Pd1-specific chimeric antigen receptor as immunotherapy
A chimeric antigen receptor and specific technology, applied in antibody mimics/scaffolds, immunoglobulin superfamily, blood/immune system cells, etc., can solve problems such as limiting CART cell response and efficacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Example 1: Adoptive transfer of murine T cells expressing chimeric PD1-Dap10 receptors as immunotherapy for lymphoma.
[0078] summary
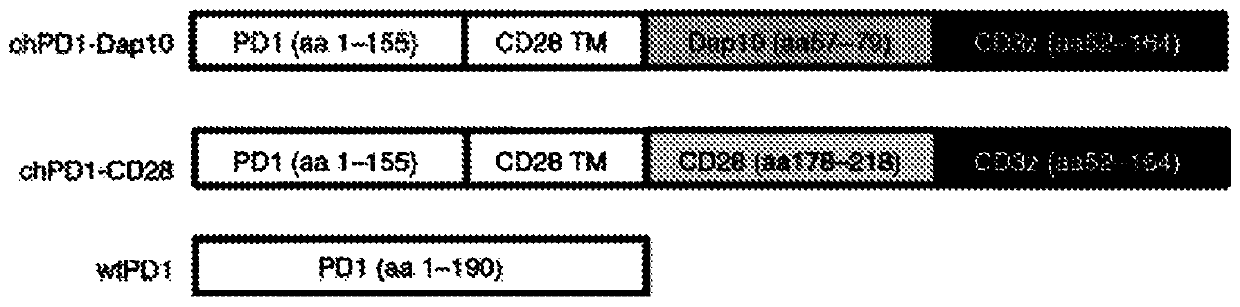
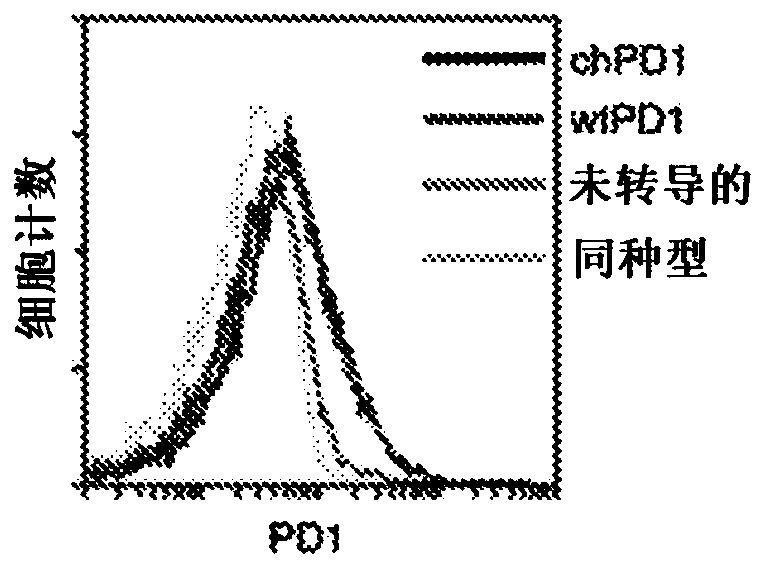
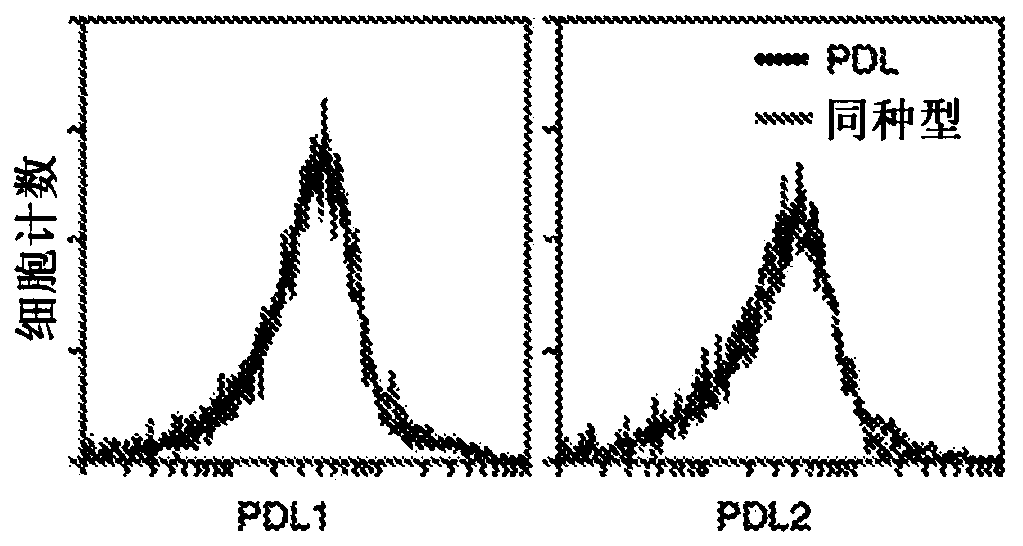
[0079] Adoptive transfer of T cells is a promising cancer therapy, and expression of chimeric antigen receptors enhances tumor recognition and T cell effector functions. Provided herein is a murine chimeric PD1 receptor (chPD1) comprising a PD1 extracellular domain fused to the cytoplasmic domain of CD3delta. In addition, chimeric antigen receptor therapies use various co-stimulatory domains to enhance efficacy. Therefore, inclusion of the Dap10 or CD28 co-stimulatory domain in the chPD1 receptor was compared to determine which domain induces the best antitumor immunity in a mouse lymphoma model. chPD1 T cells secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines and lyse RMA lymphoma cells. Adoptive transfer of chPD1T cells significantly reduced established tumors and resulted in tumor-free survival in lymphoma mice. When comparing chPD1 receptors c...
Embodiment 2
[0121] Example 2: Human T cells expressing chimeric PD1-Dap10 receptors as immunotherapy.
[0122] Adoptive transfer of tumor-reactive T cells is a promising antitumor therapy against many cancers. To enhance tumor recognition by T cells, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), which consist of a signaling domain fused to a receptor that recognizes tumor antigens, can be produced and expressed in T cells. As shown in Example 1, since ligands for the PD1 receptor are expressed in many cancer types, PD1 is a target for novel chimeric antigen receptors. In this study, a human chimeric PD1 receptor (chPD1) consisting of the PD1 receptor extracellular domain and the CD3δ activation domain was developed. As described in Example 1, the Dap10 co-stimulatory domain is also included in the chPD1 receptor. The nucleic acid sequence of CAR is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3. To determine whether this novel CAR could target multiple tumors, the ant...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com