Block generation and transaction verification method suitable for energy blockchain
A blockchain and transaction technology, applied in the field of blockchain data transaction verification, can solve problems such as difficulty in adapting to the centralization of transactions in the energy industry, difficulty in quickly merging transactions, and difficulty in operation and maintenance, achieving fast verification speed and reducing storage space. Wasteful, verifying the effect of a high success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
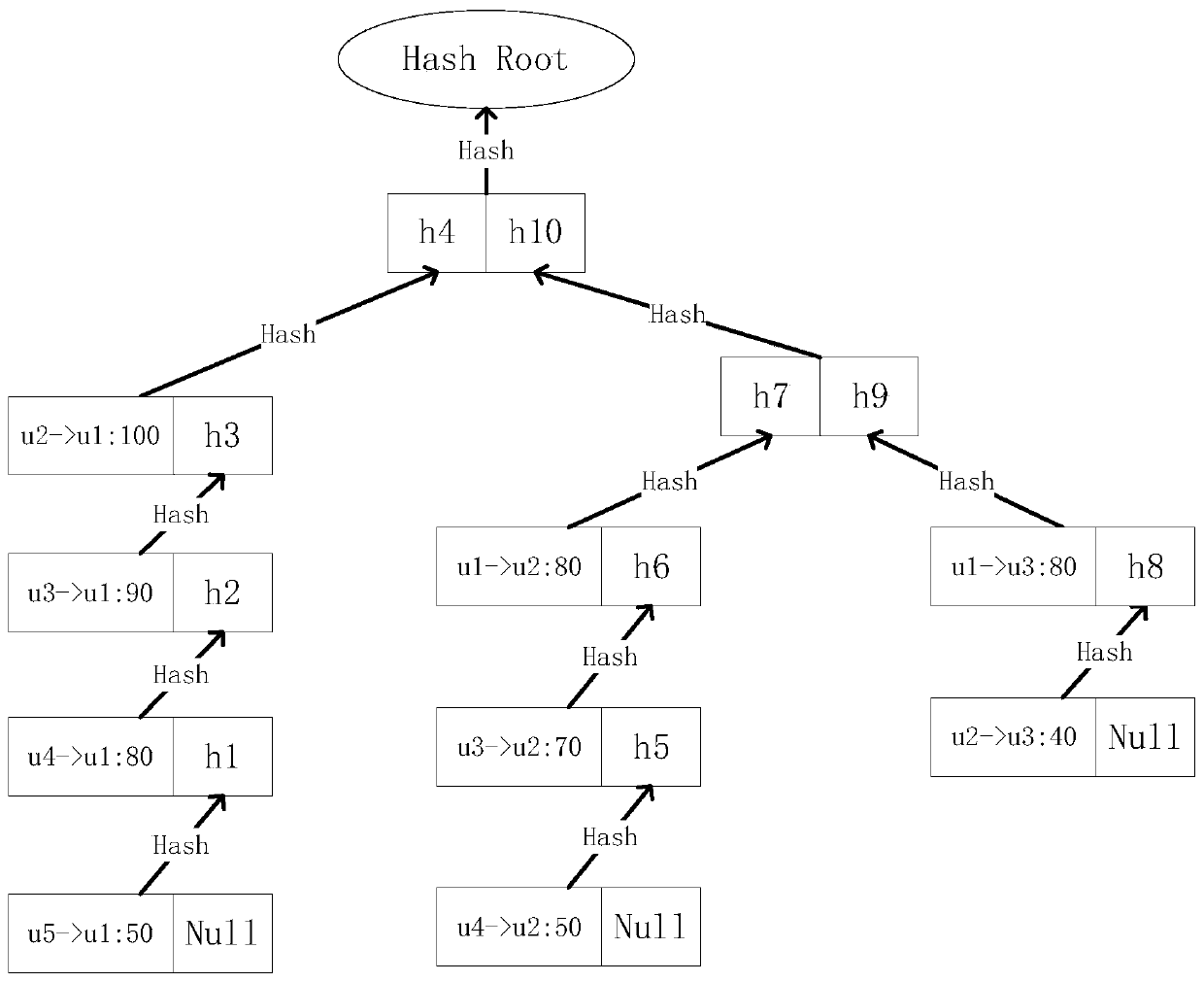
[0045] This embodiment assumes that in a block generation cycle of an energy transaction scenario, there are three bookkeeping nodes p1, p2, and p3, and there are transactions between five accounts u1-u5, -> indicates the flow of funds, and the transactions are respectively : U2->u1:100, U3->u1:90, U4->u1:80, U5->u1:50, U1->u2:90, U3->u2:70, U4->u2:50, U1->u3: 80, U2->u3: 40.
[0046] 1. p1, p2, and p3 respectively calculate a mathematical problem, and broadcast it to the whole network immediately after solving it. Assuming that p1 is solved at this time, after receiving the result, p2 and p3 know that p1 should keep the account this time, p2, p3 stop calculation;
[0047] 2.p1 obtains all transactions that occurred in the entire network in this bookkeeping cycle, calculates the accounts involved, and obtains the account status from the previous block. If there is no such account status in the previous block, go to the previous block. blocks, and so on. In this example, the...
example 2
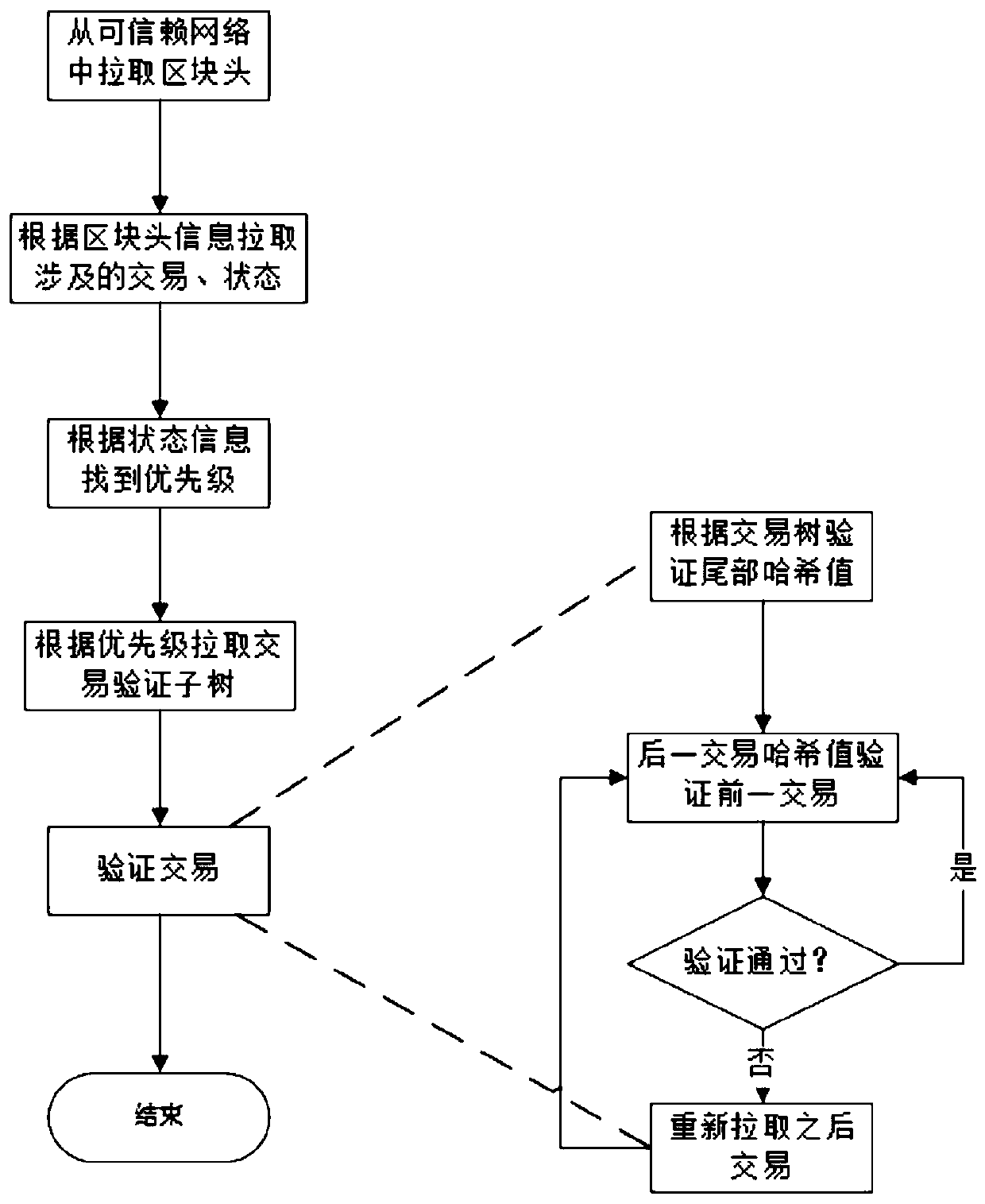
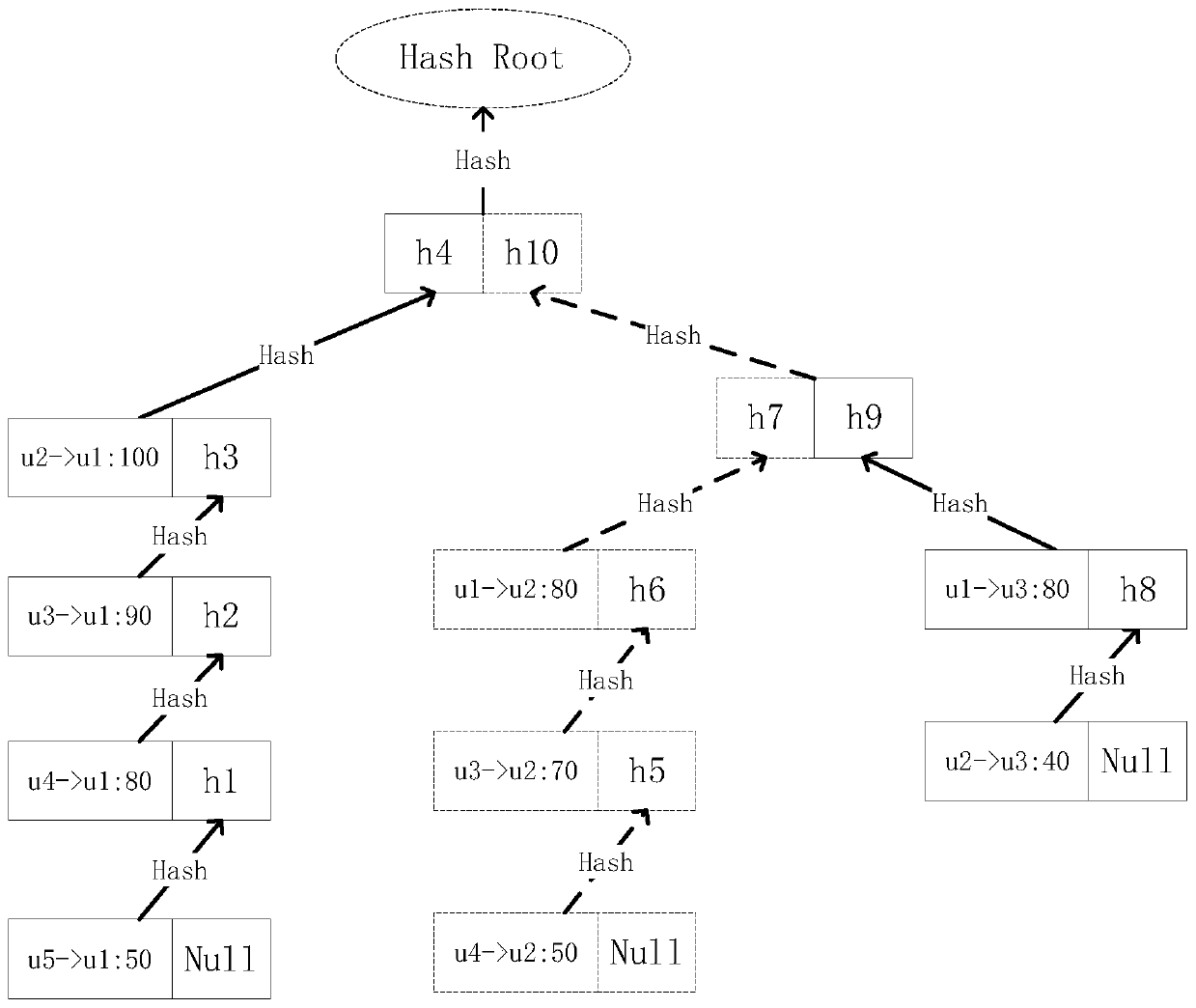
[0064] This embodiment assumes that in a block generation cycle of an energy transaction scenario, transactions between five accounts u1-u5 were packaged in the previous cycle, -> indicates the flow of funds, and the transactions are: U2->u1:100, U3->u1:90, U4->u1:80, U5->u1:50, U1->u2:90, U3->u2:70, U4->u2:50, U1->u3:80, U2 -> u3: 40. After the last bookkeeping is over, u2 needs to verify all transactions reached in the previous cycle.
[0065] 1. U2 requests all block headers from p1, p2, and p3 through the client, and after receiving the request, p1, p2, and p3 send all block headers to the client in turn. The client records the block headers returned by most nodes locally in order.
[0066] 2. The client obtains the transaction tree saved in the block of the previous cycle from any node, and at the same time obtains all transactions packaged by u2 in the previous cycle from the other node.
[0067] 3. The client starts to verify the transaction
[0068] 3.1 First sort ...
example 3
[0076] In this embodiment, it is assumed that in one billing cycle, the height of the block to be packaged is 20, and there are u1 u2 u3 u4 u55 users participating in the transaction, among which, the last transaction of the u1 account was a block with a height of 10, and the last transaction of u3 is a block with a height of 15, the last transaction of u4 was a block with a height of 18, the last transaction height of u2 and u5 was 19, node p1 packs the block, and will verify the account status, the steps are as follows:
[0077] 1. Find the previous block, which is a block with a height of 19, find the states of u2 and u5, and find that there are no states of u1, u3, and u4;
[0078] 2. Continue to iterate forward until the block with a height of 10. At this time, all the account statuses involved in this transaction have been obtained;
[0079] 3. P1 verifies u1-u5, and if the verification is passed, it starts accounting:
[0080] 3.1 Pack all transactions into a transacti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com