Compositions and methods for inhibiting T cell exhaustion
A composition and cell technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, for targeting specific cell fusions, drug combinations, etc., to solve problems such as CART cell exhaustion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0222] Gene expression analysis of T cell exhaustion
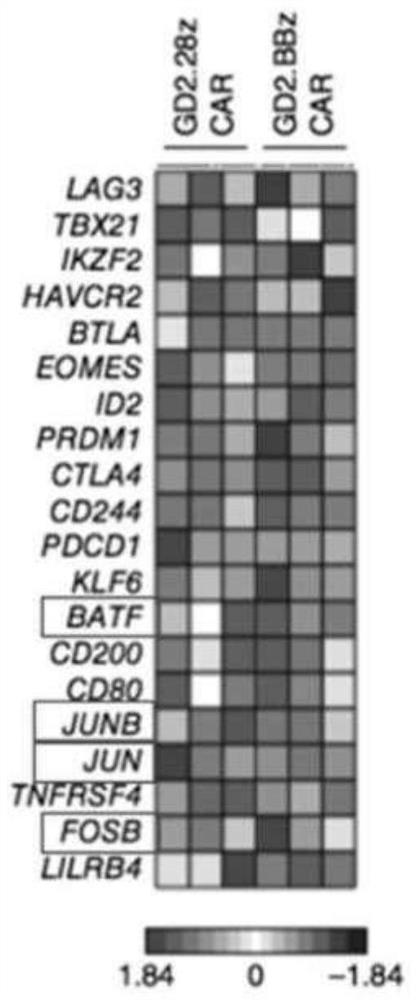
[0223] Antigen-independent complementary signaling by chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) promotes differentiation and exhaustion of T cells, limiting their potency. For example, GD2-specific CARs have been described to self-aggregate in the absence of antigen, leading to activation of chronic downstream T-cell activation signaling cascades. While GD2-CARs incorporating a CD28 costimulatory domain rapidly developed hallmark features of T cell exhaustion, GD2-CARs incorporating a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, despite similar aggregation and signaling, showed less There was less evidence of T cell exhaustion and greater retention of functionality. Among GD2-28z-expressing T cells, the most prominent features of T-cell exhaustion include increased surface expression of inhibitory receptors (e.g., PD1, TIM3, LAG3, CD39), decreased expression of memory markers (e.g., CD62L and CCR7), As well as decreased production of cytokines (...
Embodiment 2
[0226] Construction of CAR T cells forcibly expressing c-Jun and c-Fos
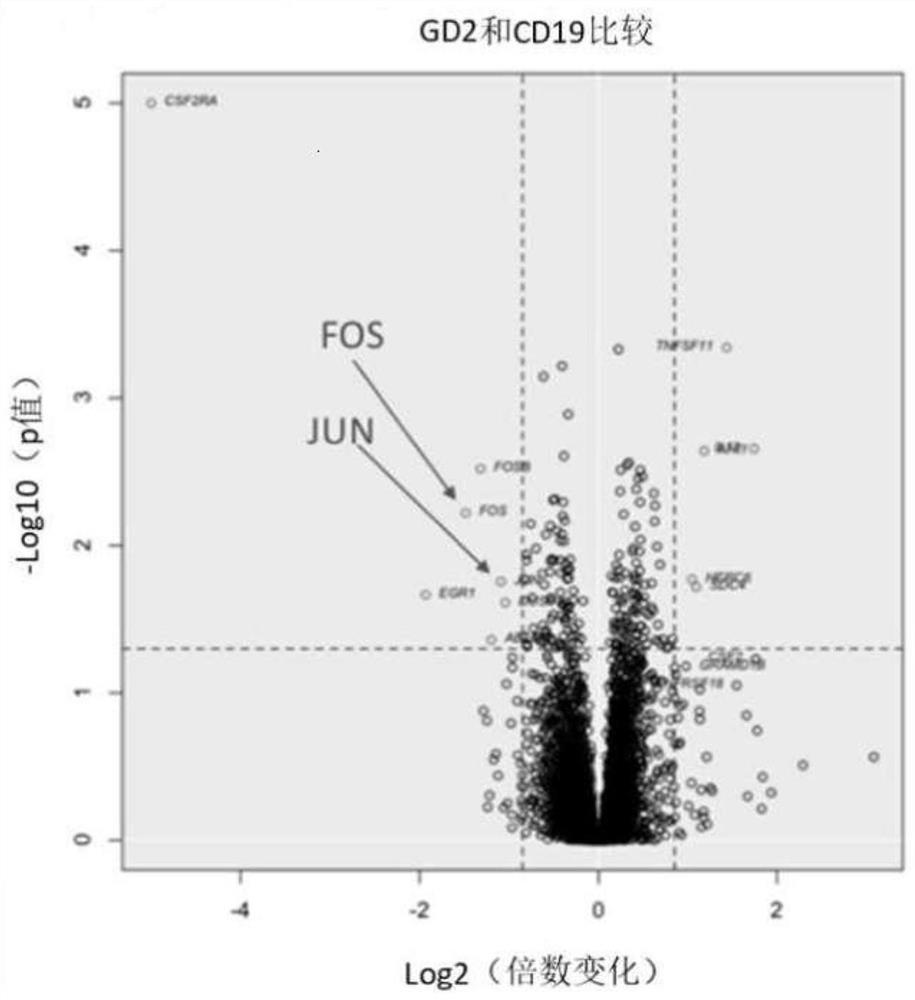
[0227] To determine whether replacement of AP-1 could alleviate exhaustion symptoms in GD2-28Z CAR T cells, lentiviral expression constructs that forced the expression of c-Jun and c-Fos under constitutive promoters were constructed (see Figure 2a). This construct also encodes a truncated nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR (tNGFR)) expression cassette as a surface marker for T cell transduction. Activated primary human T cells were subsequently transduced with CD19, GD2-BBZ, or high-affinity (HA) GD2-28Z CARs with (AP-1) or without (wo) AP-1 expression vectors.
Embodiment 3
[0229] Expression of c-Jun and c-Fos in CAR T cells
[0230] On day 8 of T cell culture, AP-1-transduced CD4 or CD8 CAR T cells were sorted using NGFR. In CD4 (see Figure 2b) and CD8 (see Figure 2c) CAR T cells, constitutive expression of AP-1 decreased the frequency of exhaustion-associated inhibitory receptors PD1, TIM3, LAG3, and CD39 and elevated memory markers CD62L frequency. CAR T cells were co-cultured with tumor cells expressing CD19 and GD2 antigens with (AP-1) or without (wo) AP-1 cotransduction to assess the function of AP-1-transduced CAR T cells Variety. In most cases, AP-1-transduced CAR T cells released more IL2 (see Figure 2d) and IFNg (see Figure 2e) than CAR T cells without AP-1 transduction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com