Biotelemetry device that can be ingested and implanted in vivo
A technology of biological telemetry and biological medium, which is applied in the direction of radio detectors, endoscopes, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc. in the body, and can solve the problems of large volume, energy consumption, and high price of pH detection sensors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The various embodiments and aspects described below can be combined or simplified in many ways. Only certain embodiments of the examples have been described in detail to ensure clarity of description, but these examples are not intended to limit the general scope of the principles presented from this specification taken as a whole.
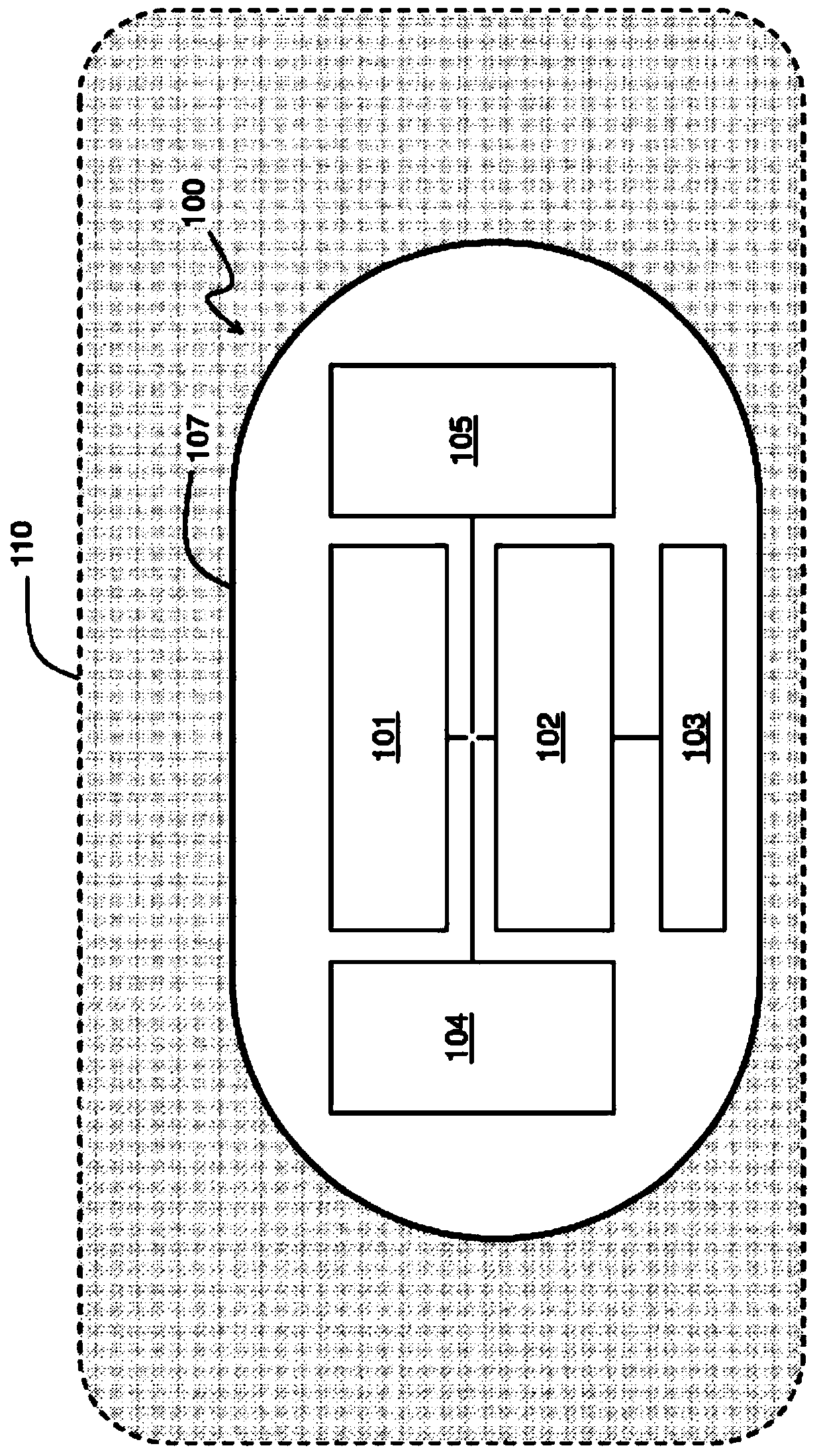
[0041] figure 1 An example of a biotelemetry device 100 in the form of an ingestible capsule is schematically shown.
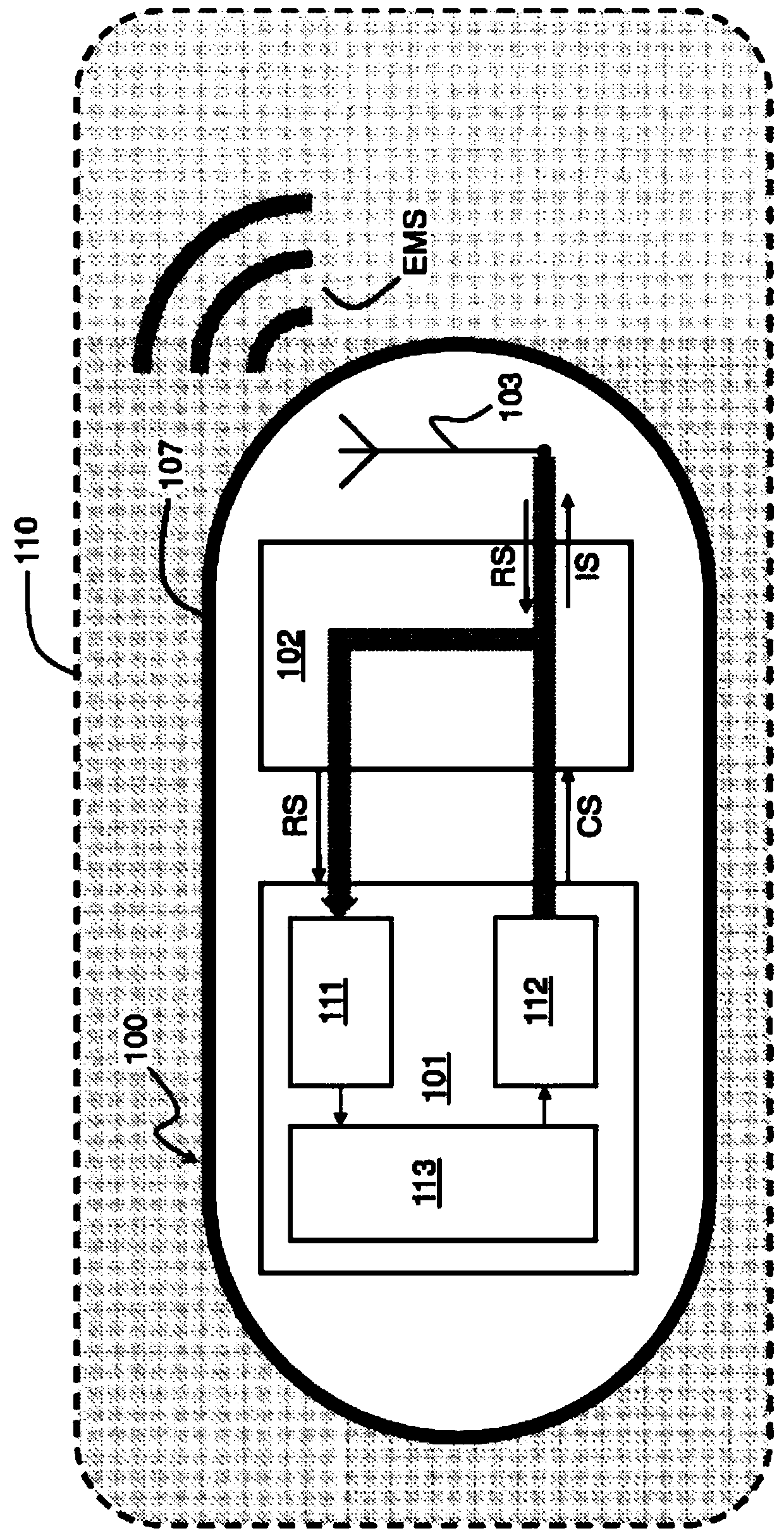
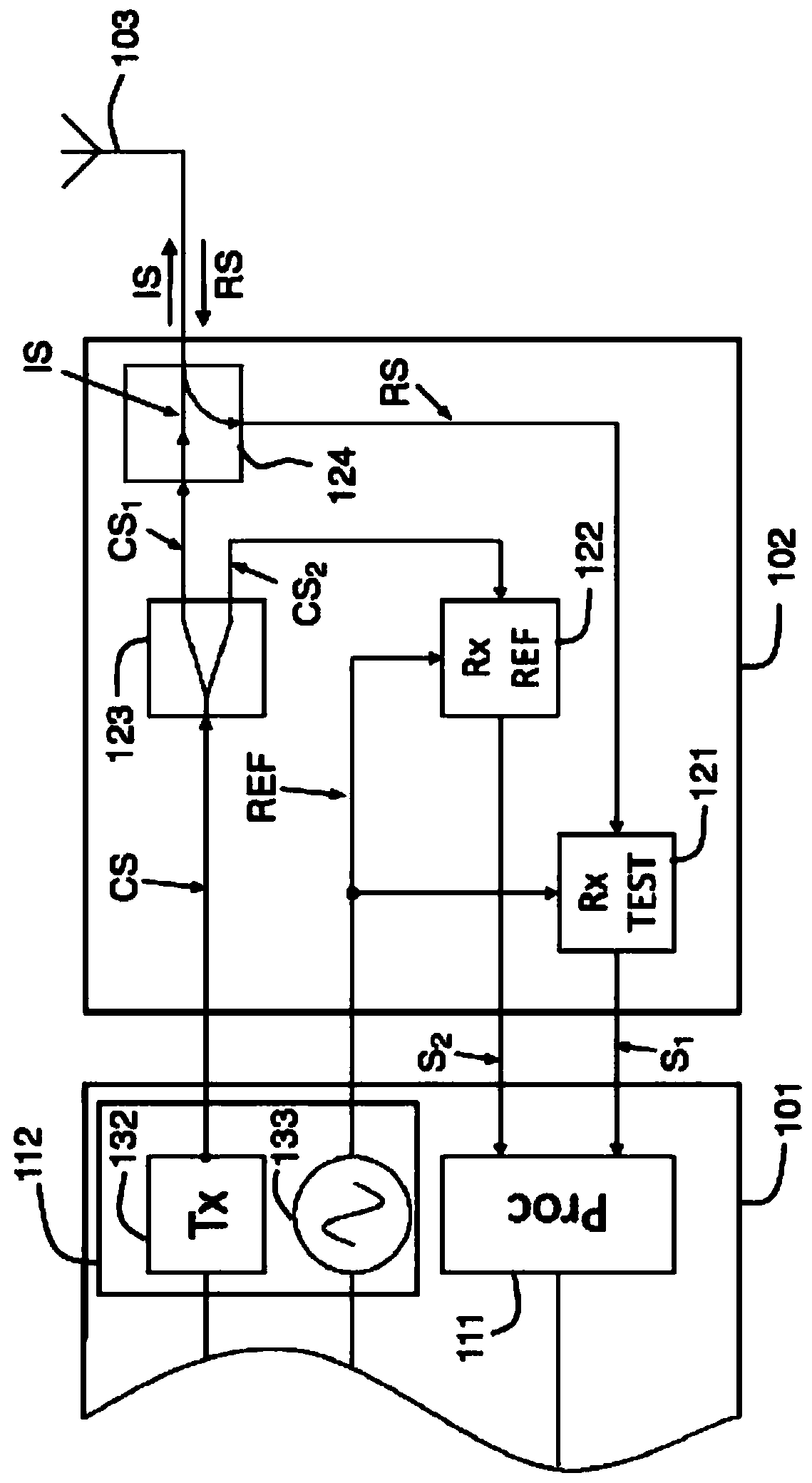
[0042] The biological telemetry device 100 includes a microcontroller 101 , a radio frequency circuit 102 , a wireless communication unit 103 and a power supply 104 . Optionally, biotelemetry device 100 may include additional circuitry 105, such as biomedical application circuitry or sensors.
[0043] In one or more embodiments, the biotelemetry device 100 may be implemented by one or more integrated circuits, each integrated circuit integrating one or more components of the biotelemetry device 100 .
[0044] In one or m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com