Micro-grid day-ahead optimal scheduling method of microgrid considering risks
A technology for optimizing scheduling and micro-grid, applied in the field of electricity, can solve problems such as the accuracy cannot meet the requirements of scheduling, the uncertainty of power output power, and the strong volatility of wind power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
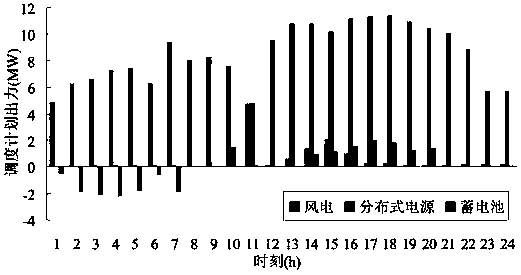
[0152] Example 1: In this example, the risk cost is not considered in the optimization scheduling of the microgrid, that is, β=0 is set. The simulation results show that the total operation of the microgrid does not take into account the uncertainty of wind power and the forced outage of distributed power sources. The cost is 7629$.
[0153] Table 1 below shows the start-stop state and storage battery state of the distributed power supply in Embodiment 1. image 3 Contribute to the day-ahead scheduling plan of each power source in the microgrid.
[0154]
[0155]
[0156] Table 1 Start-stop status of each power supply in the microgrid (β=0)
[0157] From Table 1, image 3 Comprehensive analysis shows that the microgrid is mainly powered by the wind farm during the 1st to 11th period, and the battery is in the charging state most of the time; the microgrid is mainly powered by the distributed power supply during the 12th to 24th period, and the battery is in the dischar...
Embodiment 2
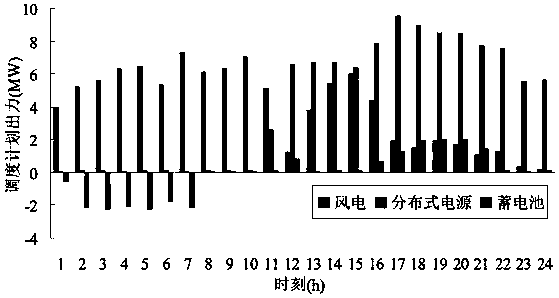
[0158] Embodiment 2: This embodiment studies the influence of different risk levels on the day-ahead optimal scheduling of microgrids. When β=0.9, the total operating cost of the microgrid is 10267$. Compared with Example 1, the total operating cost of the system increases significantly when the operating risk is taken into consideration. Because when the risk cost ratio in the model objective function is large, the system must purchase more electricity from the main grid to ensure the safety and stability of the operation, and less dispatch of wind power and distributed power output, resulting in a substantial increase in operating costs; obviously The added cost is to compensate the power imbalance that may be caused by uncertain factors in the system.
[0159] The following table 2 shows the start-stop status and storage battery status of the distributed power supply in embodiment 2, and the shaded part in table 2 is the status difference compared with table 1. Figure 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com