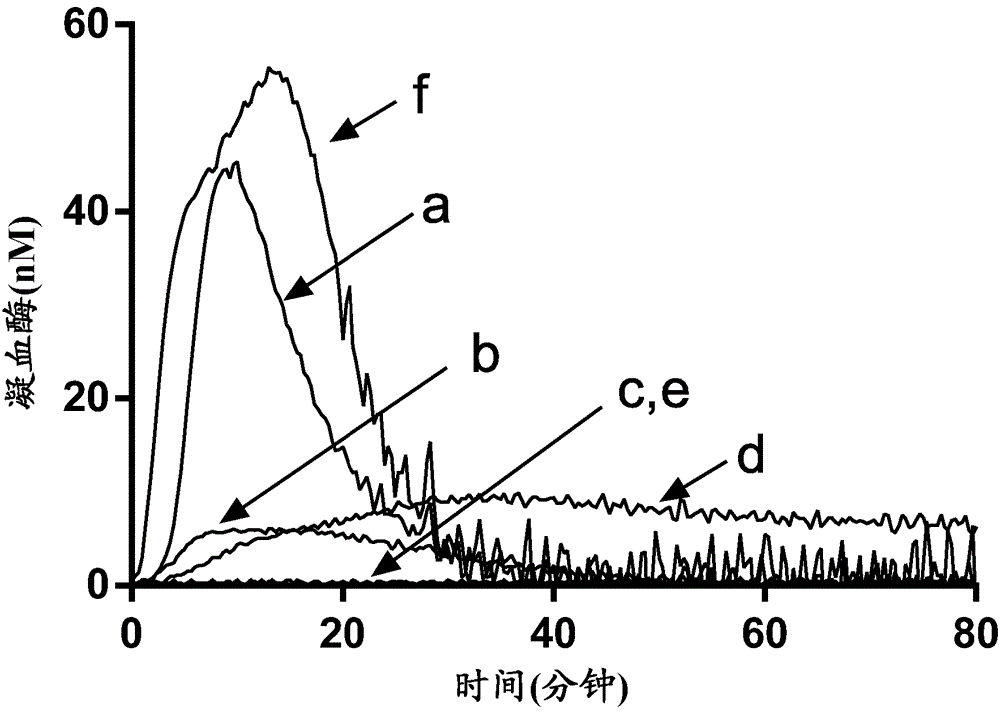
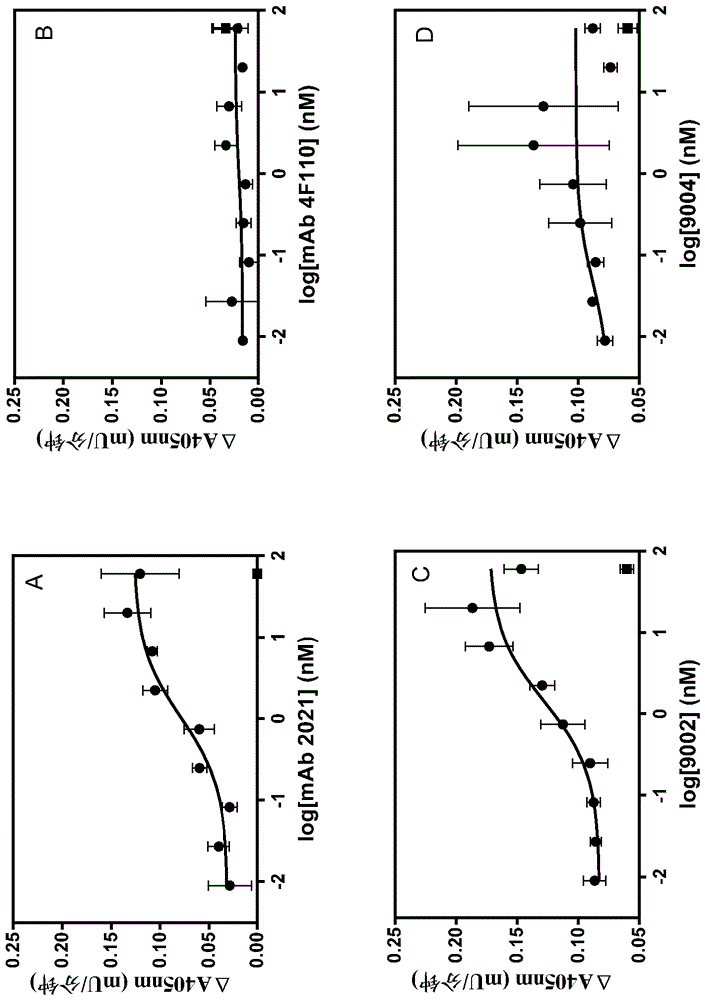
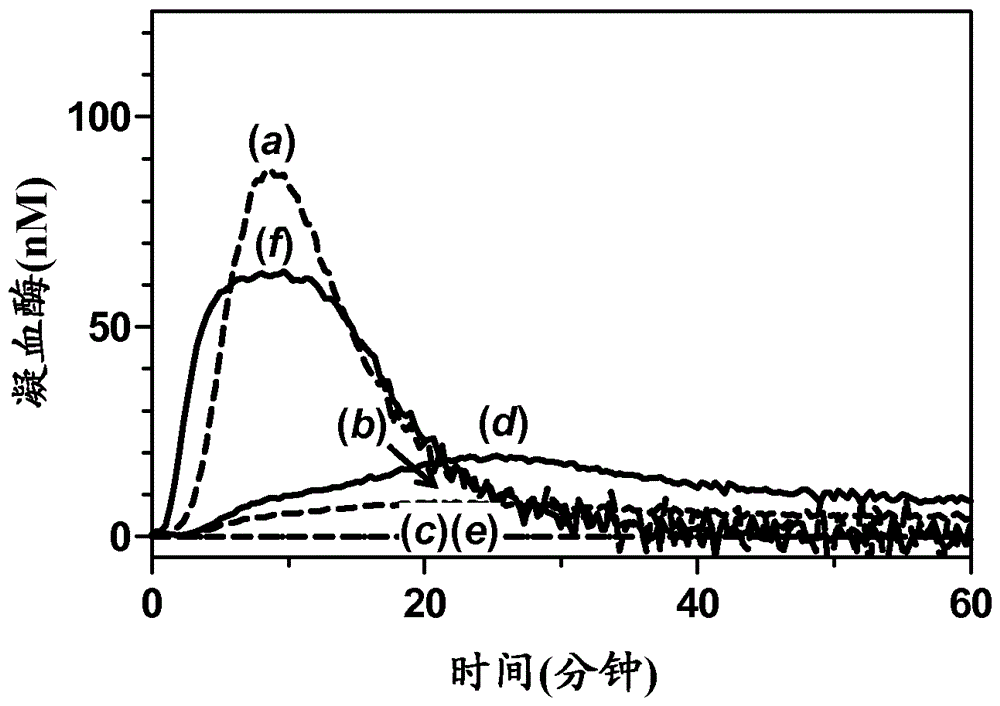
Antibodies capable of specifically binding two epitopes on tissue factor pathway inhibitor
A bispecific antibody and tissue factor technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, protease inhibitor immunoglobulins with anti-peptide structure, antibody medical components, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to completely neutralize the activity of TFPIα
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0507] Example 1: Immunization, Fusion and Screening
[0508] RBF mice are immunized with human TFPIα (SEQ ID NO: 1) or a fragment of TFPI (eg, corresponding to residues 1-161 of SEQ ID NO: 1). Mice were injected subcutaneously: 20 μg of human TFPI mixed with complete Freund's adjuvant was used for the first injection. For subsequent immunizations, incomplete Freund's adjuvant with the same antigen concentration was used. Ten days after the final immunization, human TFPI-specific antibodies were screened from mouse eye blood by ELISA. Mice with positive serum titers were boosted with 10 [mu]g human TFPI[alpha] or TFPI(1-161) by intravenous injection and sacrificed 3 days later. The spleen was aseptically removed and dispersed into a single cell suspension. Fusion of splenocytes and myeloma cells was performed by the PEG method or by electrofusion. The resulting hybridoma cells were cloned by limiting dilution into microtiter plates. Supernatants from each hybridoma were i...
Embodiment 2
[0510] Example 2: Cloning and sequencing of mouse anti-TFPIKPI-3 / C-terminal specific mAbs TFPI4F110, TFPI22F66 and TFPI22F71
[0511] The heavy and light chain sequences of murine TFPI antibodies: TFPI4F110, TFPI22F66 and TFPI22F71 were cloned and sequenced as described in WO2012 / 001087.
[0512]Total RNA was extracted from hybridoma cells using the RNeasy-MiniKit from Qiagen and used as a template for cDNA synthesis. cDNA was synthesized in a 5'-RACE reaction using the SMART™ RACE cDNA Amplification Kit from Clontech. Subsequent target amplification of HC and LC sequences was performed by PCR using PhusionHotStart polymerase (Finnzymes) and the complete primer mix (UPM) included in the SMART™ RACE kit as forward primers. Reverse primers with the following sequences were used for HC (VH domain) amplification:
[0513] 5'-CTTGCCATTGAGCCAGTCCTGGTGCATGATGG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 17)
[0514] Reverse primers with the following sequences were used for TFPI22F66 and TFPI22F71LC (VL domai...
Embodiment 3
[0520] Example 3: Cloning and sequencing of mouse anti-TFPIKPI-3 / C-terminal specific mAbs 22F74, 41F41, 41F30, 22F132, and 22F79 and cloning and sequencing of mouse anti-TFPIKPI-1 mAbs 2F3, 2F22, 2F45, 1F91, and 2F35.
[0521] The murine heavy and light chain sequences of the anti-TFPI antibody were cloned and sequenced as follows.
[0522] Total RNA was extracted from hybridoma cells using the RNeasy-MiniKit from Qiagen and used as a template for cDNA synthesis. cDNA was synthesized in a 5'-RACE reaction using the SMART™ or SMARTer™ RACE cDNA amplification kit from Clontech. Subsequent target amplification of HC and LC sequences was performed by PCR using PhusionHotStart polymerase (Finnzymes) and the complete primer mix (UPM) included in the SMART™ / SMARTer™ RACE kit as forward primers. Reverse primers with the following sequences were used for HC (VH domain) amplification:
[0523] 5'-CCCTTGACCAGGCATCCCAG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 20)
[0524] Reverse primers with the following sequ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| polydispersity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polydispersity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com