Dynamic knowledge graph representation learning method and system based on anchor points
A technology of knowledge graph and learning method, applied in the field of anchor-based dynamic knowledge graph representation learning method and system, which can solve the problems of low efficiency, time-consuming and laborious, and achieve the effect of entity alignment and relationship fusion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
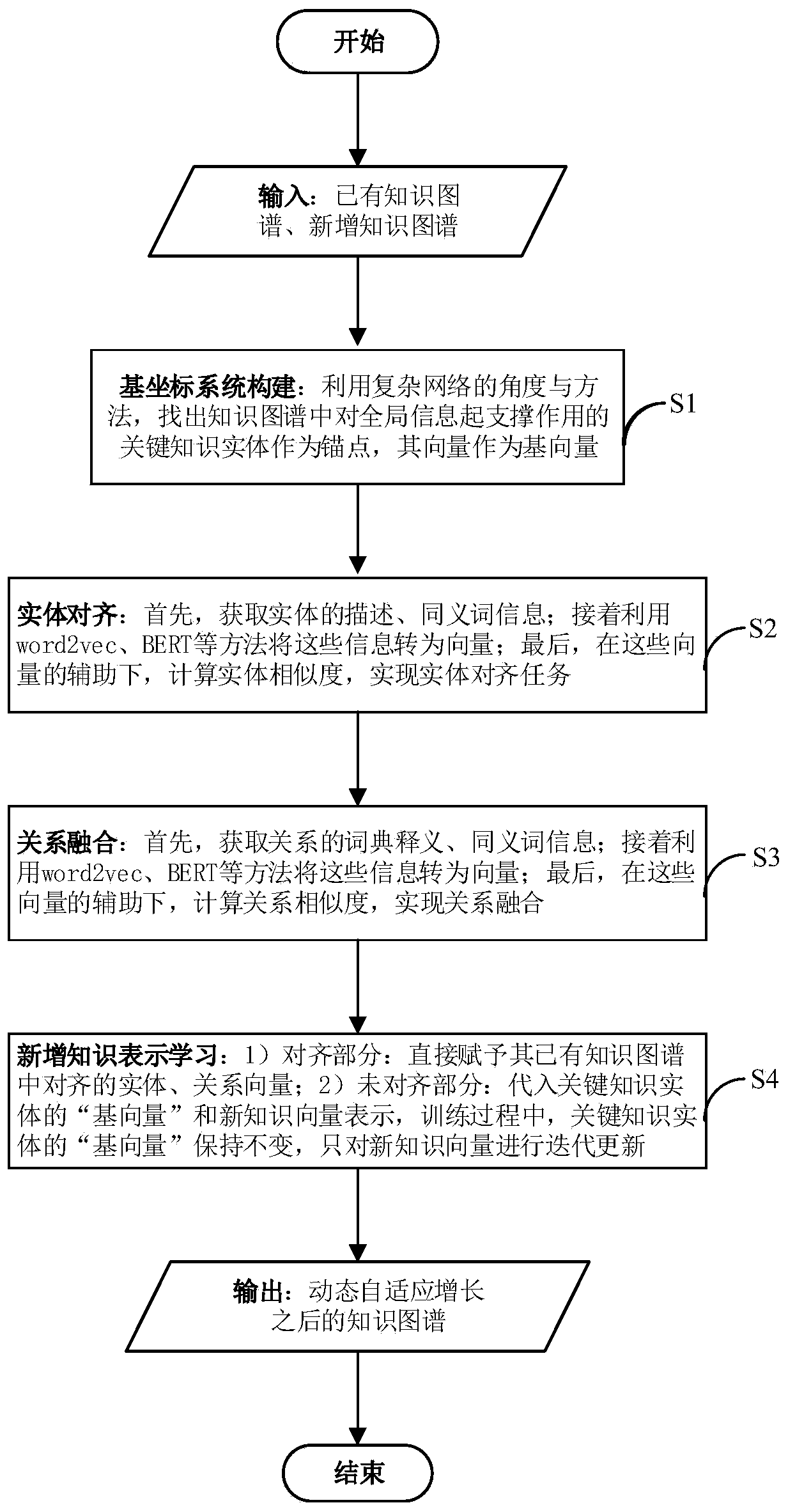
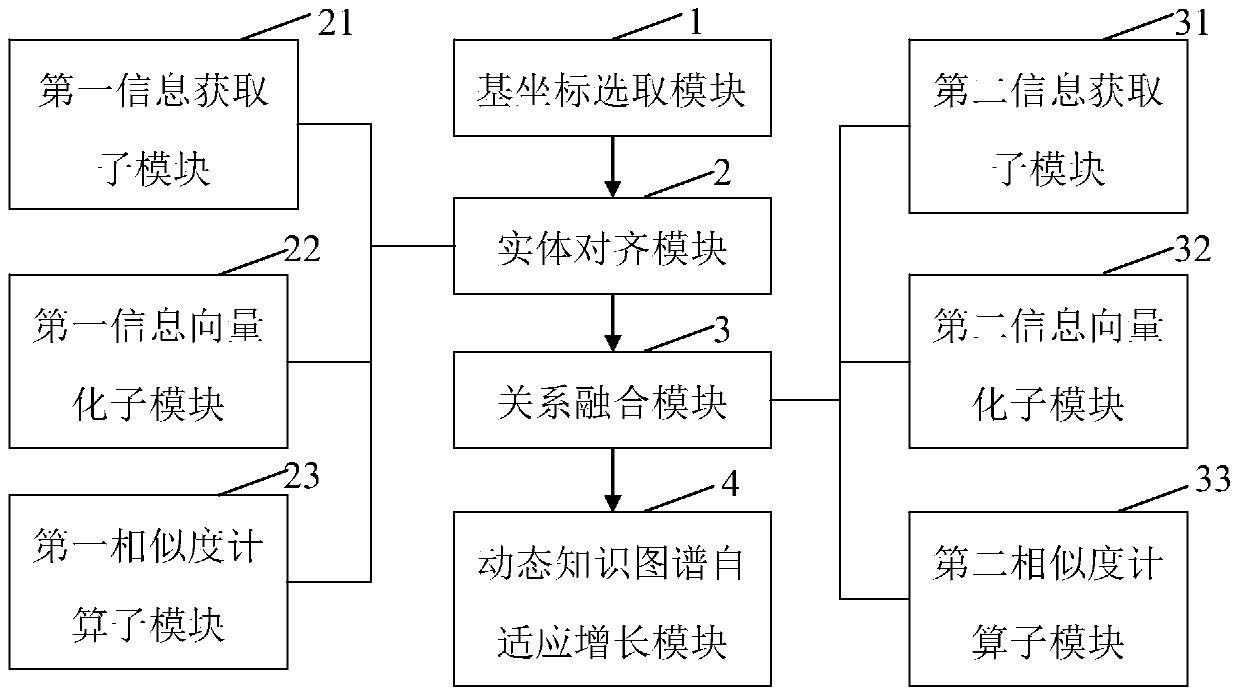
[0034] Please refer to figure 1 , this embodiment provides an anchor-based dynamic knowledge map representation learning method, including the following steps:
[0035]S1. Construct the base coordinate system: use the complex network analysis method to find out the key knowledge entities that support the global information in the existing knowledge map as anchor points, and use the vector of the anchor point as the base vector to construct the base coordinates system.
[0036] Specifically, the knowledge map is analyzed by complex network partitioning technology, and the greedy algorithm that introduces the minimum point covering algorithm is used to find nodes (that is, entities) that have more information interactions with other nodes in the existing knowledge map and are scattered as anchor points; The greedy algorithm that introduces the minimum point covering algorithm is applicable to any data presented in the form of a network. The specific process of using the algorit...
Embodiment 2
[0054] This embodiment adopts the k-shell algorithm when selecting the anchor point, and all the other processes are the same as in embodiment one, and the specific process of the k-shell algorithm is:
[0055] (1) Calculate the degree of all entities in the existing knowledge graph;
[0056] (2) Take out all entities with a degree of 1, put them into the shell_1 layer, continue to calculate the degree of the remaining entities in the existing knowledge map, take out the entities with a degree of 1, and put them into the shell_1 layer again; repeat the above process until Entities with a degree of 1 are fetched;
[0057] (3) Take out all entities with a degree of 2, put them into the shell_2 layer, continue to calculate the degree of the remaining entities in the existing knowledge map, take out the entities with a degree of 2, and put them into the shell_2 layer again; repeat the above process until Entities with a degree of 2 are fetched;
[0058] (4) Calculate the degree ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com