Poultry offal taking out device
A technology for taking out devices and viscera, which is applied in the field of poultry viscera taking out devices, which can solve the problems of unstable clamping, decreased success rate of clamping, uneven retention, etc., to increase the joint area of clamping, improve the success rate of clamping, The effect of reducing frictional damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
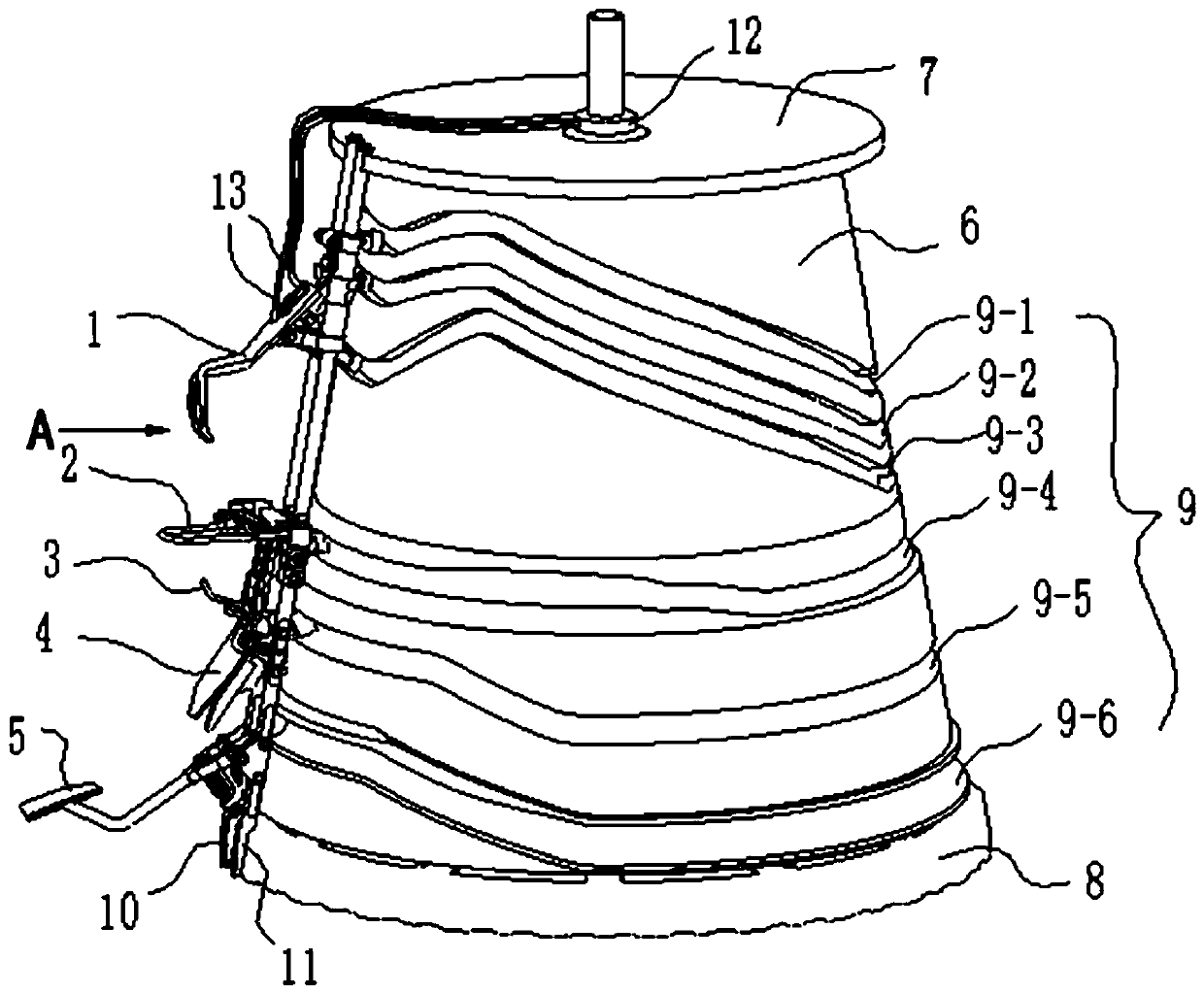
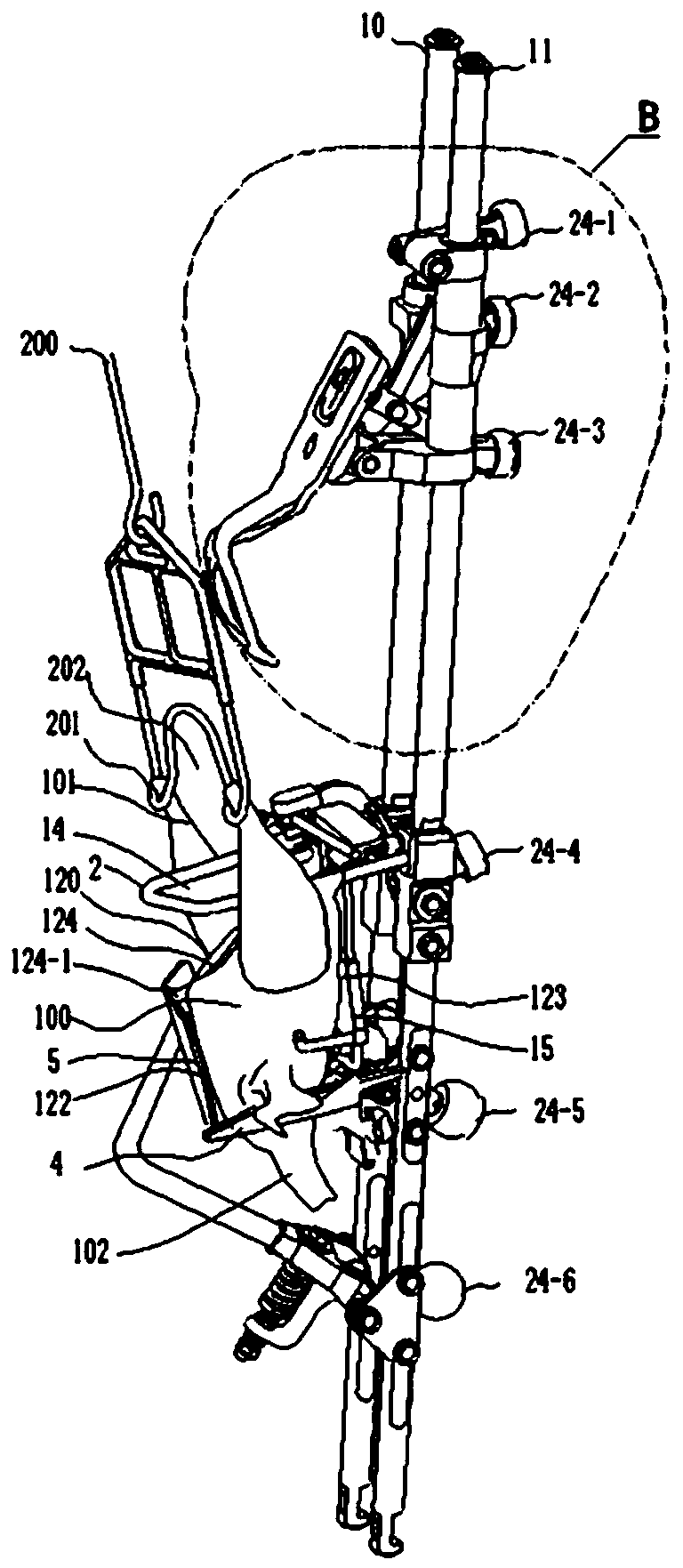
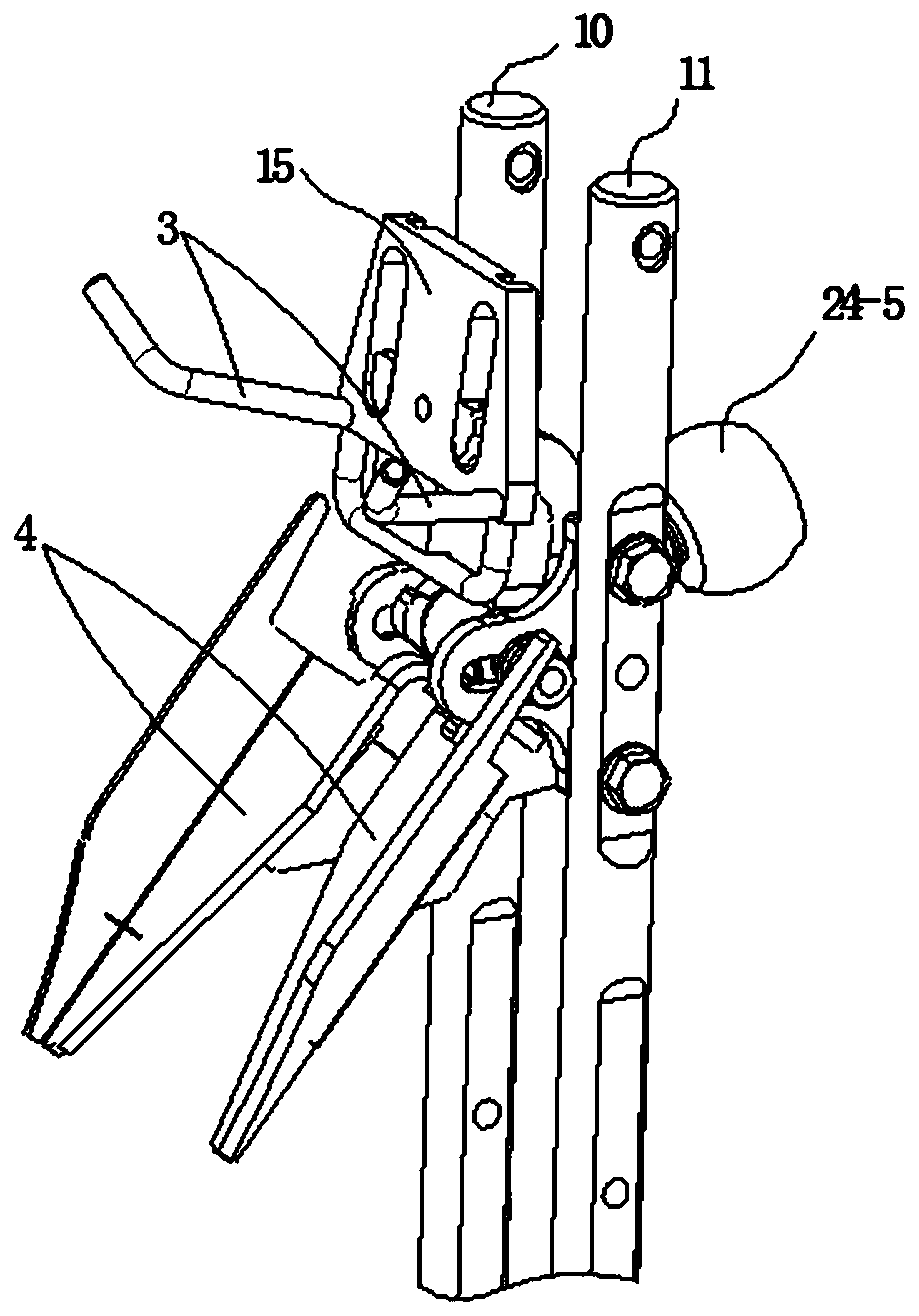
[0081] Studies have shown that chicken breast bones are relatively smooth, have cartilage tissue, have certain rigidity and strength, and can withstand moderate impacts. The chicken legs are on the top and the neck is on the bottom. The two lobes of the chicken liver are unfolded along the sternum of the cavity. The structure of the viscera harvesting device is reasonable, and the path from the inner side of the chicken breast to the junction of the chest cavity and neck is designed appropriately, which will reduce damage to the viscera, especially the liver.
[0082] Studies have shown that when the evisceration device moves downward, filling moderate temperature water between the liver lobe and the sternum will reduce the friction strength between the evisceration device and the liver, reduce the downward movement of the liver with the evisceration device, and reduce the clipping force. Squeeze and crush the edge of the liver lobe with the holding device. During the eviscer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com