Method for in vivo generation of multispecific antibodies from monospecific antibodies
An antibody and specific technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, chemical instruments and methods, specific peptides, etc., can solve difficult problems such as high throughput and contamination of bsAb products, and achieve efficient production effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
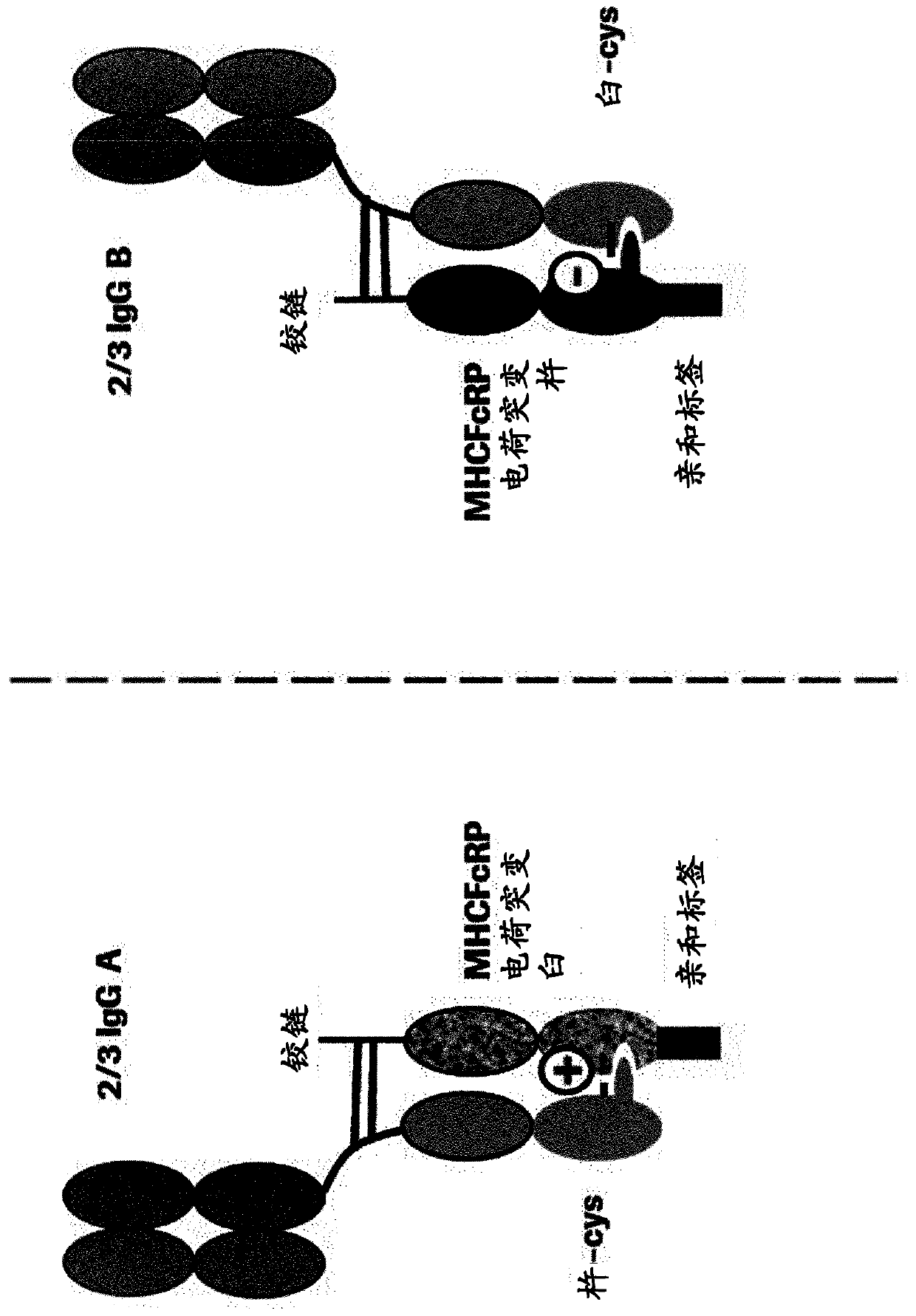
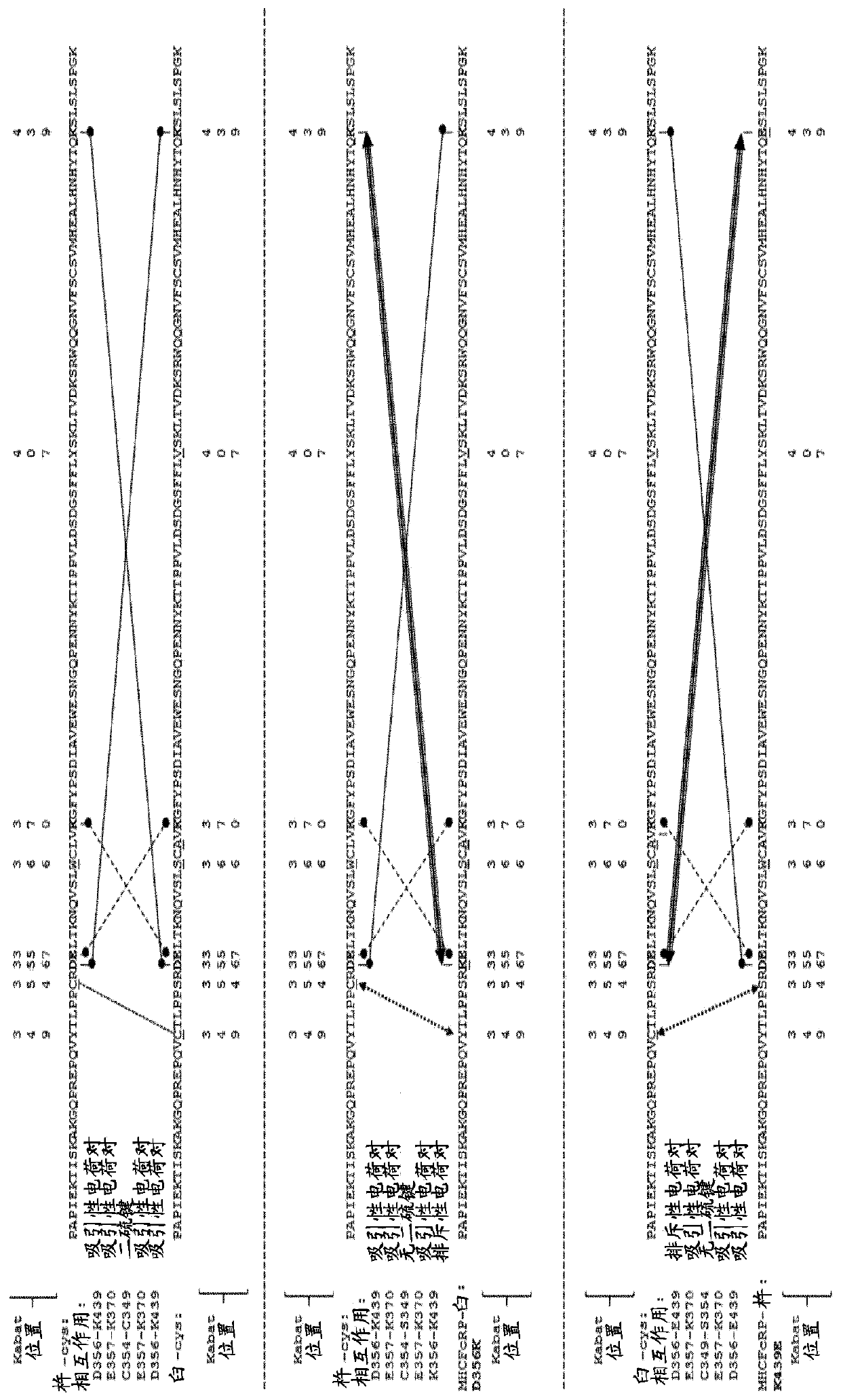
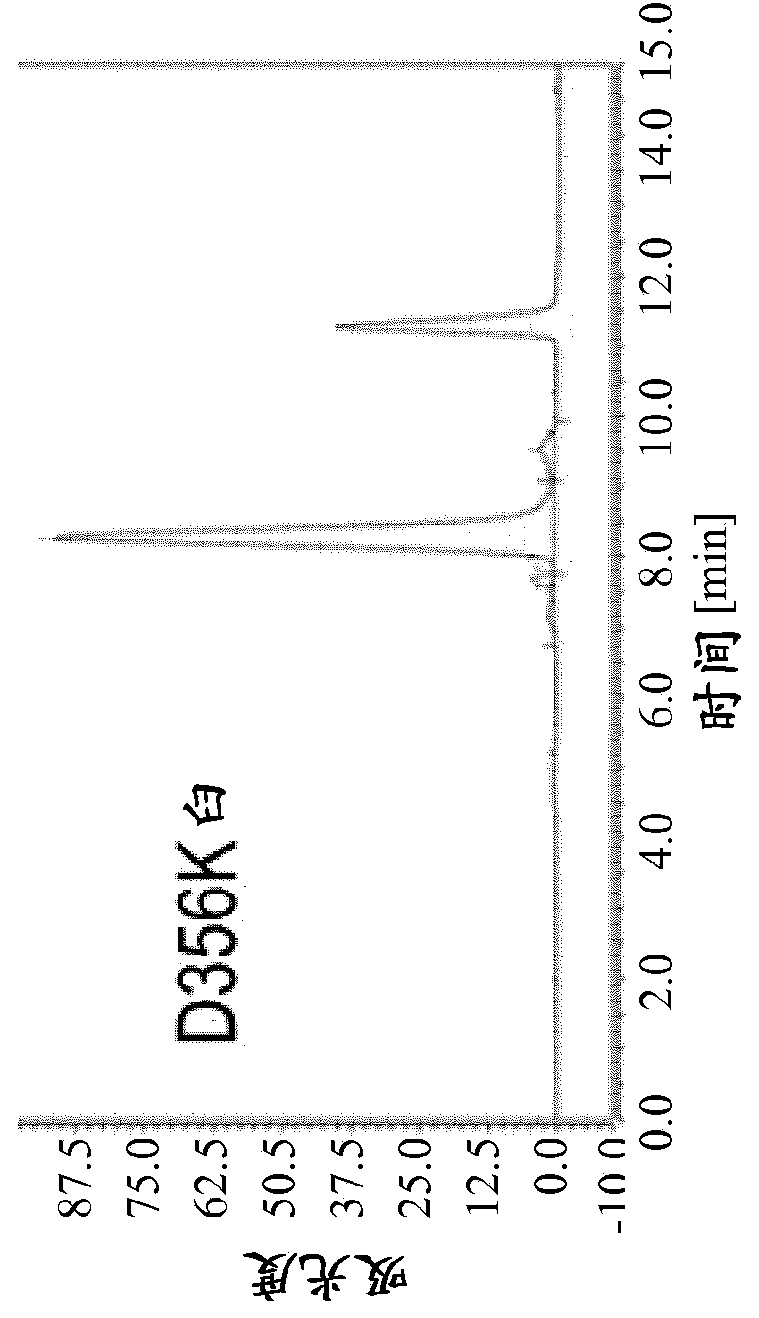
[0578] The present invention is based at least in part on the discovery that multispecific antibodies can be obtained by half-antibody exchange reactions using as starting materials incomplete antibodies such as 2 / 3-IgGs or 2 / 3-BiFabs comprising antibody light chains, anti- Heavy chains and antibody heavy chain fragments, wherein the heavy chain-heavy chain interaction is destabilized by an asymmetric interfering mutation, preferably in the heavy chain fragment, wherein the interfering mutation on the one hand facilitates the dissolution of the initial incomplete antibody On the other hand, it promotes the production of correctly assembled full-length bi / multispecific antibodies. It was further found that the method of the invention can be carried out even without a reducing agent using the starting compound if the heavy chain-heavy chain disulfide bond in the starting incomplete antibody is removed (the generation of the starting material and exchange reactions and generation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com