Pixel circuit, driving method and display device
A technique for pixel circuits and drive transistors, applied in the field of drive methods, display devices, and pixel circuits, capable of solving problems such as uneven pixel brightness and uneven luminous brightness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
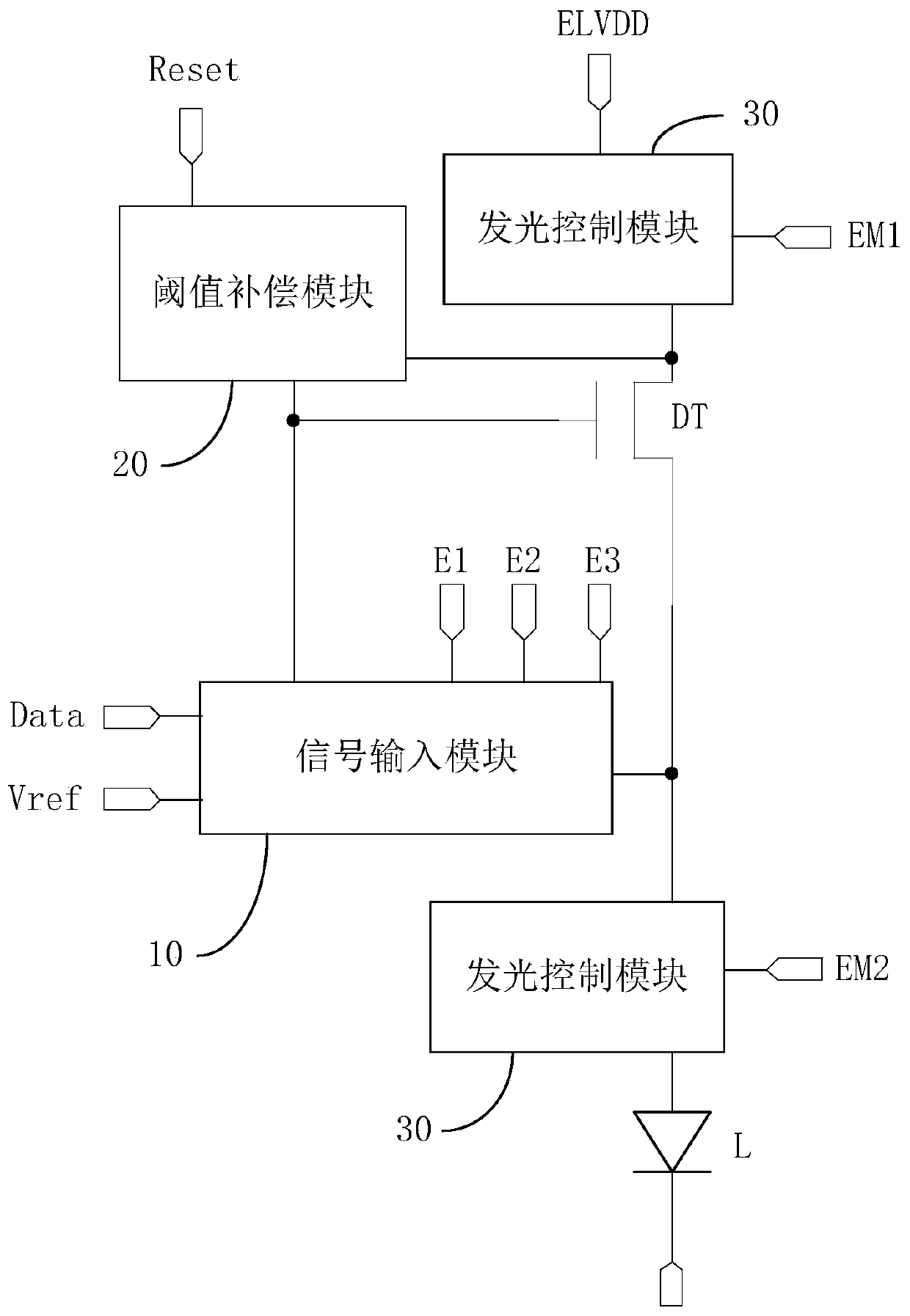
[0058] In specific implementation, in the pixel circuit provided by the embodiment of the present invention, such as image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 8 As shown, the driving transistor DT can be an N-type transistor. For the case where the driving transistor DT is a P-type transistor, the design principle is the same as that of the present invention, and also belongs to the protection scope of the present invention.
[0059] During specific implementation, in the pixel circuit provided by the embodiment of the present invention, the first terminal of the light emitting device L is electrically connected to the light emitting control module, and the second terminal of the light emitting device L is electrically connected to the second power supply terminal ELVSS. Moreover, in specific implementation, the light emitting device L may be at least one of: organic light emitting diodes (Organic Light Emitting Diode, OLED) and quantum dot light emitting diodes (Quantum Dot Light Emitt...
Embodiment 2
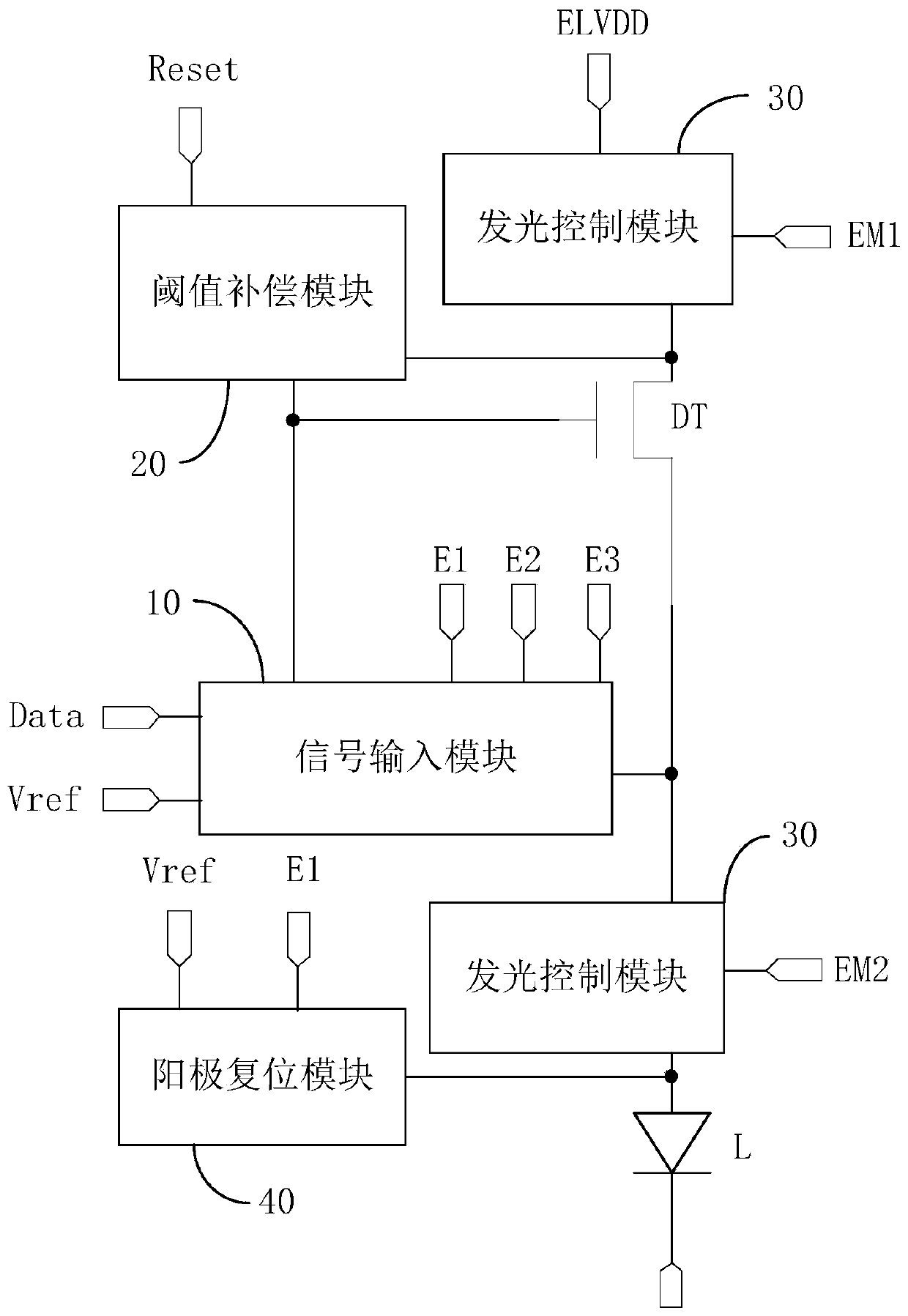
[0095] The schematic structural diagram of the pixel circuit corresponding to the embodiment of the present invention is as follows Figure 5 As shown, some implementations of the above-mentioned embodiments are modified. The following only describes the differences between this embodiment and the above-mentioned embodiments, and the similarities will not be repeated here.
[0096] In specific implementation, in the pixel circuit provided by the embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 5 As shown, the signal input module 10 may also include: a fourth switching transistor T4, a fifth switching transistor T5, a sixth switching transistor T6, and a second capacitor C2; wherein,
[0097] The gate of the fourth switching transistor T4 is electrically connected to the first control signal terminal E1, the first pole is electrically connected to the data signal terminal Data, and the second pole is respectively connected to the first pole of the second capacitor C2 and t...
Embodiment 3
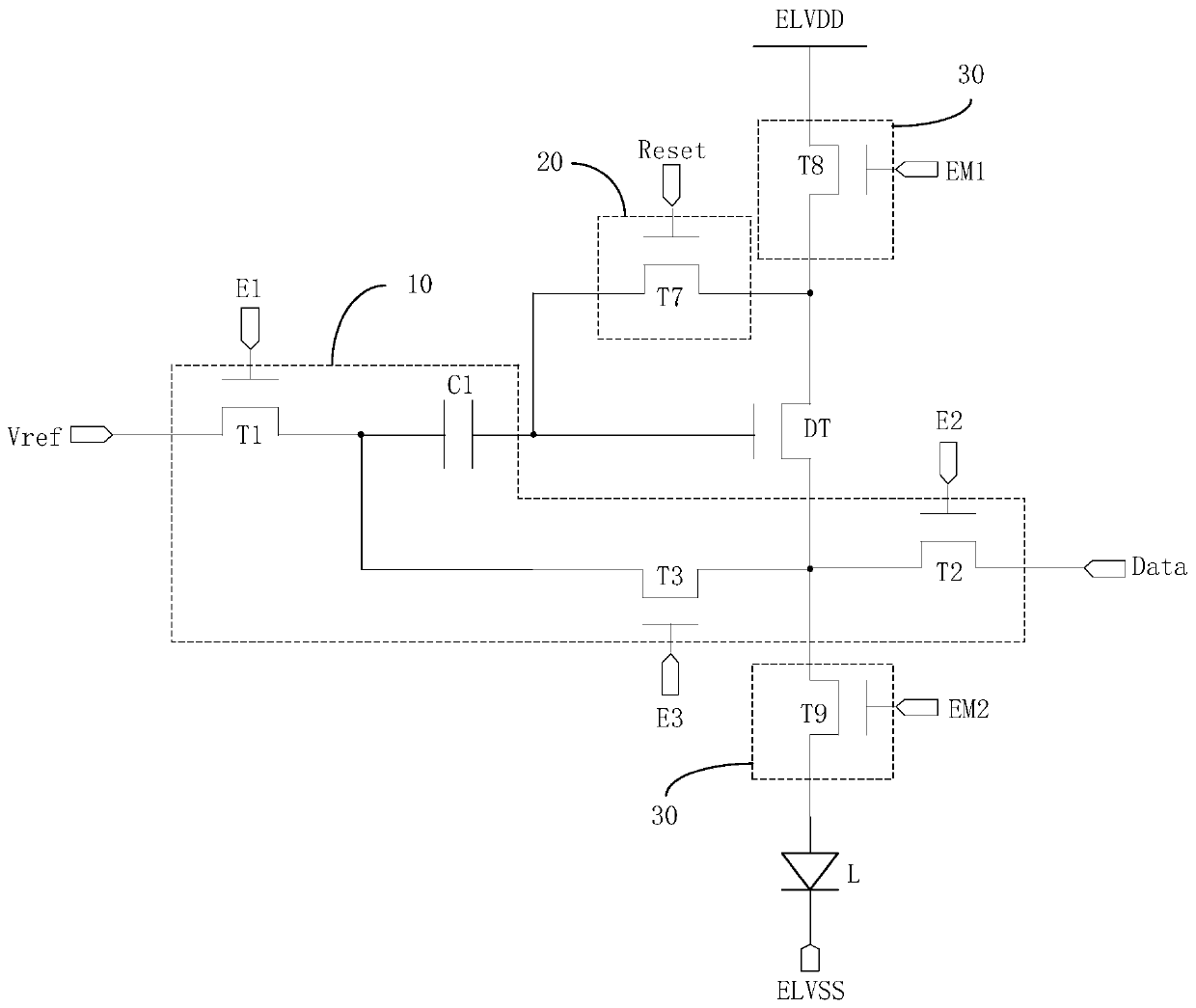
[0113] by Figure 4 The pixel circuit shown as an example, combined with the circuit signal timing Figure 10 The working process of the above-mentioned pixel circuit provided by the embodiment of the present invention is described. The following only describes the differences between this embodiment and the above-mentioned embodiments, and the similarities will not be repeated here.
[0114] Specifically, choose the Figure 10 The three stages of t1, t2 and t3 in the input timing diagram shown. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the reset signal terminal Reset and the first control signal terminal E1 and the second control signal terminal E2 may be the same terminal; the second light emission control signal terminal EM2 and the third control signal terminal E3 may be the same terminal.
[0115] In the t1 stage, Reset=1, EM1=1, EM2=0.
[0116] Since Reset=1, the tenth switching transistor T10 is turned on, so the voltage VREF of the reference signal terminal Vref is output to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com