Semi-supervised target labeling method and system for three-dimensional point cloud data
A three-dimensional point cloud and point cloud data technology, applied in the computer field, can solve the problems of large three-dimensional point cloud data, increase user burden, complex labeling operations, etc., and achieve the effects of improving labeling efficiency, reducing labeling costs, and intuitive labeling process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The following is a detailed description of the embodiments of the present invention: this embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and provides detailed implementation methods and specific operation processes. It should be noted that those skilled in the art can make several modifications and improvements without departing from the concept of the present invention, and these all belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
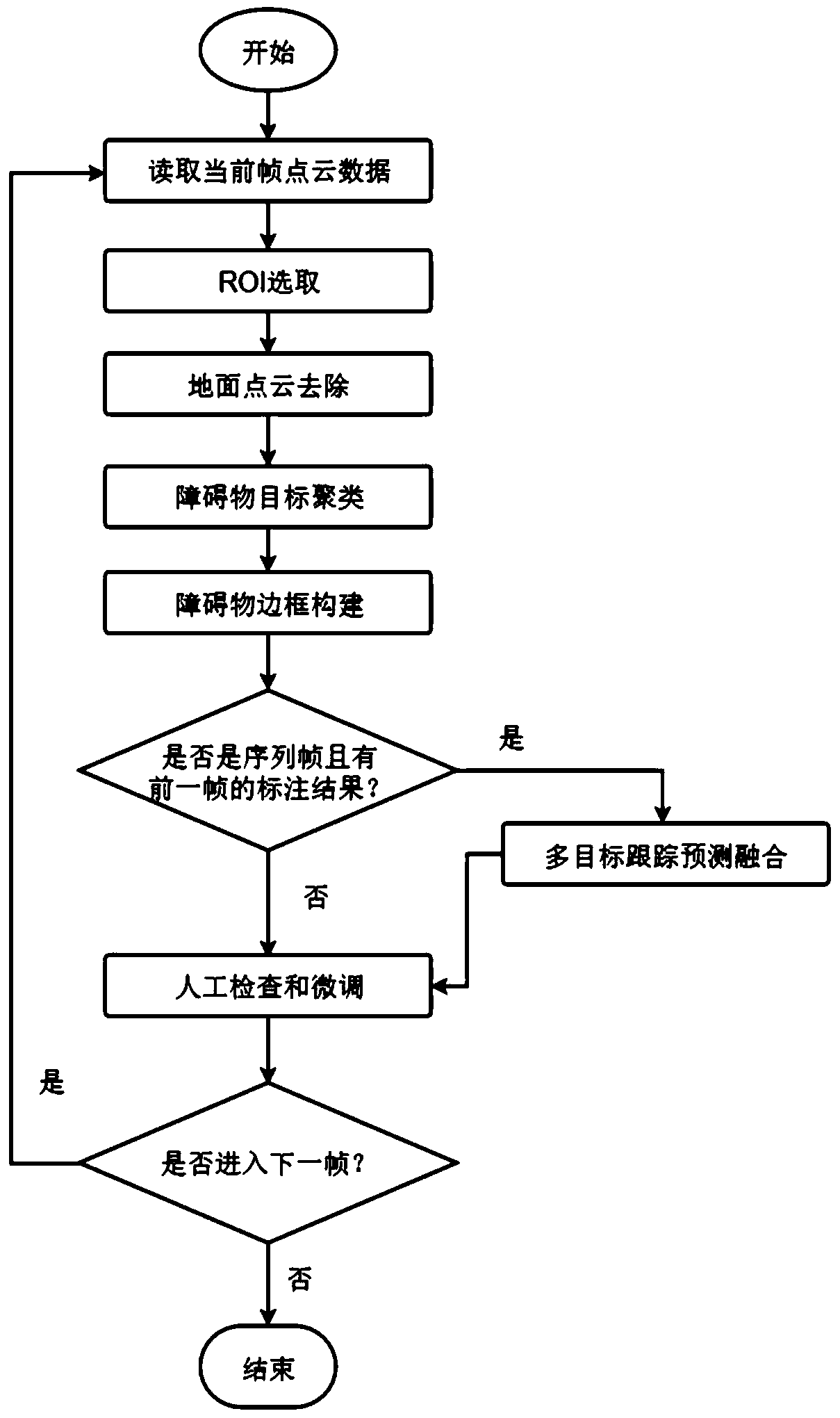
[0050] An embodiment of the present invention provides a semi-supervised target labeling method for 3D point cloud data, comprising the following steps:
[0051] Step 1, read the original 3D point cloud data of the current frame;
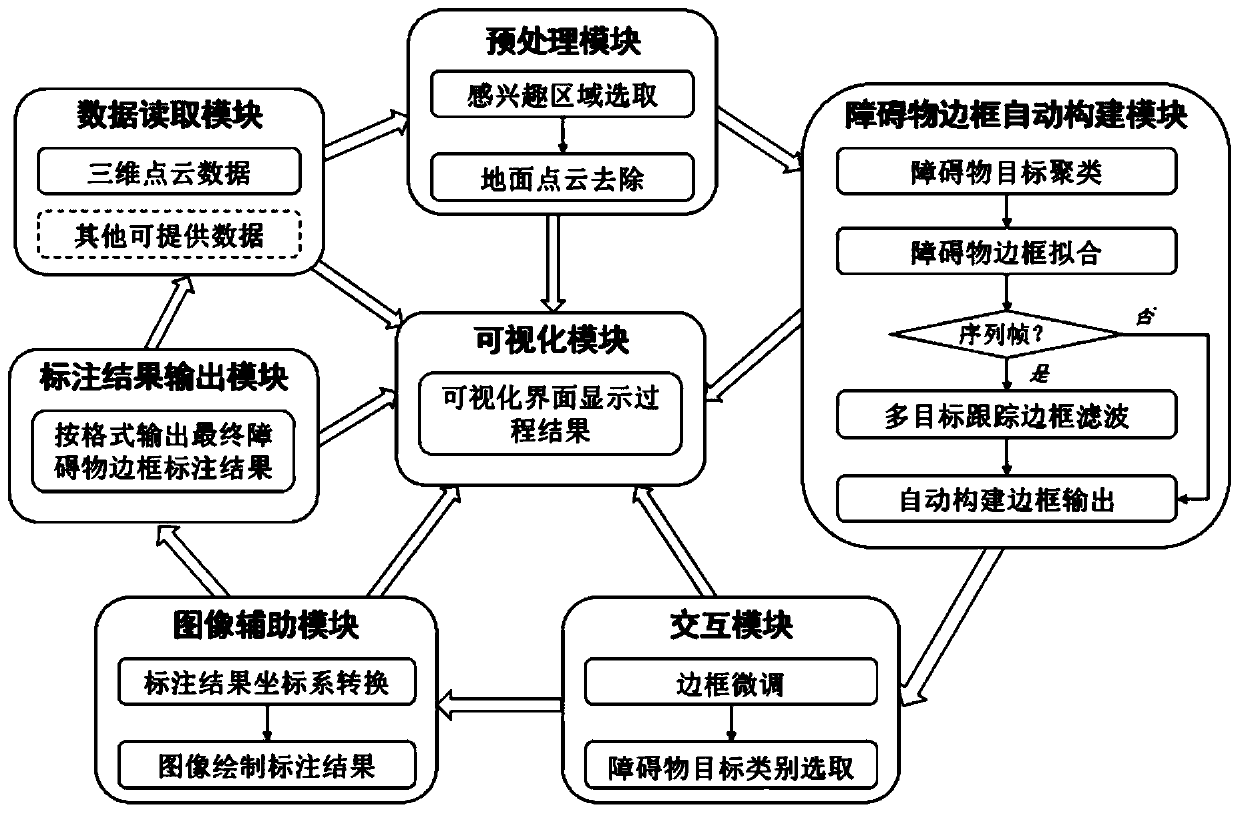
[0052]Step 2, preprocessing the original point cloud data read in step 1, specifically including: Region of Interest (ROI) selection and robust ground segmentation, so that the point data beyond the region of interest and ground point data are filtered out f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com