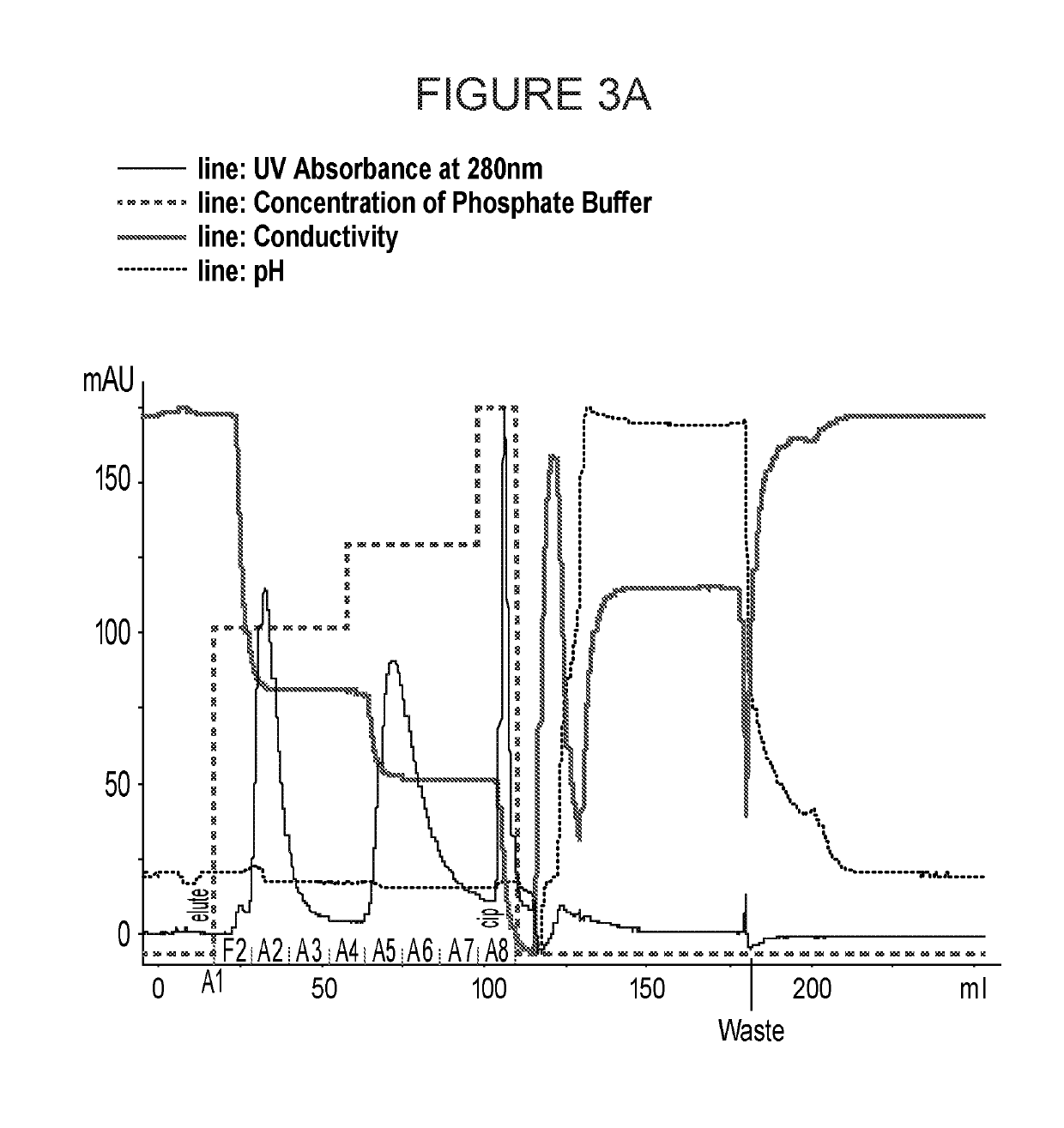
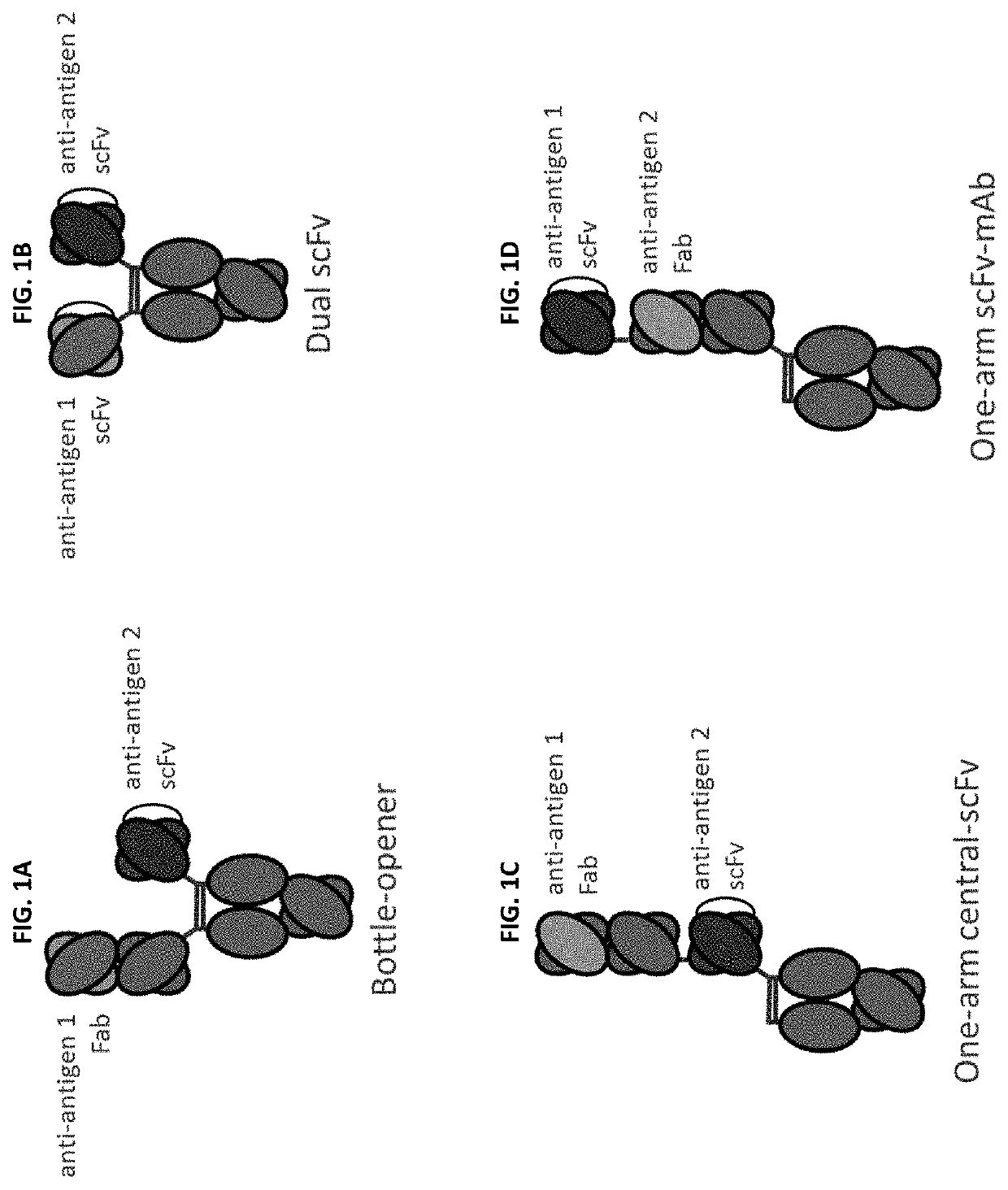
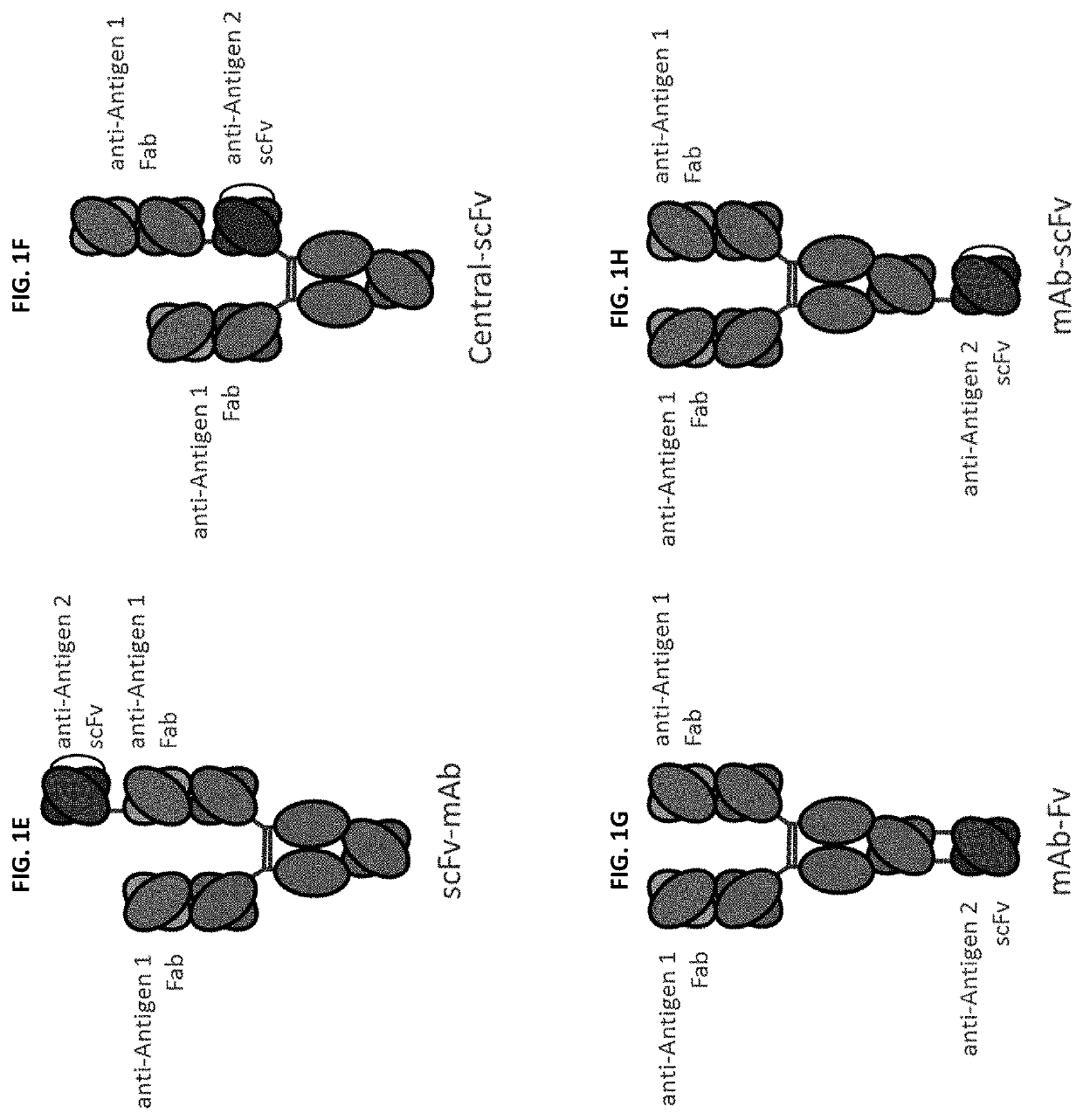
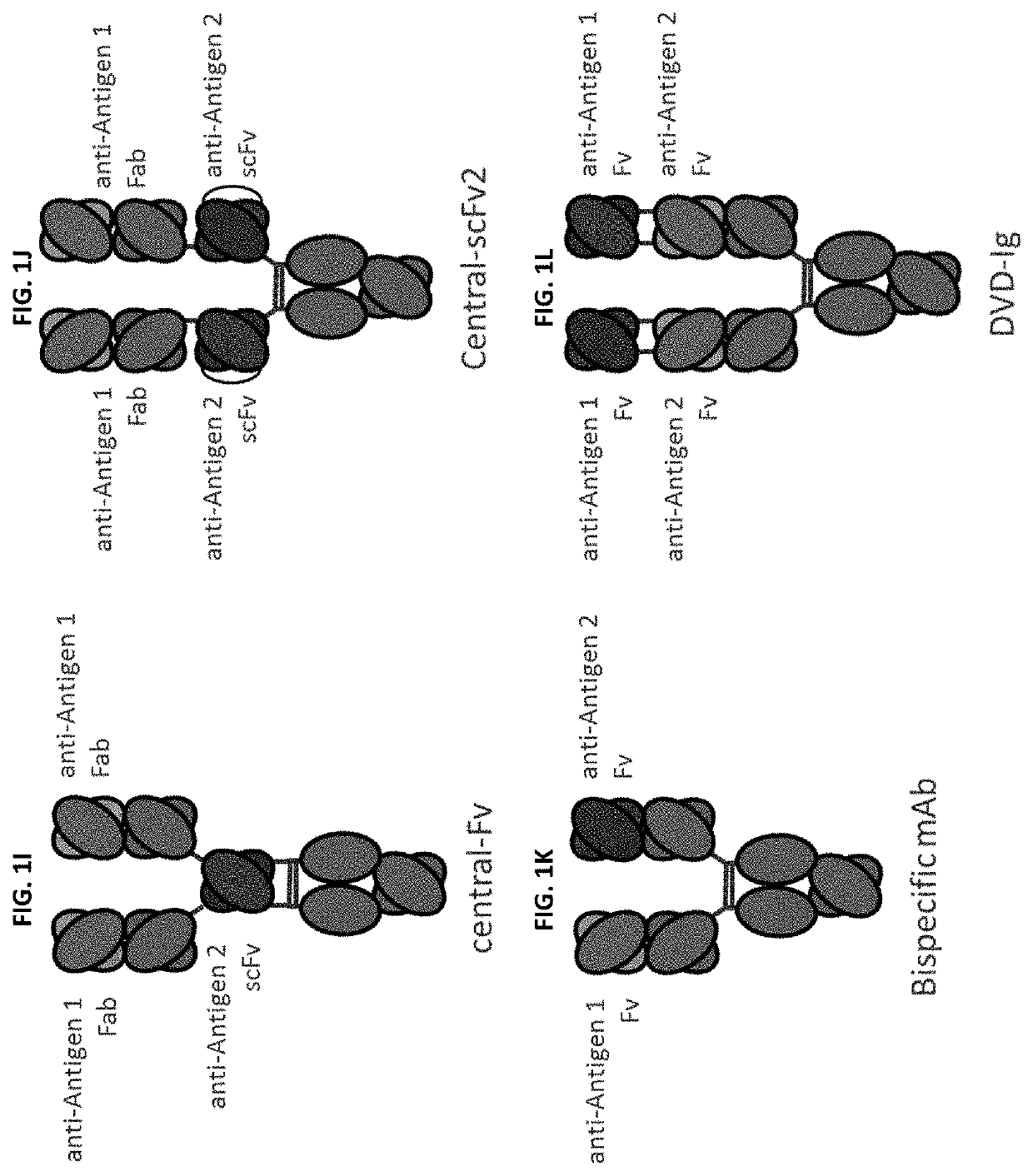
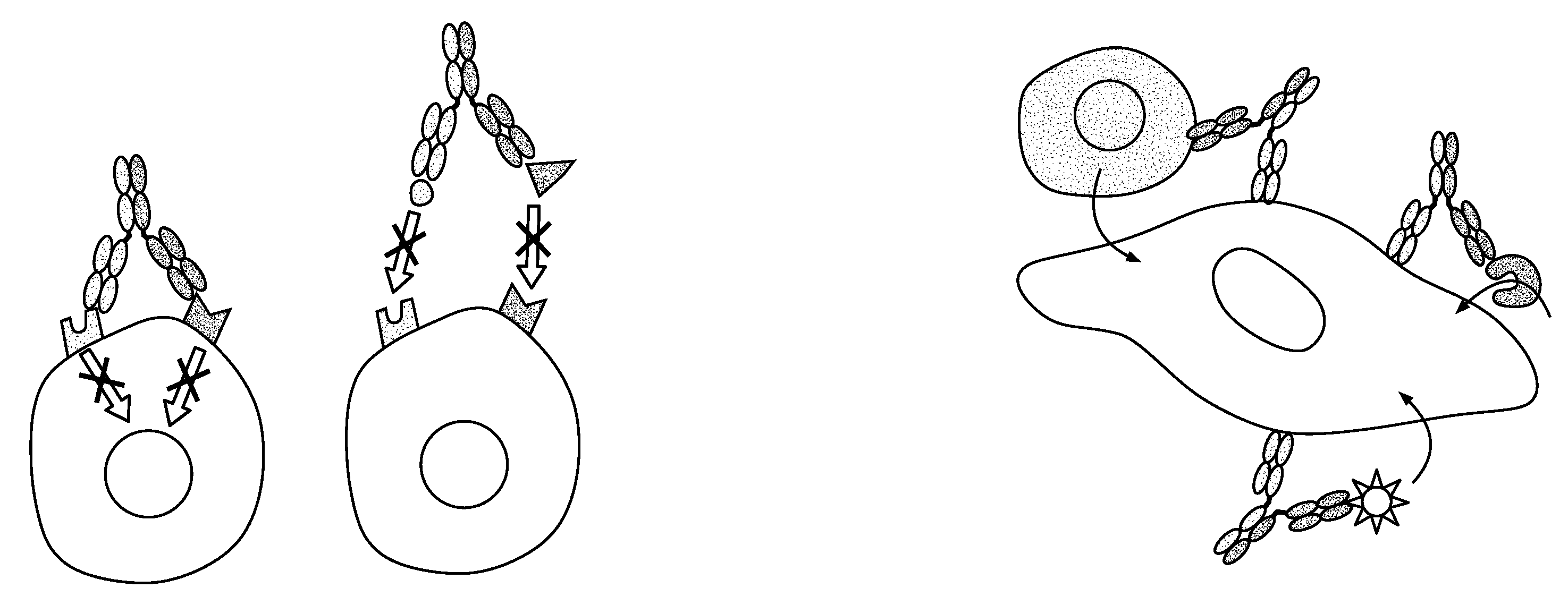Patents
Literature
35 results about "Monospecific antibody" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
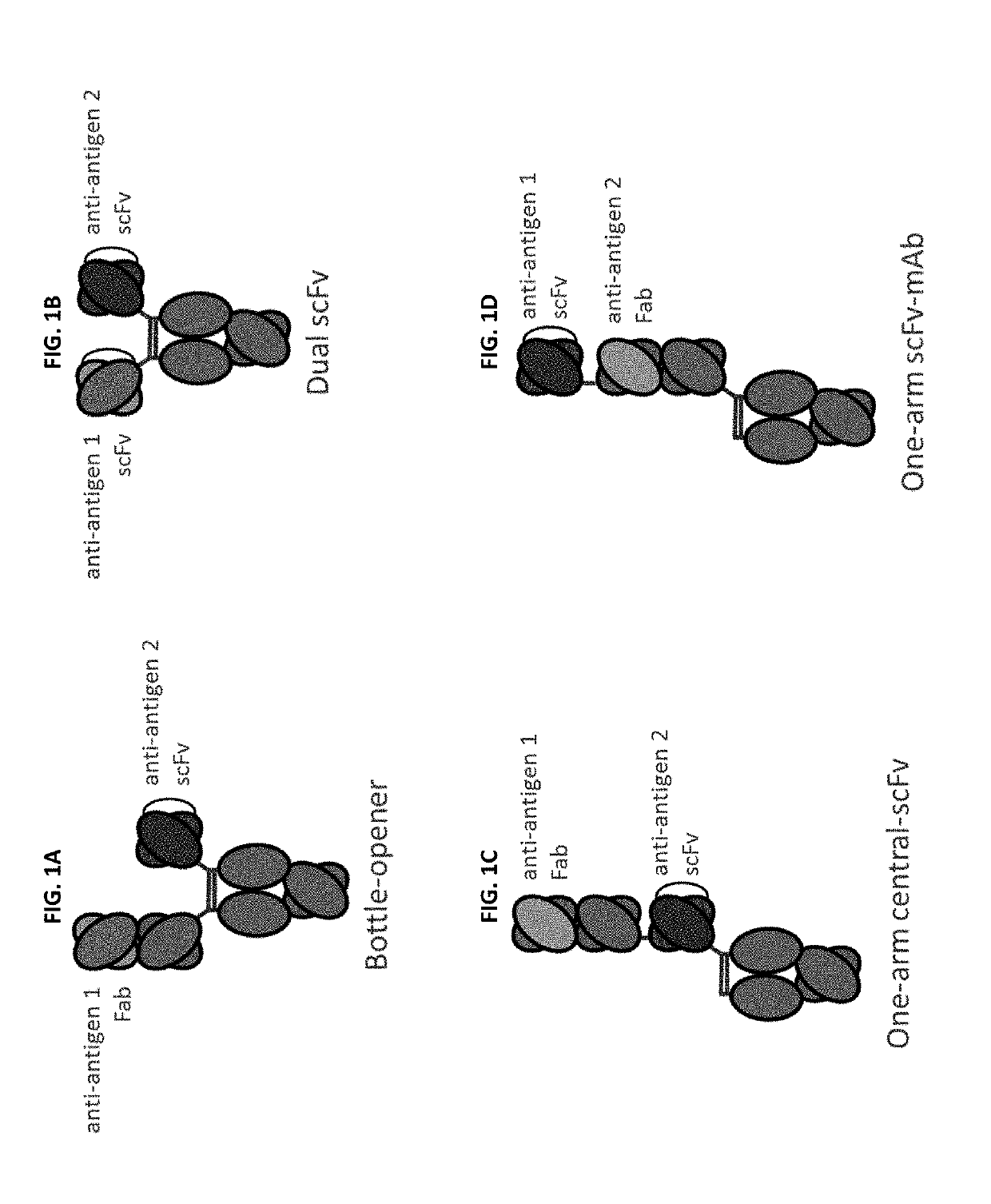
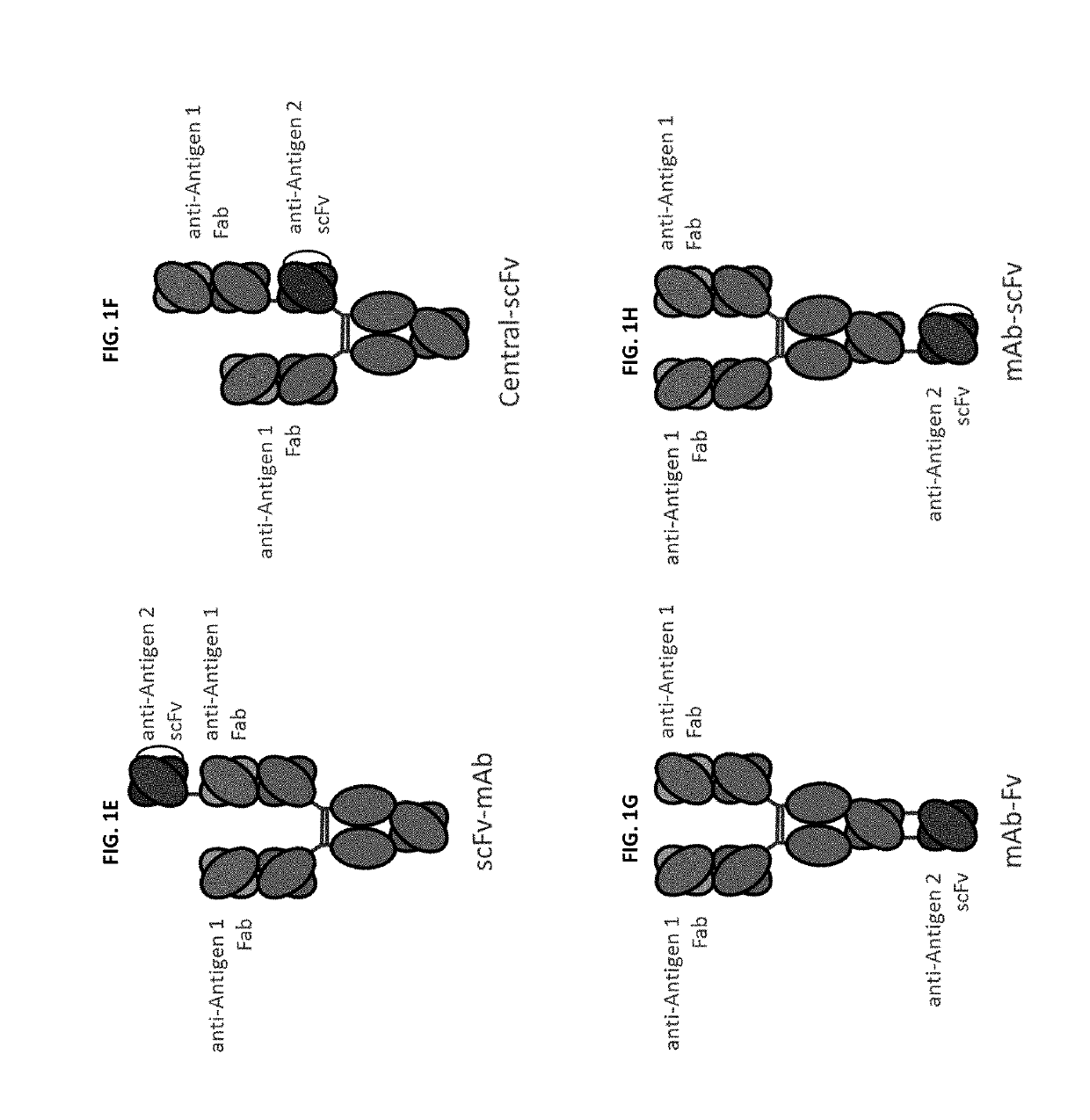
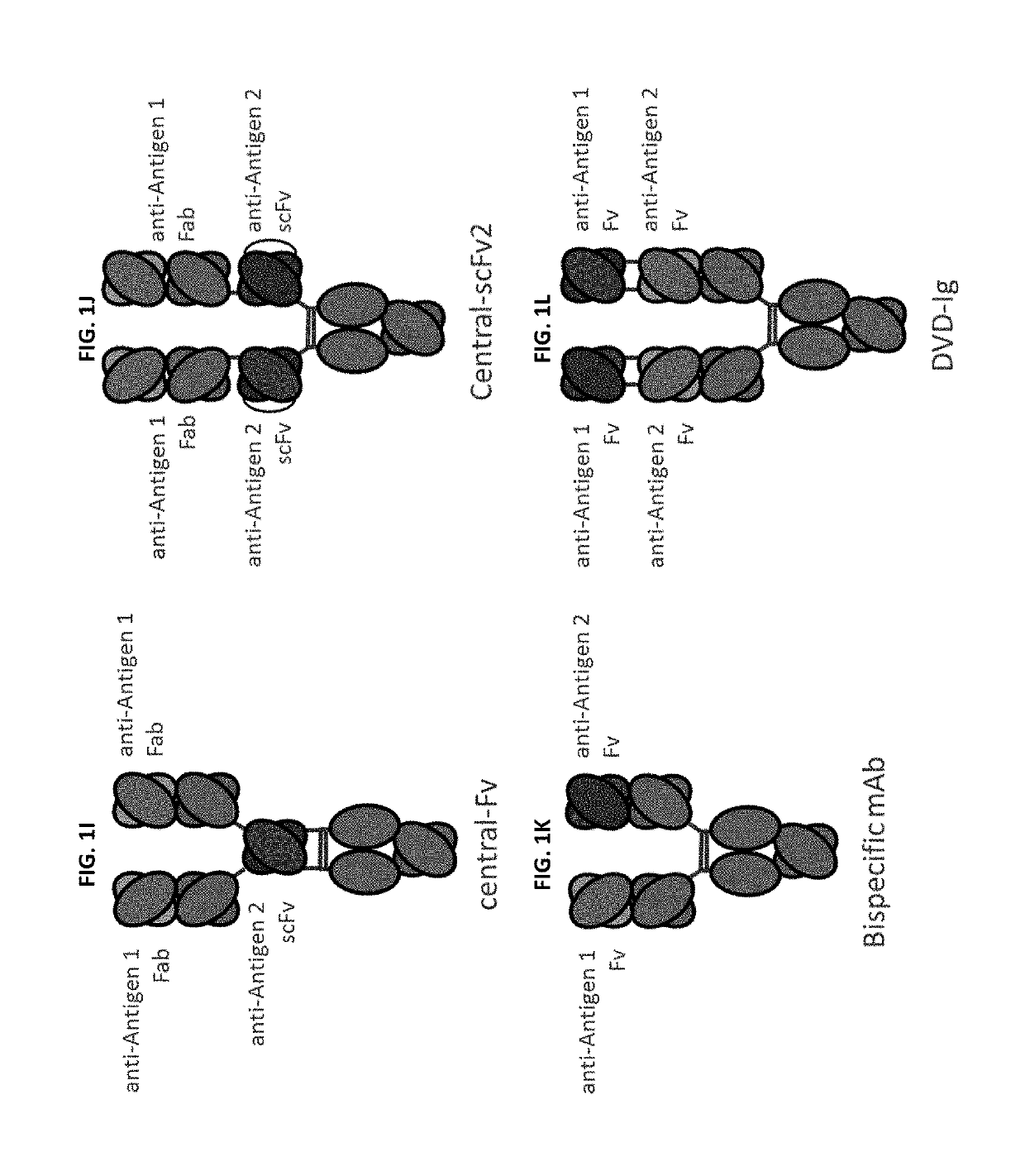
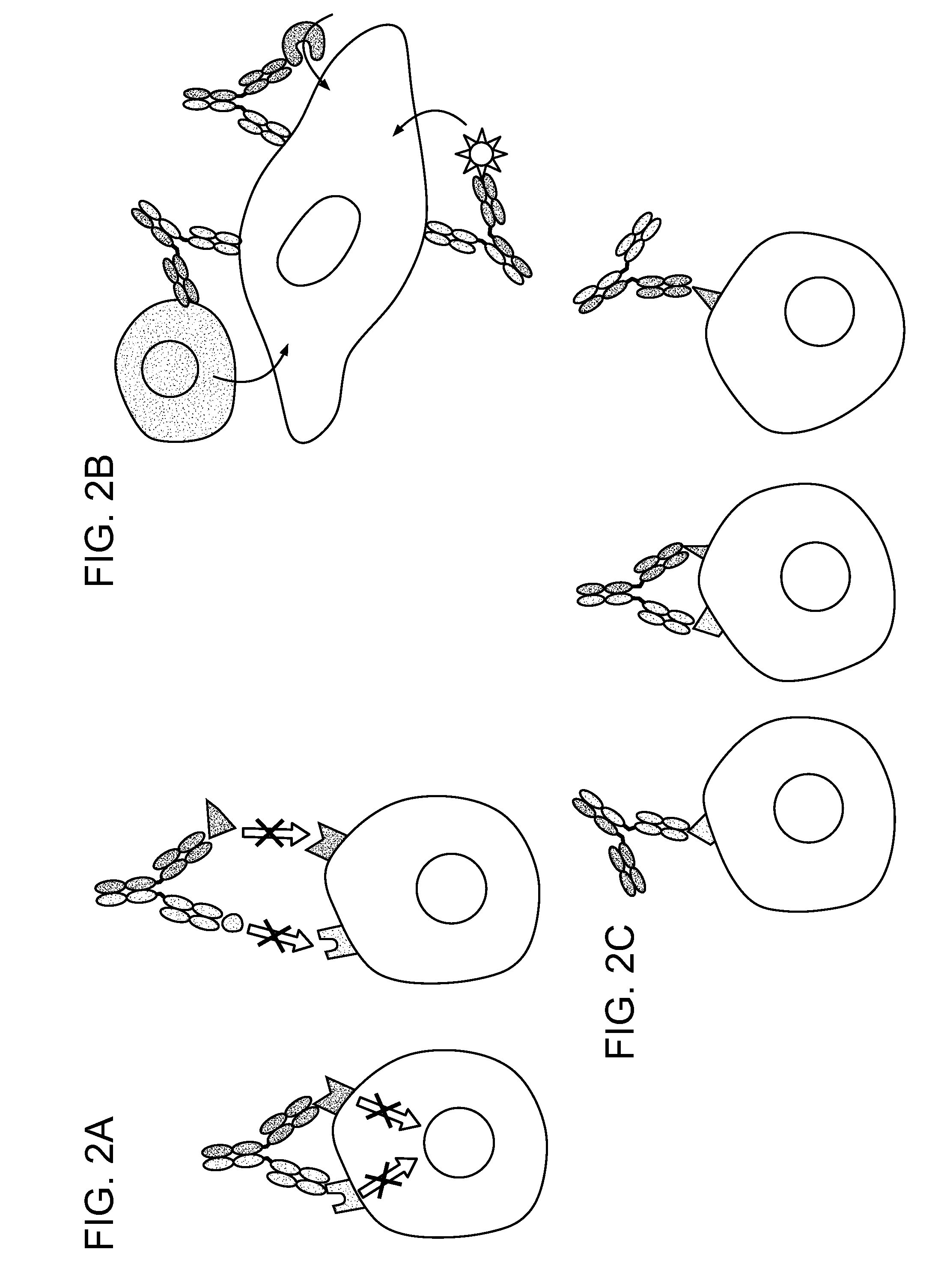
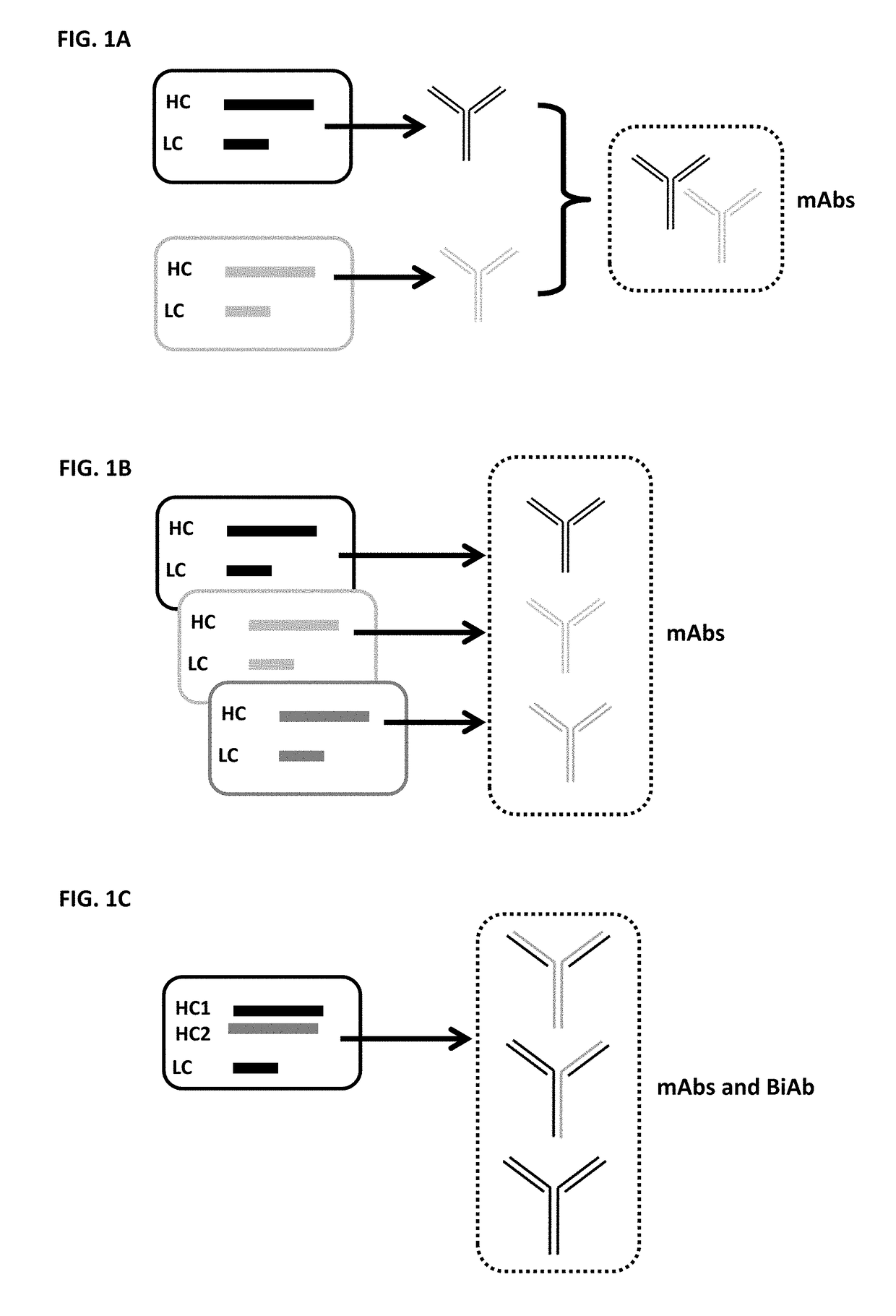
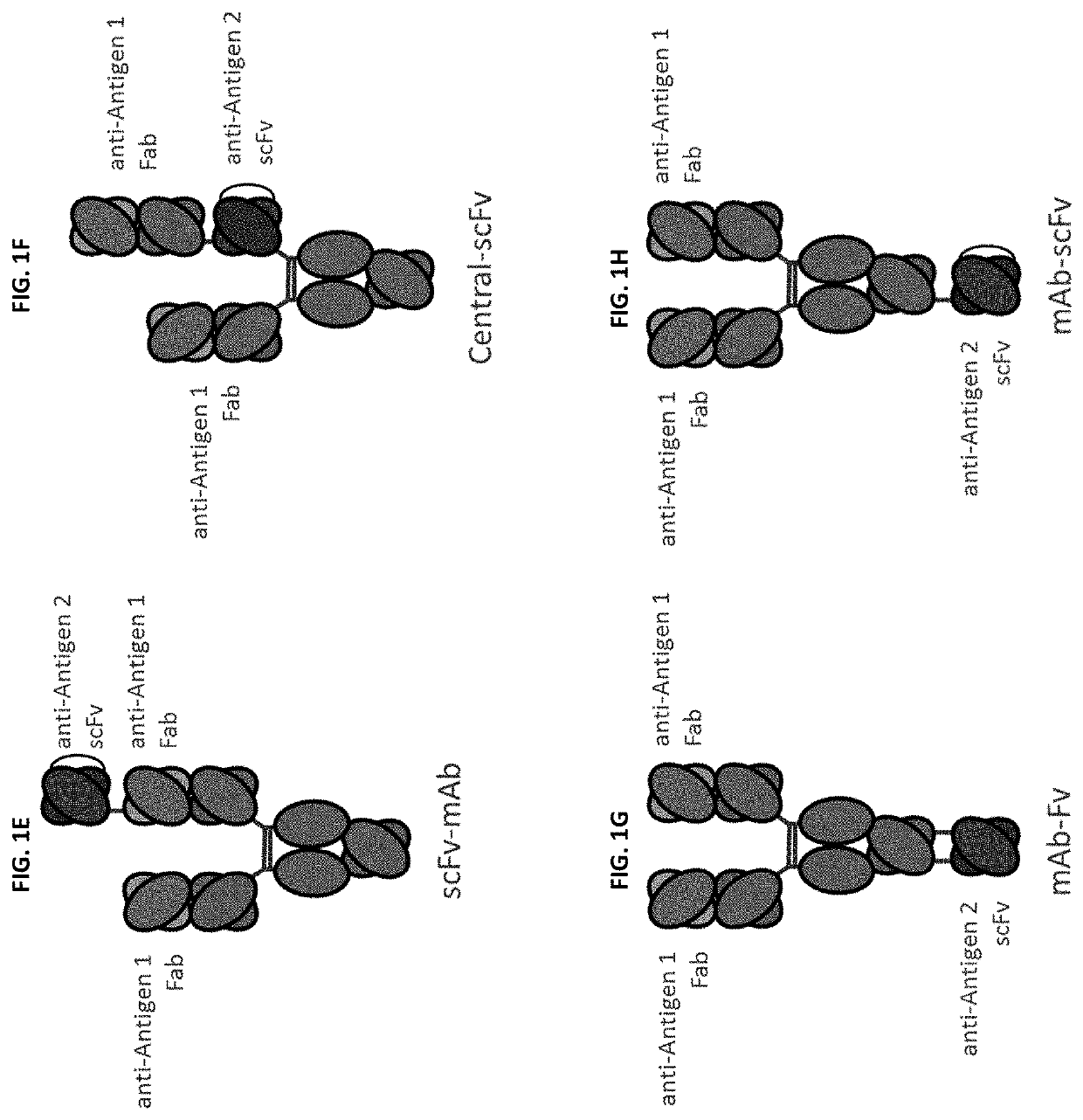
Monospecific antibodies are antibodies whose specificity to antigens is singular (mono- + specific) in any of several ways: antibodies that all have affinity for the same antigen; antibodies that are specific to one antigen or one epitope; or antibodies specific to one type of cell or tissue. Monoclonal antibodies are monospecific, but monospecific antibodies may also be produced by other means than producing them from a common germ cell. Regarding antibodies, monospecific and monovalent overlap in meaning; both can indicate specificity to one antigen, one epitope, or one cell type (including one microorganism species). However, antibodies that are monospecific to a certain tissue, or all monospecific to the same tissue because clones, can be polyvalent in their epitope binding.
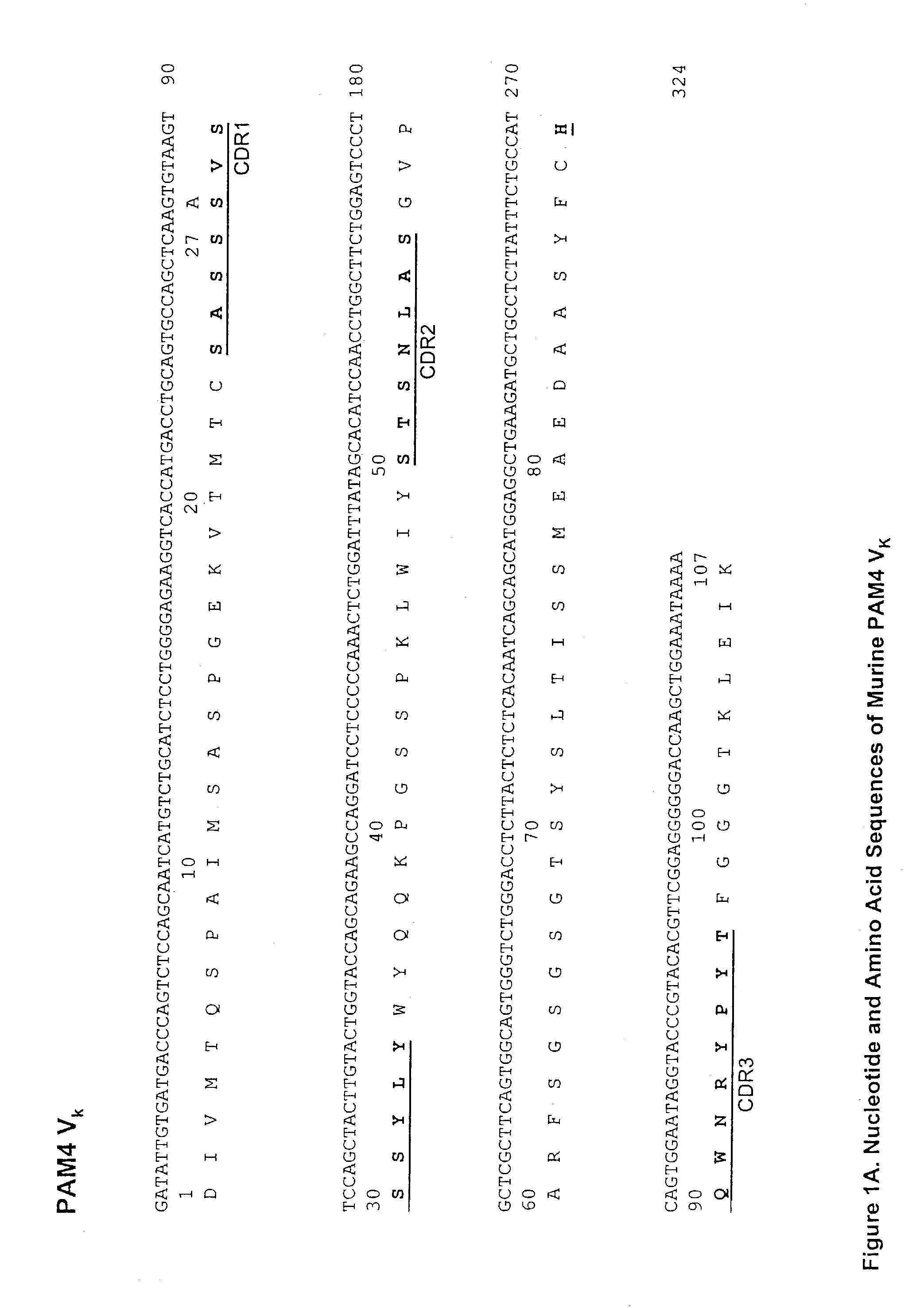
Monoclonal antibody hPAM4
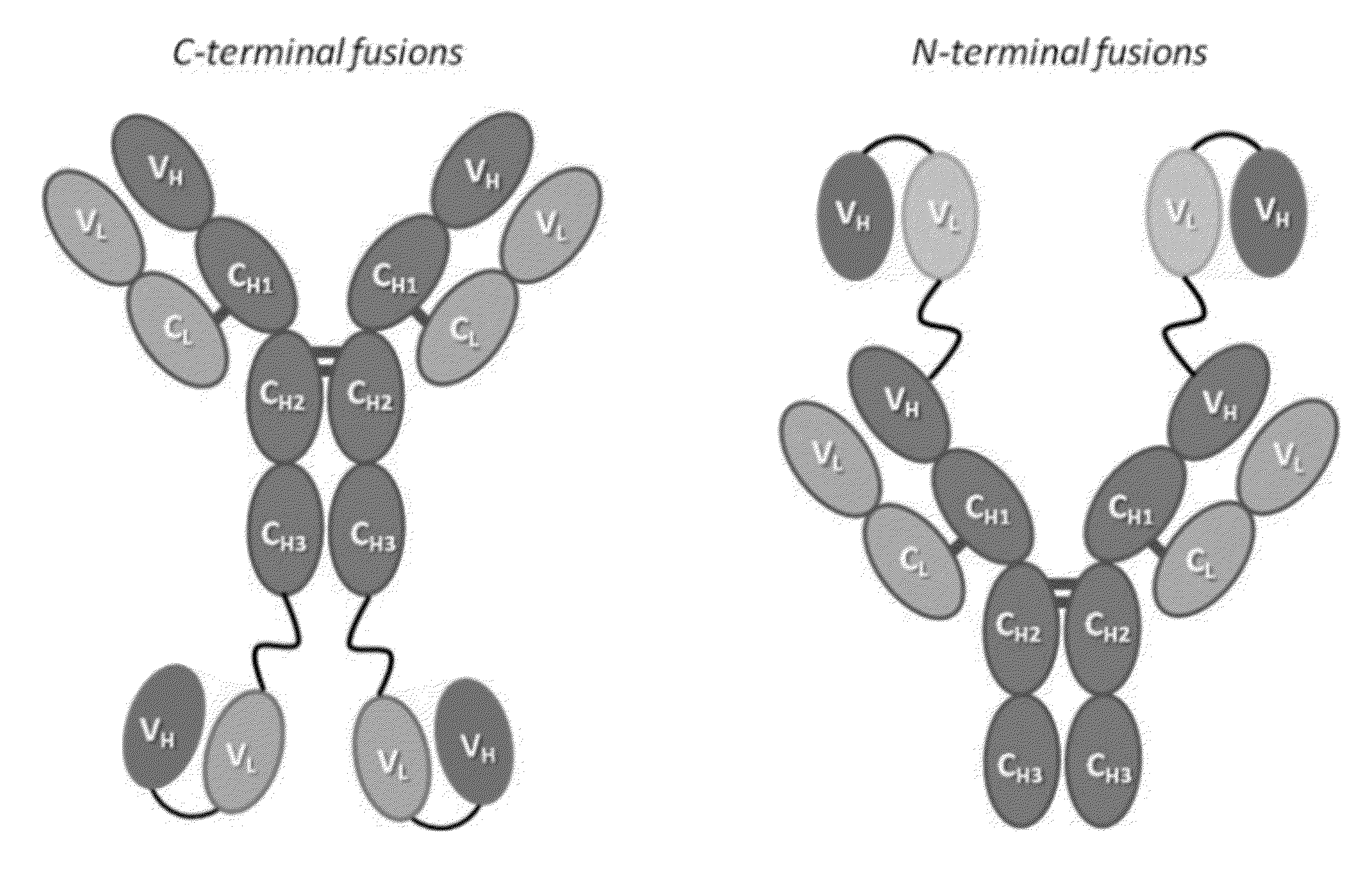
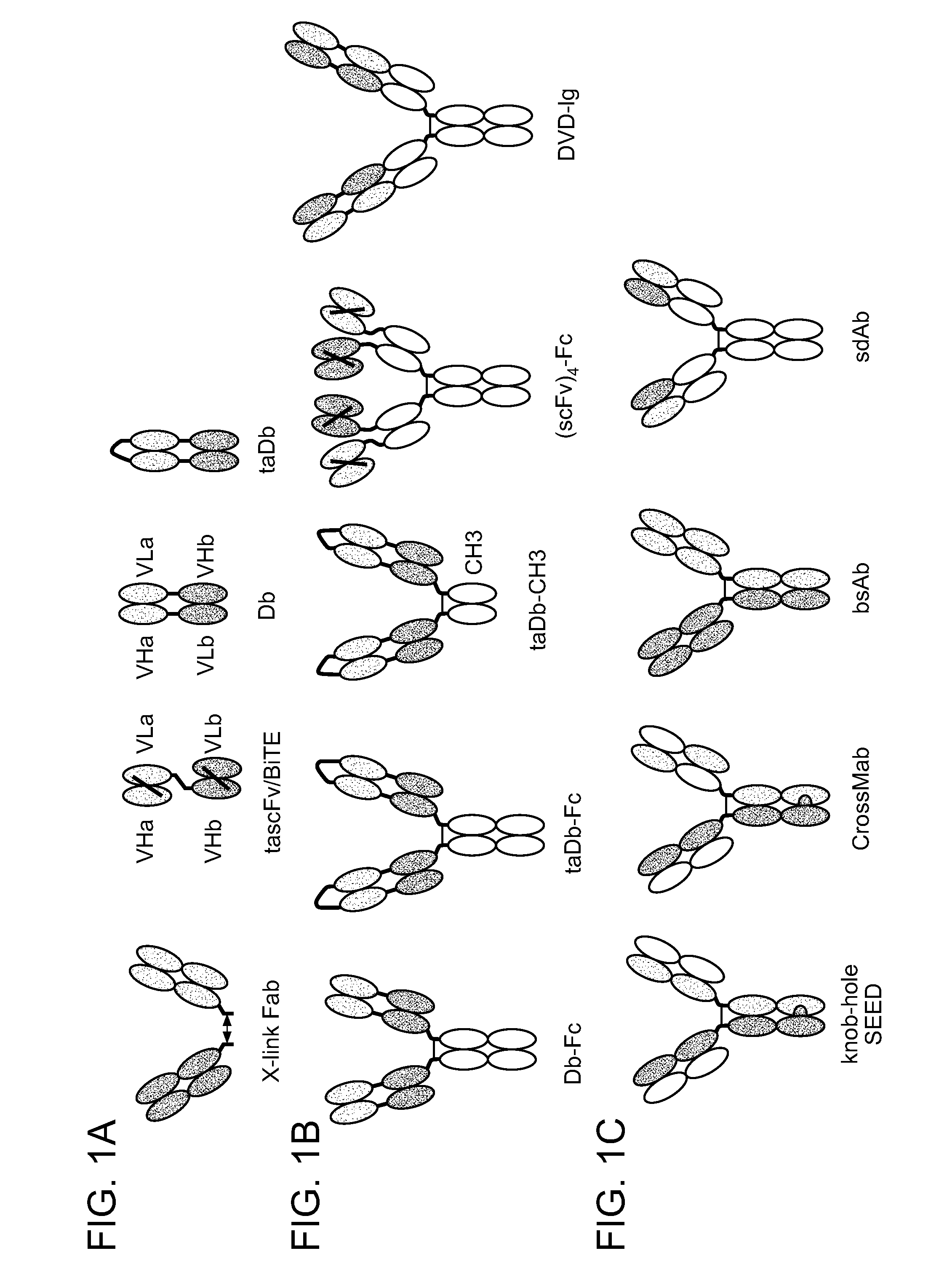
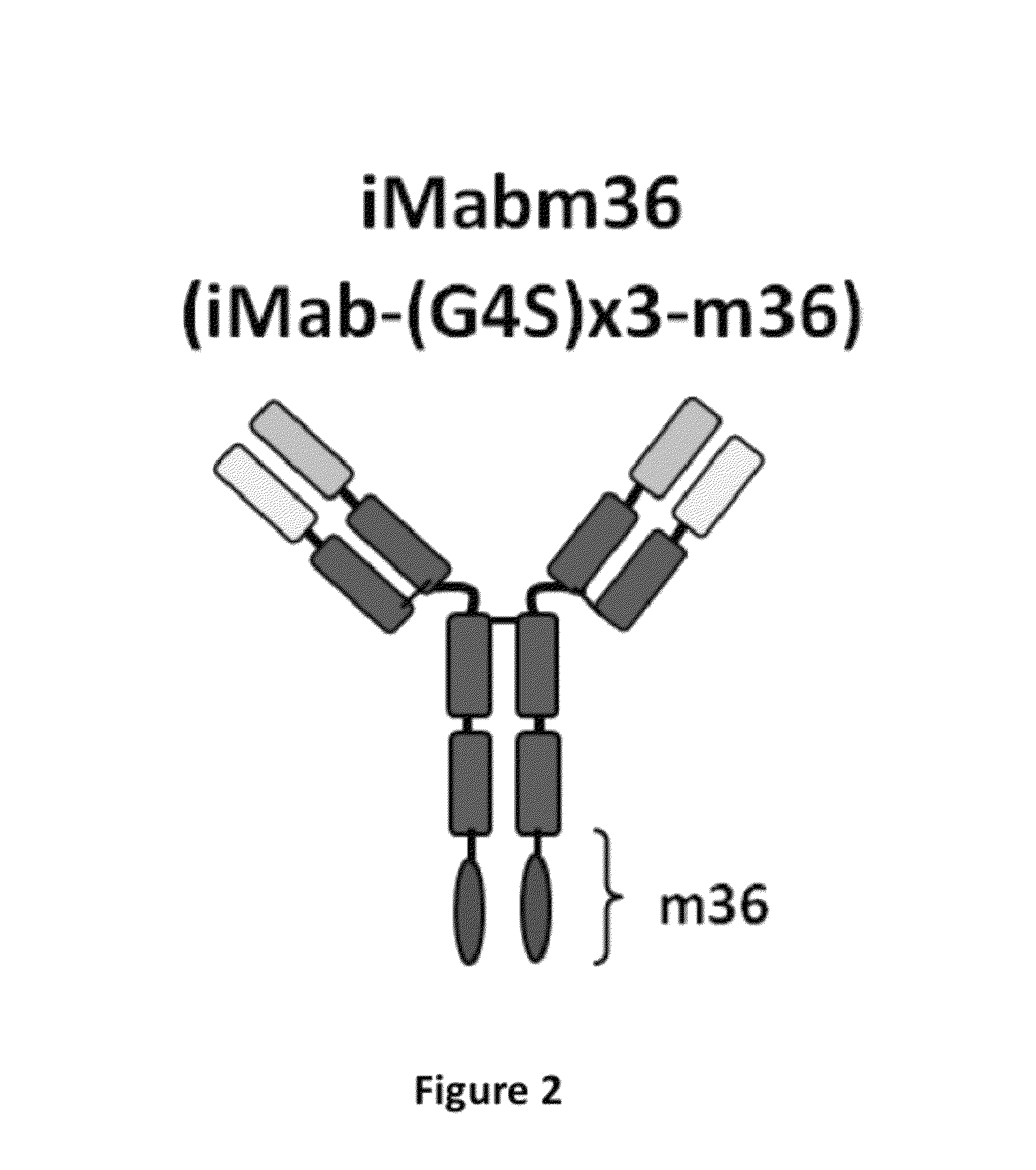
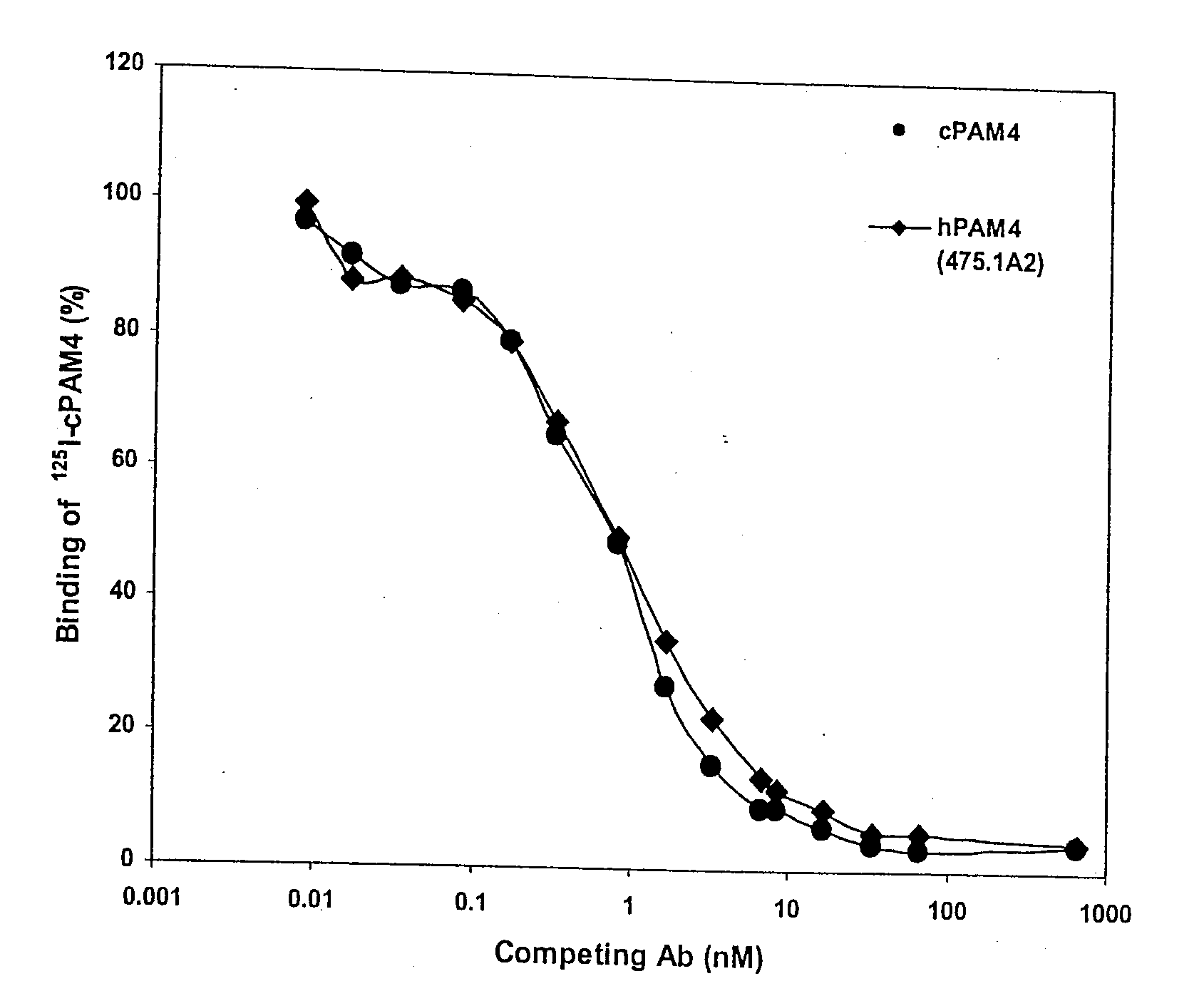
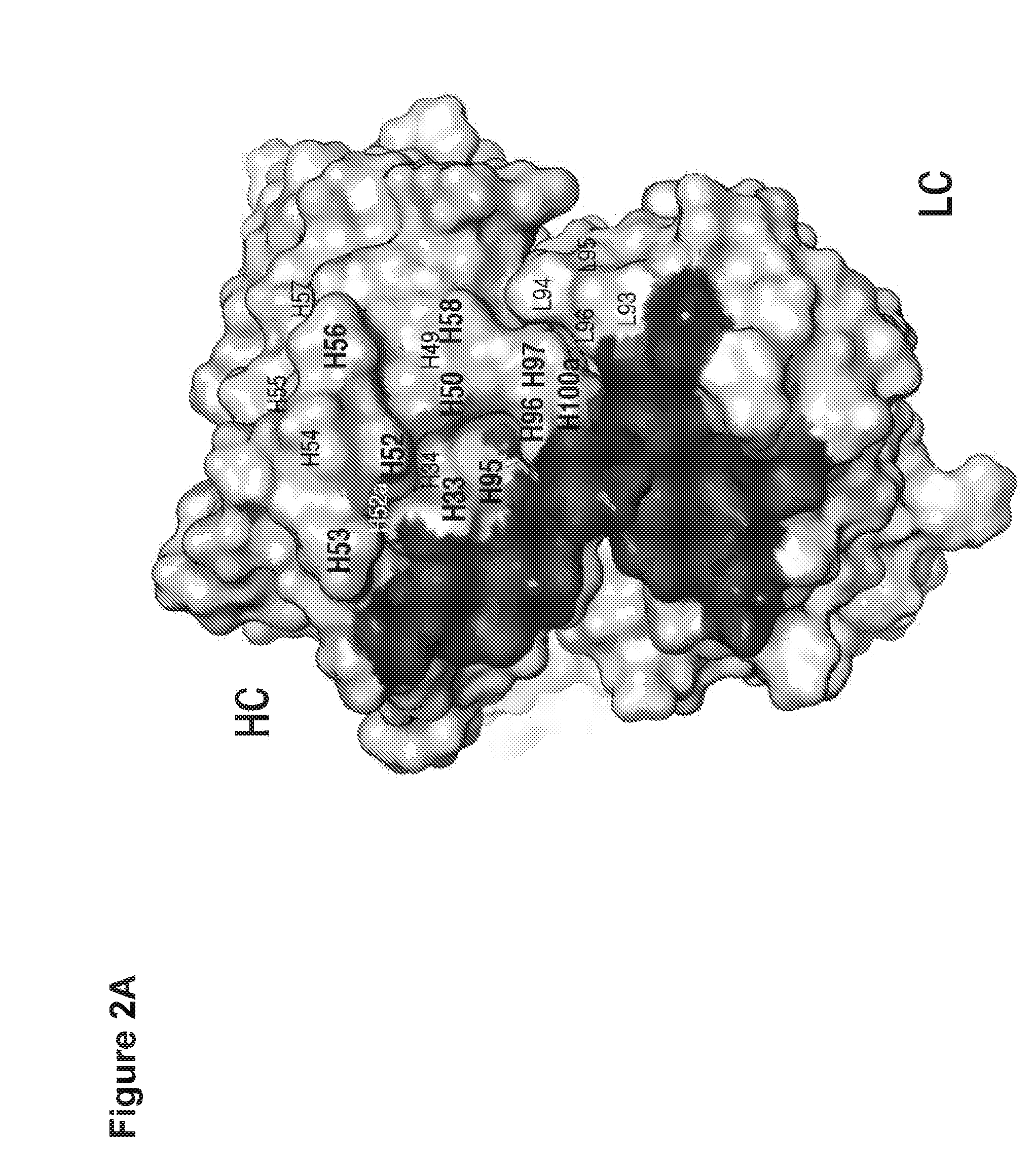
This invention relates to monovalent and multivalent, monospecific antibodies and to multivalent, multispecific antibodies. One embodiment of these antibodies has one or more identical binding sites where each binding site binds with a target antigen or an epitope on a target antigen. Another embodiment of these antibodies has two or more binding sites where these binding sites have affinity towards different epitopes on a target antigen or different target antigens, or have affinity towards a target antigen and a hapten. The present invention further relates to recombinant vectors useful for the expression of these functional antibodies in a host. More specifically, the present invention relates to the tumor-associated antibody designated PAM4. The invention further relates to humanized and human PAM4 antibodies, and the use of such antibodies in diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
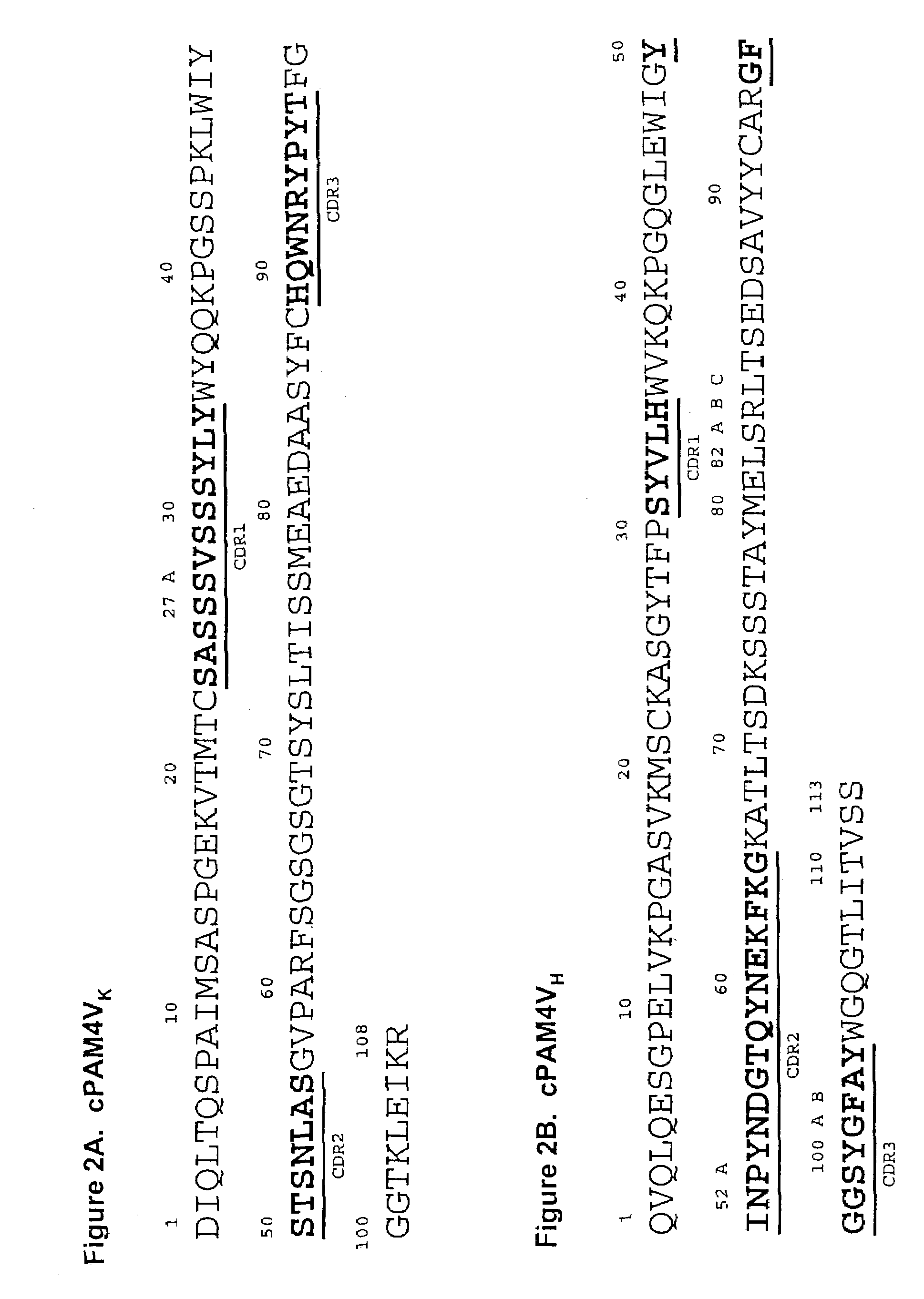
Monoclonal antibody cPAM4
This invention relates to monovalent and multivalent, monospecific antibodies and to monovalent and multivalent, multispecific antibodies. One embodiment of these antibodies has one or more identical binding sites where each binding site binds with a target antigen or an epitope on a target antigen. Another embodiment of these antibodies has two or more binding sites where these binding sites have affinity towards different epitopes on a target antigen or different target antigens, or have affinity towards a target antigen and a hapten. The present invention further relates to recombinant vectors useful for the expression of these functional antibodies in a host. More specifically, the present invention relates to the tumor-associated antibody designated PAM4. The invention further relates to chimeric PAM4 antibodies, and the use of such antibodies in diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Fusion proteins for HIV therapy
InactiveUS20120121597A1Improved potency and breadth against HIVImprove barrier propertiesHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHiv envelopeBinding site
Disclosed herein are fusion antibodies created to provide both an antigen-binding site that targets the CD4 receptor and an antigen-binding site that targets the HIV envelope. The fusion antibodies disclosed herein provide improved potency and breadth against HIV as compared to monospecific antibodies, and additionally provide high barrier against viral resistance. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical formulations and therapeutic methods utilizing such fusion proteins.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
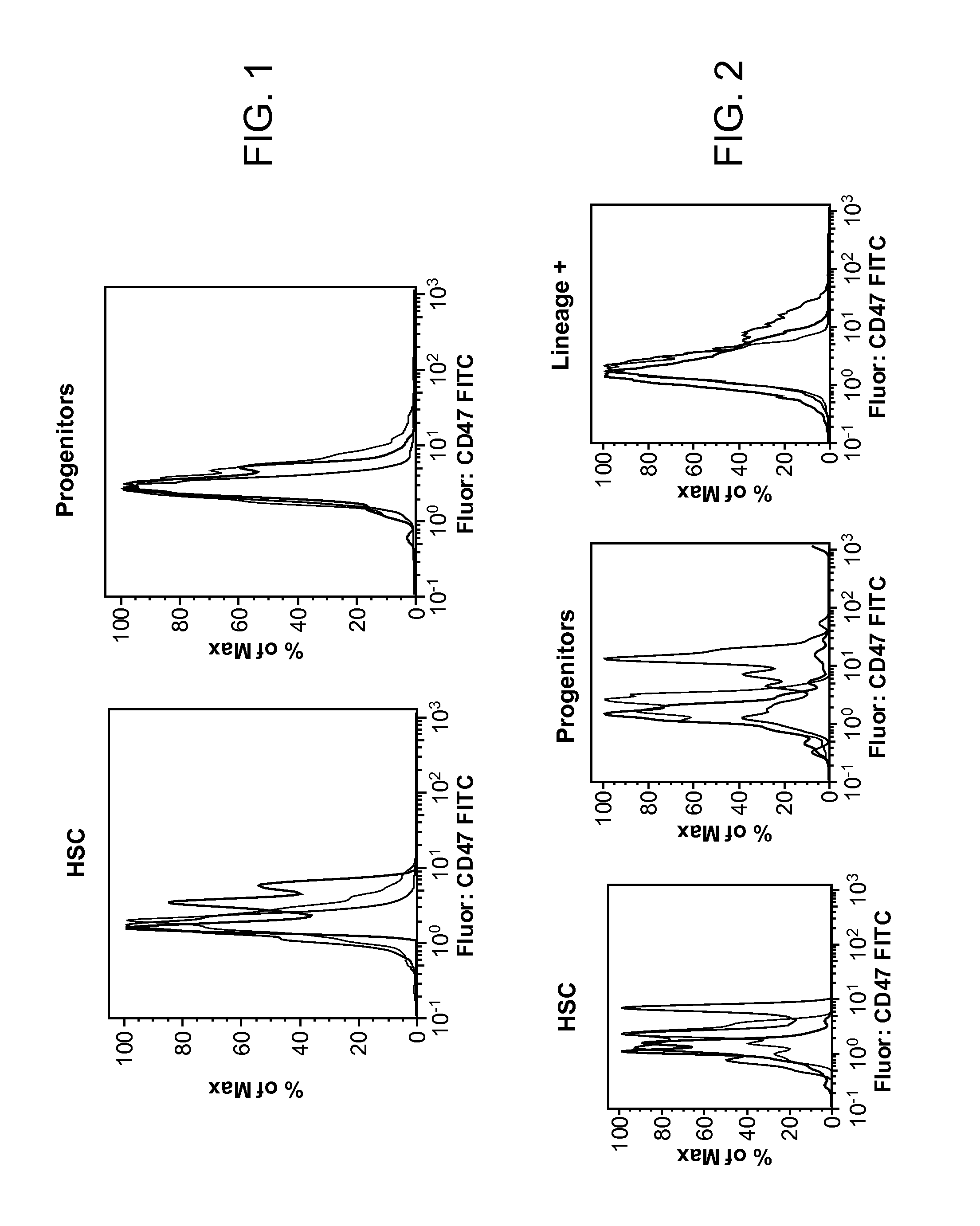
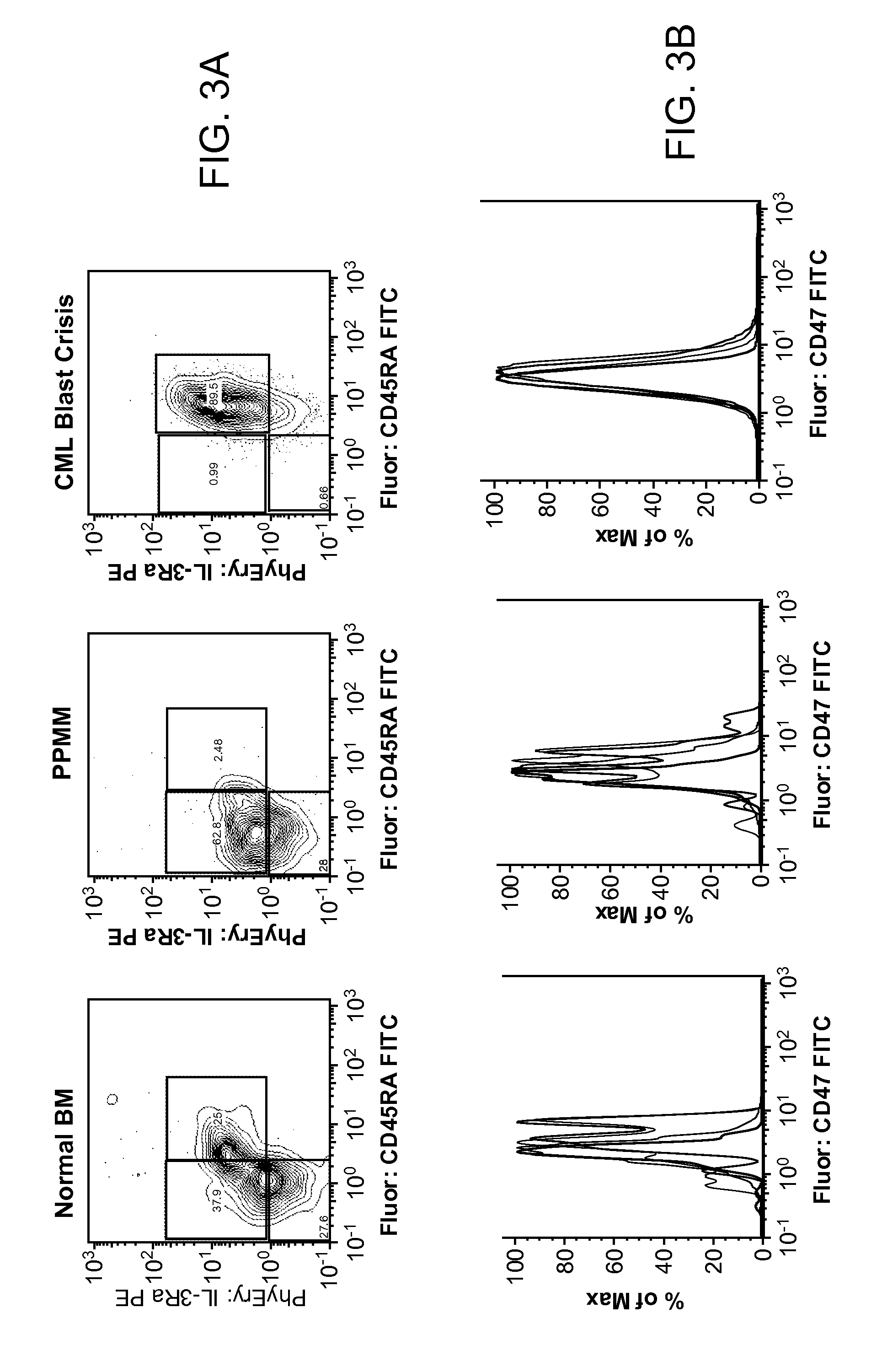
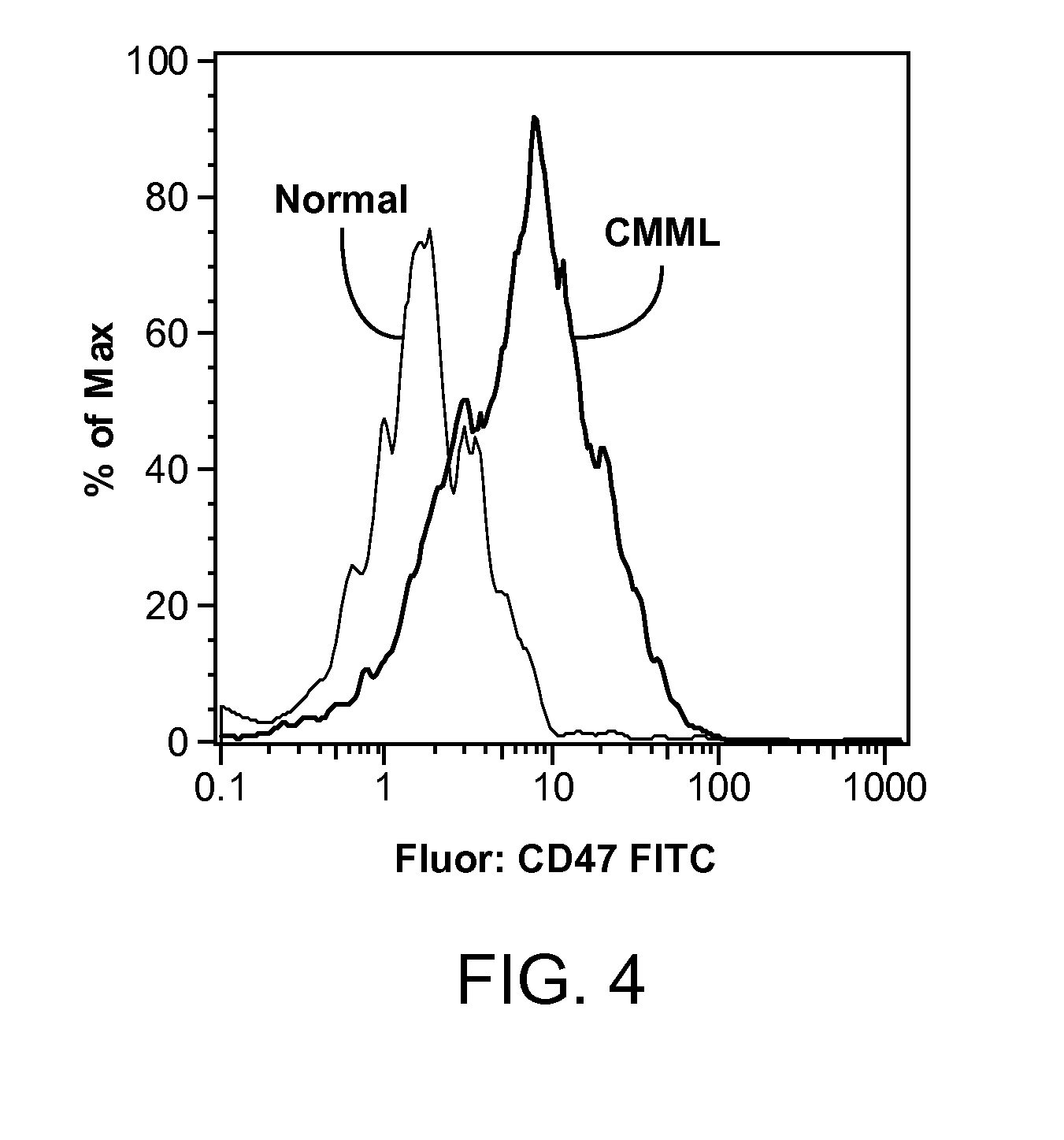
Synergistic Anti-CD47 Therapy for Hematologic Cancers
ActiveUS20120282174A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRadioactive preparation carriersSurface markerCD20
Methods are provided for treatment of hematologic cancers, particularly lymphomas and leukemias, including without limitation myelogenous and lymphocytic leukemias. A combination of antibodies specific for CD47; and specific for a cancer associated cell surface marker are administered to the patient, and provide for a synergistic decrease in cancer cell burden. The combination of antibodies may comprise a plurality of monospecific antibodies, or a bispecific or multispecific antibody. Markers of interest include without limitation, CD20, CD22, CD52, CD33; CD96; CD44; CD123; CD97; CD99; PTHR2; and HAVCR2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Synergistic anti-CD47 therapy for hematologic cancers
Methods are provided for treatment of hematologic cancers, particularly lymphomas and leukemias, including without limitation myelogenous and lymphocytic leukemias. A combination of antibodies specific for CD47; and specific for a cancer associated cell surface marker are administered to the patient, and provide for a synergistic decrease in cancer cell burden. The combination of antibodies may comprise a plurality of monospecific antibodies, or a bispecific or multispecific antibody. Markers of interest include without limitation, CD20, CD22, CD52, CD33; CD96; CD44; CD123; CD97; CD99; PTHR2; and HAVCR2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
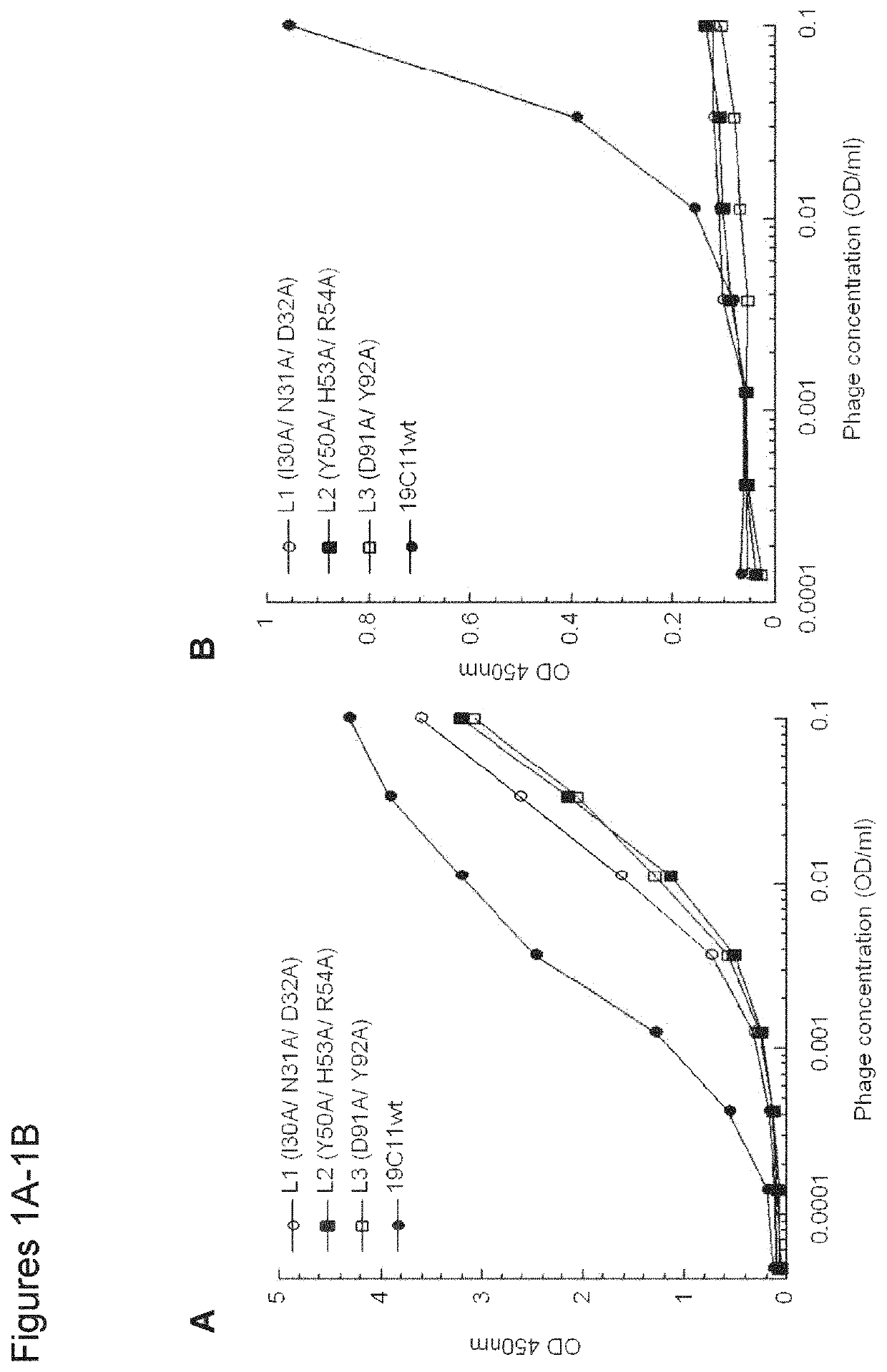
Bispecific and monospecific antibodies using novel Anti-pd-1 sequences
ActiveUS20190263909A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMonospecific antibodyAnti pd 1
Owner:XENCOR INC
Methods of purifying bispecific antibodies
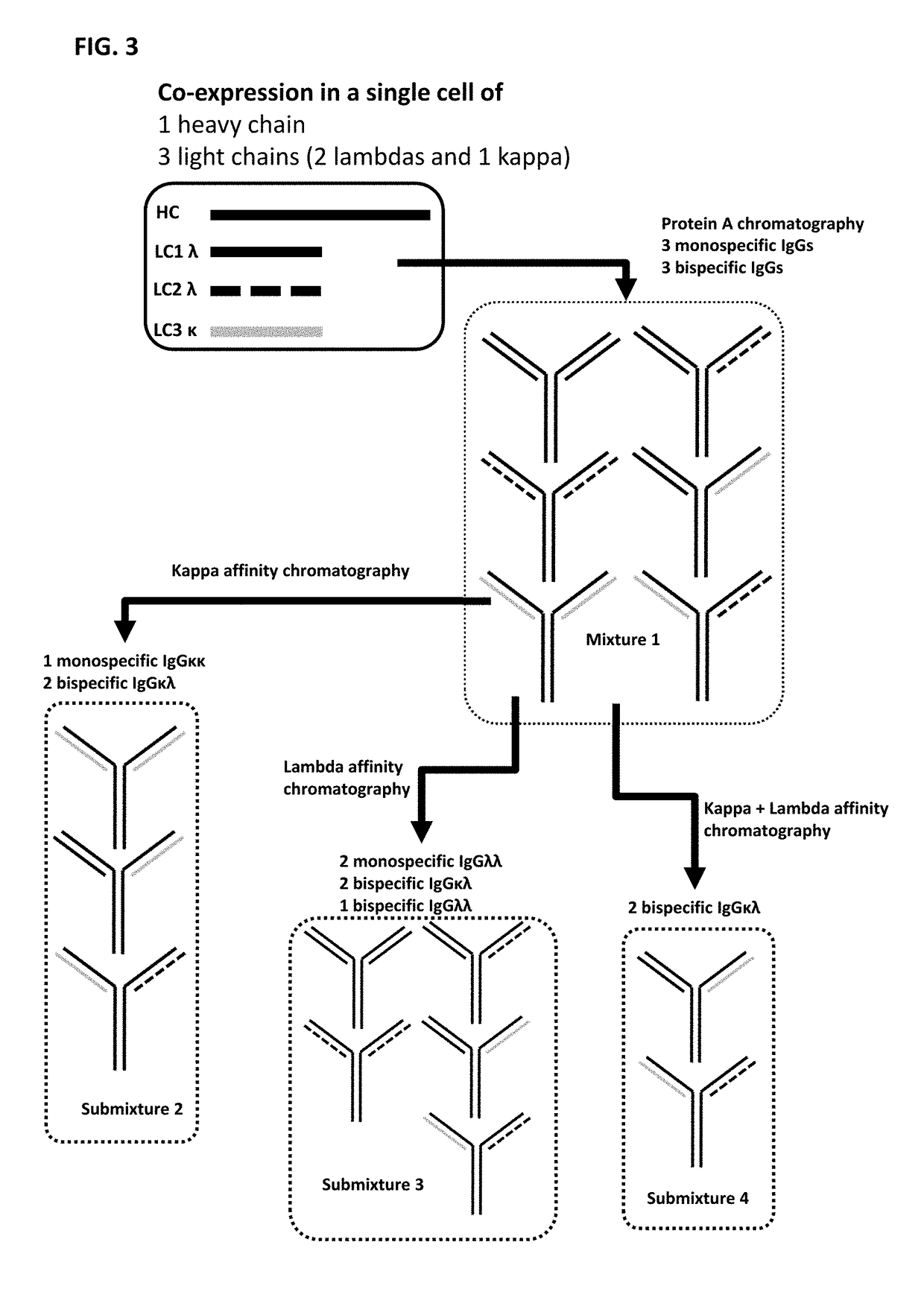
ActiveUS20160264685A1Reduce concentrationFavorable manufacturing characteristicHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide preparation methodsHeavy chainBinding site
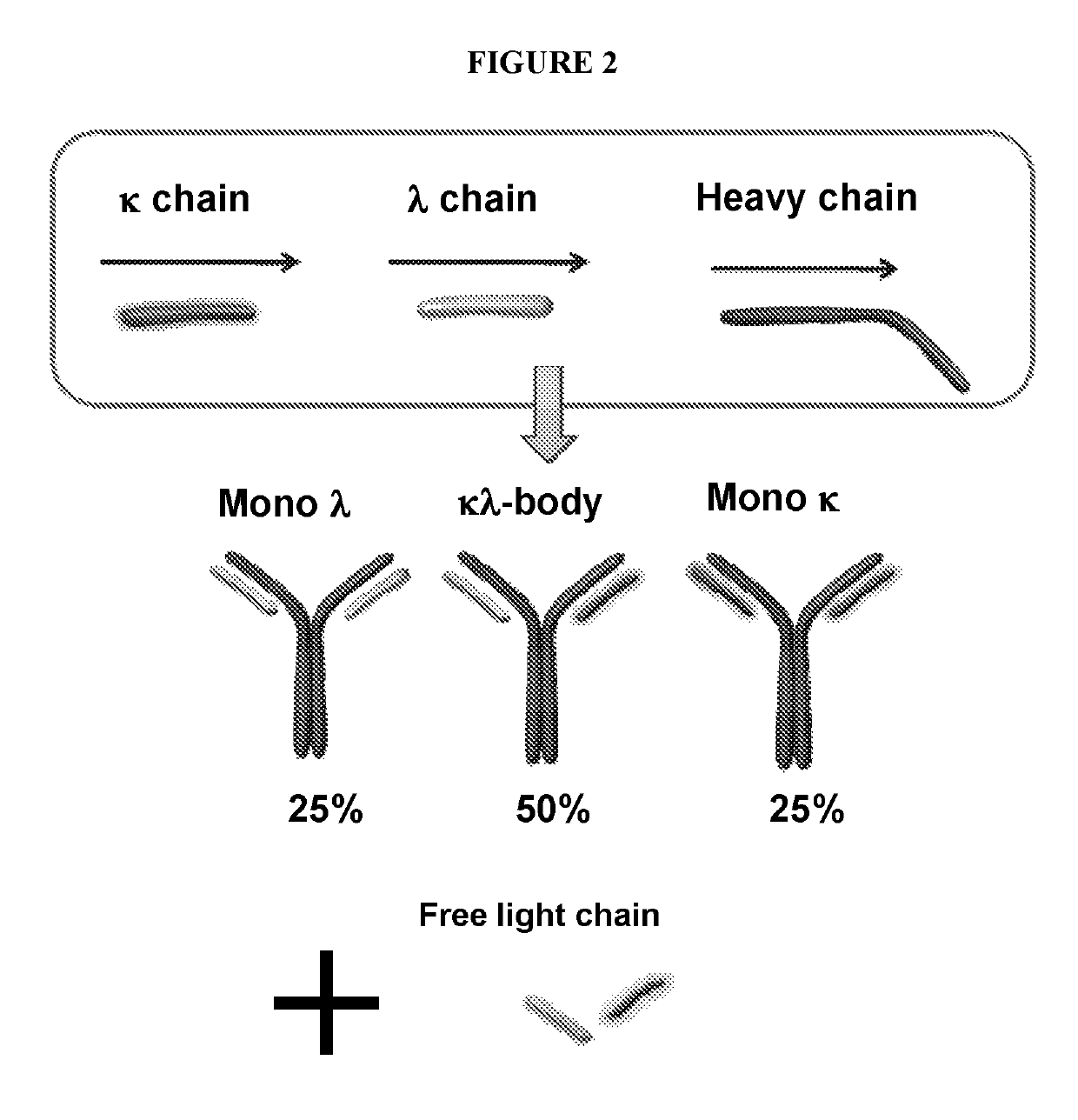
The invention relates to the purification of bispecific antibodies carrying a different specificity for each binding site of the immunoglobulin molecule from a mixture of monospecific antibodies. The bispecific antibodies are composed of a single heavy chain and two different light chains, one containing a Kappa constant domain and the other a Lambda constant domain. This invention in particular relates to the isolation of these bispecific antibodies from mixtures that contain monospecific antibodies having two Kappa light chains or portions thereof and monospecific antibodies having two Lambda light chains or portions thereof. The invention also provides the methods of efficiently purifying these bispecific antibodies.
Owner:NOVIMMUNE
Methods For The Generation Of Multispecific And Multivalent Antibodies
ActiveUS20140179547A1Favorable manufacturing characteristicMaximize productionHybrid immunoglobulinsDNA preparationHeavy chainBispecific monoclonal antibody
Owner:NOVIMMUNE
Separation and extraction method for cytomembrane microvesicles (MVs) and exosomes (EXs)
InactiveCN105716928AIncreased sensitivityQuick analysisPreparing sample for investigationDiseasePhosphate
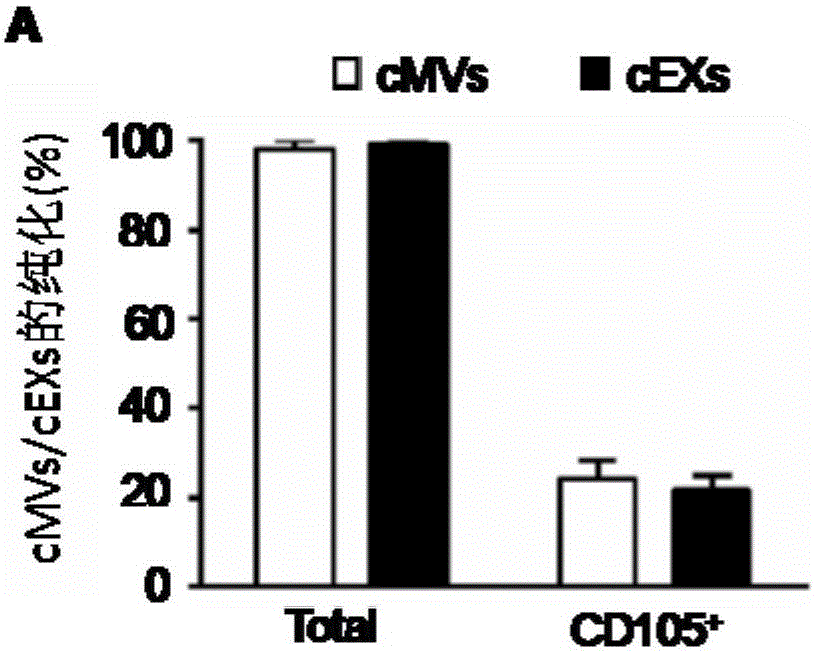
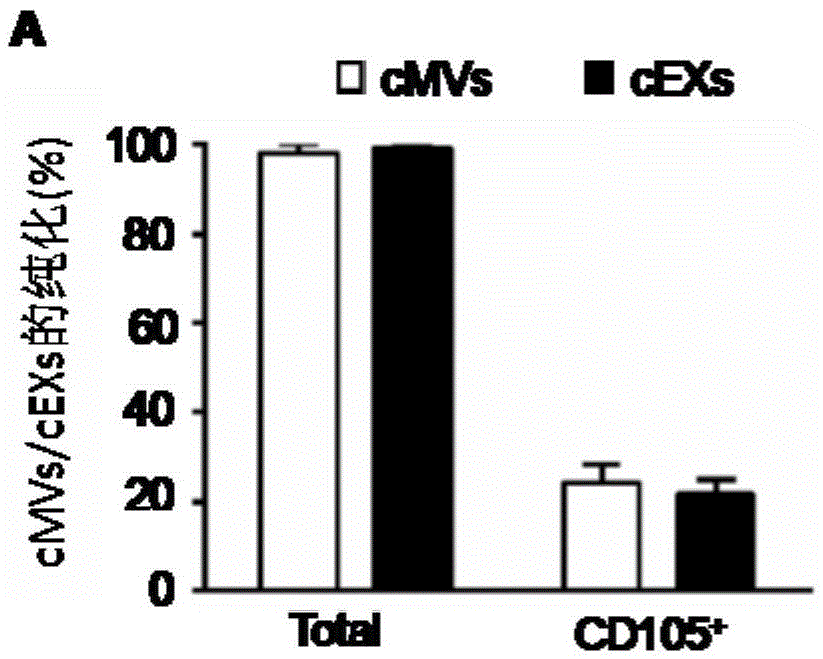
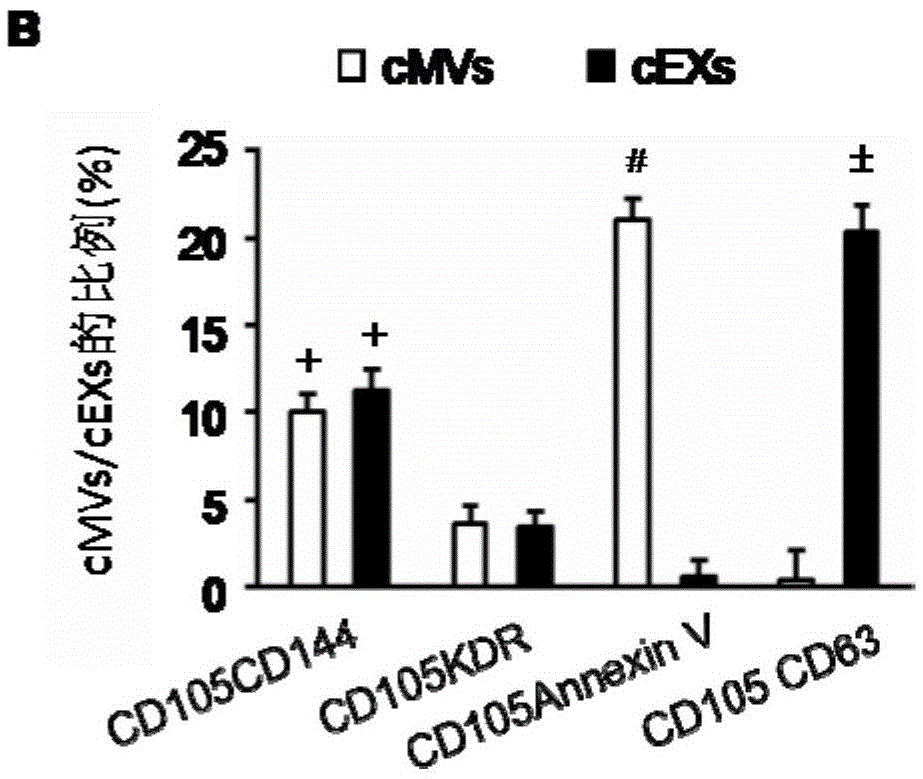
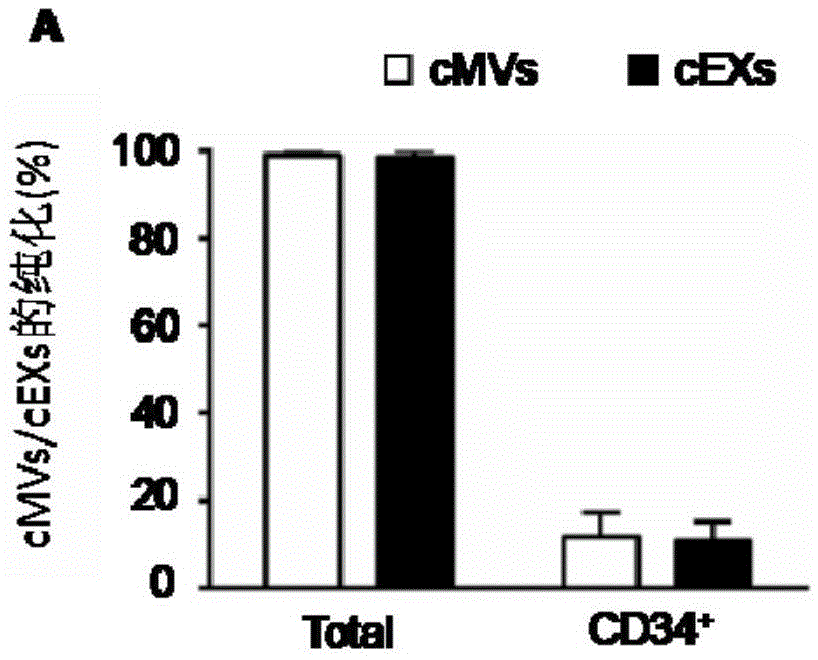
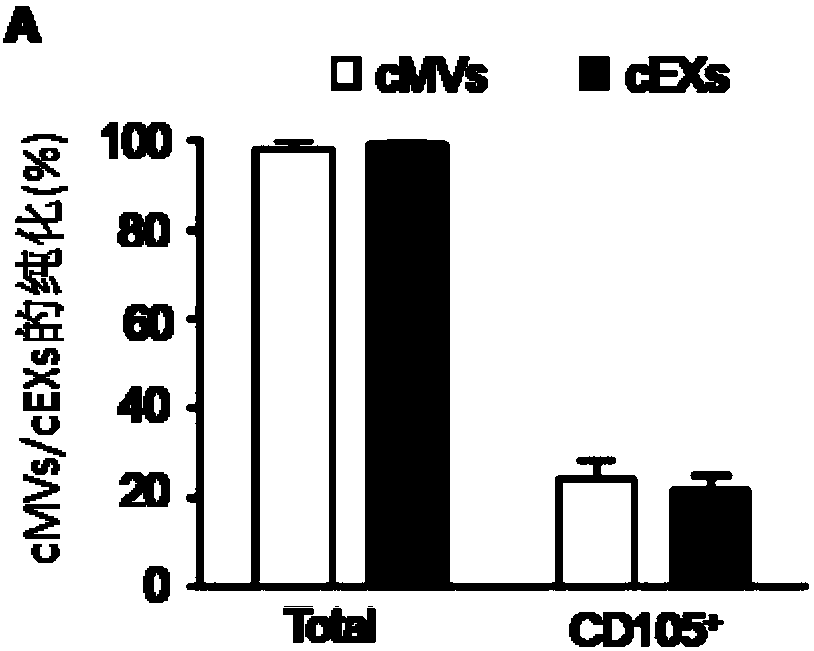
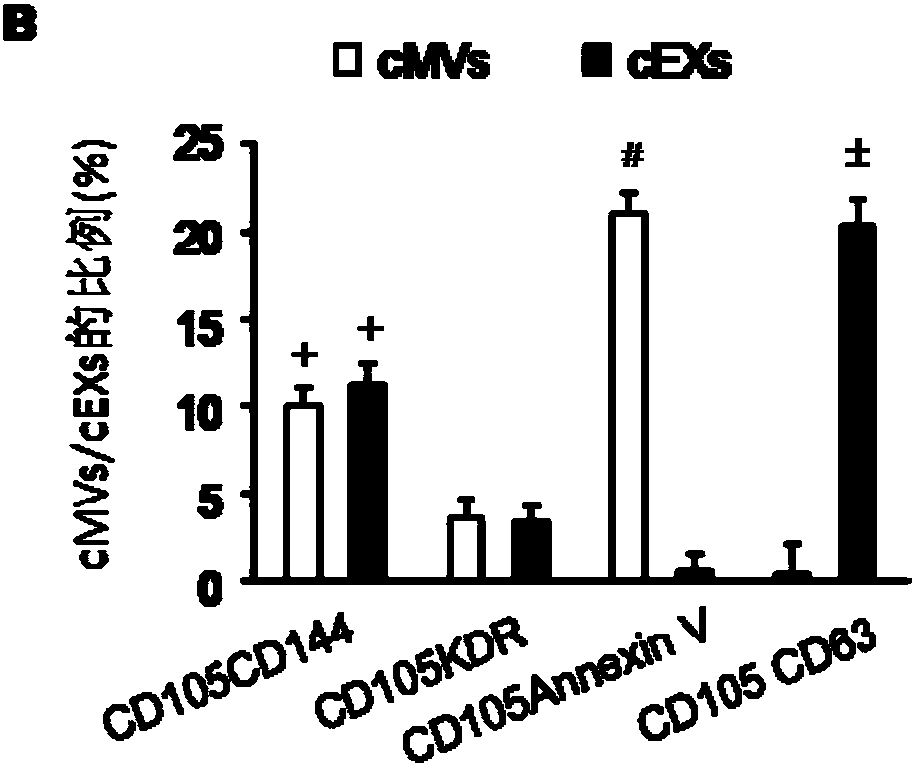
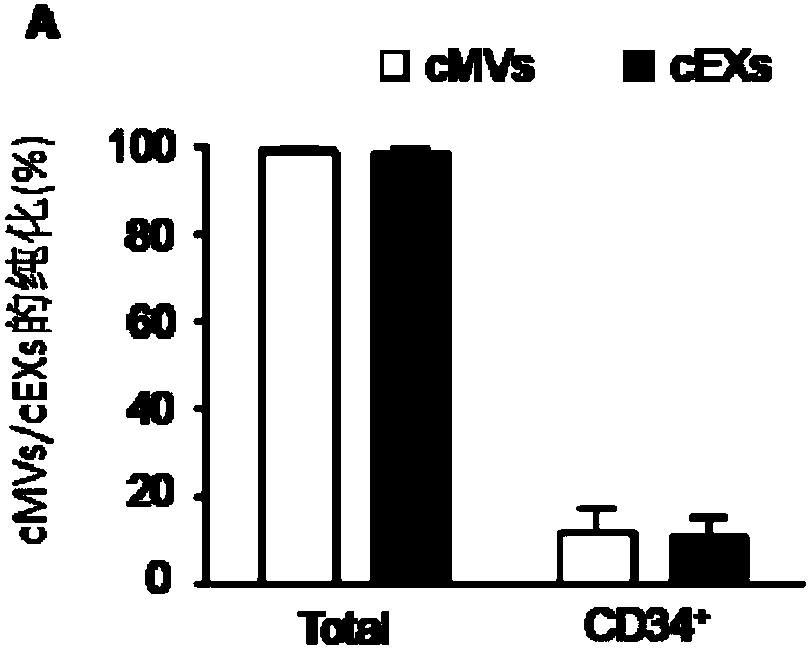
The invention relates to a separation and extraction method for cytomembrane microvesicles (MVs) and exosomes (EXs). The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that a, 3-10 ml of a peripheral blood sample is drawn and placed in an anticoagulation tube to be stored, the sample is diluted with phosphate buffer normal saline (PBS) by 2-4 times, and then centrifugation is carried out to obtain supernate plasma; b, the supernate plasma is subjected to centrifugal separation again, and sediment is MVs; c, ultra-centrifugation is carried out on the supernate plasma in the step b, and sediment is EXs. According to the method, a previous method adopting mono-specificity antibodies is broken through, and the specificity and sensibility of the extracted cell MVs and EXs are higher than those in the prior art. A specificity and sensibility direction is provided for a further study of the MVs and the EXs as biomarkers of diseases.
Owner:WUHAN DAFU BIOTECH CO LTD
Fusion antibodies for HIV therapy
InactiveUS8637024B2Improved potency and breadth against HIVImprove barrier propertiesHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsHiv envelopeBinding site
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Monoclonal Antibody hPAM4
InactiveUS20080050311A1Compounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeAbnormal tissue growth
This invention relates to monovalent and multivalent, monospecific antibodies and to multivalent, multispecific antibodies. One embodiment of these antibodies has one or more identical binding sites where each binding site binds with a target antigen or an epitope on a target antigen. Another embodiment of these antibodies has two or more binding sites where these binding sites have affinity towards different epitopes on a target antigen or different target antigens, or have affinity towards a target antigen and a hapten. The present invention further relates to recombinant vectors useful for the expression of these functional antibodies in a host. More specifically, the present invention relates to the tumor-associated antibody designated PAM4. The invention further relates to humanized and human PAM4 antibodies, and the use of such antibodies in diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
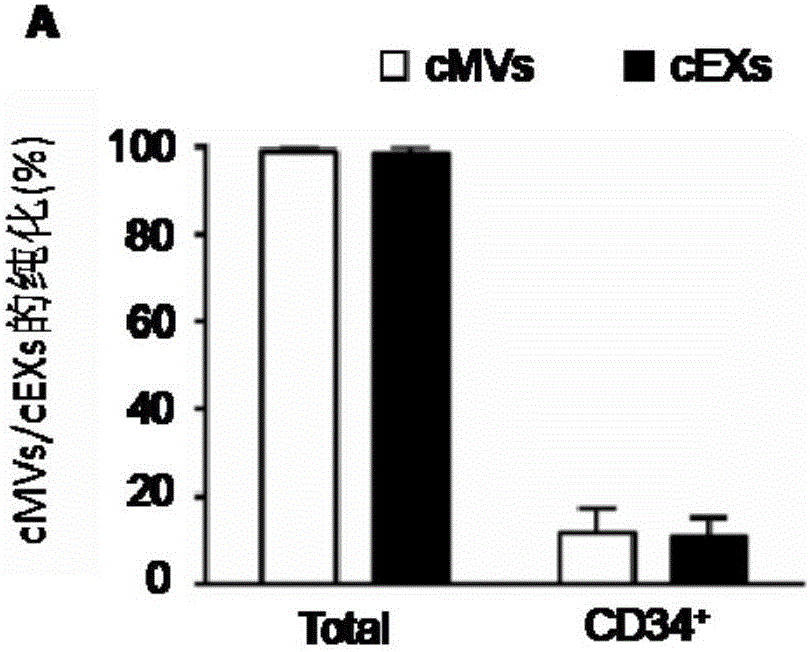
Method for detecting EVs (extracellular vesicles) released by ECs (endothelial cells) and EPCs (endothelial progenitor cells) in blood
The invention relates to a method for detecting EVs (extracellular vesicles) released by ECs (endothelial cells) and EPCs (endothelial progenitor cells) in blood. EC-MVs (microvesicles), EPC-MVs, EC-EXs (exosomes) and EPC-EXs are separated from a circulatory system with two specific antibody linked immunomagnetic sand methods. The method breaks through a single specific antibody method, and the specificity and the sensitivity of extracted cells MVs and EXs are higher than those in the prior art. Besides, the cells MVs and EXs are detected with an NTS (nanoparticle tracing analysis) technique in combination of a specific antibody micro-beads method and a Q-dots method. The method can quickly, accurately and objectively analyze the levels of EC-MVs, EPC-MVs, EC-EXs and EPC-EXs in complicated samples such as blood and has advantages which a traditional analysis method does not possess. Besides, the specific and sensitive method is provided for further research of MVs and EXs serving as biomarkers of diseases.
Owner:WUHAN DAFU BIOTECH CO LTD
Antibodies capable of specifically binding two epitopes on tissue factor pathway inhibitor
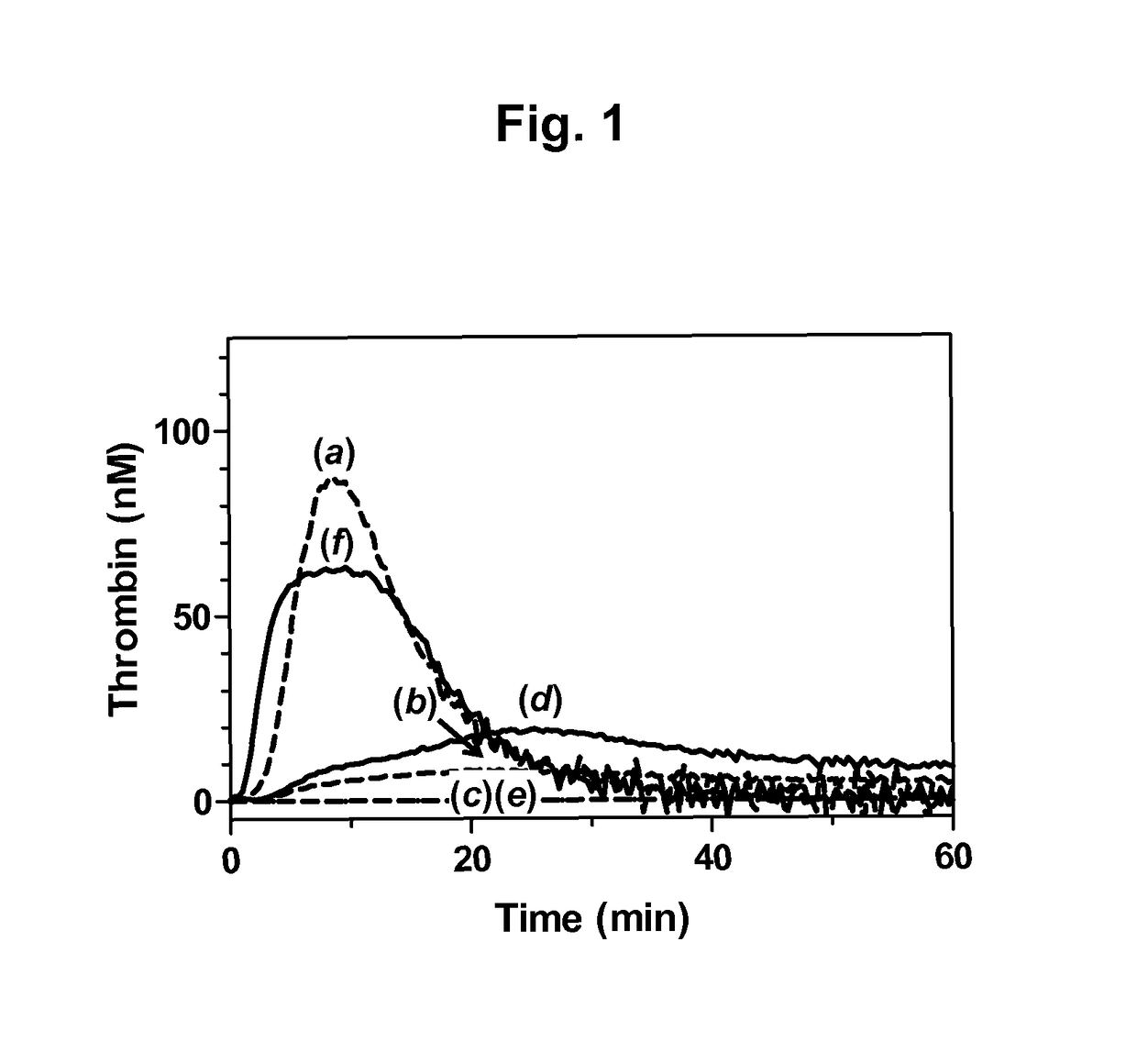
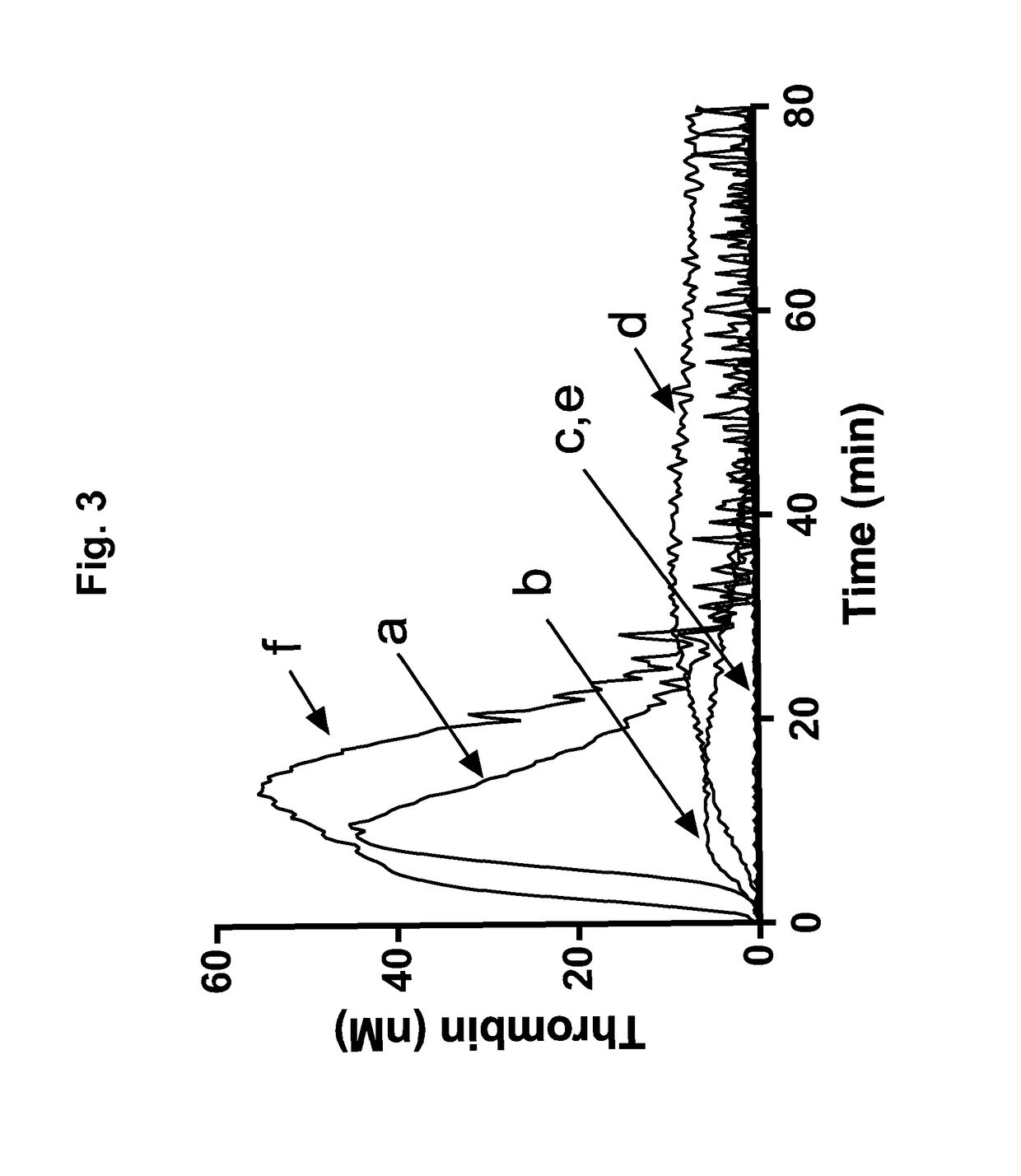
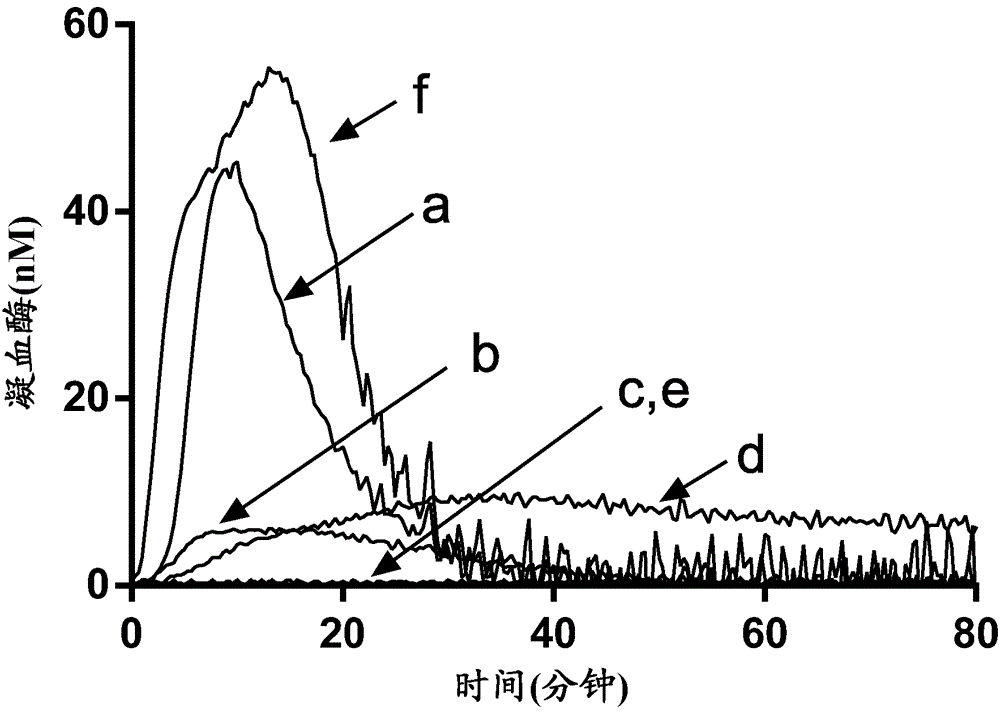
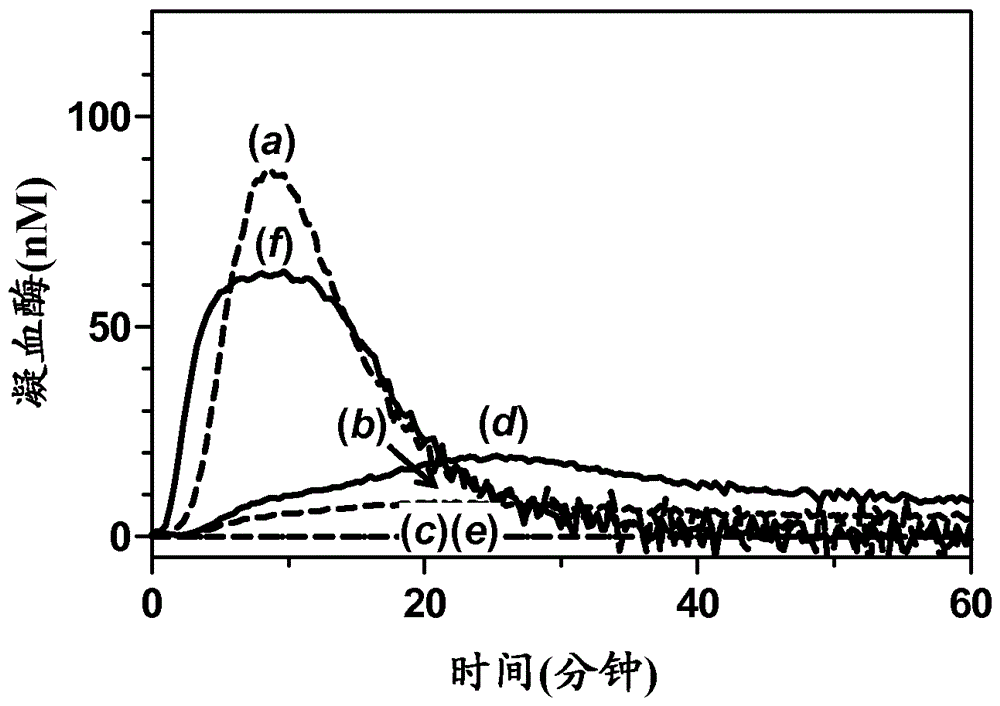
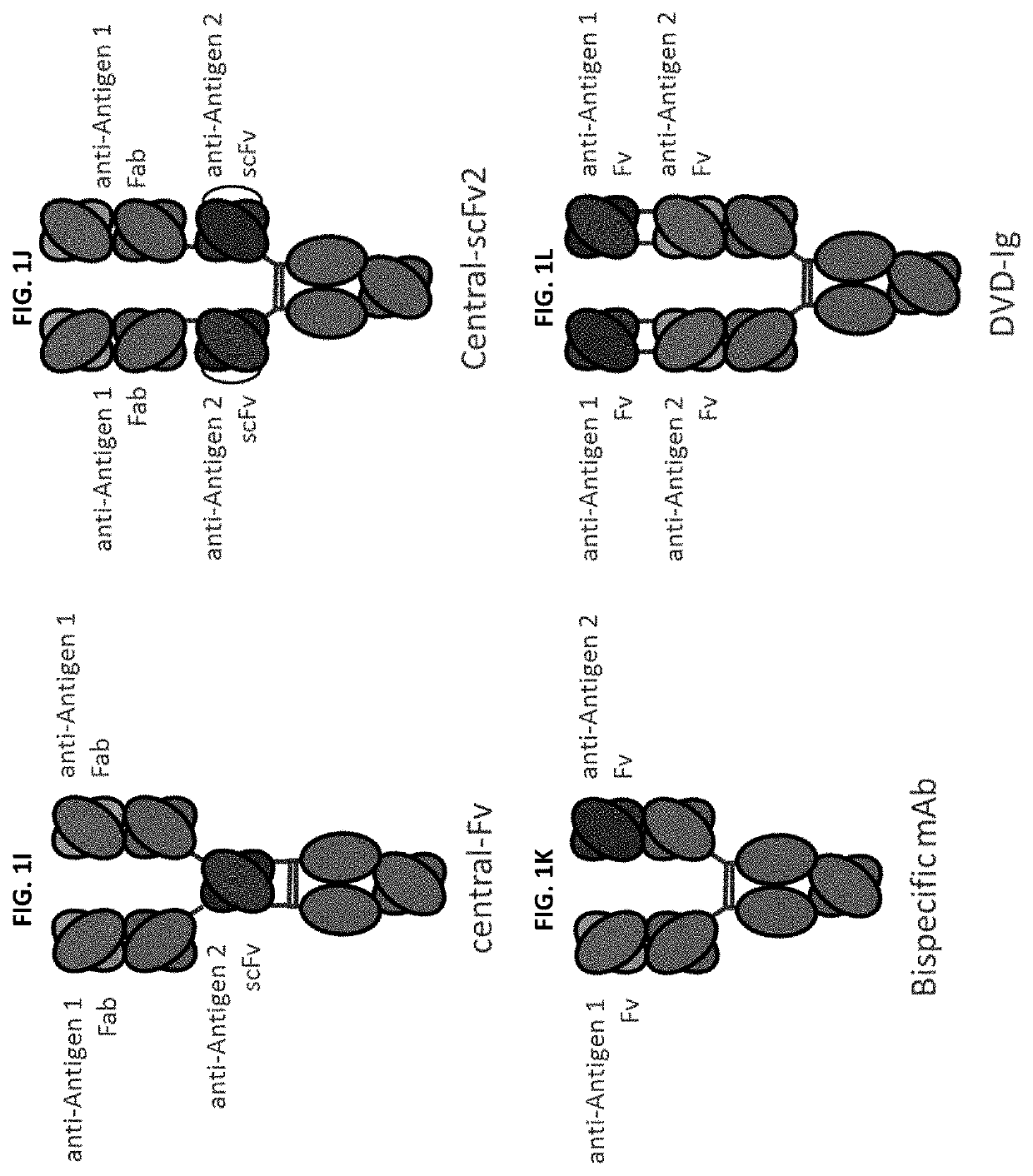
The application discloses a combination of two monospecific TFPI antibodies, wherein one antibody is capable of specifically binding TFPI (1-181) and the other antibody is capable of specifically binding TFPI (182-276), as well as bispecific anti-TFPI antibodies derived from two such monospecific antibodies. Both the combination of the two monospecific antibodies and the bispecific antibody strongly enhance thrombin generation by neutralising full length TFPIα, even where the concentration of TFPI is abnormally elevated.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Antibodies capable of specifically binding two epitopes on tissue factor pathway inhibitor
The application discloses a combination of two monospecific TFPI antibodies, wherein one antibody is capable of specifically binding TFPI (1-181) and the other antibody is capable of specifically binding TFPI (182-276), as well as bispecific anti-TFPI antibodies derived from two such monospecific antibodies. Both the combination of the two monospecific antibodies and the bispecific antibody strongly enhance thrombin generation by neutralising full length TFPI[alpha], even where the concentration of TFPI is abnormally elevated.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
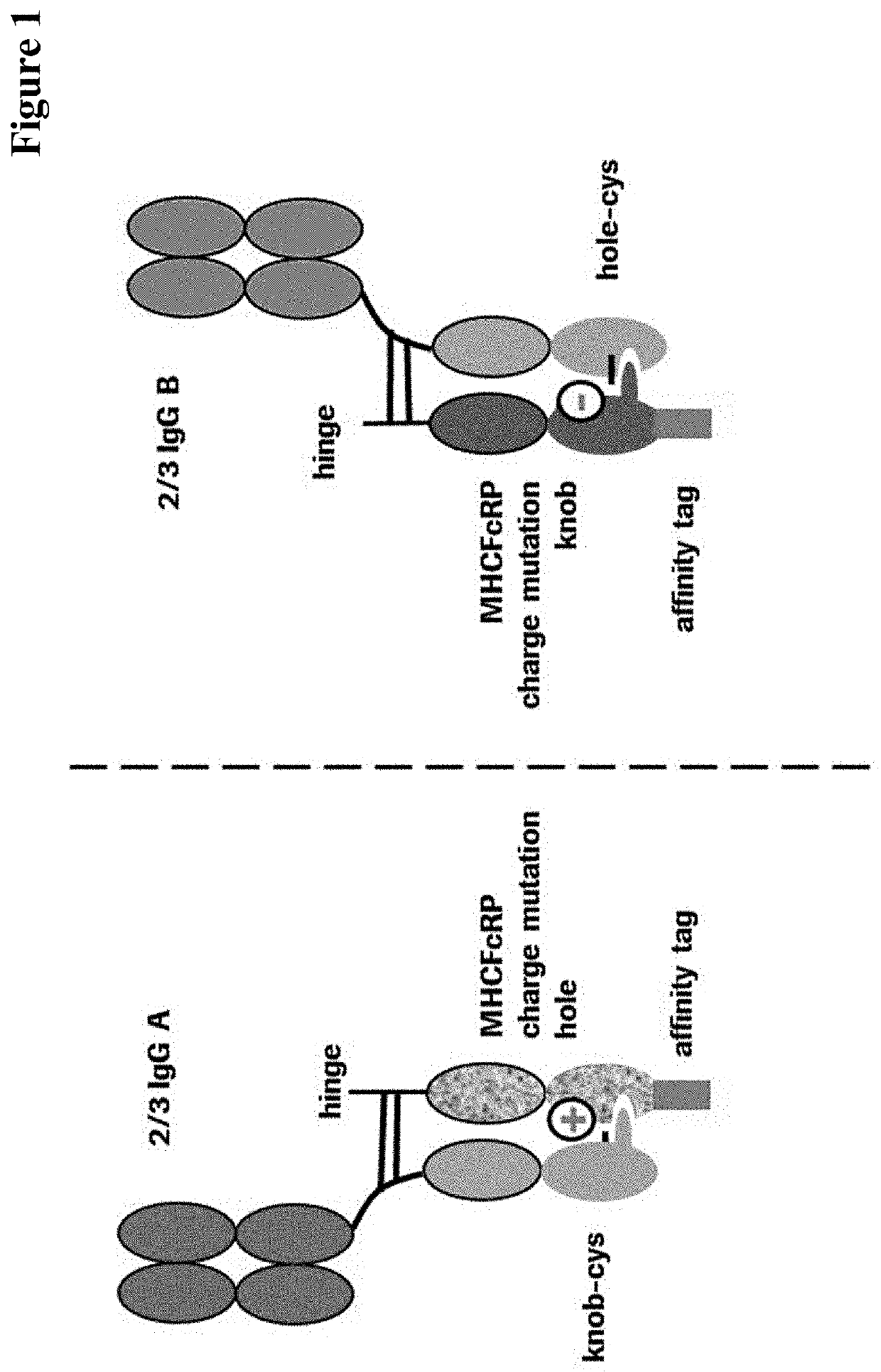
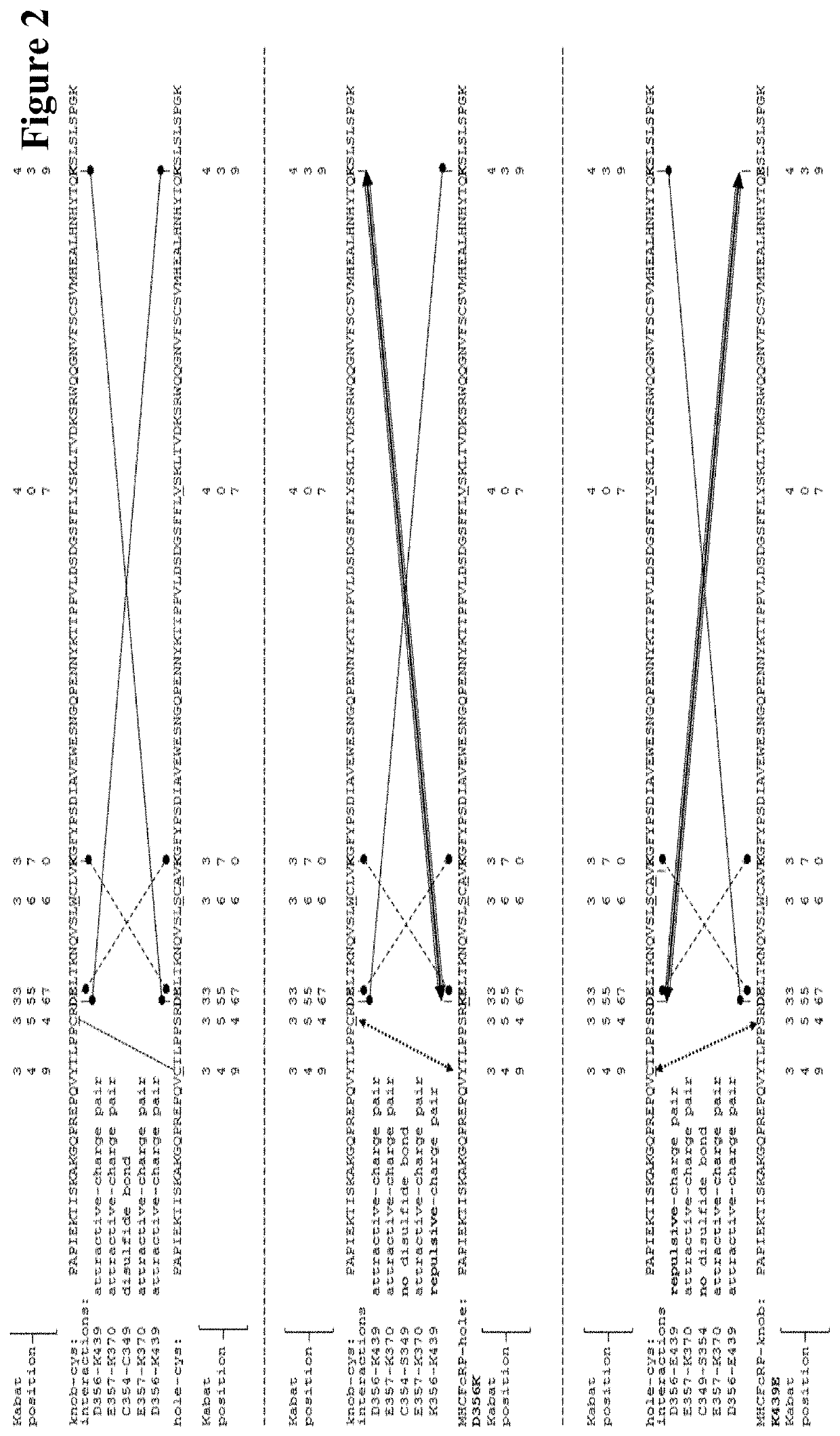
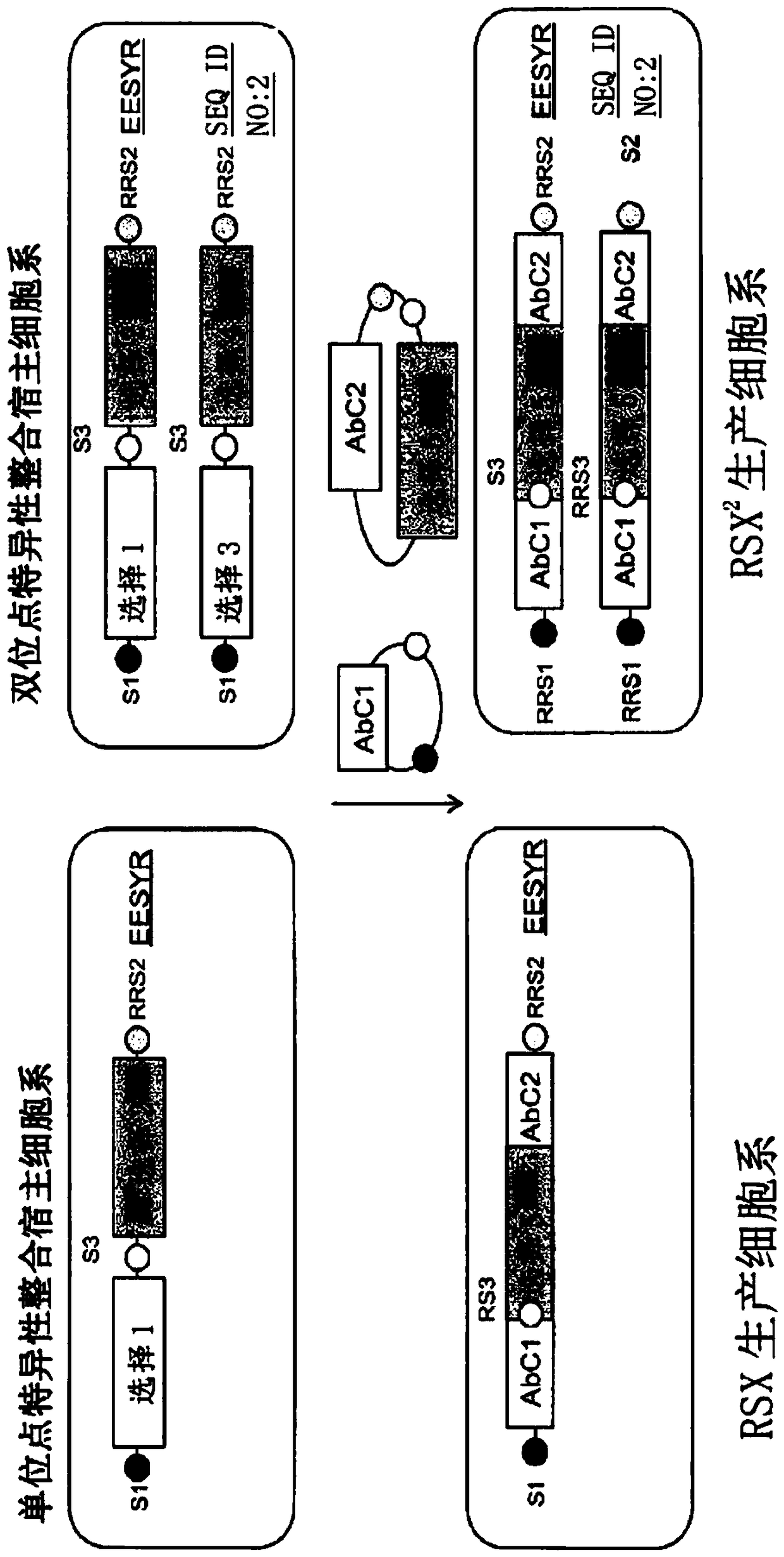
Method for generating multispecific antibodies from monospecific antibodies
PendingCN111246885AHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsDisulfide bondingAntiendomysial antibodies
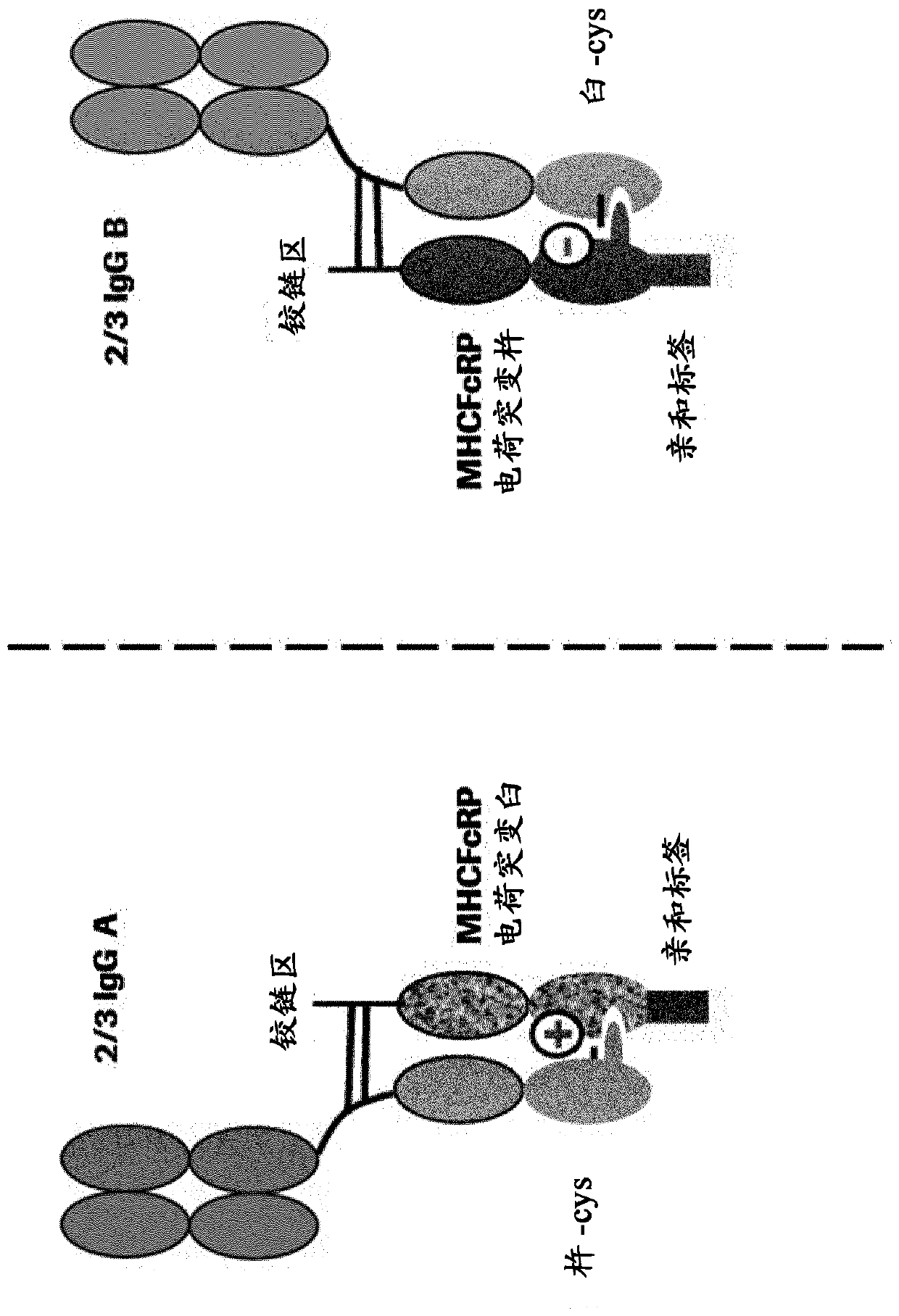
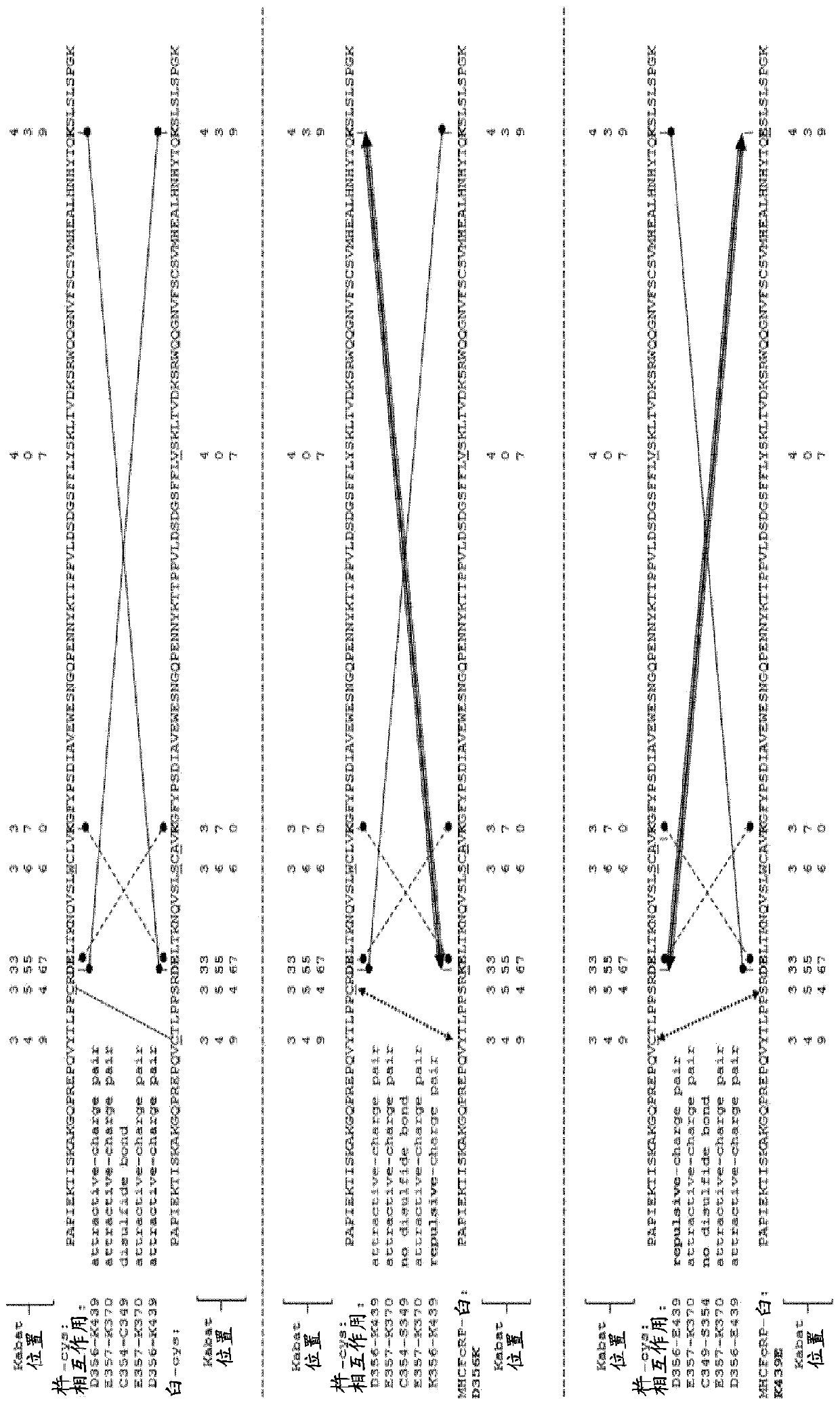
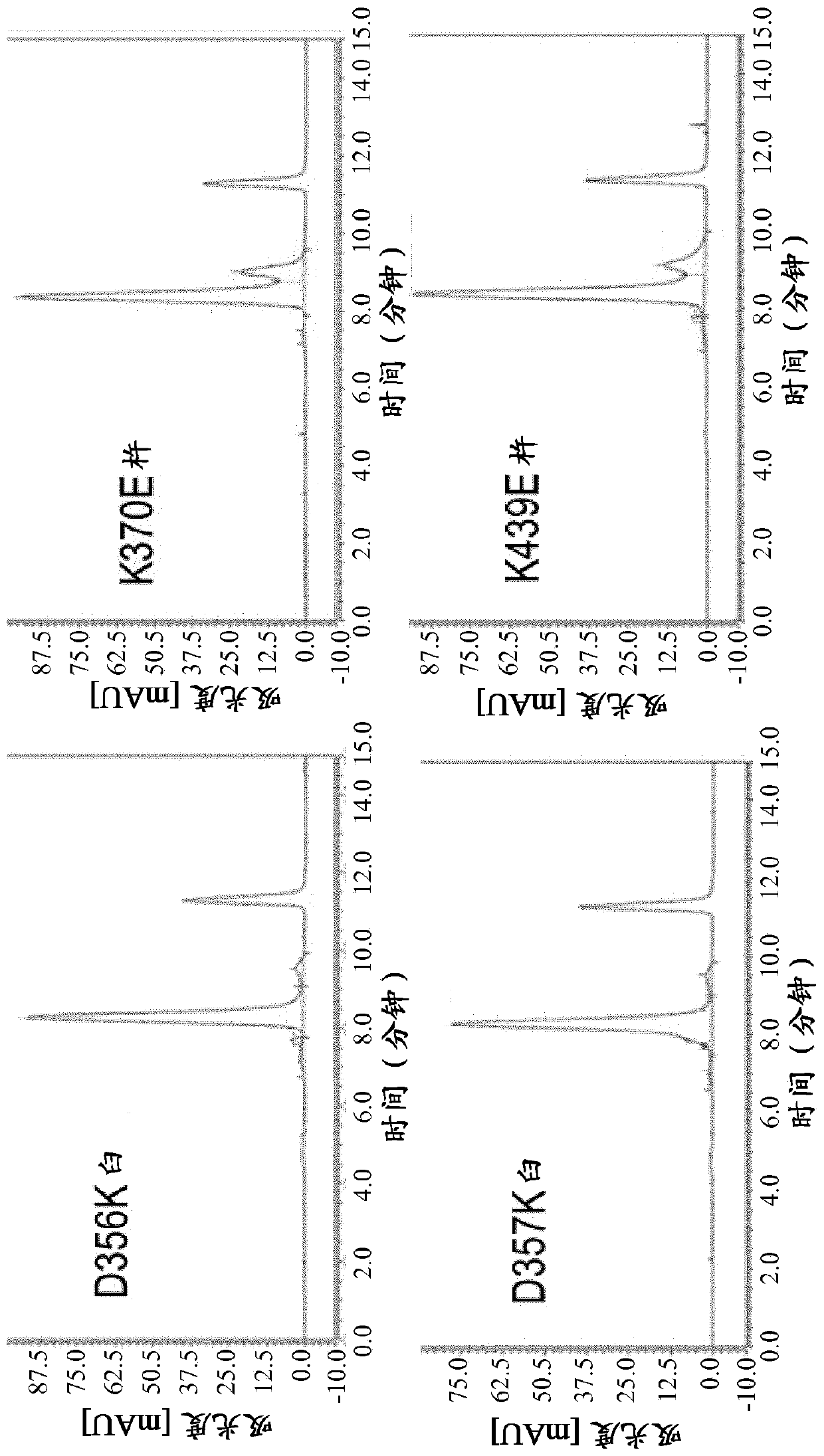
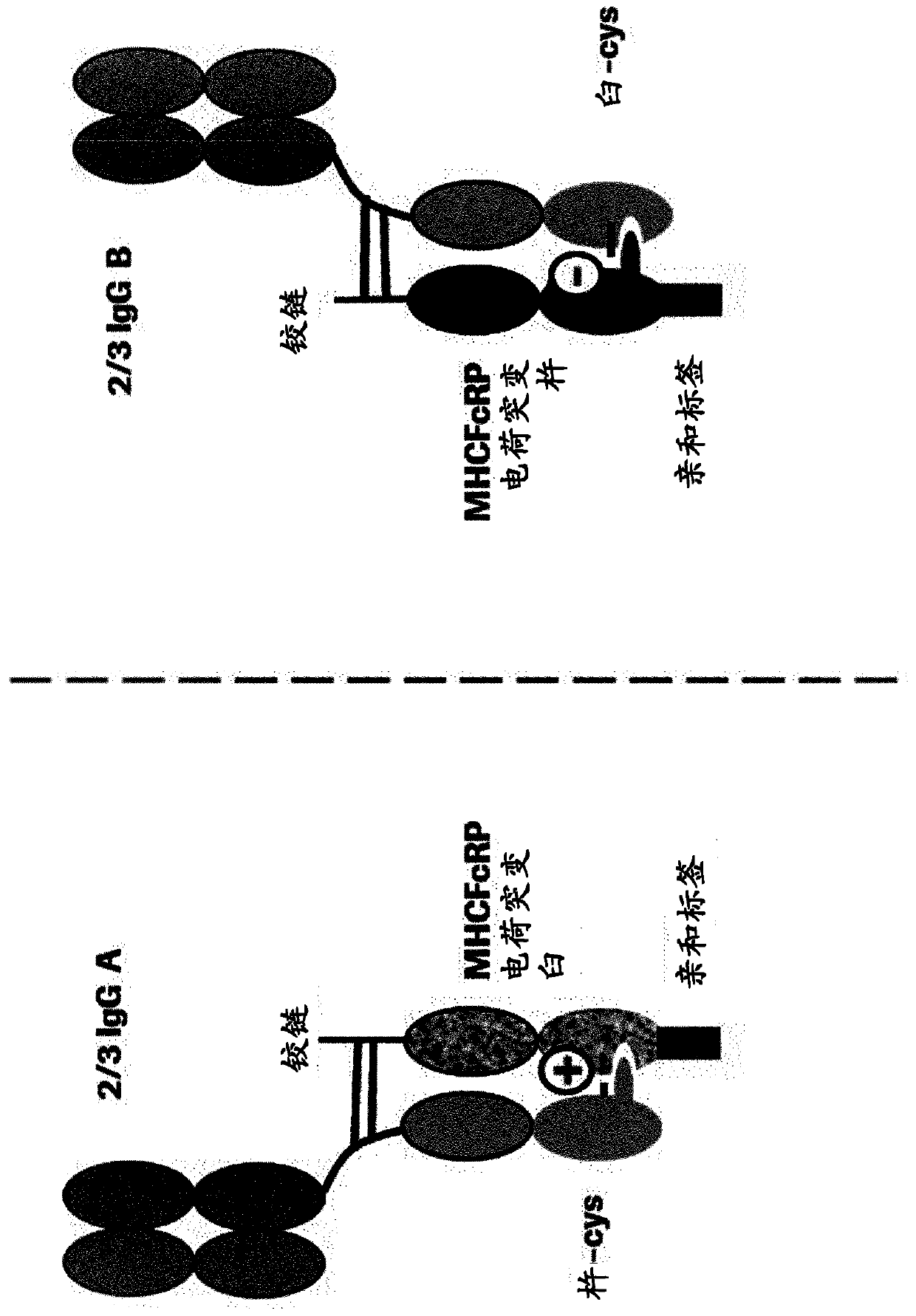
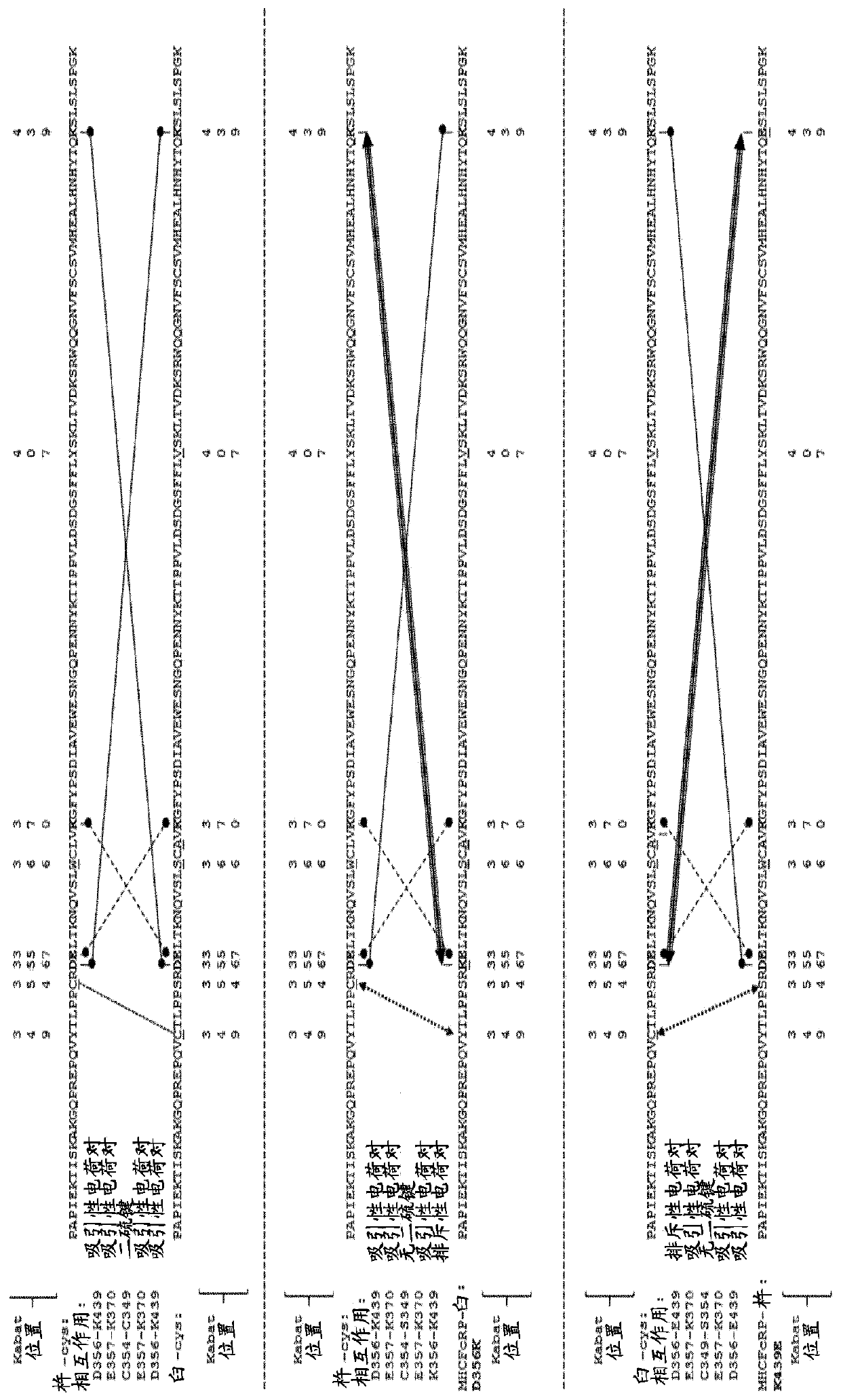
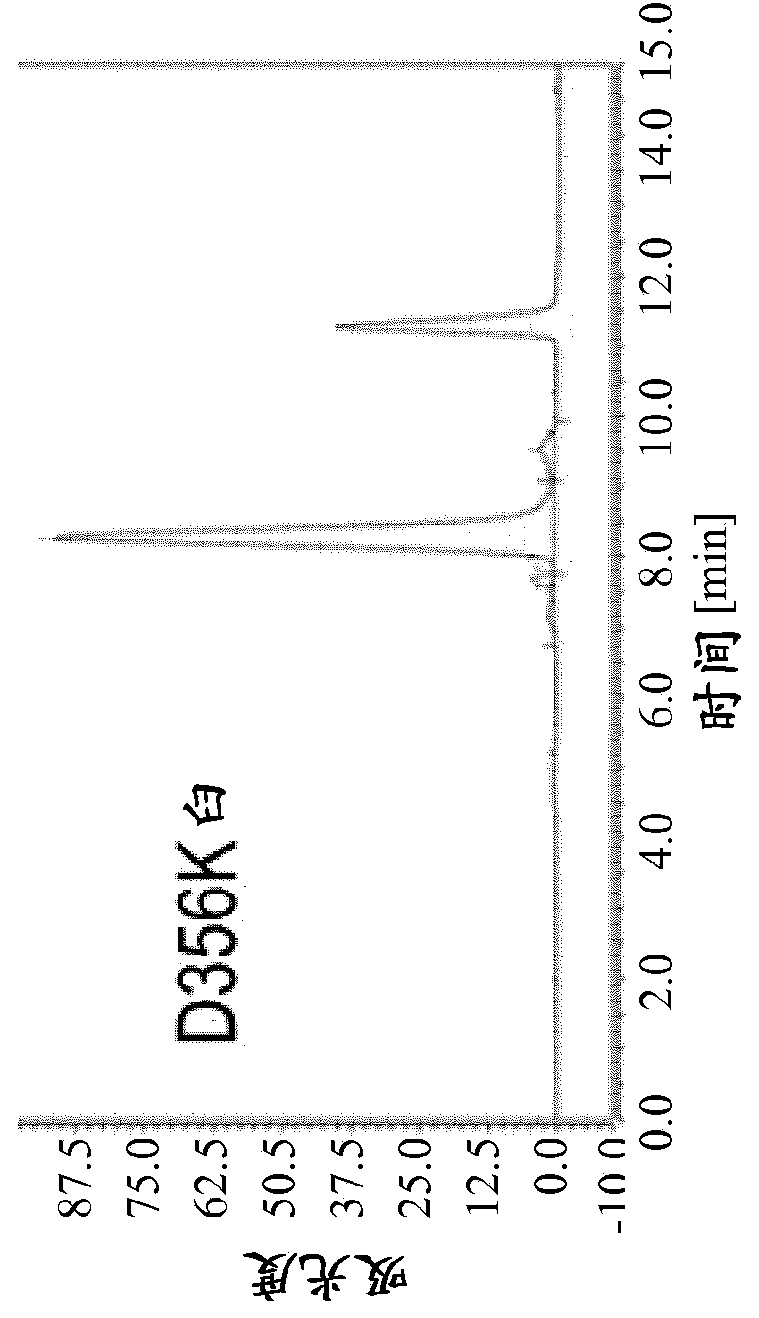
Herein is reported a method for the generation of multispecific antibodies by a half- antibody exchange reaction between two 2 / 3-IgGs destabilized in one half by asymmetric perturbing mutations fostering the generation of correctly assemble full length bispecific antibodies. The method can be performed in the absence of reducing agents and does not require hinge region disulfide bonds in the starting 2 / 3-IgGs.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
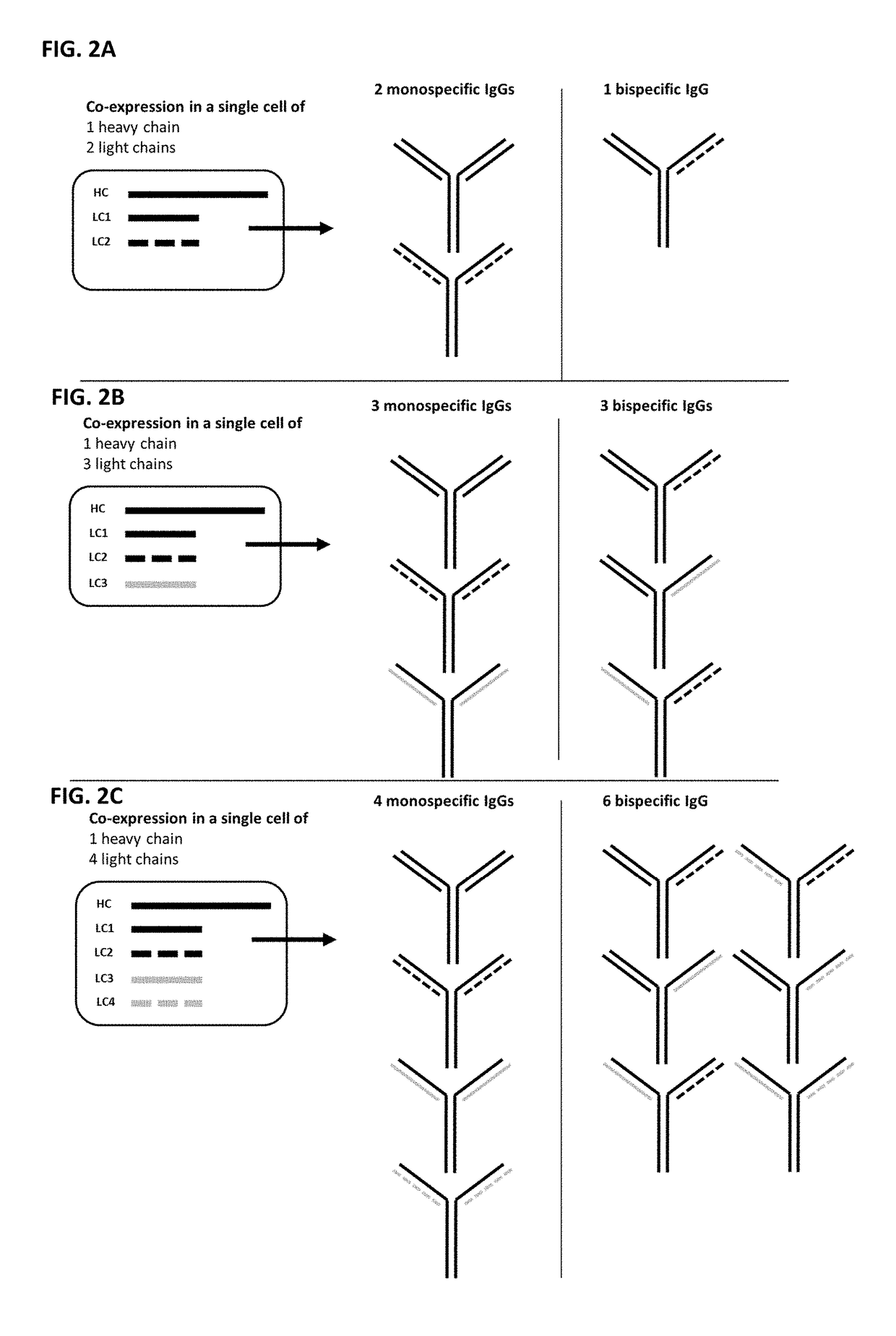
Generating multispecific antibody mixtures and methods of uses thereof
ActiveUS20190031714A1Low costHybrid immunoglobulinsSerum immunoglobulinsHeavy chainBispecific antibody
The invention relates to the generation of multispecific antibody mixtures include a subset of antibodies isolated from a mixture of two or more monospecific antibodies and one or more bispecific antibodies, wherein all antibodies in the subset have the same common heavy chain. The invention also relates to methods of isolating, purifying, or otherwise producing such a subset of antibodies by using at least one affinity chromatography step. The invention also relates to methods of using such a subset of antibodies in a variety of therapeutic indications.
Owner:NOVIMMUNE
Methods of purifying bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS10457749B2Favorable manufacturing characteristicHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsHeavy chainBinding site
The invention relates to the purification of bispecific antibodies carrying a different specificity for each binding site of the immunoglobulin molecule from a mixture of monospecific antibodies. The bispecific antibodies are composed of a single heavy chain and two different light chains, one containing a Kappa constant domain and the other a Lambda constant domain. This invention in particular relates to the isolation of these bispecific antibodies from mixtures that contain monospecific antibodies having two Kappa light chains or portions thereof and monospecific antibodies having two Lambda light chains or portions thereof. The invention also provides the methods of efficiently purifying these bispecific antibodies.
Owner:NOVIMMUNE
Bispecific and monospecific antibodies using novel Anti-pd-1 sequences
PendingUS20220204624A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesMonospecific antibody
Owner:XENCOR INC
Method for in vivo generation of multispecific antibodies from monospecific antibodies
PendingCN111372947AHybrid immunoglobulinsSerum immunoglobulinsDisulfide bondingMonospecific antibody
Herein is reported a method for the generation of multispecific antibodies directly on the cell-surface at the site of action by a half-antibody exchange reaction between two 2 / 3-IgGs or two 2 / 3-BiFabs destabilized in one half by asymmetric perturbing mutations fostering the generation of correctly assembled full length bi-or multi-specific antibodies. The method is performed in the absence hingeregion disulfide bonds in the starting 2 / 3-IgGs or 2 / 3-BiFabs.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Bispecific and monospecific antibodies using novel anti-PD-1 sequences
ActiveUS11312770B2Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesMonospecific antibody
Owner:XENCOR INC
Method for detecting MERS-CoV in Camilidae
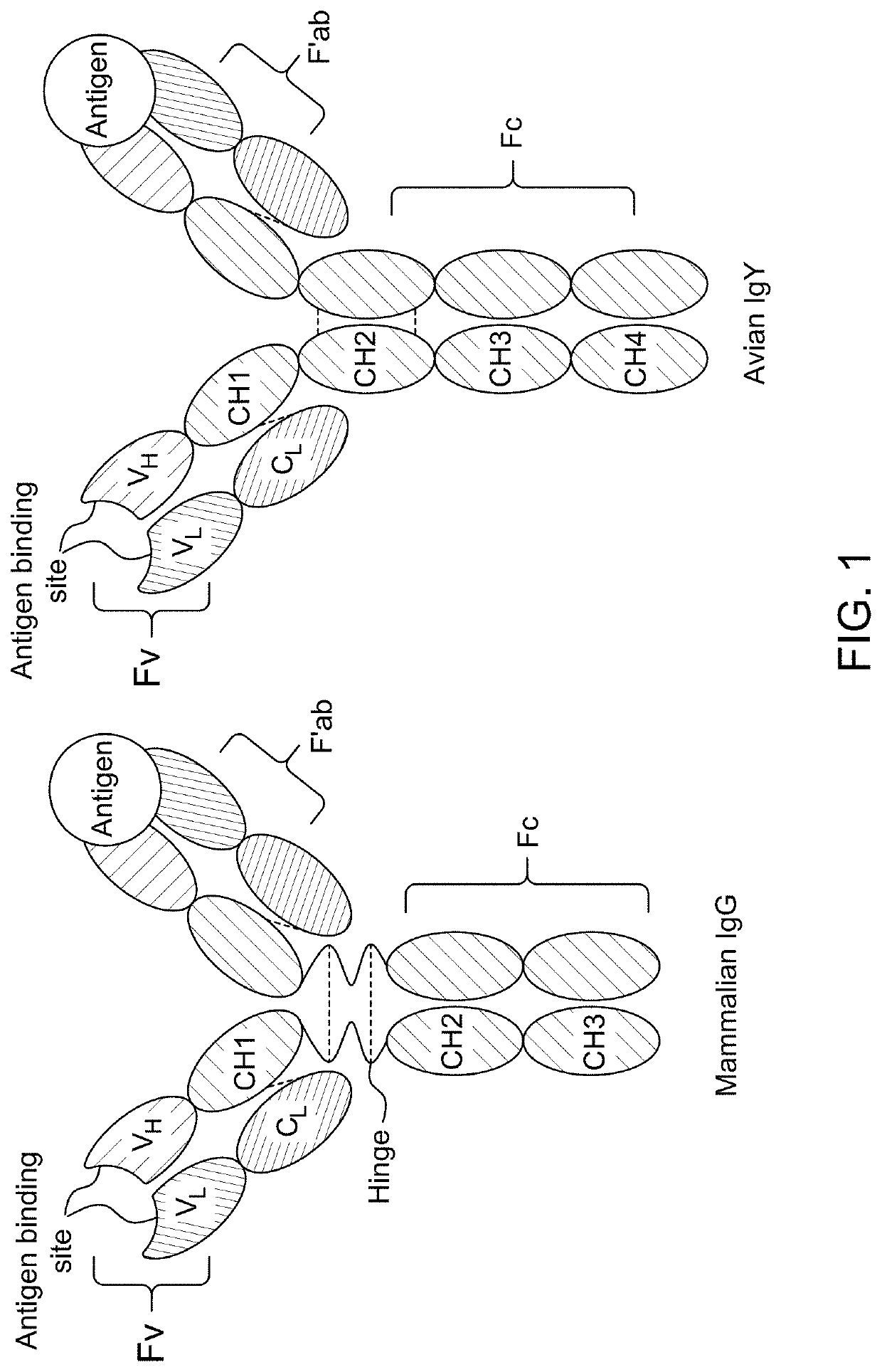
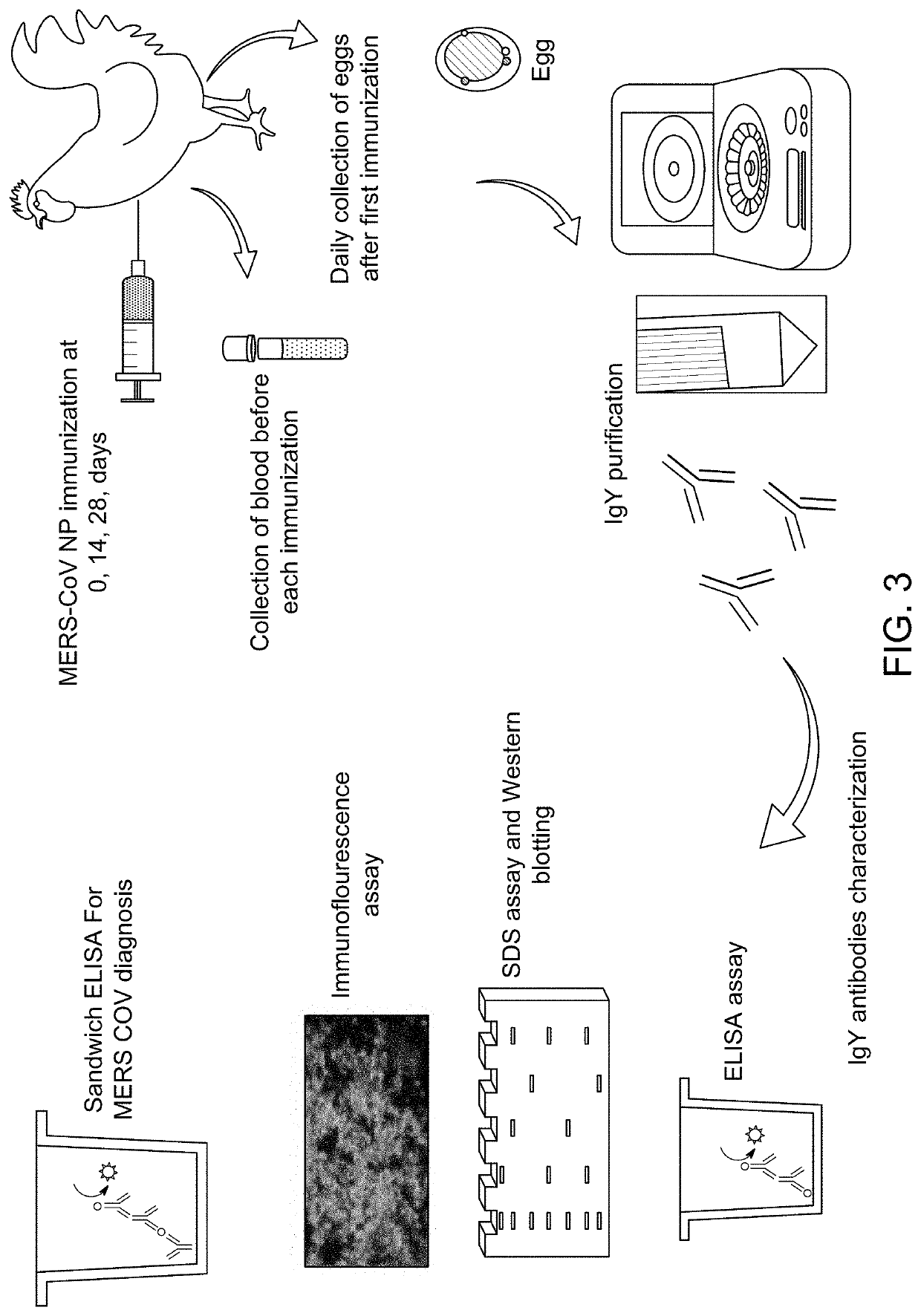
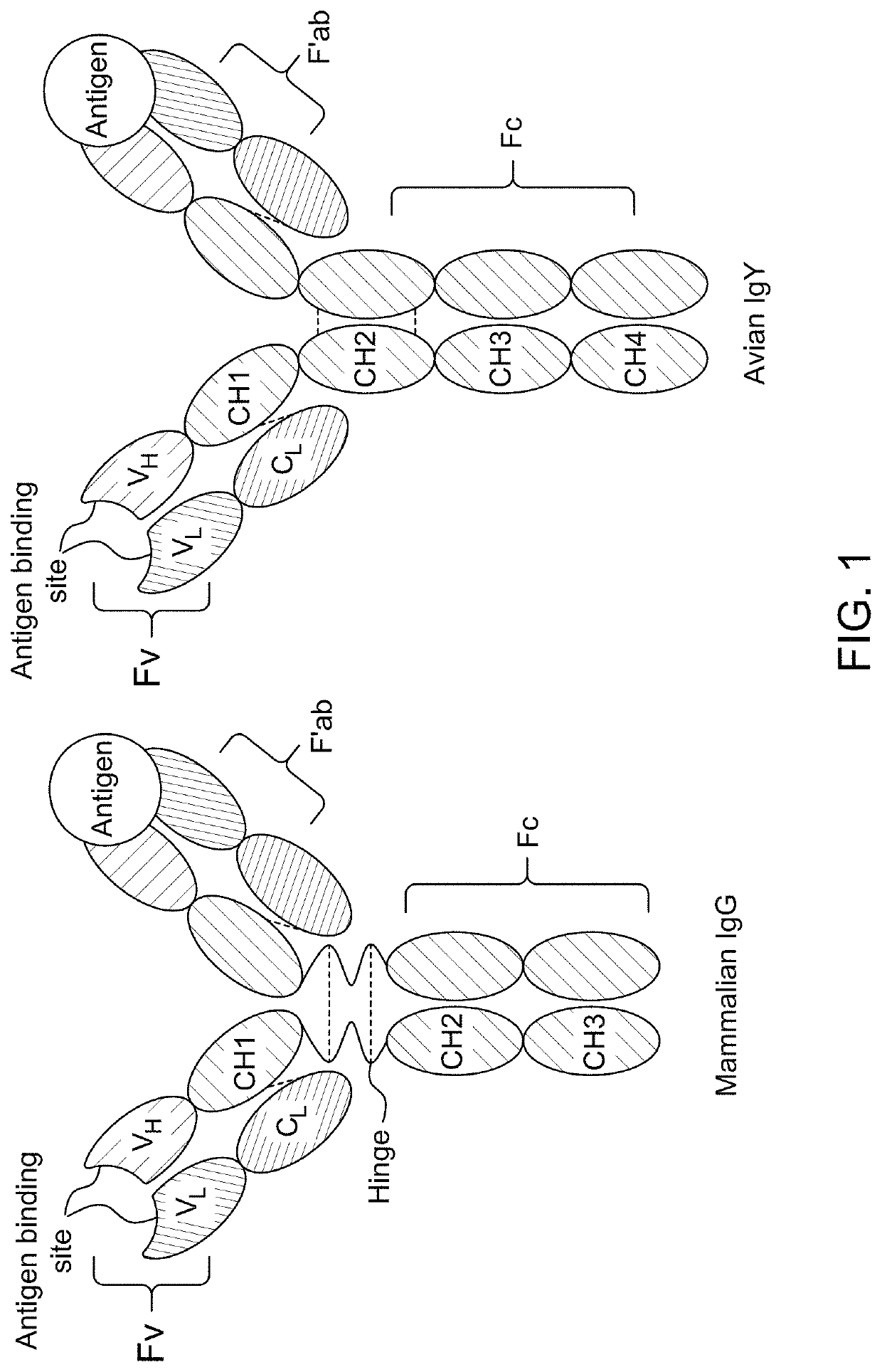
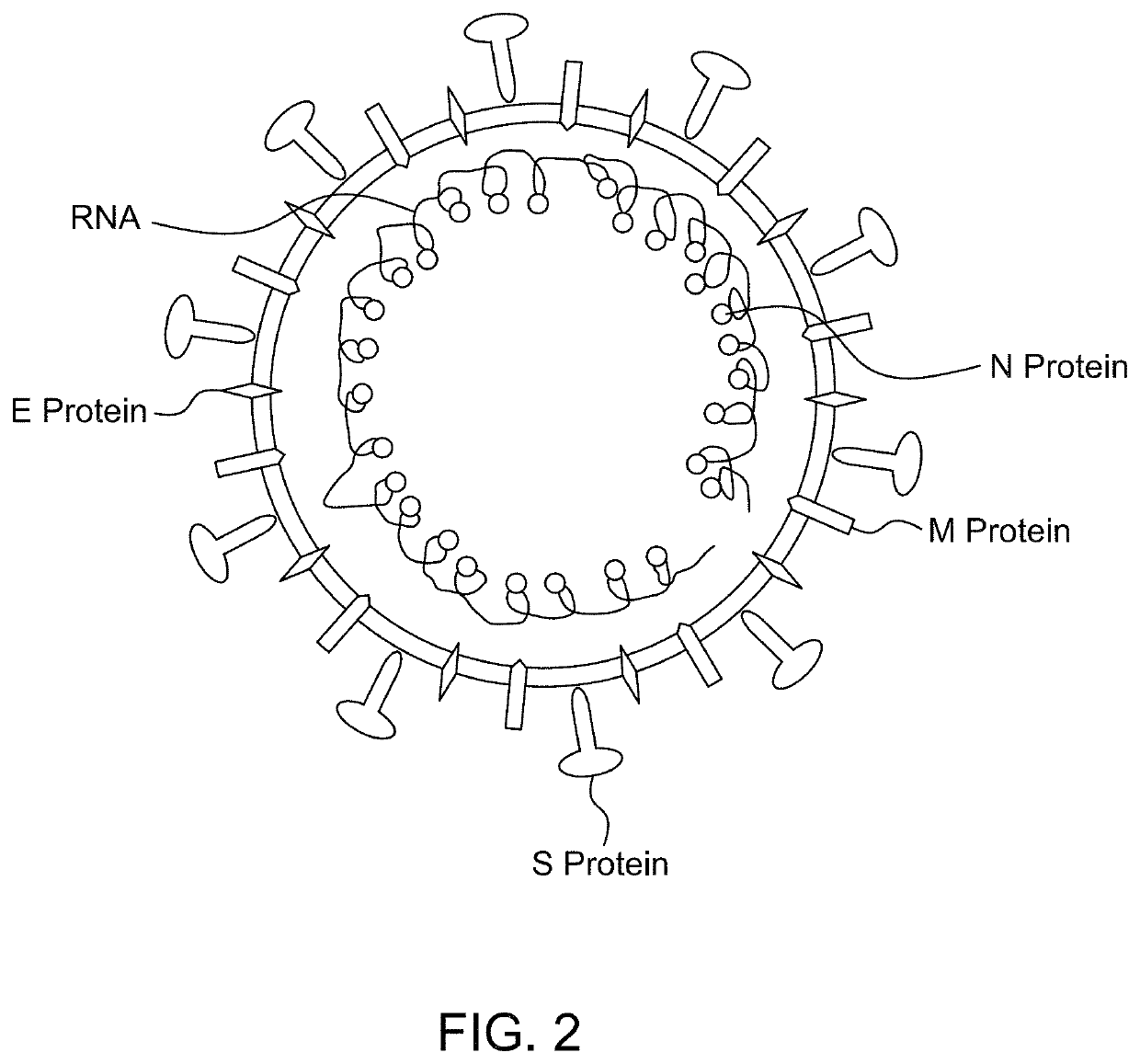
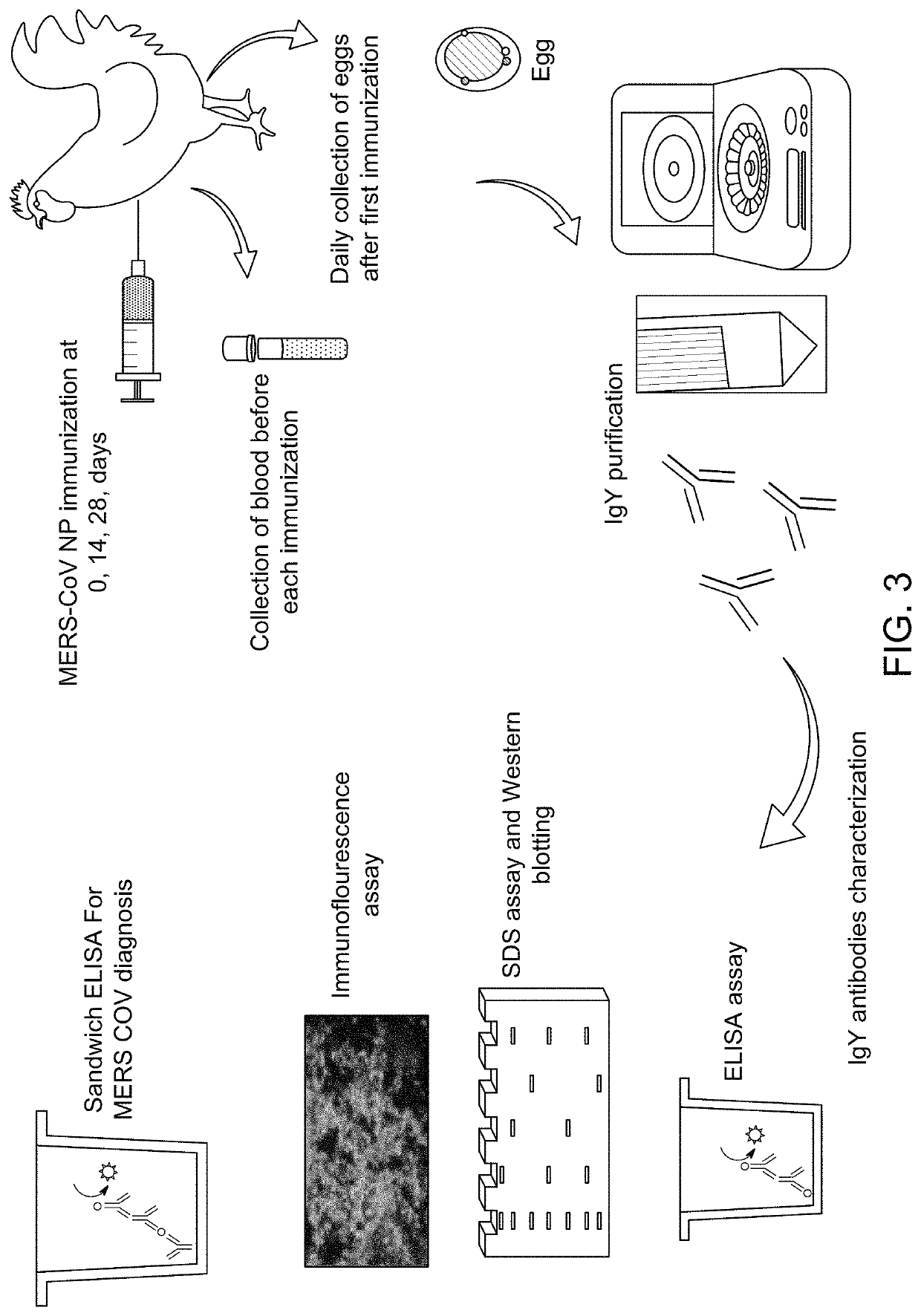
ActiveUS11131672B1Improve abilitiesImproving immunogenicityEgg immunoglobulinsSsRNA viruses positive-senseMonospecific antibodyBiochemistry
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Method for in vivo generation of multispecific antibodies from monospecific antibodies
PendingUS20200255522A1Eliminate riskCorrect formatHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisulfide bondingAntiendomysial antibodies
Herein is reported a method for the generation of multispecific antibodies directly on the cell-surface at the site of action by a half-antibody exchange reaction between two 2 / 3-IgGs or two 2 / 3-BiFabs destabilized in one half by asymmetric perturbing mutations fostering the generation of correctly assembled full length bi- or multi-specific antibodies. The method is performed in the absence hinge region disulfide bonds in the starting 2 / 3-IgGs or 2 / 3-BiFabs.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Antibody binding detection method for detecting MERS-CoV
ActiveUS11307202B1Improve abilitiesImproving immunogenicityEgg immunoglobulinsSsRNA viruses positive-senseMonospecific antibodyBiochemistry
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Dual specific antibodies
ActiveUS10683348B2Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntigen Binding FragmentBispecific antibody
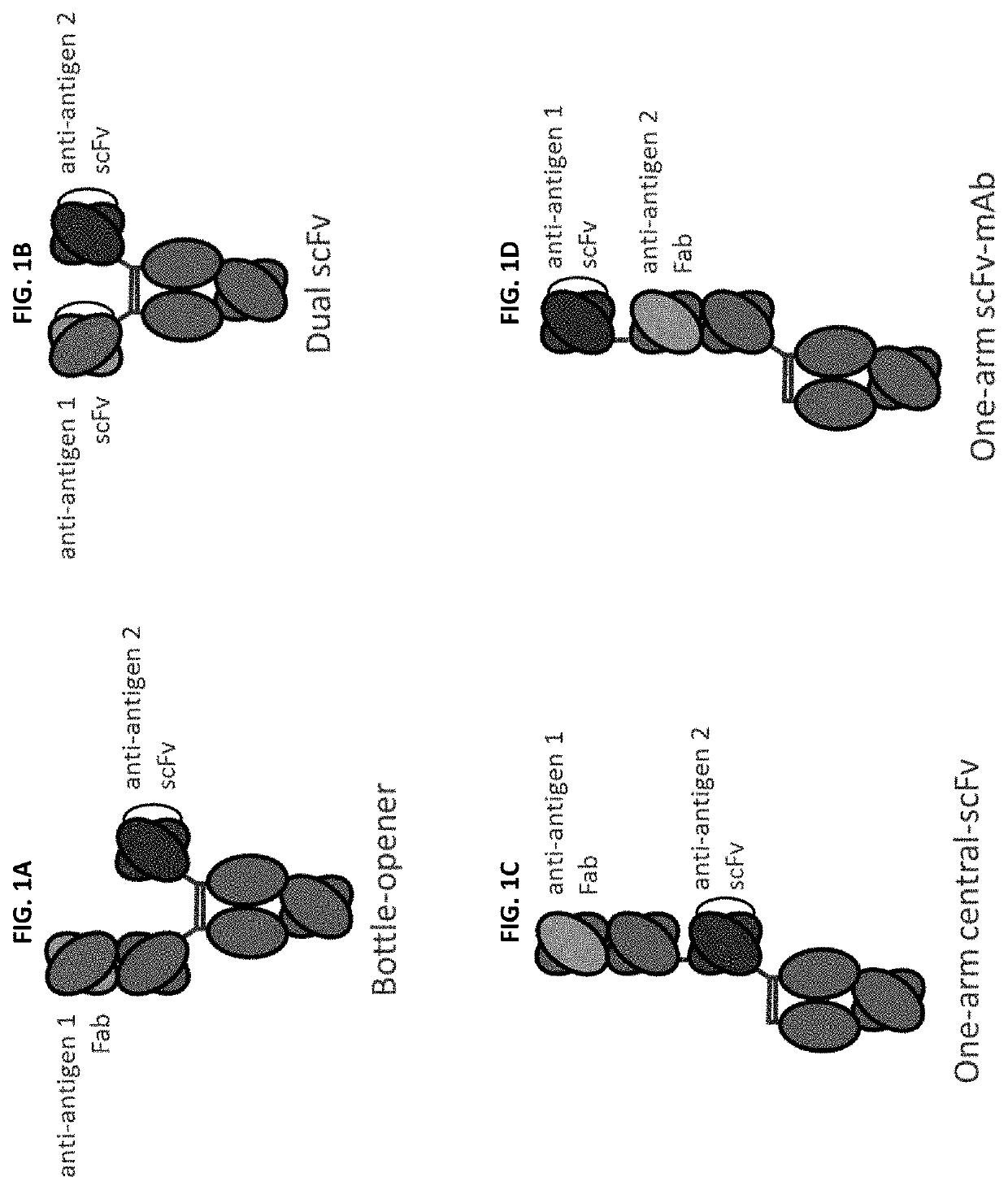
The invention provides dual specific antibodies and methods of making and using such antibodies. In general, the dual specific antibodies are generated by identification of a monospecific antibody having light chain variable region VL residues that are electrostatic or hydrophobic and altering the nucleic acid sequence encoding one or more solvent accessible residues in the VH of the antibody either alone or in combination with alteration of the nucleic acid sequence encoding the VL of the antibody. The altered VH and the VL are expressed and dual specific antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, are selected. Exemplary dual specific antibodies are also provided as well as methods of using the antibodies.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Anti-fc epsilon-r1 alpha (fcer1a) antibodies, bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind fcer1a and cd3, and uses thereof
PendingCN112888482AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention provides novel full-length human antibodies that bind to human Fc epsilon-R1 alpha (monospecific antibodies). The present invention also provides novel bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) that bind to both Fc epsilon-R1 alpha and CD3 and activate T cells via the CD3 complex in the presence of Fc epsilon-R1 alpha-expressing cells. The bispecific antigen-binding molecules of the invention are useful for the treatment of diseases and disorders in which an up regulated or induced Fc epsilon-R1 alpha-targeted immune response is desired and / or therapeutically beneficial. For example, the bispecific antibodies of the invention are useful for the treatment of allergies, including anaphylaxis.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Dual specific antibodies
ActiveUS20160257744A1Stable expressionExtended half-lifeImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntibody ingredientsAntigen Binding FragmentBispecific antibody
The invention provides dual specific antibodies and methods of making and using such antibodies. In general, the dual specific antibodies are generated by identification of a monospecific antibody having light chain variable region VL residues that are electrostatic or hydrophobic and altering the nucleic acid sequence encoding one or more solvent accessible residues in the VH of the antibody either alone or in combination with alteration of the nucleic acid sequence encoding the VL of the antibody. The altered VH and the VL are expressed and dual specific antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, are selected. Exemplary dual specific antibodies are also provided as well as methods of using the antibodies.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
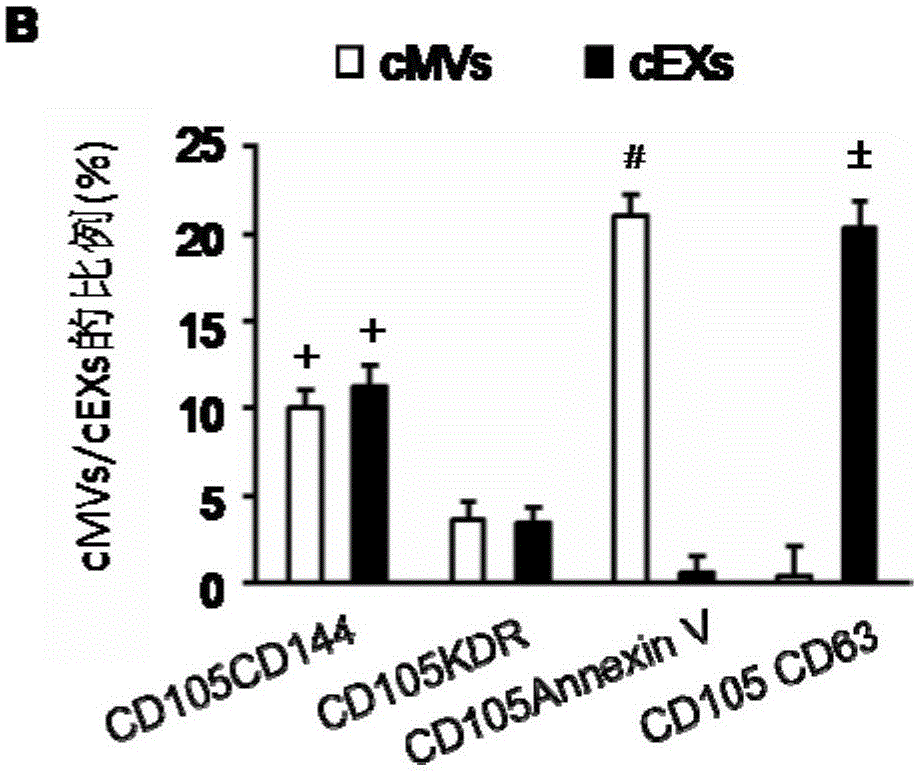
Application of reagents for detecting cd105, cd144, cd34, kdr, annexin V and CD63 in preparation of reagents for detecting extracellular vesicles released by endothelial and endothelial progenitor cells in blood
The invention relates to a method for detecting EVs (extracellular vesicles) released by ECs (endothelial cells) and EPCs (endothelial progenitor cells) in blood. EC-MVs (microvesicles), EPC-MVs, EC-EXs (exosomes) and EPC-EXs are separated from a circulatory system with two specific antibody linked immunomagnetic sand methods. The method breaks through a single specific antibody method, and the specificity and the sensitivity of extracted cells MVs and EXs are higher than those in the prior art. Besides, the cells MVs and EXs are detected with an NTS (nanoparticle tracing analysis) technique in combination of a specific antibody micro-beads method and a Q-dots method. The method can quickly, accurately and objectively analyze the levels of EC-MVs, EPC-MVs, EC-EXs and EPC-EXs in complicated samples such as blood and has advantages which a traditional analysis method does not possess. Besides, the specific and sensitive method is provided for further research of MVs and EXs serving as biomarkers of diseases.
Owner:WUHAN DAFU BIOTECH CO LTD
Anti-cxcr4 antibodies
PendingCN110234352ARadioactive preparation carriersImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseCXCR4
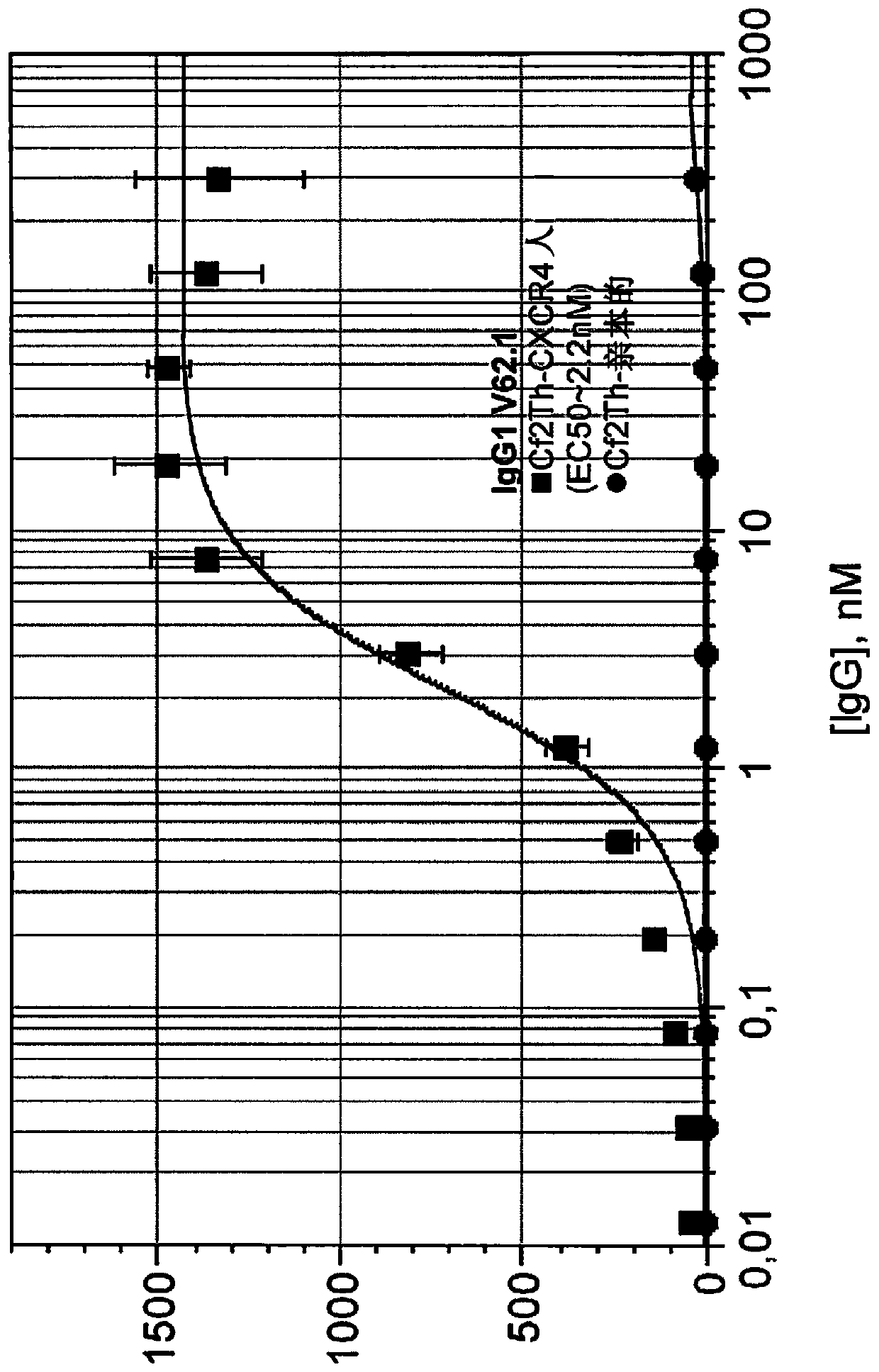
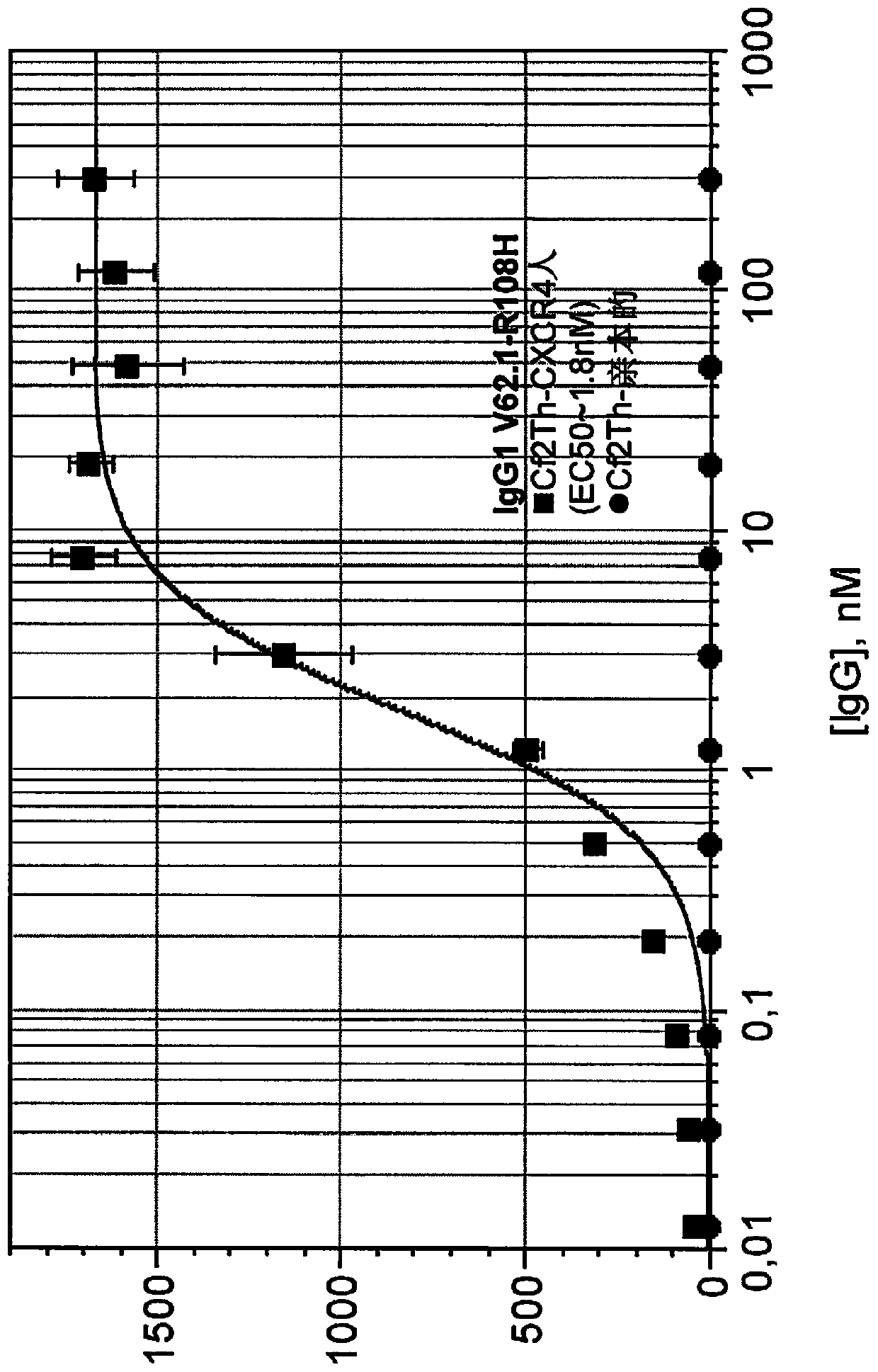
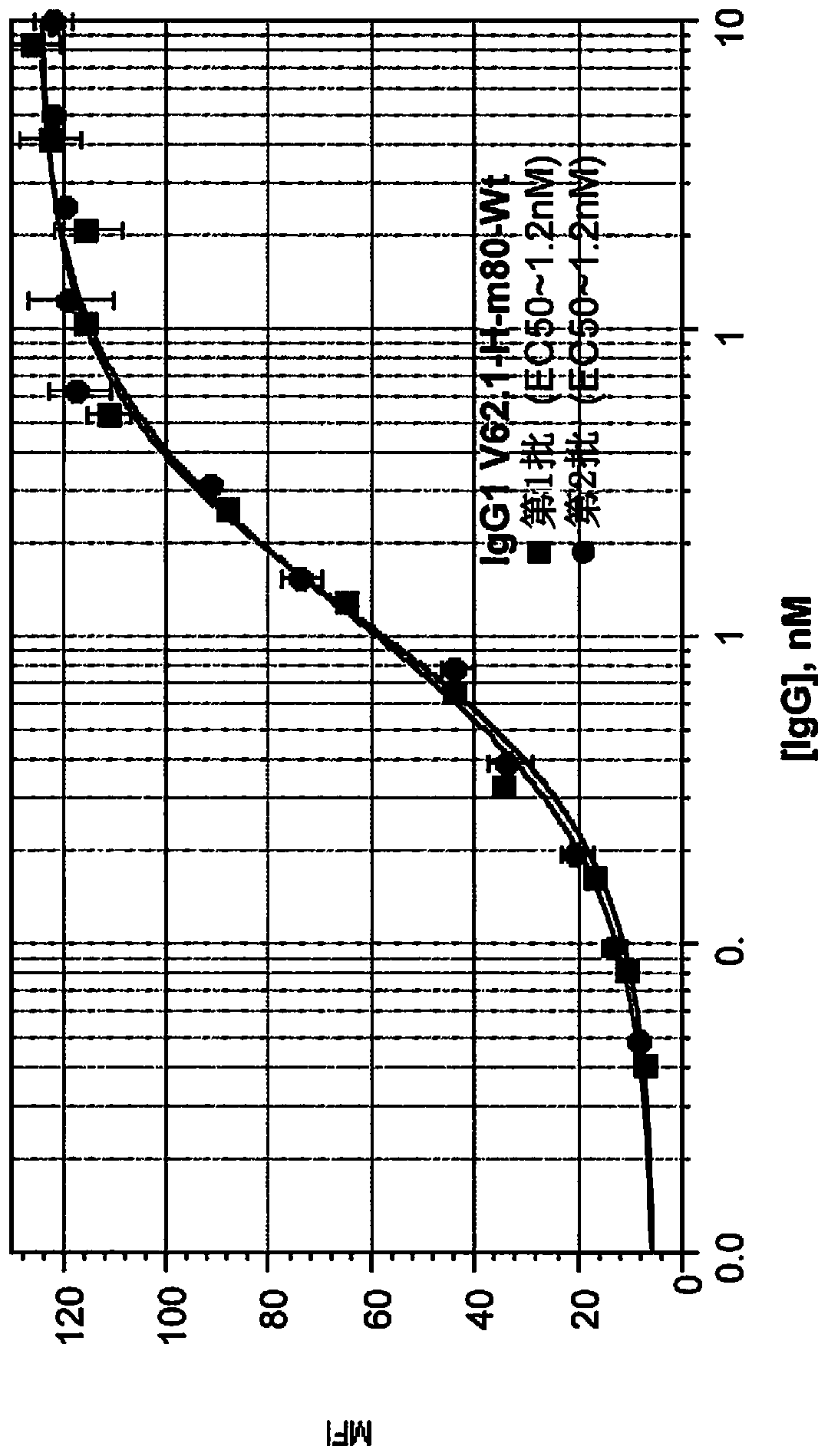
The present invention relates to monospecific antibodies against CXCR4 or binding fragments thereof, to the use of such anti-CXCR4 antibodies or binding fragments in treating diseases whose pathogenesis is related to activation of CXCR4, as well as to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such anti-CXCR4 antibodies or binding fragments.
Owner:エムエスエムプロテインテクノロジーズインコーポレイテッド
Compositions and methods for making antibodies based on use of expression-enhancing loci
ActiveCN109195986AHybrid immunoglobulinsGenetically modified cellsBispecific antibodyAntigen binding
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com