Method and device for realizing distributed local sound mixing
An implementation method and distributed technology, applied in the transmission system, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of unsolvable performance, unsatisfactory, high cost, etc., and achieve the effects of saving RTP stream resources, reducing equipment costs, and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
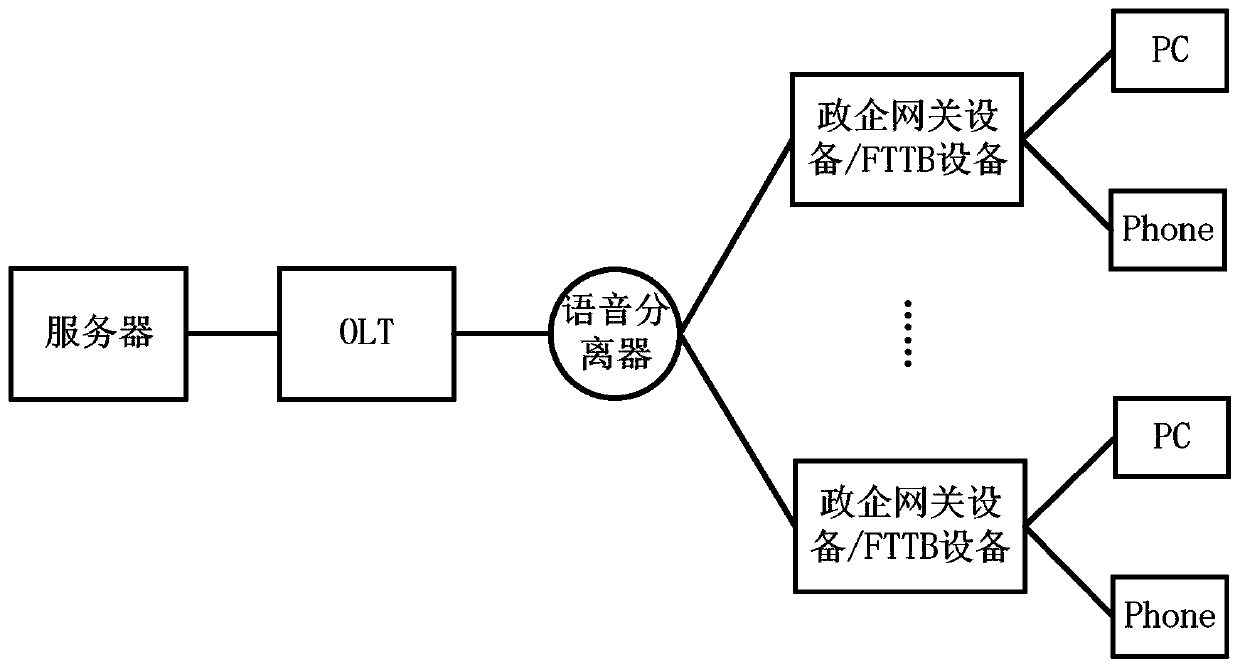
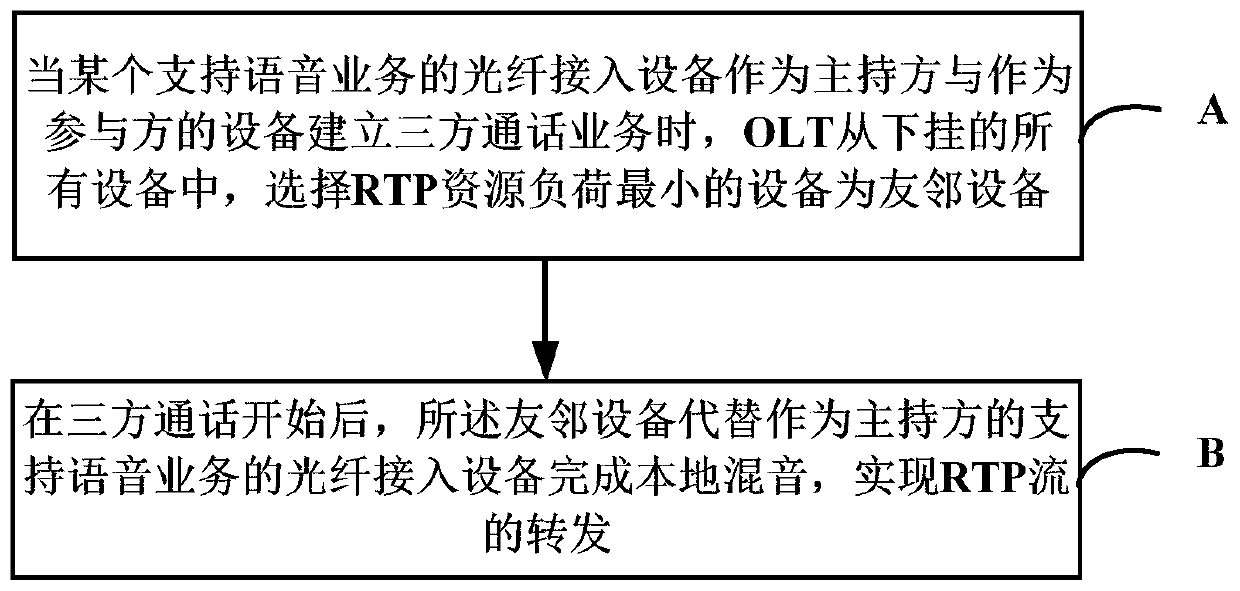
[0042] This embodiment provides a method for implementing distributed local audio mixing, which is used in an application scenario of a three-party call. see figure 1 As shown, the three-party call application scenario includes an OLT connected to a server, and a plurality of optical fiber access devices supporting voice services are connected to the OLT. see figure 2 As shown, the implementation method of the distributed local mixing includes the following steps:
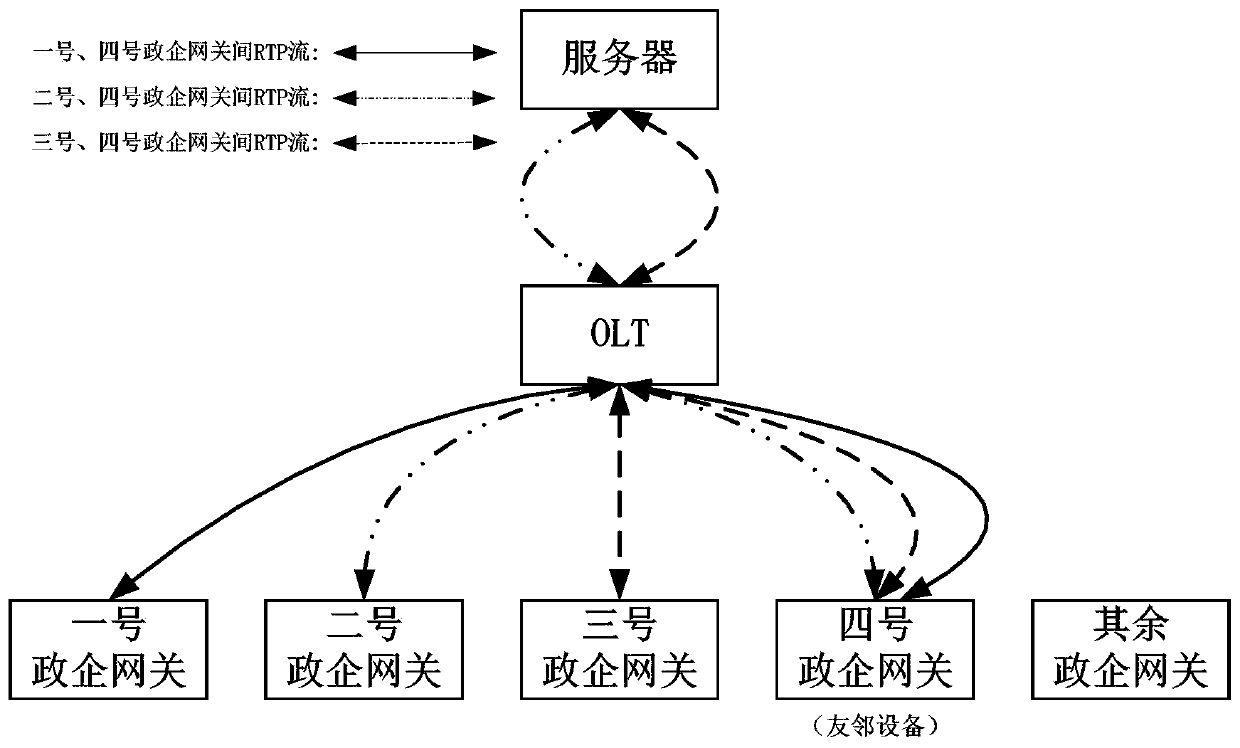
[0043] A. When a fiber-optic access device that supports voice services acts as the host and establishes a three-party call service with a device that acts as a participant, the OLT selects the device with the smallest RTP resource load as the neighbor device from all the connected devices;
[0044] B. After the three-party call starts, the neighbor device replaces the fiber optic access device supporting the voice service as the moderator to complete the local audio mixing, and realizes the forwarding of the RT...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The implementation method of a distributed local audio mixing provided by this embodiment, its basic steps are the same as those of Embodiment 1, the difference is that, as an optional implementation mode, in this embodiment, each voice service Fiber access devices record their own RTP resource usage in real time. The RTP resource usage is zero by default. When the fiber access device that supports voice services has a port that goes off-hook to open a channel, the RTP resource usage is increased by 1; when the fiber access device that supports voice services has a port that is switched off, The RTP resource usage is reduced by 1.
[0053] On this basis, in step A of the method, the OLT selects the device with the smallest RTP resource load as the neighbor device from all the connected devices, which specifically includes the following steps: the OLT obtains the RTP resource usage of all the connected devices ; By comparing the size of the RTP resource usage, select th...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The implementation method of a distributed local audio mixing provided by this embodiment has the same basic steps as the first embodiment, the difference is that, as an optional implementation, the OLT maintains a three-party call record table, the The table records the source IP address of the host device, the POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service, analog telephone service) port number of the host device, and the first source UDP (User Datagram Protocol, User Datagram Protocol) corresponding to the POTS port of the host device port number, the second source UDP port number corresponding to the POTS port of the host device, the source IP address of the neighbor device, and the first source UDP port number and the second source UDP port number used by the neighbor device to assist the three-party call, Third source UDP port number.
[0059] On this basis, in step B of the method, the neighbor device replaces the fiber access device supporting the voice service as the modera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com