Robot map construction and positioning method, robot
A map construction and robot technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of limited application scope of robots, increased cost and labor effort, and difficulty in accurate identification of sensors, achieving high-precision modular stitching composition, improved positioning accuracy, and suitable wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
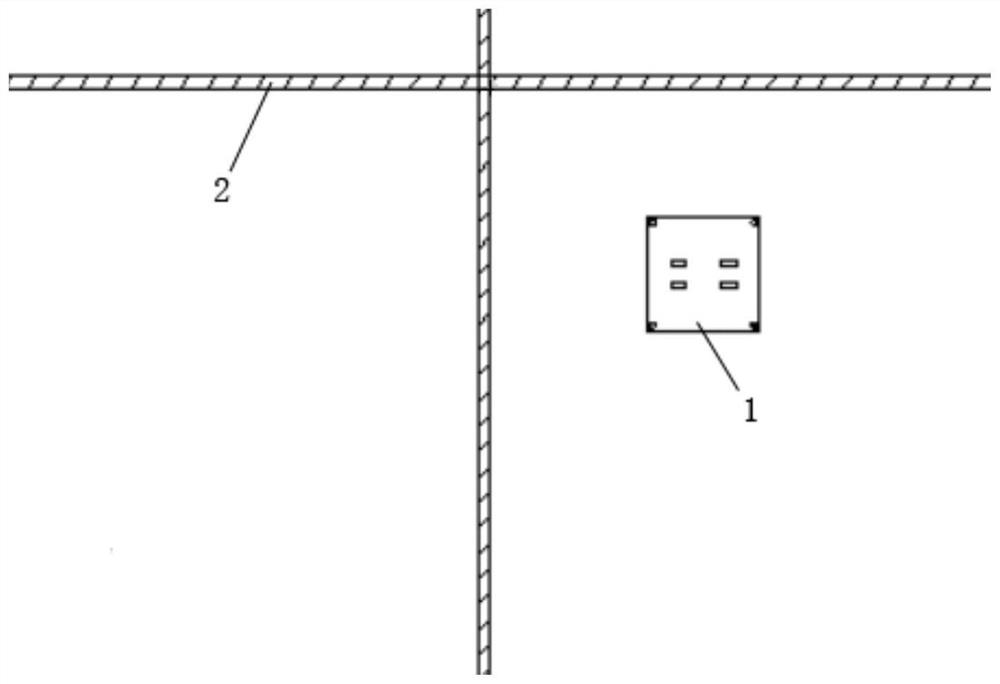
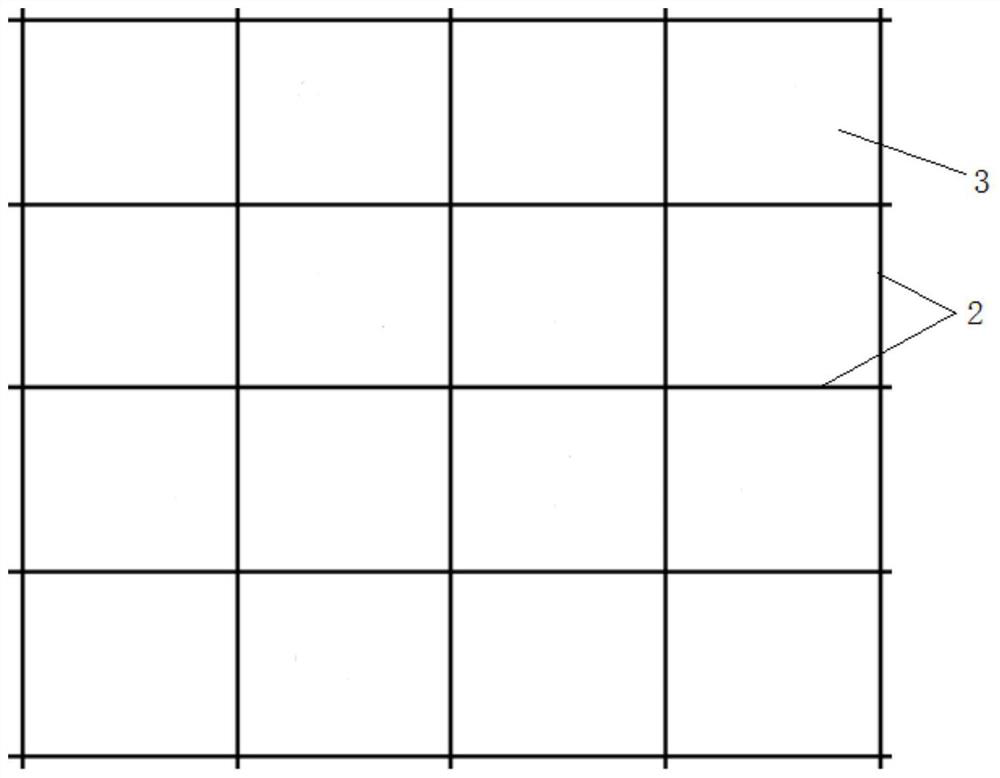
[0055] This embodiment discloses a robot map construction method, wherein, such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the robot 1 can be placed and moved on the working surface, the working surface has a plurality of dividing lines 2, and these dividing lines divide the working surface into a plurality of square sub-blocks 3, the working surface includes but not limited to walls, floors and curtain walls, Corresponding dividing lines include, but are not limited to, gaps between boards, bricks or tiles, gaps between glass, and sealants.
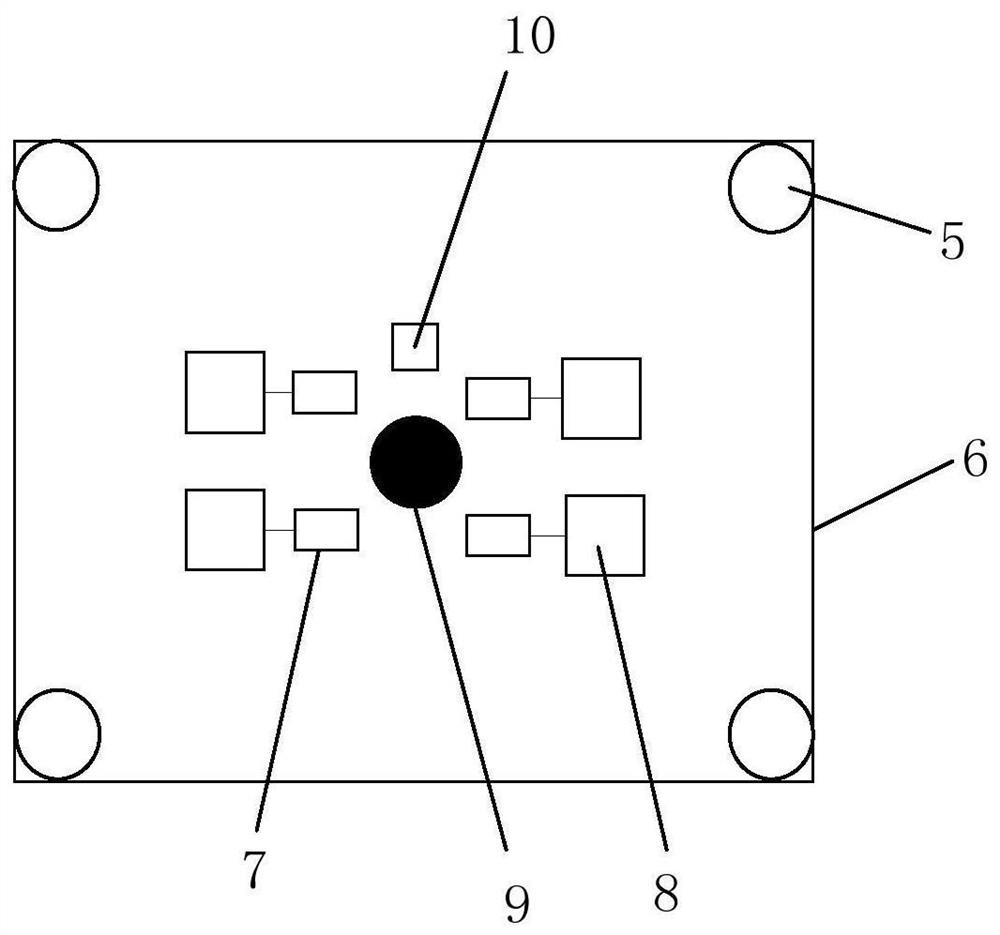
[0056] The types of robots include, but are not limited to, AVG logistics smart cars, household robots and smart service robots. The robot of the present embodiment comprises square plate body 6, inductor 5, attitude sensor 10, moving mechanism, driving mechanism and controller 9, wherein, inductor, attitude sensor, moving mechanism, driving mechanism and controller are all installed in the body superior. The sensor is located on the edge of...
Embodiment 2
[0071] This embodiment discloses a positioning method for a robot, wherein, as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the robot 1 can be placed and moved on the working surface, the working surface has a plurality of dividing lines 2, and these dividing lines divide the working surface into a plurality of square sub-blocks 3, the working surface includes but not limited to walls, floors and curtain walls, Corresponding dividing lines include, but are not limited to, gaps between boards, bricks or tiles, gaps between glass, and sealants.
[0072] The types of robots include, but are not limited to, AVG logistics smart cars, household robots and smart service robots. The robot of the present embodiment comprises square plate body 6, inductor 5, attitude sensor 10, moving mechanism, driving mechanism and controller 9, wherein, inductor, attitude sensor, moving mechanism, driving mechanism and controller are all installed in the body superior. The sensor is located on the edge of the...
Embodiment 3
[0084] This embodiment discloses a positioning method for a robot, wherein, as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the robot 1 can be placed and moved on the working surface, the working surface has a plurality of dividing lines 2, and these dividing lines divide the working surface into a plurality of square sub-blocks 3, the working surface includes but not limited to walls, floors and curtain walls, Corresponding dividing lines include, but are not limited to, gaps between boards, bricks or tiles, gaps between glass, and sealants.
[0085] The types of robots include, but are not limited to, AVG logistics smart cars, household robots and smart service robots. The robot of the present embodiment comprises square plate body 6, inductor 5, attitude sensor 10, moving mechanism, driving mechanism and controller 9, wherein, inductor, attitude sensor, moving mechanism, driving mechanism and controller are all installed in the body superior. The sensor is located on the edge of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com