Methods for aiding in diagnosing and evaluating a mild traumatic brain injury in a human subject using cardiac troponin I
A technology for subjects and brain injury, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, diagnosis, disease diagnosis, etc., can solve problems such as unresearched relationship between cardiac injury and neurological outcomes, spectral bias in findings, and unresearched cardiac injury effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0551] Study 1 - TBI Population
[0552] Study 1 is a large and complex project. Its institutional and public-private partnerships include more than 11 clinical sites, seven cores, and a total of nearly 50 partner institutions, companies and charities. An earlier pilot study, based on clinical data from three clinical sites, helped refine the TBI common data element and create a prototype of the TBI information commons space used in Study 1.
[0553] Subject Groups: A total of 2,700 to 3,000 TBI patients were equally enrolled by clinical care pathways into 3 clinical groups: 1. Patients who were evaluated in the emergency department and discharged (ED); 2. Patients who were admitted but not admitted to the ICU Patient (ADM); and 3. Patient admitted to ICU (ICU). Each clinical group additionally enrolled 100 (n=300) patients with extracranial trauma but no TBI as controls, and a total of 3000 patients were enrolled. This stratification scheme facilitates Comparative Effects ...
Embodiment 2
[0587] Study 2 - Development of a Multimodal Classification Scheme for Traumatic Brain Injury.
[0588] The goal of this study was to develop a brain injury classification scheme that indicates the nature (type) and severity of the injury. For example, serum biomarkers reveal cell types. Trauma patients were analyzed in three groups: brain injury only, non-brain injury only, and combined injury. Trauma groups with brain injury and non-brain injury were compared with each other and with combined brain / non-brain injury. These trauma groups were compared to a non-trauma control group. CSF of trauma patients was compared with CSF of non-trauma patients. A secondary objective was to determine whether any of the described measures, alone or in combination, had utility as predictors of clinical outcomes after TBI.
[0589] An objective multimodal classification scheme and outcome measure for traumatic brain injury was developed based on several measures: 1) blood-based biomarkers...
Embodiment 3
[0617] Study 2 - Analysis
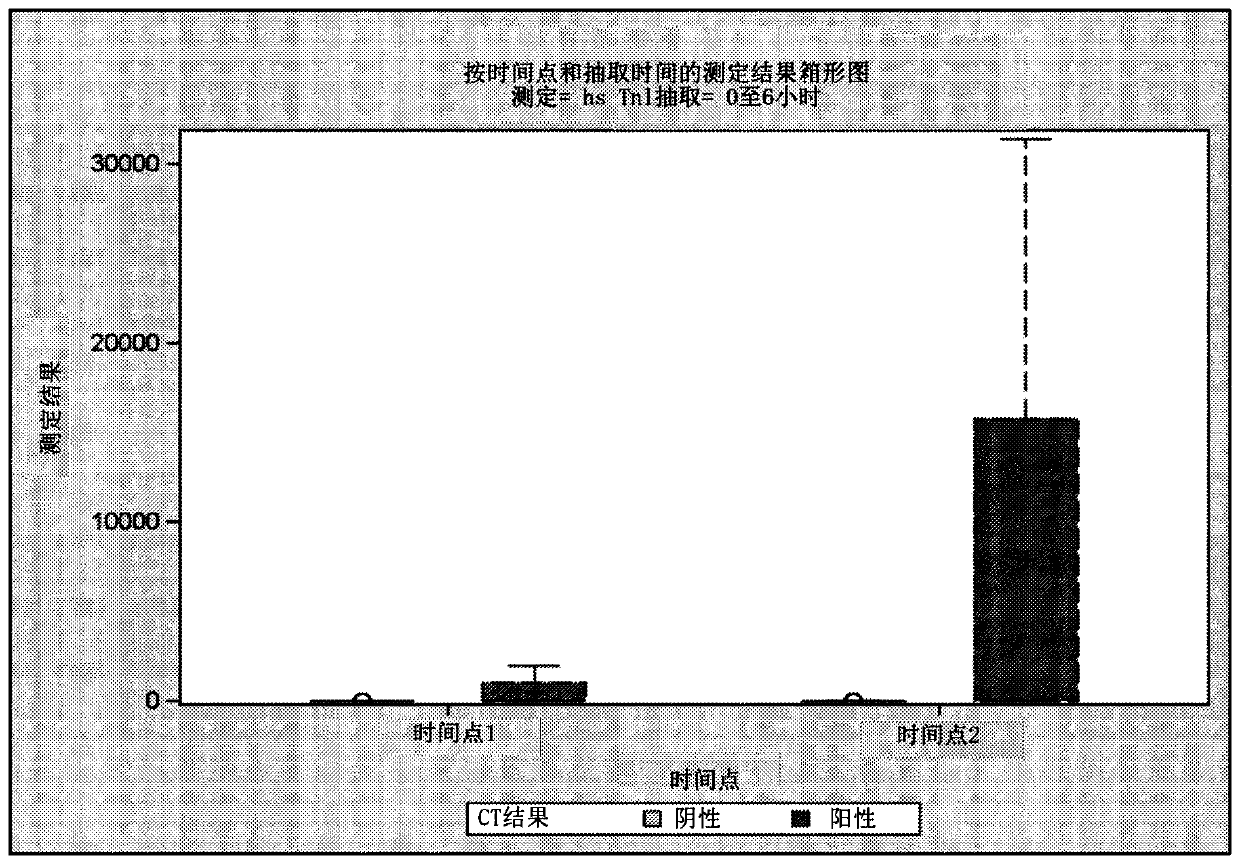
[0618] As described in Example 5, high sensitivity troponin I (hsTnI) was measured in samples obtained from subjects using the Abbott Architect STAT hsTnI assay. Figure 6 and Figure 7 showed, based on CT scan results ( Figure 6 ) and GCS score ( Figure 7 ), hsTnI levels correlate with injury throughout the first 24 hours post-injury (range approximately 2-23 hours).
[0619] Samples taken from subjects within 2 hours of injury: hsTnl levels are measured in samples taken from human subjects within approximately 2 hours of suspected injury. Figure 8 ROC analysis (AUC=0.430) of the correlation of hsTnl levels with CT status (positive vs. negative CT scan results) is shown. Table 12 shows the sensitivity and specificity of using hsTnI cut-off levels to predict positive CT scan results.
[0620] Table 12 CT scan – hsTnI reference level analysis
[0621]
[0622] Figure 9 ROC analysis (AUC=0.588) of association of hsTnI with GCS score outc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com