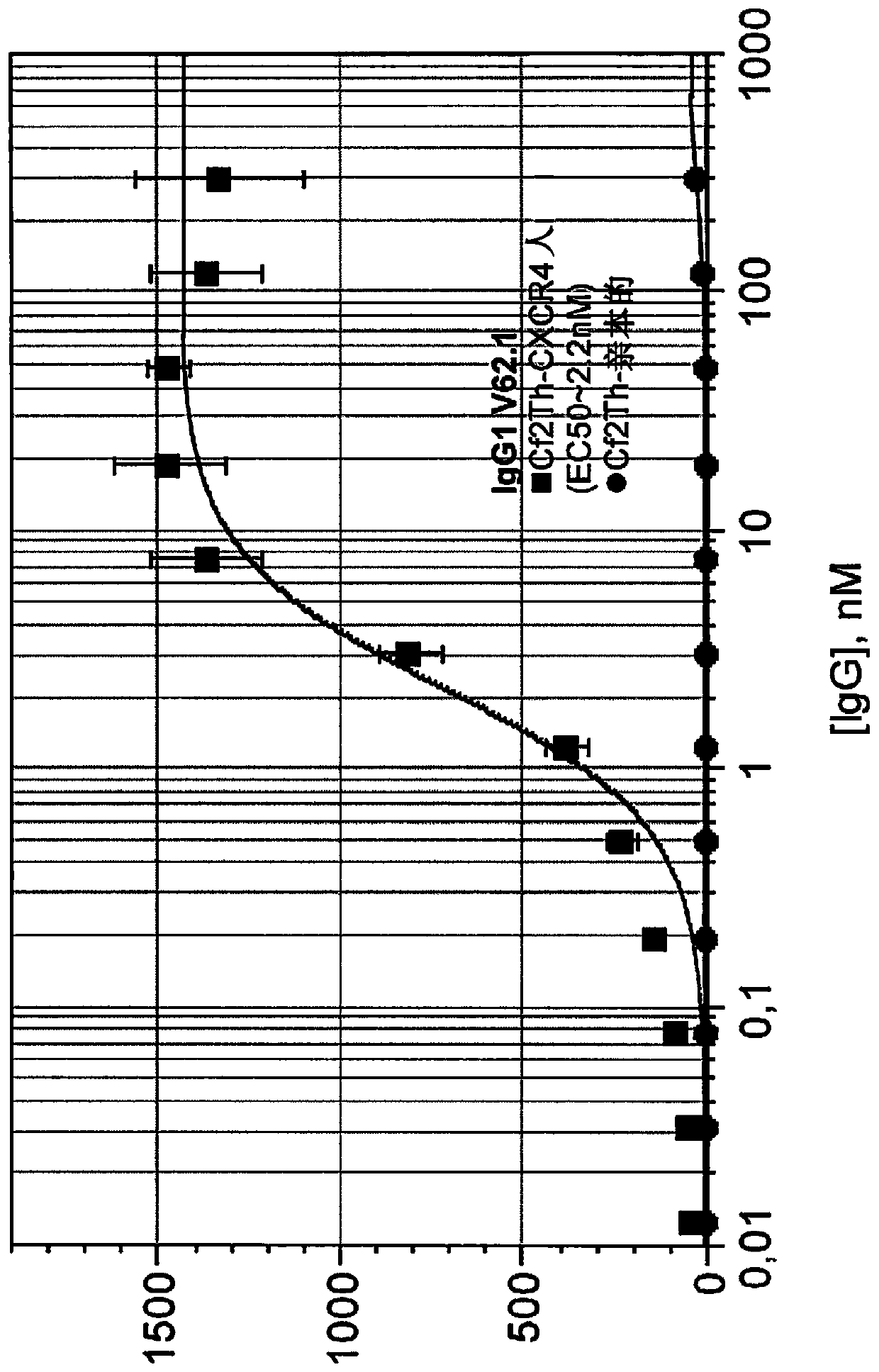
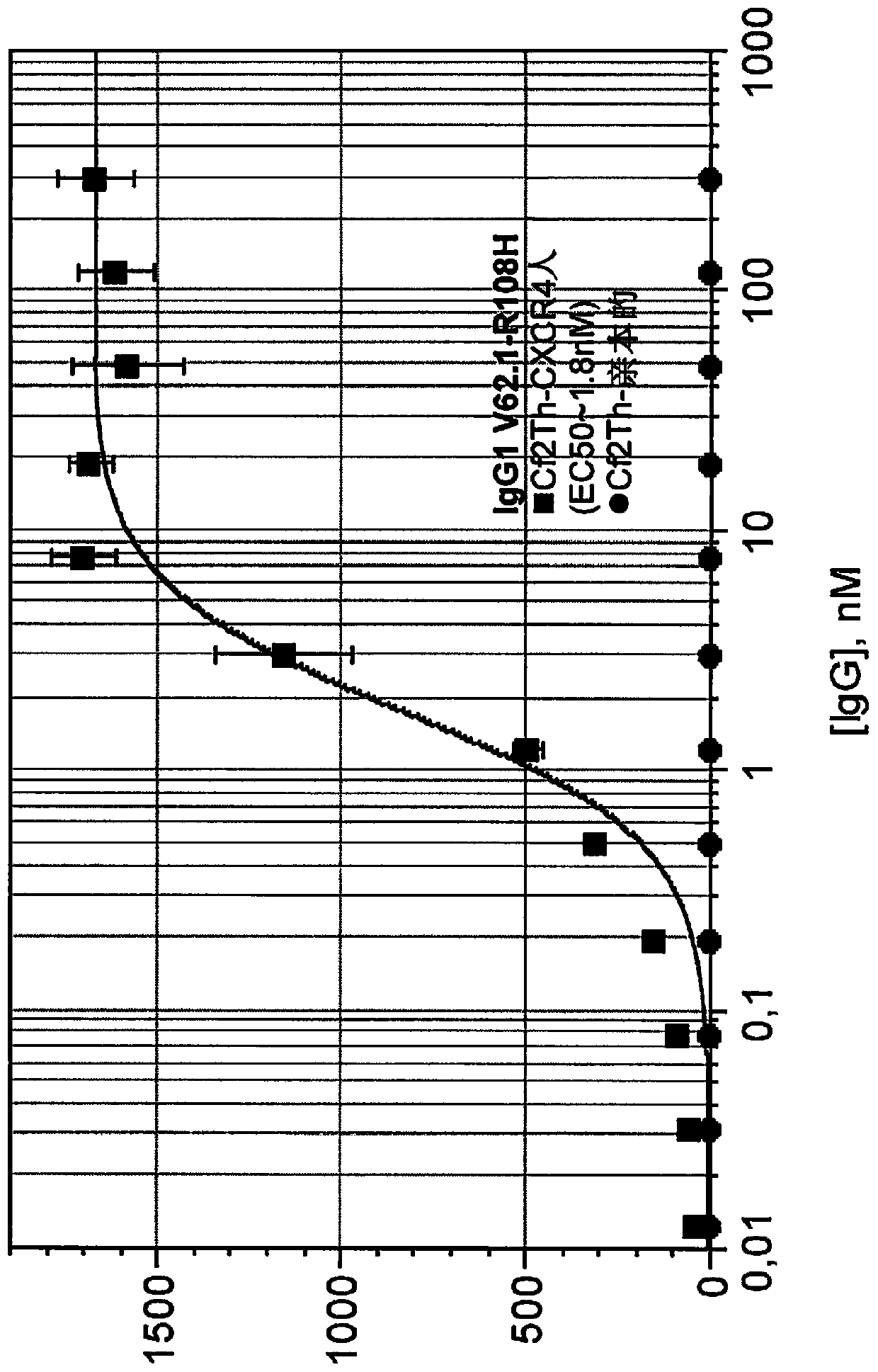
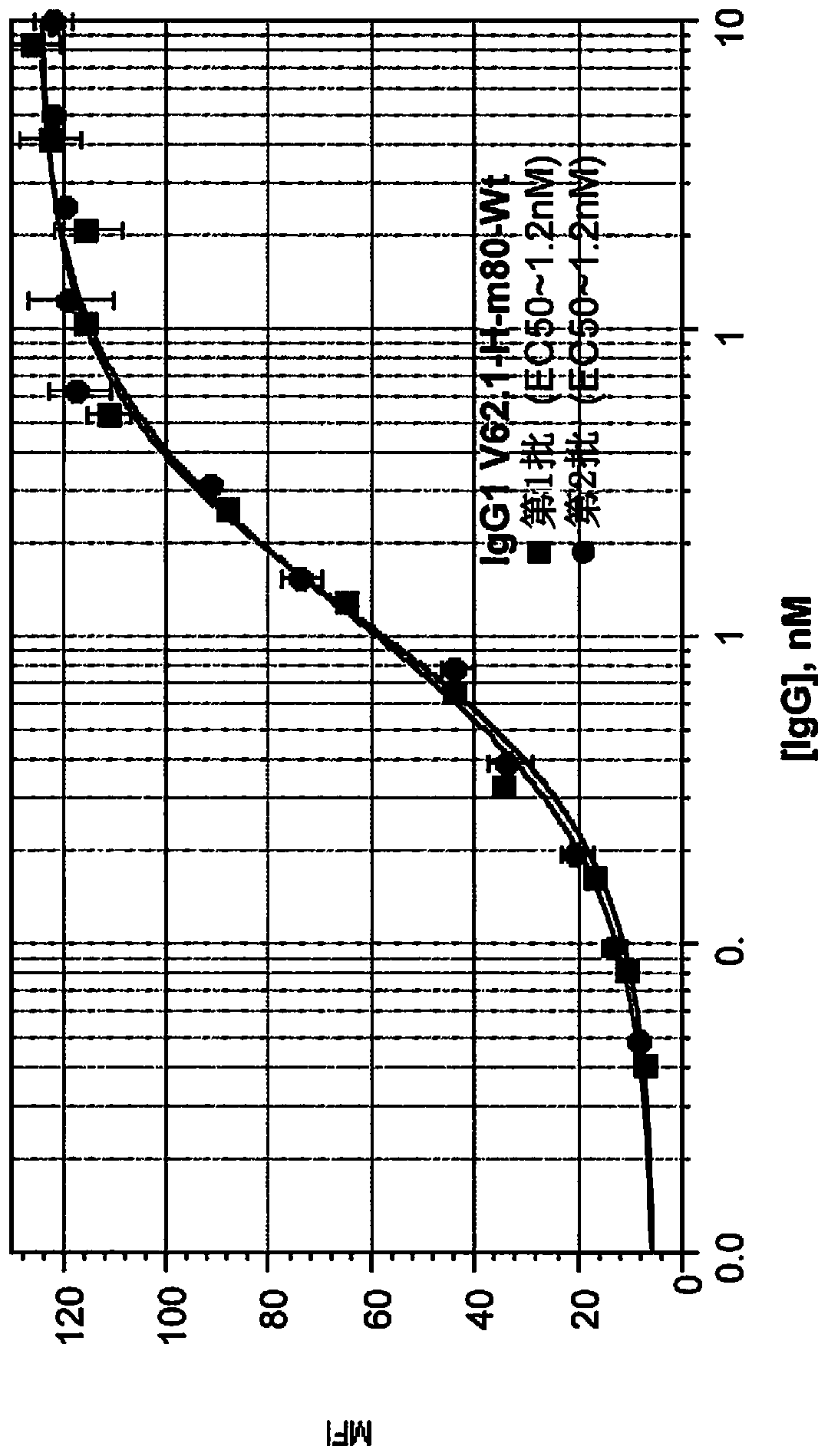
Anti-cxcr4 antibodies
An antibody and CDR2L technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, anti-tumor drugs, radioactive carriers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Example 1: Preparation of Fab phage library and screening of phage antibodies
[0088] The antibodies of the invention were originally derived from a Fab library of size 10^11 comprising a pSF1 phagemid carrying a Fab E. coli codon-optimized synthetic gene encoding a human Fab heavy chain with randomized CDRs and human Fab light chain. For the heavy chain the framework DP47 was used, for the light chain the framework DPK22 was used.
[0089] Procedures as described in Knappik et al. (2000) J.Mol.Biol.296:57-86; Lee et al. (2004) J.Mol.Biol.340:1073-93; Hoet et al. (2005) 23:344-8 were used and CDR randomization schemes to generate phage libraries.
[0090] More specifically, in the Fab library, heavy chain CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 and light chain CDR3 were randomized. For randomization of heavy chain CDR3, trinucleotide-based oligonucleotides were employed as described in Knappik et al., while for the other CDRs standard nucleotide mixtures were used to generate CDR oli...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2: Affinity maturation
[0098] Initial candidates were then subjected to affinity maturation as described above. Two affinity maturation libraries were generated by randomization by CDR2H or CDR3L, respectively. Each of these libraries was subjected to two rounds of high stringency selection. Selected Fabs are expressed individually and clones with improved binding properties are retained. The best clones were reconstituted into IgG characterized by the best CXCR4 binding affinity and selectivity and the best ability to prevent ligand-induced Ca-flux. As a final step, the most promising heavy and light chains were recombined and the resulting IgG recharacterized as previously described.
[0099] In addition, CDR3H is matured by introducing point mutations. The resulting mutated Fab fragments were characterized to identify optimal CXCR4 binders.
[0100] The following mature antibody candidates were further obtained:
[0101]
[0102]
[0103] *R10...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3: Synthesis of IgG Antibody
[0106] The CHO / pTT transient transfection system from the National Research Council Biotechnology Research Institute of Canada (NRC-BRI) was used according to the protocol provided by NRC-BRI. See International Patent Application Publication WO2009 / 137911 Al. More specifically, each IgG of interest was produced in CHO-3E7 cells co-transfected with pTT vectors expressing the light and heavy chains of that IgG, respectively, using polyethyleneimine (PEI) as the transfection reagent.
[0107]IgG containing cell culture medium was collected and IgG was purified on protein A plus agarose (Pierce) using standard methodology. Use sterile, endotoxin-free solutions for all purification procedures.
[0108] In the following examples, the Fab fragment of interest or the IgG antibody of interest is referred to as "test Fab", "test antibody" or "test IgG", as appropriate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com