Language sequence model decoding method
A decoding method and sequence technology, applied in computing models, natural language data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to obtain global optimal solutions, reduce the number of generated vertices and the amount of calculation, speed up the solution process, The effect of reducing computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
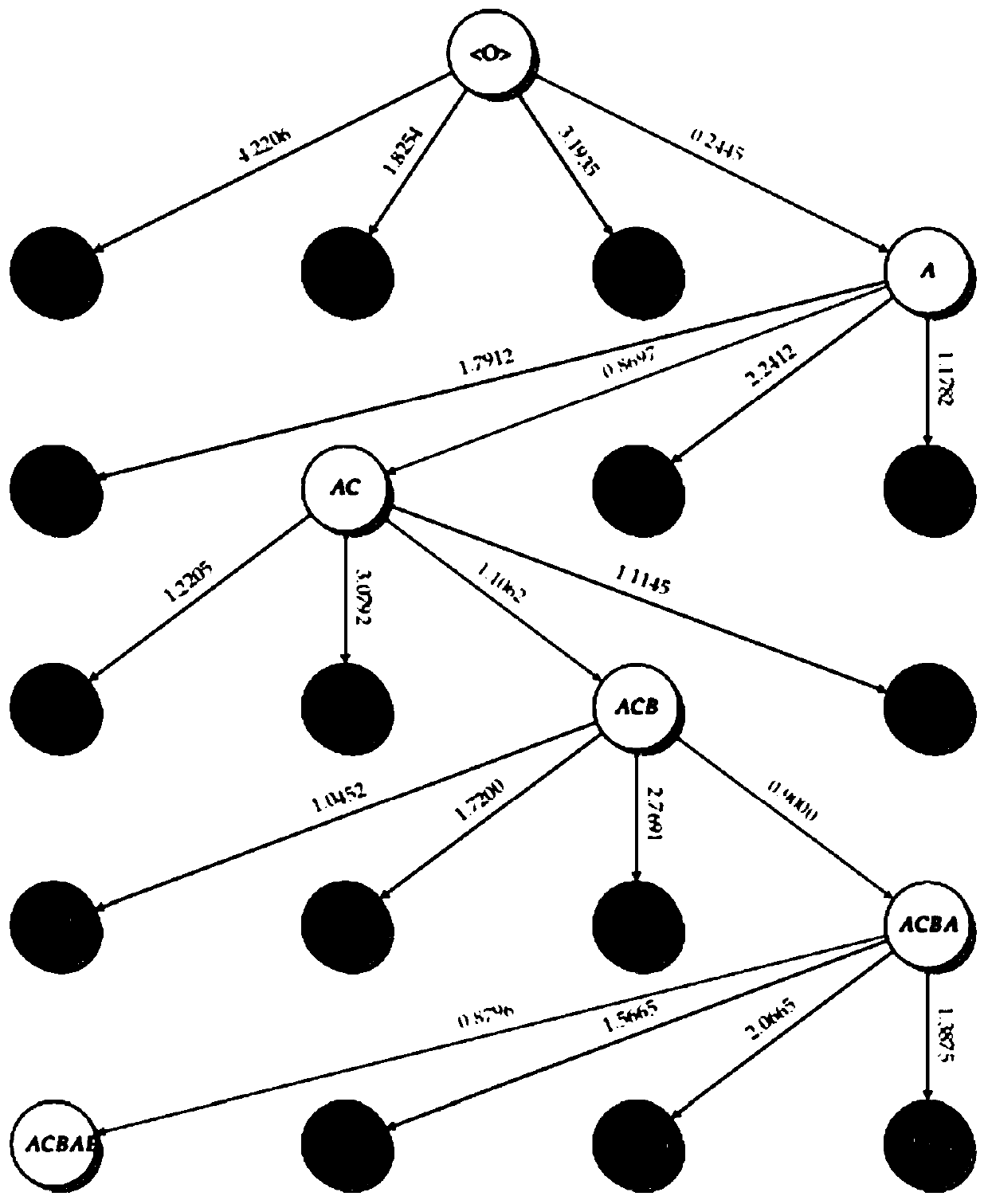
[0081] Such as figure 1 Shown, a language sequence model decoding method comprises the following steps:
[0082] S1. Initialization: Based on the sequence model, use the greedy algorithm to generate the initial language sequence, and construct the directed graph to obtain the current shortest path length from the starting point to the end point and the shortest path length from the current vertex to the starting point in the initial language sequence;
[0083] S2. Extension: Input the current vertex information in the sequence model to generate a language sequence, and filter out temporary vertices according to the conditional probability of each word element in the language sequence;
[0084] S3, clipping: according to the existence of temporary vertices, filter to obtain ordinary vertices;
[0085] S4. Selection: Select a new current vertex from common vertices. If the word element corresponding to the new current vertex is the end word element, the language sequence corres...
Embodiment 2
[0145] In order to further verify the effectiveness of the present invention, this embodiment uses the language sequence model that has been trained, respectively uses the decoding algorithm based on the greedy algorithm to decode and compares the result sequence obtained by decoding based on the Dijkstra algorithm proposed by the present invention, as shown in Table 12- The comparison results shown in Table 14:
[0146] Table 12
[0147]
[0148]
[0149] Table 13
[0150]
[0151]
[0152] Table 14
[0153]
[0154] From the comparison results of Table 12 to Table 14, it can be seen that the decoding based on the greedy algorithm can only obtain a sequence of local optimal solutions, while the overall probability value of the sequence obtained by decoding based on the idea of Dijkstra algorithm in the present invention is obtained based on the decoding of the greedy algorithm Several times or even ten times of the sequence probabil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com