TCAM allocation method based on graph division
An allocation method and graph partitioning technology, applied in the computer field, can solve the problems of no global view, lack of scheduling strategy, and affecting compiler efficiency of TCAM allocation results, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below through specific embodiments in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
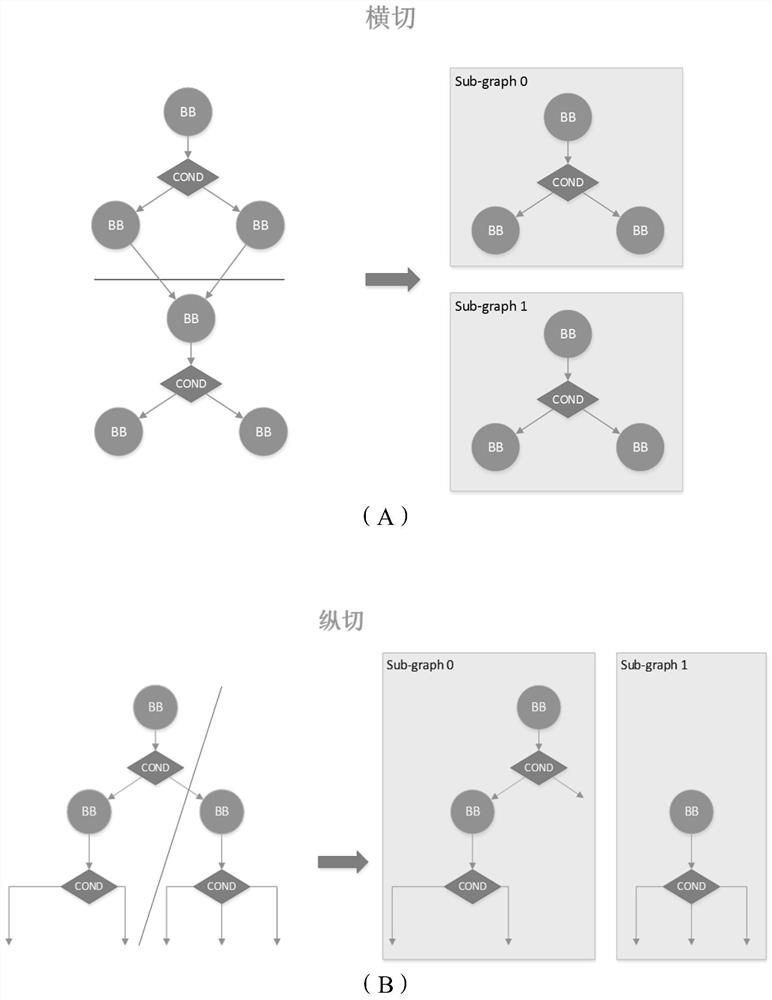
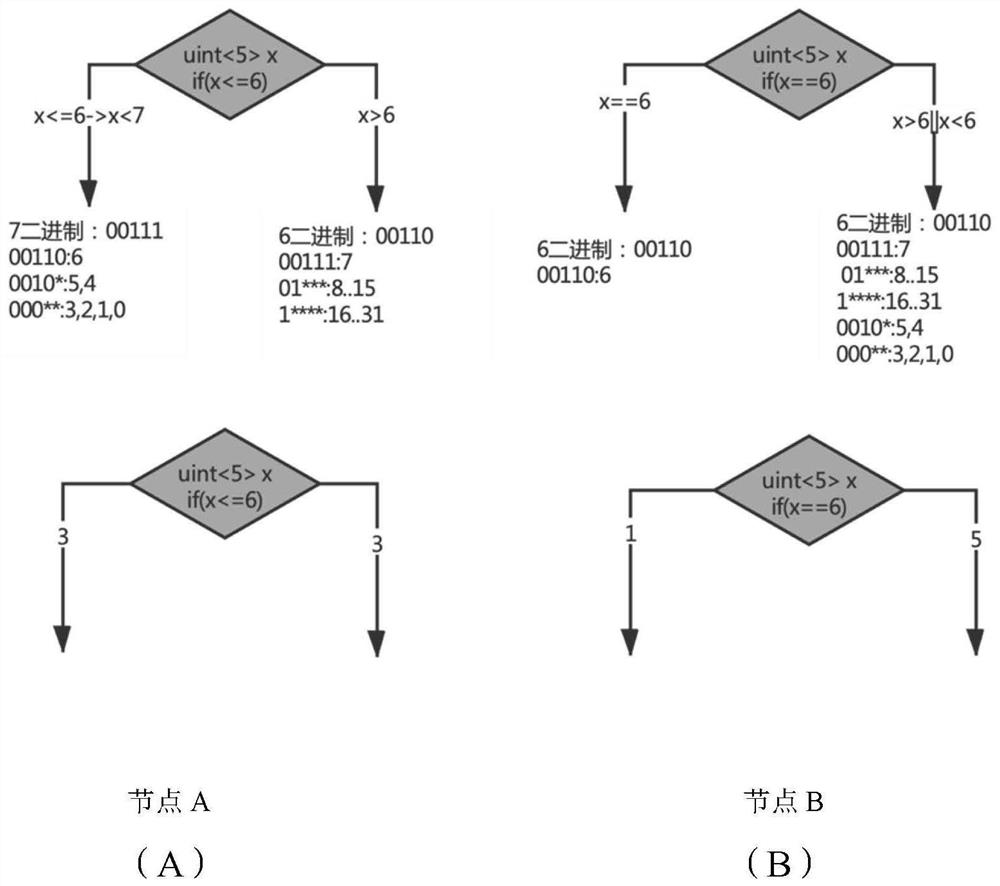
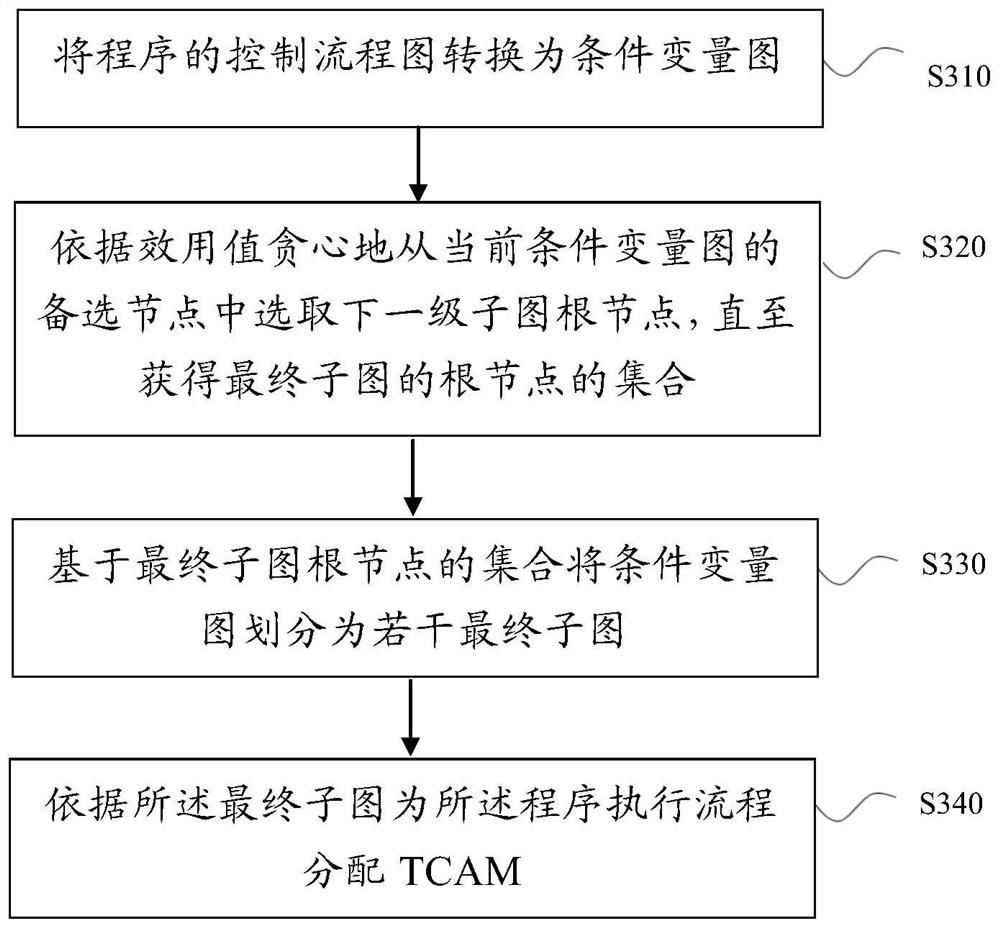
[0030] In the chip architecture of TCAM, it is usually possible to quickly match the program execution process based on the characteristics of TCAM, abstract the program execution process into a control flow chart (CFG), and solve the allocation of hardware resources by mapping the resources on the CFG to the TCAM. However, due to limited TCAM resources, it is often impossible to deploy the resources of the entire CFG on the same TCAM at one time. Therefore, it is necessary to divide the CFG into multiple sub-graphs, allocate hardware resources for each sub-graph separately, and finally...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com