Method for degrading organic dye by using heterogeneous Fenton system
A heterogeneous Fenton and organic dye technology, applied in the field of water pollution treatment, can solve the problems of slow degradation rate of organic matter, low oxidation efficiency, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing removal rate and improving removal efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
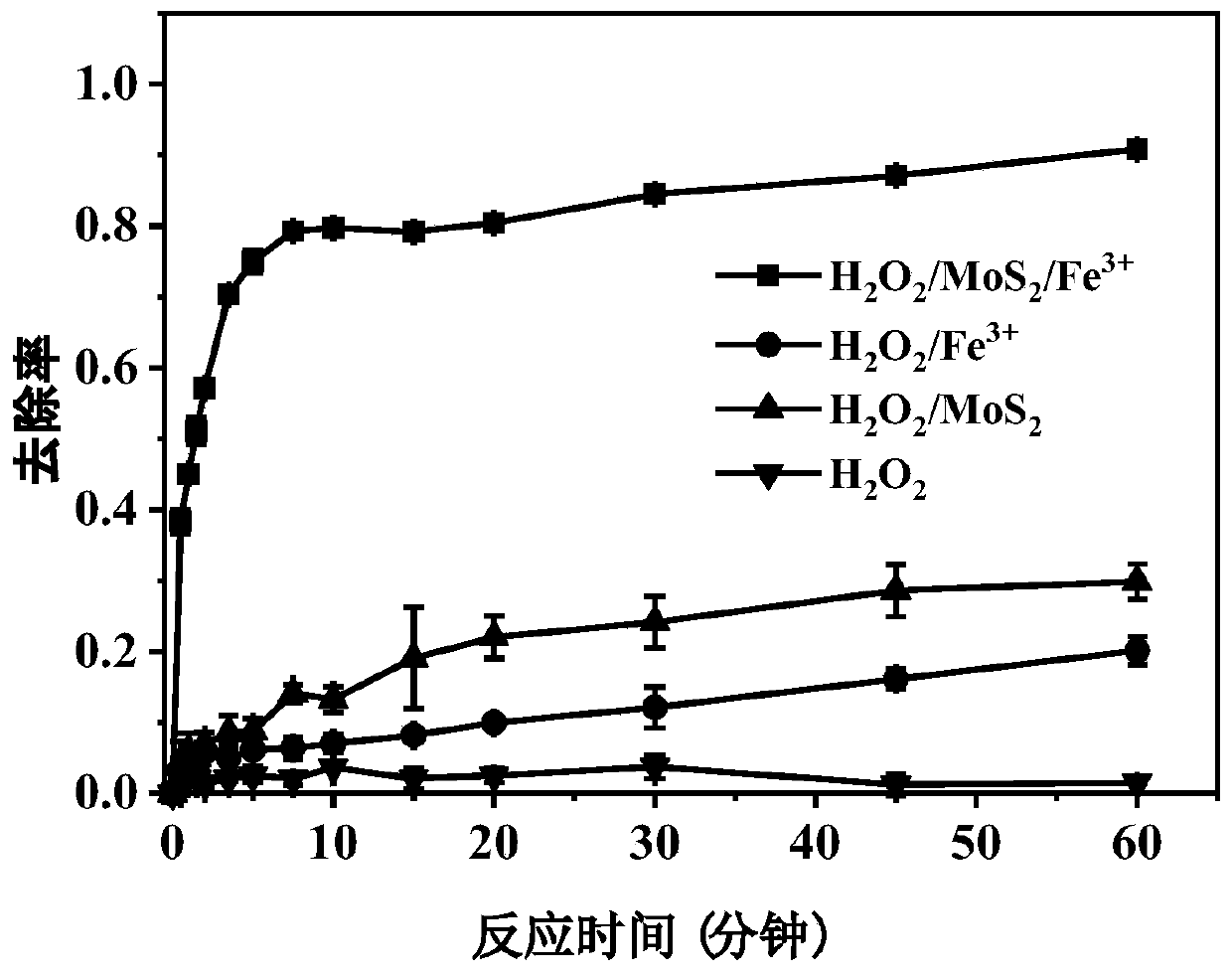
[0029] The influence of different systems of embodiment 1 on removing rhodamine B
[0030] (1) hydrogen peroxide
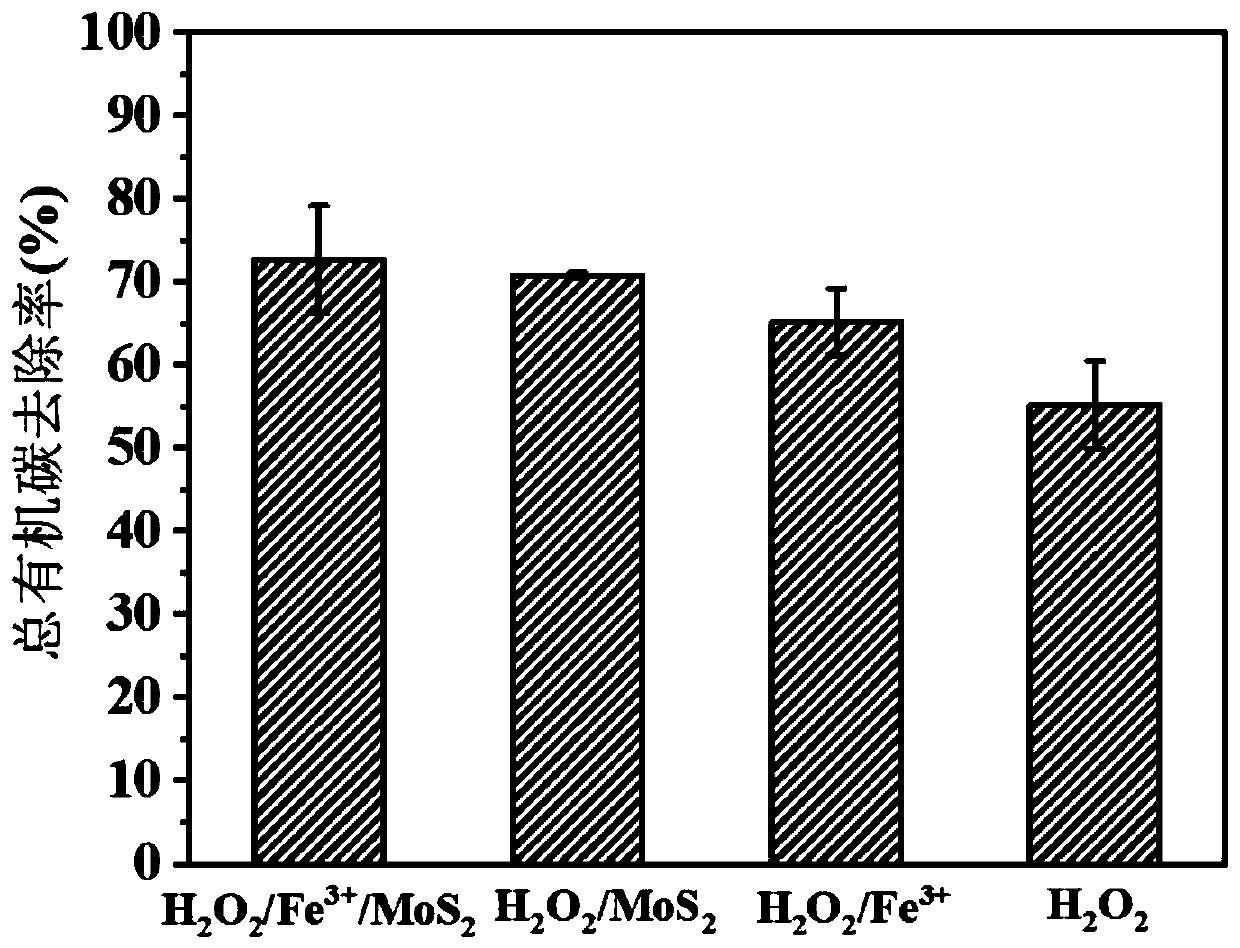
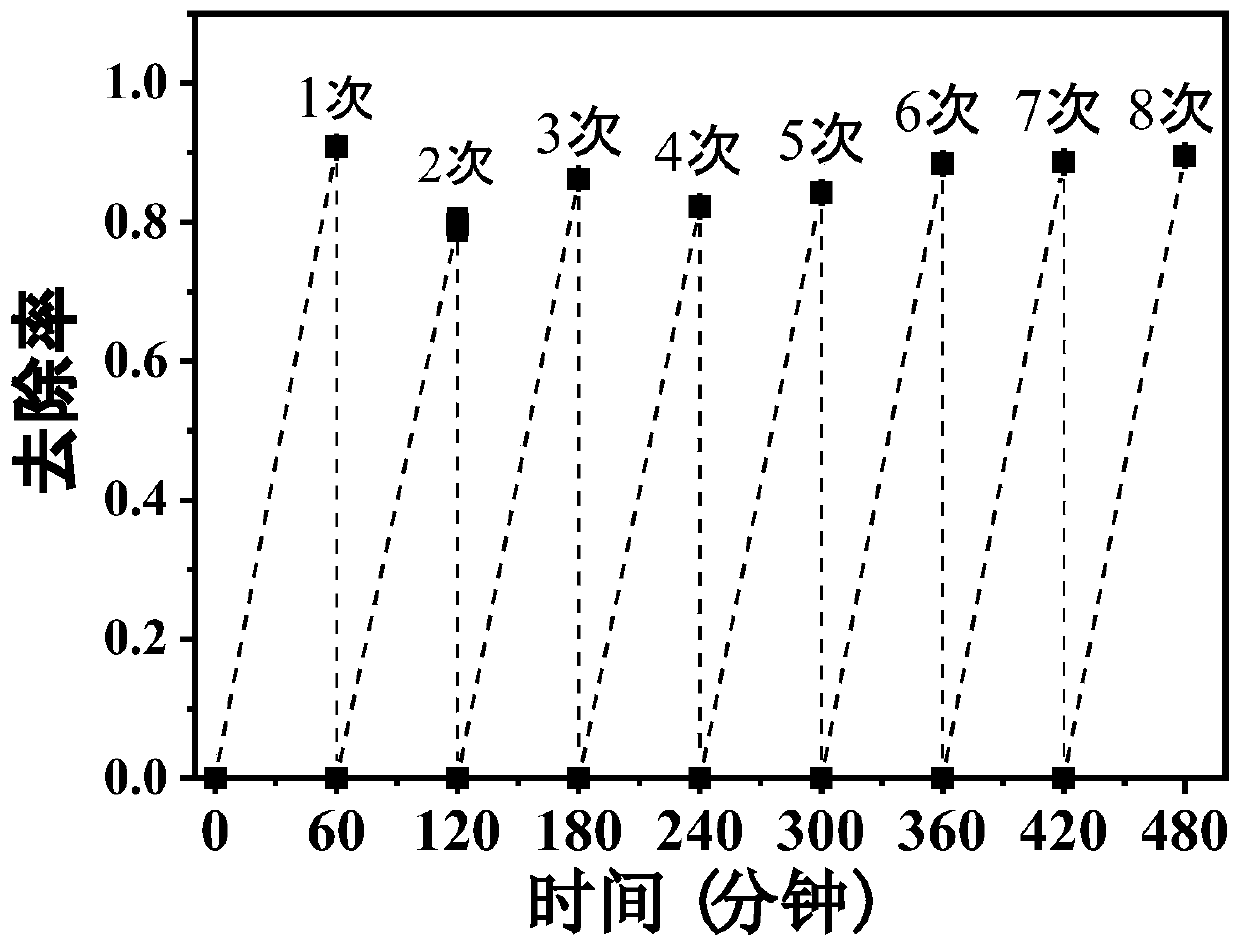
[0031] After adding 89mL of ultrapure water into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 10mL of rhodamine B mother liquor, and use H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH to 3.0, stir evenly and take a "zero" sample, then add 97.9mM H 2 o 2 1mL of aqueous solution constitutes a 100mL reaction system, so that the H in the reaction system 2 o 2 Add the final concentration of 0.979mM, shake and react at 25°C for 60 minutes, take water samples at 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, and 60 minutes respectively, and use UV spectrophotometry detects the absorbance value A at a wavelength of 558nm, and the standard curve A=0.212C+0.0039(R) measured by the rhodamine B standard solution of different concentration gradients (C) 2 =0.9998) obtain Rhodamine B concentration in the sample, and calculate Rhodamine B removal rate (%) by formula (1), the result is as follows figure 1 As ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Different H 2 o 2 Effect of Concentration on Removal of Rhodamine B
[0043] After adding 88mL of ultrapure water into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 0.03g of molybdenum disulfide, ultrasonic (300W) at room temperature for 1 minute, add 10mL of rhodamine B mother solution and 1mL of 15mM ferric chloride aqueous solution, and use H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH to 3.0, stir evenly, take the "zero" sample, and then add H 2 o 2 1mL of aqueous solution constitutes 100mL system, so that the final concentration of ferric chloride in the reaction system is 0.15mM, H 2 o 2 The final concentration of adding was 0.024mM, 0.098mM, 0.490mM, 0.979mM respectively, and the reaction was shaken at 25°C for 60 minutes, and the rhodamine B removal rate was calculated with the method in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0044] Table 1 Different concentrations of H 2 o 2 Effect on removal rate
[0045] h 2 o 2 (mM)
Embodiment 3
[0046] The impact of embodiment 3 different concentrations of iron ions on the removal rate
[0047] After adding 88mL of ultrapure water into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 0.03g of molybdenum disulfide, ultrasonicate (300W) for 1 minute at room temperature, add 10mL of rhodamine B mother solution, add 2.5mM, 1mM, 5mM, 10mM, 15mM 1mL ferric chloride aqueous solution, with H 2 SO 4 Adjust pH=3.0, stir well and take "zero" sample, then add 97.9mM, H 2 o 2 1mL of aqueous solution constitutes a 100mL reaction system, so that the H in the reaction system 2 o 2 Add the final concentration of 0.979mM, Fe 3+ The final concentrations were 0.025mM, 0.01mM, 0.05mM, 0.1mM, 0.15mM respectively, and the reaction was shaken at 25°C for 60 minutes, and the removal rate was calculated with the method in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0048] Table 2 The influence of different concentrations of iron ions on the removal rate
[0049] Fe 3+ (mM)
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap