Driving method of symmetrical half-bridge LC series resonance sine power conversion circuit
A symmetrical half-bridge and conversion circuit technology, applied in the field of DC conversion, can solve problems such as weak transient response capability and weak soft switching characteristics of transistors, and achieve strong transient response capability, good load supply voltage stability, and voltage stability Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
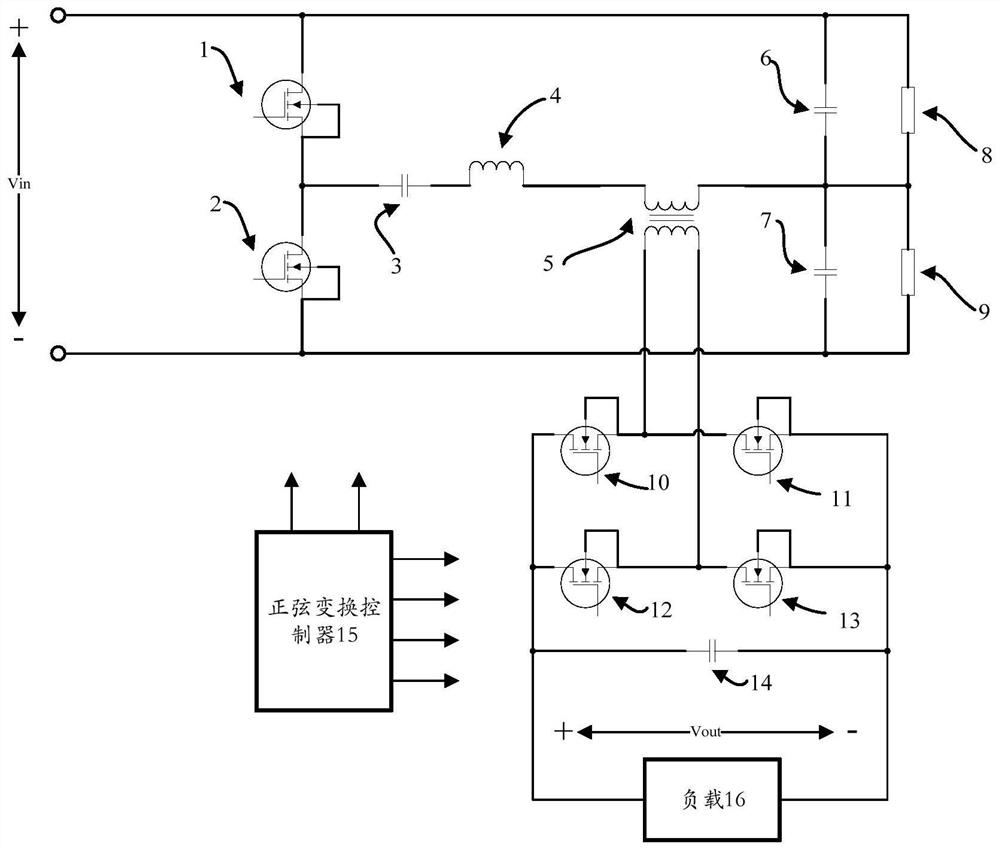
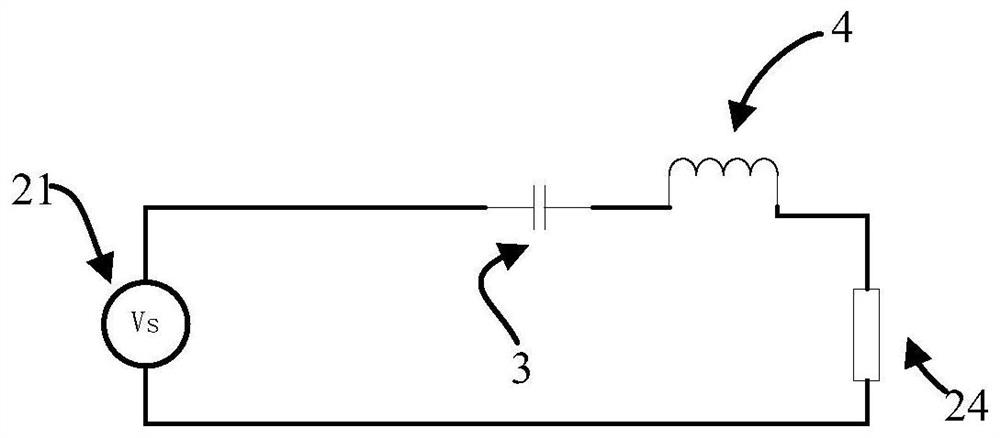
[0040] The following combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 This embodiment will be described.
[0041] Through the driving method of the symmetrical half-bridge LC series resonant sinusoidal power conversion circuit in this embodiment, the symmetrical half-bridge converting circuit generates a high-frequency constant-width chopping voltage, which is connected by a resonant capacitor, a resonant inductor and a high-frequency The resonant tank circuit formed by the primary series connection of the transformer is controlled by the sinusoidal conversion controller, so that the frequency of the resonant tank circuit, the chopping voltage and the secondary synchronous rectification are matched, and in the resonant tank circuit, a circuit with the same phase and frequency as the chopping voltage is formed. The sine wave resonant current realizes the soft switching of two half-bridge transistors and four synchronous rectification transistors, and also maintains the gain constant of the co...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The following combination Figures 4 to 6 The second embodiment will be described.
[0067] The second embodiment shows an implementation of a sinusoidal transformation controller, such as Figure 4 As shown, the sinusoidal conversion control circuit 15 includes a pulse width controller 151, a gate driver 152 and an isolation transformer 153 connected in sequence, and the sinusoidal conversion control circuit 15 also includes: a first drive circuit and a second drive circuit, wherein the first drive The circuit is arranged at the first output end of the sinusoidal transformation control circuit 15, and the second driving circuit is arranged at the second output end of the sinusoidal transformation control circuit 15;
[0068] The output end of the pulse width controller 151 is connected to the input end of the gate driver 152, and the pulse width controller 151 is used to input a control signal to the gate driver 152;
[0069] Specifically, the pulse width controller 15...
Embodiment 3
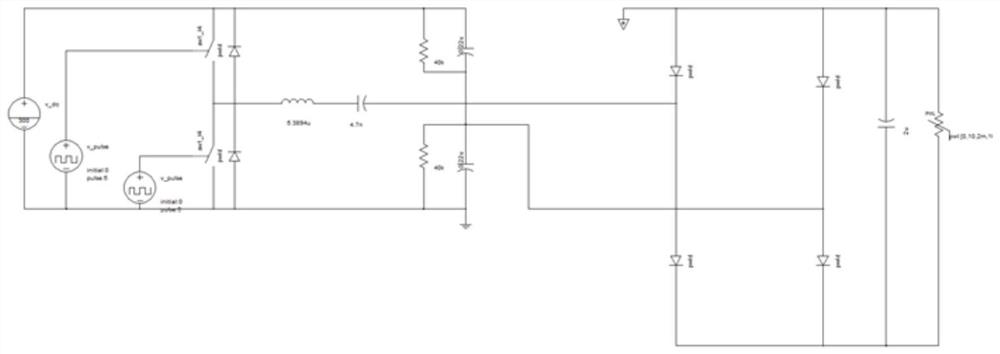
[0092] The following is attached Figures 7 to 10 The third embodiment will be described.
[0093] This embodiment provides a driving method for a symmetrical half-bridge LC series resonant sinusoidal power conversion circuit, which is suitable for the circuits in the first and second embodiments above. The above-mentioned circuits are driven by the driving method in this embodiment. Methods include:
[0094] Step S1, connecting an LC series resonant circuit in series between the primary end of the high-frequency transformer and the symmetrical half-bridge circuit;
[0095] Step S2, determining the switching frequency of the symmetrical half-bridge sinusoidal power conversion circuit according to the resonant angular frequency of the LC series resonant circuit;
[0096] In step S3, according to the switching frequency, a transistor turn-on instruction is sent to the symmetrical half-bridge sinusoidal power conversion circuit, and the transistor turn-on instruction is used to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com