Functionalized scaffold to promote meniscus repair
A technology derived from meniscus and platelets, applied to medical preparations containing active ingredients, bone/connective tissue cells, prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of tissue availability and limited indications of allografts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] overall plan
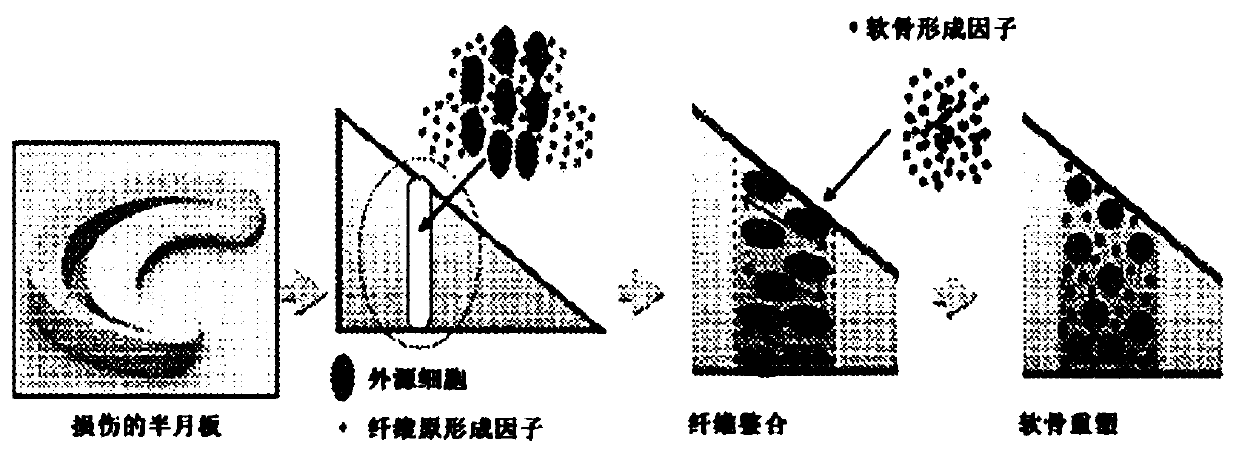
[0065] Forceful twisting, rotation, or excessive flexion of the knee joint can cause a traumatic tear of the meniscus. A meniscal tear can cause knee pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited knee extension. Current surgical approaches to address meniscus tears include sutures and meniscectomy. However, meniscal tears in the avascular region of the medial third typically do not heal spontaneously or after surgery and are a major risk factor for the development of knee osteoarthritis (OA). The middle and inner area of the meniscus lacks blood supply and is therefore least likely to heal.
[0066] Cells that promote meniscal repair and regeneration are present in the menisci adjacent to the tear, as well as in the synovium and joint capsule. Therefore, application of chemokines to the tear site can potentially recruit cells that mediate repair. Growth factors have the potential to promote meniscal healing, and various approaches have been pursued, includ...
Embodiment 2
[0070] acellular meniscal graft
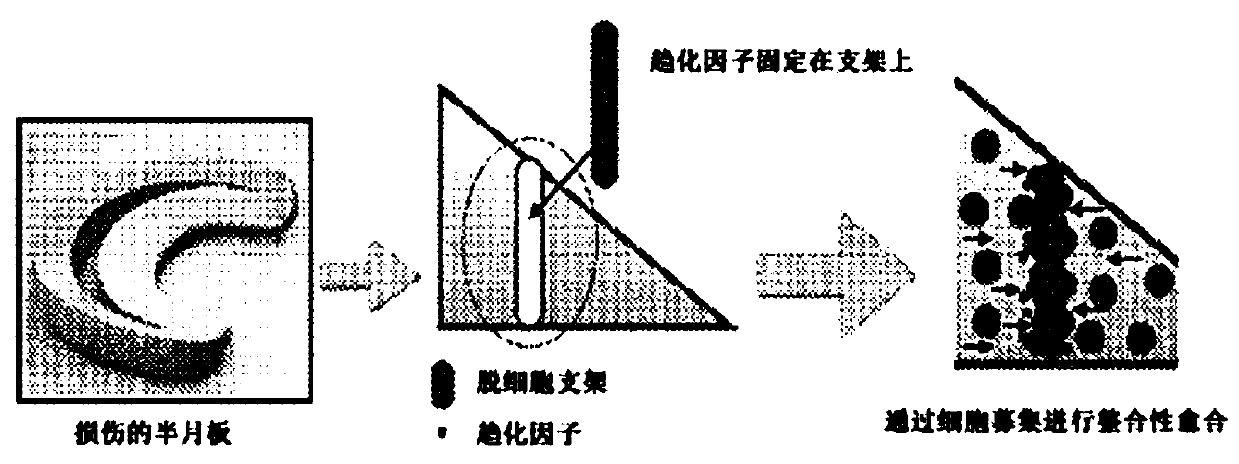
[0071] As is known to those skilled in the art, meniscus tears are the most common knee injury; although some treatments currently exist for meniscus injuries, these treatments do not result in repair or regeneration of the meniscus. In some instances, a partial or total meniscectomy is performed to treat the patient. These treatments often result in patients with osteoarthritis and / or scar tissue.
[0072] In various embodiments, the inventors have addressed this problem by developing chemotactic acellular meniscal grafts for integrative meniscal healing. In one embodiment, the inventors characterized a decellularized meniscus scaffold (DMS) for host cell infiltration. Decellularized native meniscus tissue is a promising bioscaffold for the repair of damaged human menisci. It has similar biological and mechanical properties to the natural meniscus. In addition, ideal scaffolds also contain chemokines to recruit new cell populations to ini...
Embodiment 3
[0077] significance
[0078] The bulk of the meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous meniscus-shaped structure that sits on the periphery of the joint between the tibia and femur. The two anterior and posterior horns connect to the tibial plateau. The menisci provide cushioning by translating compressive and tensile hoop stresses that are weakened at the tibial plateau by the fibrocartilaginous tendon endings.
[0079] A meniscus tear is the most common knee injury. Normal menisci and abnormally developed menisci, especially discoid menisci, are at increased risk of tearing. Even stable discoid menisci can present mechanical symptoms of a meniscus tear. A number of conditions are associated with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries, such as chronic ACL insufficiency and acute ACL rupture. Different injury patterns may be associated with different risk factors such as sex, age, body weight, and injury mechanism. Although the outer third of the meniscus is potentially healing...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com