Synthesis method and application of co-based mof material with tunable pore size with nucleic acid screening function
A nucleic acid molecule and nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of synthesis of Co-based MOF materials, can solve the problems that the interaction of biological macromolecules is in its infancy, and achieve the effects of easy adjustment, simple preparation process, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Synthesis of MOF ligands
[0047] (1): Add 4-bromo-2-methoxybenzoic acid methyl ester and pinacol diboronic acid ester to the N,N-dimethylformamide solution according to the equivalent ratio of 1:1.5. Heated to 85°C under the same conditions and reacted for 5 hours, the product was separated by column chromatography, and intermediate 1 was obtained after rotary evaporation and drying.
[0048] (2): Add 4-bromo-2-methoxybenzoic acid methyl ester and intermediate 1 to 1,4-dioxane and aqueous solution in an equivalent ratio of 1:1, wherein 1,4-dioxane The volume ratio of water and water is 4:1, heated to 90 degrees under anhydrous and anaerobic conditions for 24 hours, and the product is separated by column chromatography. After rotary evaporation and drying, it is added to 50 equivalents of dichloromethane solution, and the - Add 8 equivalents of boron tribromide solution at 78 degrees, react for 12 hours, then quench with excess water, then add 5 equivalents of 1M sodiu...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Particle size distribution test:
[0060] The dried sample is prepared with a single crystal silicon zero background sample stage, and then the structure is tested on a powder X-ray diffraction instrument.
[0061] Analysis of results:
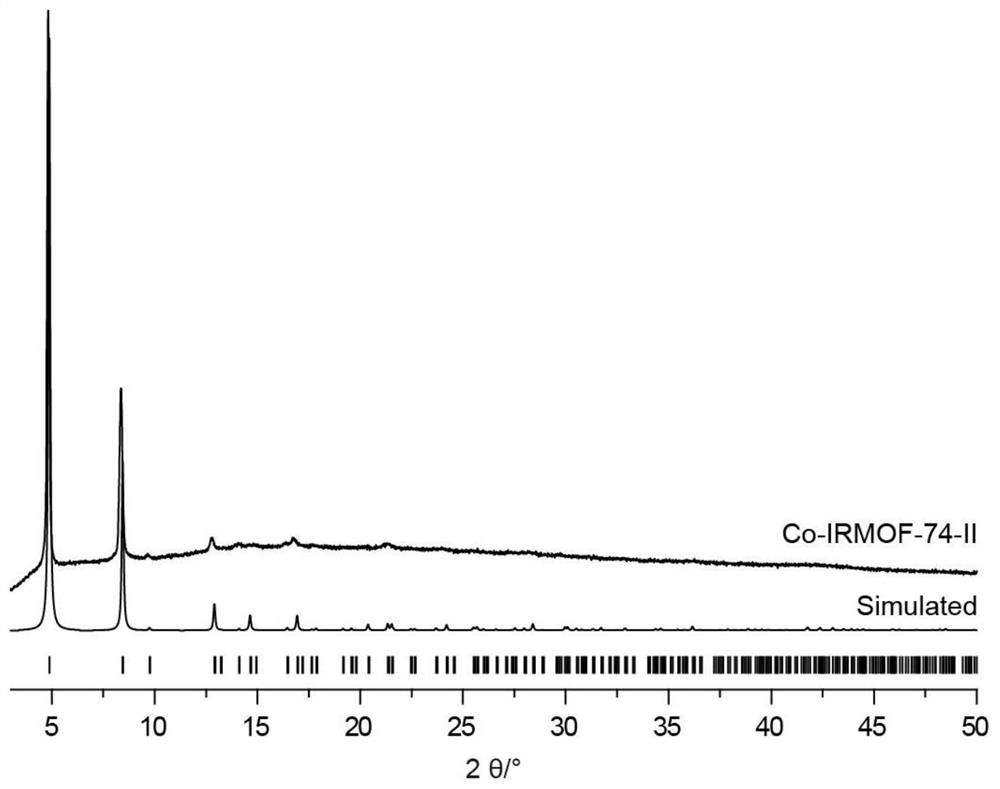
[0062] figure 1 It is the powder crystal diffraction pattern of Co-based IRMOF-74-II and simulated Co-based IRMOF-74-II in Example 1. It can be seen from the figure that the synthesized Co-based IRMOF-74-II structure conforms to the structure of the matching simulation;
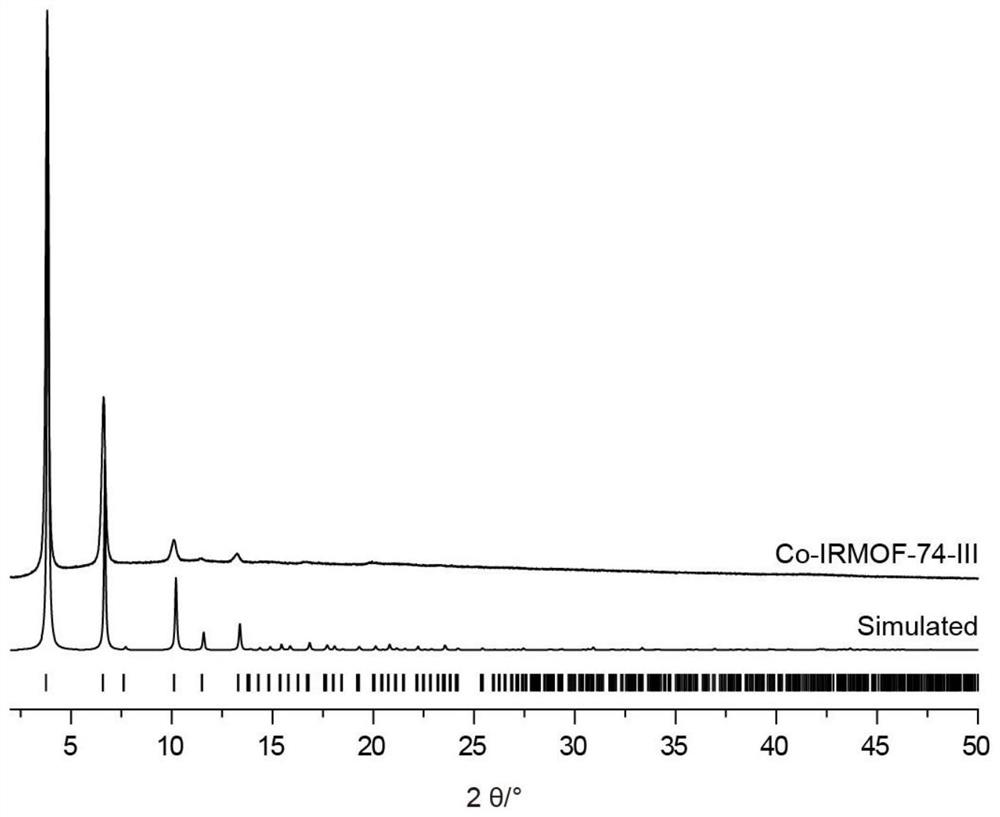
[0063] figure 2 It is the powder crystal diffraction pattern of Co-based IRMOF-74-III and simulated Co-based IRMOF-74-II in Example 1. It can be seen from the figure that the synthesized Co-based IRMOF-74-III structure conforms to the structure of the matching simulation;
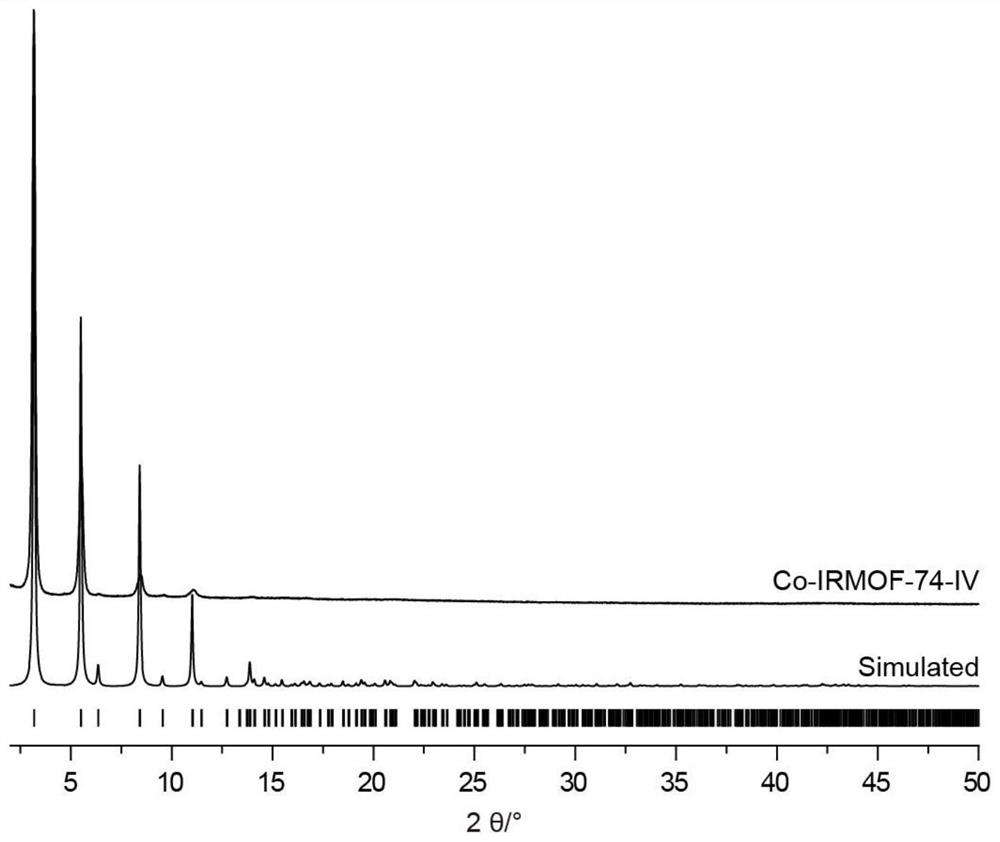
[0064] image 3 It is the powder crystal diffraction pattern of Co-based IRMOF-74-IV and simulated Co-based IRMOF-74-IV in Example 1. It can be seen from the figure that the synthesized Co-base...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Selective Adsorption of Nucleic Acids with Different Spatial Size Structures by MOF Materials
[0072] (Step 1) Design nucleic acids with different structures: ssDNA, dsDNA, G4-DNA, ssRNA, G4-RNA, hairpin-RNA. And label these nucleic acid sequences with terminal fluorescent molecules.
[0073] (Step 2) Test the adsorption efficiency of MOF materials to these nucleic acids with different structures
[0074] (Step 2a) Mix 4 μL of annealed DNA / RNA of different structures (10 μM) with 4 μL of Co-IRMOF-74-II, -III, IV (2 mg / mL) in 50 μL of aqueous solution (containing 100 mM KCl and 20 mM KAc, pH 6 .8), react in a mixer at a constant temperature of 37°C for 2 hours.
[0075] (Step 2b) Measure the fluorescence intensity of the supernatant after centrifugation. The absorption efficiency was calculated using the following formula.
[0076]
[0077]
[0078] (FIoriginal is the fluorescence intensity of pure fluorescently labeled DNA / RNA in a buffer solution without MOF ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com