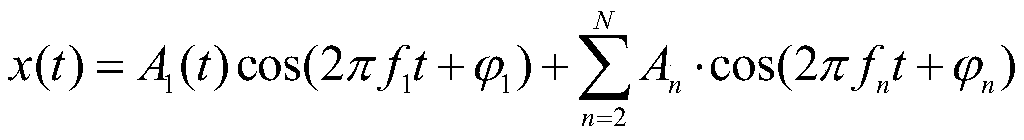Magnetizing inrush current recognition method based on second-order Taylor coefficient
A technology of excitation inrush current and identification method, which is applied in complex mathematical operations, data processing applications, electrical digital data processing, etc., and can solve problems such as weak anti-noise ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
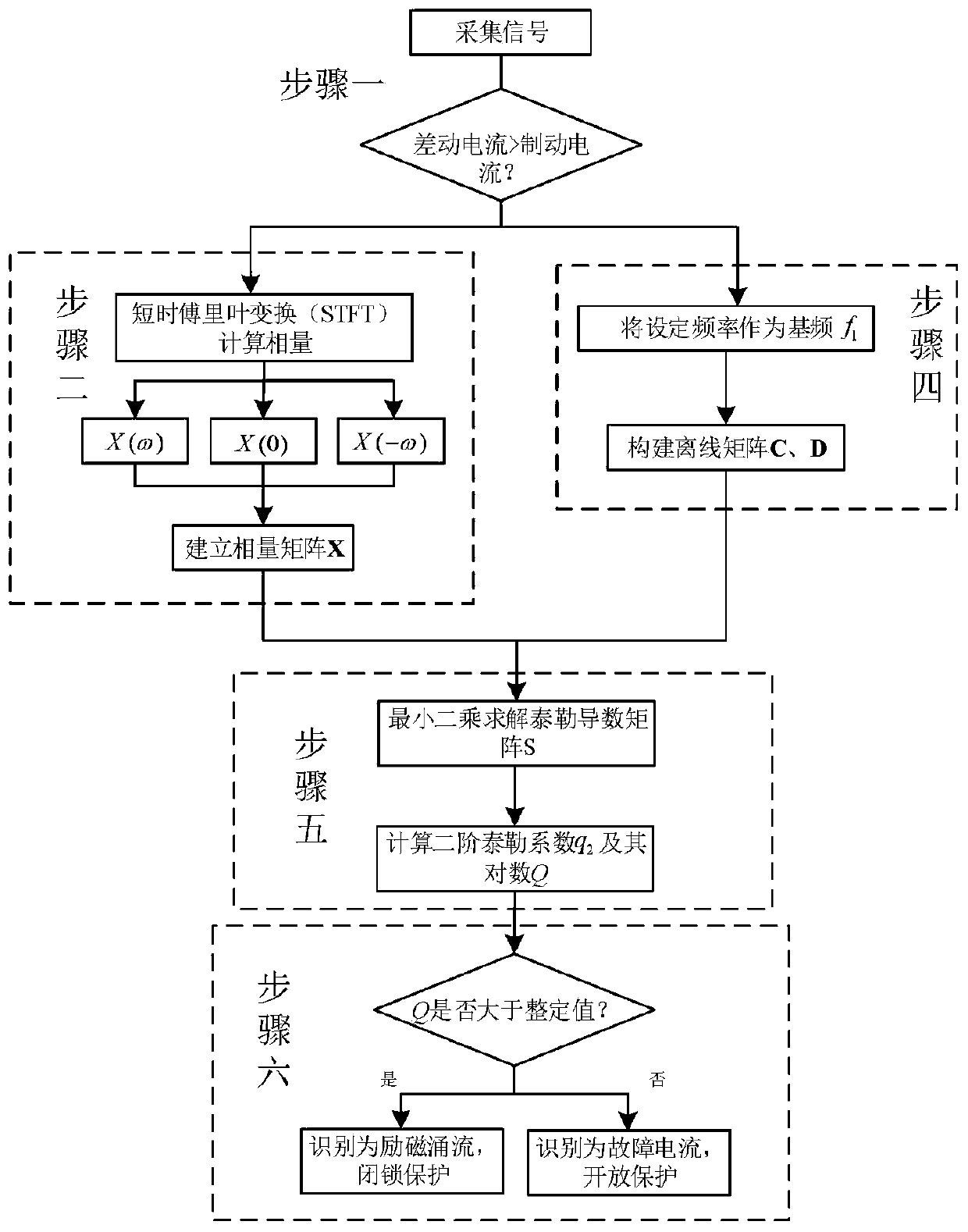
[0126] Such as Figure 1-2 As shown, a method for identifying inrush current based on the second-order Taylor coefficient includes the following steps:
[0127] Step 1: According to whether the differential current is greater than the braking current, judge whether there is a fault or a magnetizing inrush current;
[0128] Step 2: Perform short-time Fourier transform on the collected data to obtain reference time phasors X(-ω), X(0), X(ω);
[0129] Step 3: Establish the phasor form of the simplified model of the inrush current, and use the Taylor expansion of the phasor model S(t) to obtain the Taylor derivative matrix S and the second-order Taylor coefficient q 2 and its logarithm Q;
[0130] Step 4: Use the set initial frequency as the fundamental frequency, and construct offline matrix C and offline matrix D according to the fundamental frequency;
[0131] Step 5: Input the data obtained in steps 3 and 4 into the Taylor dynamic model established in step 2 to solve the Ta...
Embodiment 2
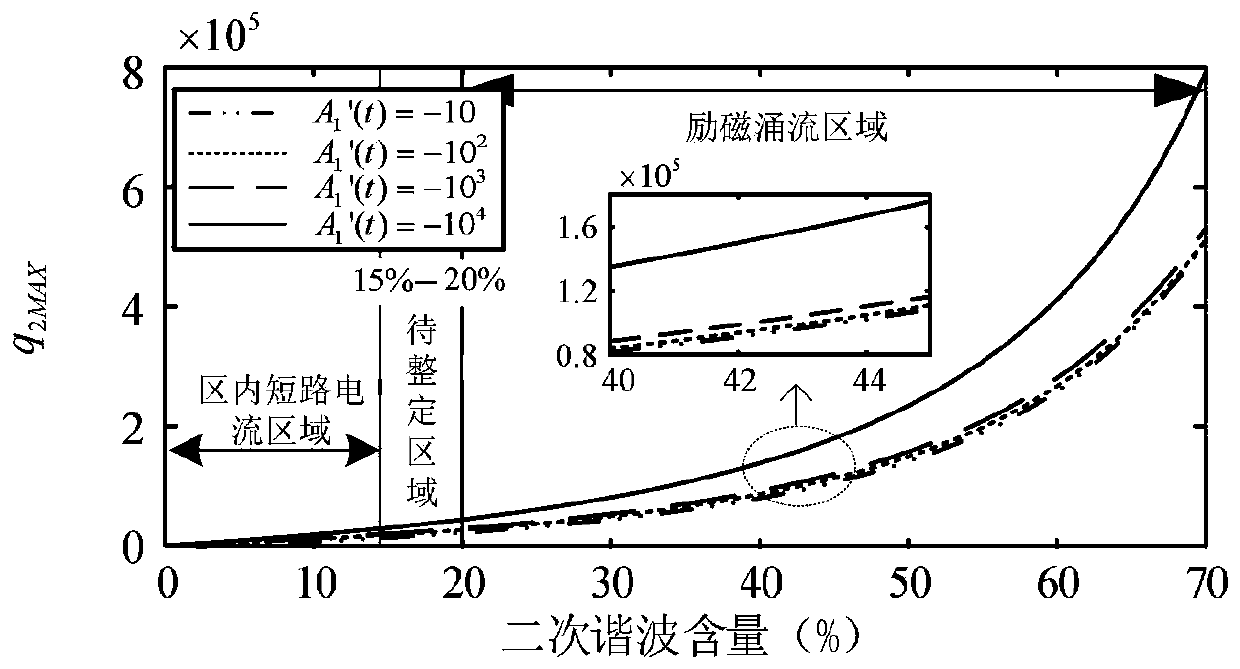
[0155] Such as Figure 1-2 As shown, based on Example 1, step 3: the dynamic model of the inrush current is established by using the Taylor series to characterize the dynamic change characteristics of the second harmonic and the fundamental wave in the case of the inrush current, which better fits the inrush current in the actual power grid. Included dynamically changing properties. The part of the phasor model S(t) is expanded by Taylor to obtain the Taylor derivative matrix S. At the same time, the magnitude / phase angle model is used to carry out Taylor expansion on the exponent part of the phasor model S(t) to obtain the second-order Taylor coefficient q 2 and its logarithm Q. The second-order Taylor coefficient extracted from the dynamic model can reflect the electrical characteristics such as the second harmonic content and the change speed of the fundamental frequency component. This makes the present invention no longer rely on a single electrical quantity when ident...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com