CT image data automatic classification method and device based on CNN and GAN
A CT image, automatic classification technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problem that radiologists are difficult to distinguish sub-centimeter pulmonary nodules, etc., to achieve strong market application prospects and the effect of promoting daily work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
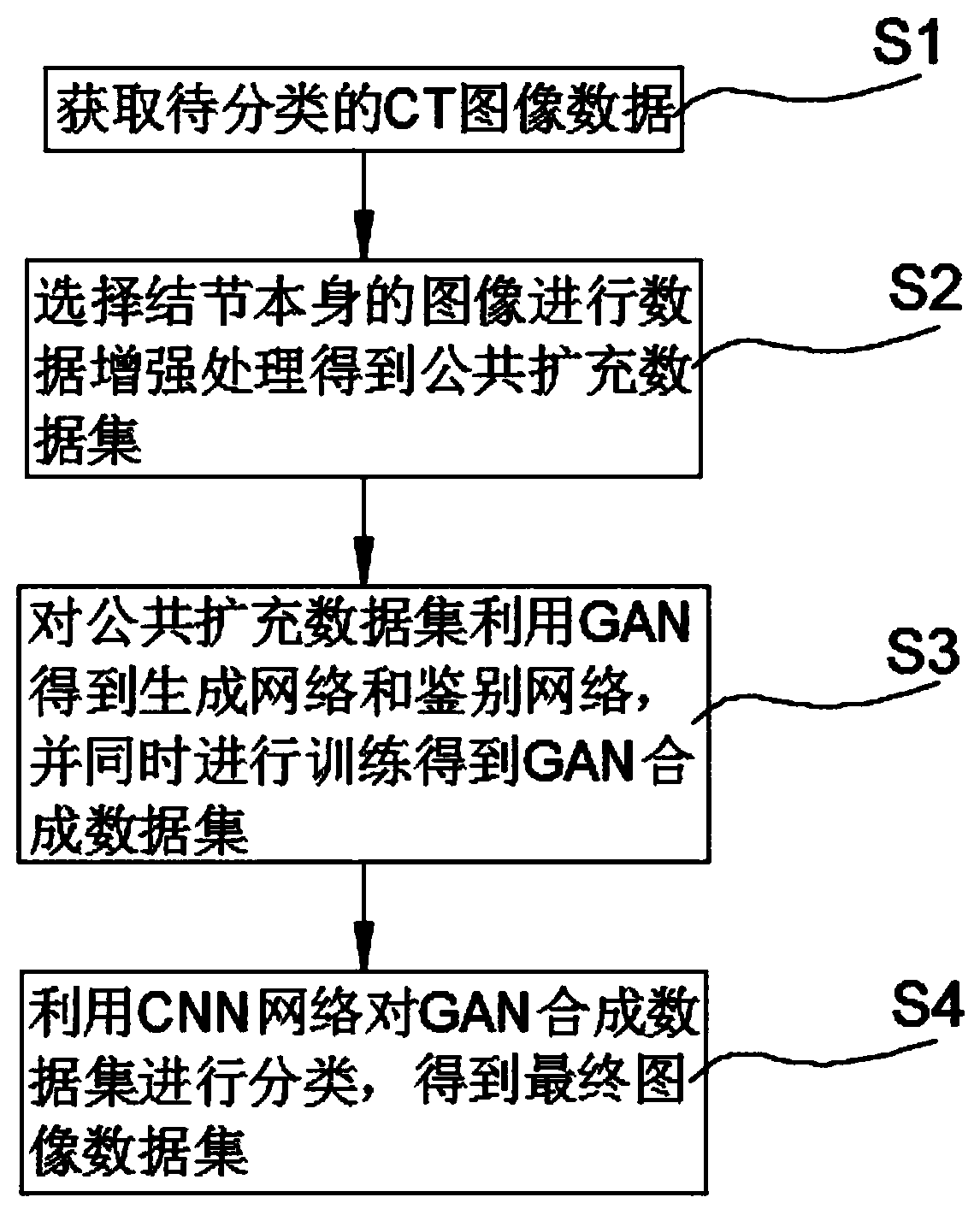
[0034] This embodiment discloses as figure 1 Shown a kind of CT image data automatic classification method based on CNN and GAN, described method comprises the following steps:
[0035] S1 acquires CT image data to be classified;
[0036] S2 selects the image of the nodule itself to perform data enhancement processing to obtain a public extended data set;
[0037] S3 uses GAN to obtain the generation network and discrimination network for the public extended data set, and simultaneously trains to obtain the GAN synthetic data set;
[0038] S4 uses the CNN network to classify the GAN synthetic data set to obtain the final image data set.
[0039] In step S2, only the image of the nodule itself is used, and the nodule area in each CT scan is calculated according to the annotation of the radiologist, only the three CTs with the largest nodule area are selected, and the nodule-centered image is cut. 64×64 pixel image and named as the original dataset.
[0040] The specific dat...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This embodiment discloses a data processing procedure, in which only the image of the nodule itself is used. The nodule area in each CT scan was calculated based on the radiologist's annotations, and only the three CTs with the largest nodule area were selected. A 64 × 64 pixel image centered on the nodule was cut and named as the original dataset.
[0052] Sufficient data is important because even small CNNs contain thousands of parameters and are prone to overfitting. To avoid this problem, a common strategy is data augmentation. Common augmentation techniques include translation, rotation, scaling and flipping. The present invention first randomly translates the image pixel by pixel. Then rotate with the nodule as the center. Afterwards, the image is rescaled with a random ratio of 80% to 120%. Finally, the nodule patch is flipped upside down and sideways. The image generated by the above operation is 64 × 64 pixels, which is consistent with the original datase...
Embodiment 3
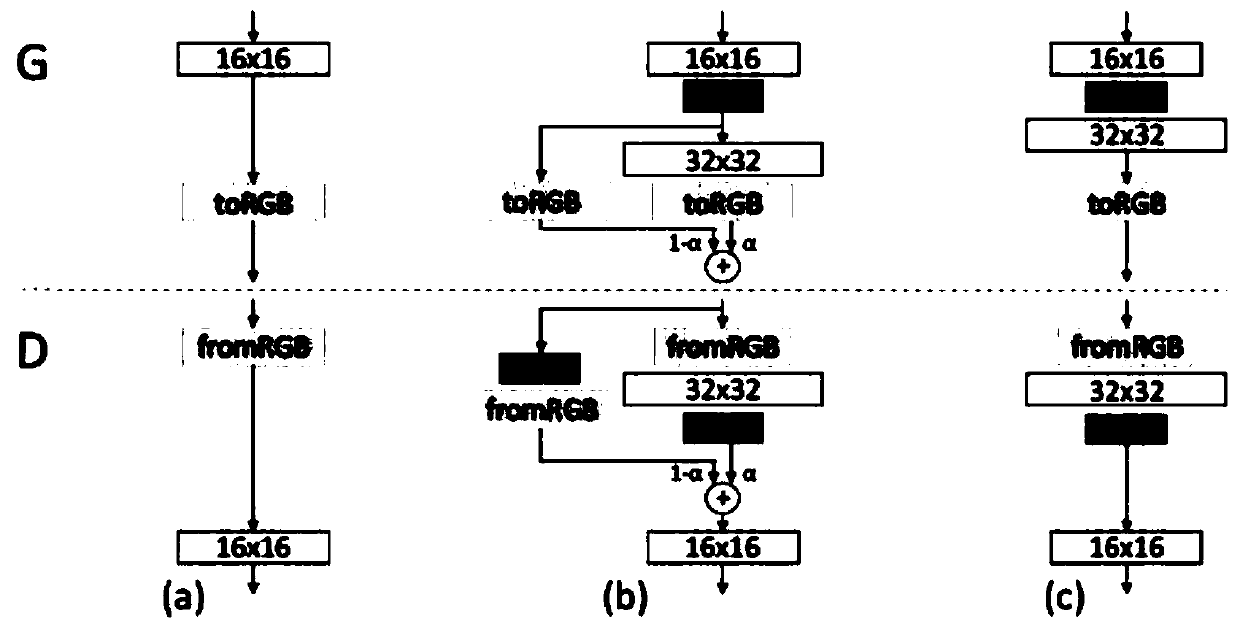
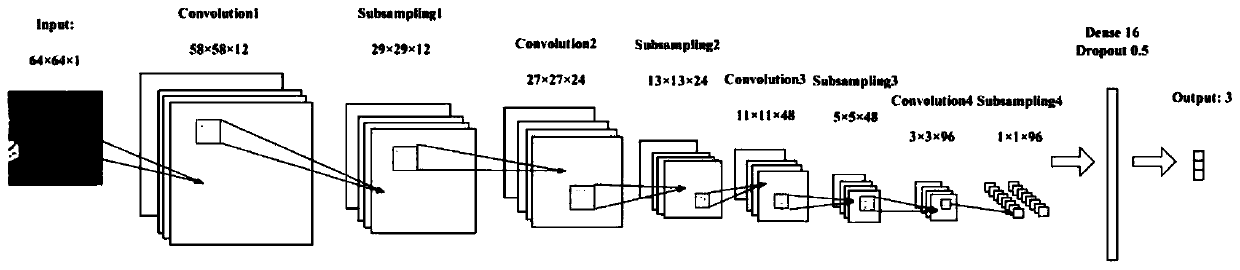
[0059] This embodiment discloses a GAN structure, a gradually growing wGAN structure for generating images of lung adenocarcinoma. The generator consists of nine convolutional layers. First, 512-dimensional random noise is input into a fully connected layer, and then a 4×4 pixel feature map is generated by the first convolutional layer. Then, the feature maps are passed through four modules consisting of two convolutional layers. The detailed structure of the blocks is shown in Table 4. These modules continuously double the height and width of the feature map, and finally generate a 64 × 64 pixel image.
[0060] The discriminator also includes nine convolutional layers. It mirrors the generator, starting with a 64×64 pixel image, passing through four blocks consisting of two convolutional layers, and ending with a 4×4 pixel feature map. Finally, a mini-batch discriminative technique is added to the convolutional layer to make the training more stable. Finally, the feature ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com