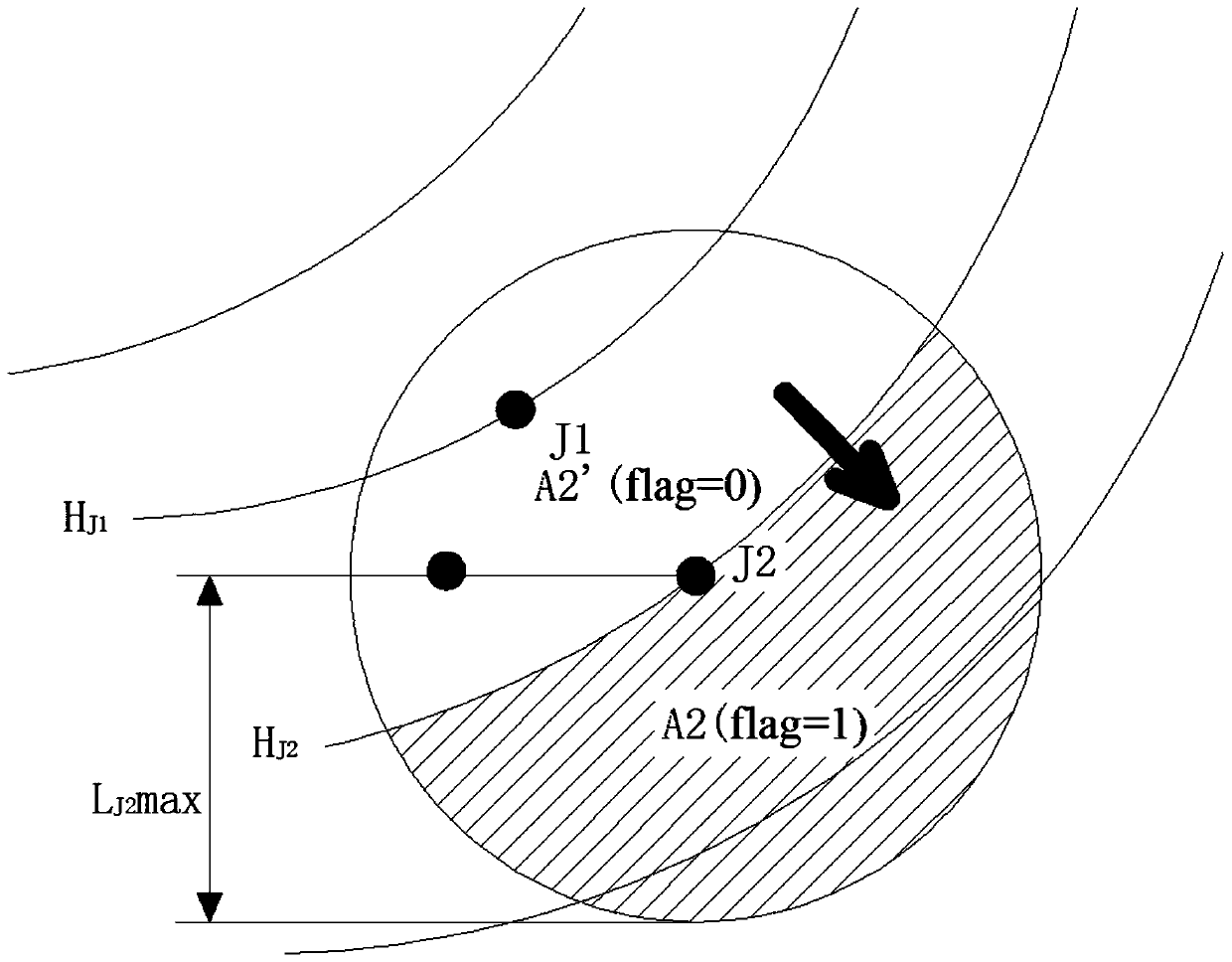
[0049] Step 1. Obtain the shortest time for pollutants from the main test hole to the observation holes in the main direction and the longest time for pollutants to go from the main test hole to the observation holes in the lateral direction through the dispersion test, so as to calculate the two monitoring times under different hydraulic gradients. The longest distance and the shortest distance that pollutants may travel downstream from the pollution source point during the interval time.
[0050] Specifically, in this embodiment, step 1 is specifically implemented through the following steps:
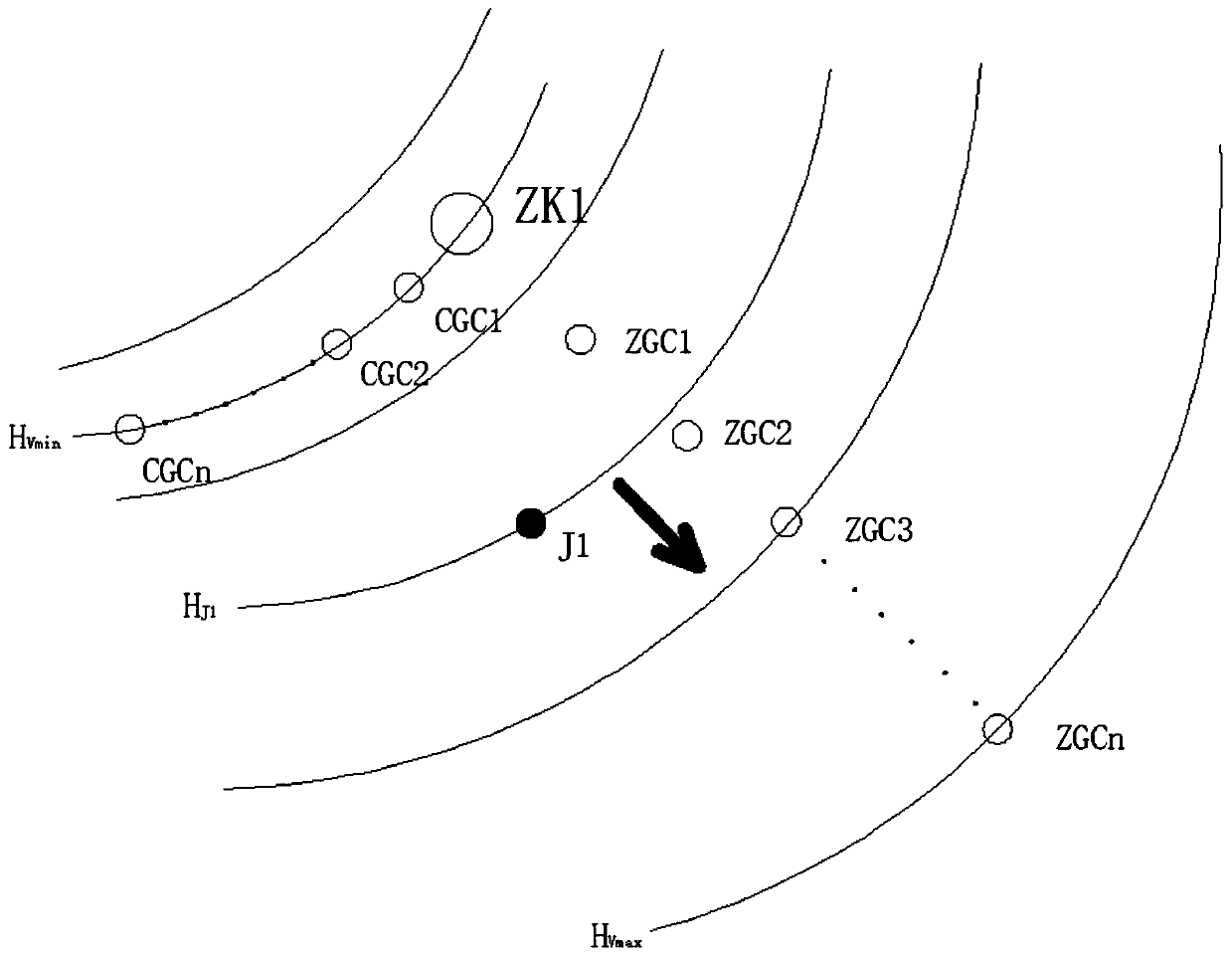
[0051] Step 1.1. Carry out a dispersion test using the porous test method, wherein, such as figure 1 As shown, the main hole of the test is marked as ZK1, the observation holes in the main direction are marked as ZGC1, ZGC2...ZGCn, and the observation holes in the lateral d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com