Curvature continuous parking path planning device and method of intelligent parking system
A curvature continuous, path planning technology, applied in the field of parking space detection and path generation devices, can solve problems such as increasing the difficulty of engineering implementation, low solution efficiency, and difficult to describe constraints.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0093] In the prior art, a common method for designing a path with continuous curvature is to first apply A-star to generate a collision-free path from the start point to the end point, and then generate a smooth geometry by numerical optimization based on this path. Path, similar methods are B-spline path, higher-order smooth curve path, Bezier path, etc. The parking paths obtained based on these numerical methods are all of continuous curvature, but there are two points that cannot be guaranteed. First, even if the curvature is continuous, it does not necessarily guarantee that the minimum curvature radius can meet the dynamic characteristics of the vehicle body; second, The solved path is not guaranteed to be collision-free. These two points are very important for practical parking engineering applications, and more perfect algorithms need to be proposed for improvement.
[0094] 1 About the spiral design:
[0095] like figure 2 As shown, the spiral path in four direction...
Embodiment 2
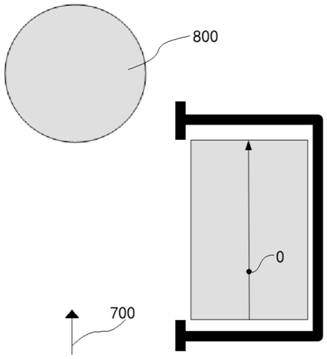
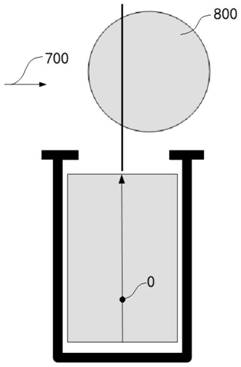
[0117] On the basis of Example 1, as Figure 4 , 5 , 8, the front of the car is facing forward, and the rear is facing backward. Figure 8 where 0 is the position of the root node ( Figure 8 The position of a certain trisection point on the line connecting the center of the short side of the middle rectangle, the exact position of the trisection point is not required, and the nearby position is also acceptable, generally the position of the center point of the rear axle of the parked vehicle), 800 is the detection and detection distance outside the parking space. The vehicles forward detect the regions where the related paths are jointly explored with a high probability. The forward direction of the in-line parking space ( Figure 8 The arrow connecting the centers of the short sides of the middle rectangle indicates the direction), and set the same direction as the forward direction of the currently parked vehicle (the arrow direction of the pre-parked vehicle 700 is the ...
Embodiment 3
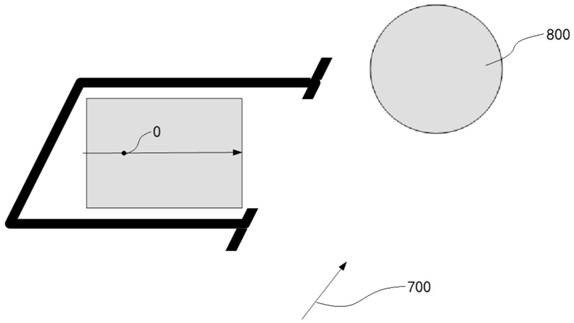
[0122] On the basis of Example 1, as Image 6 , 7 , 9, the front of the pre-parked vehicle is facing forward ( Figure 9 In 700, the arrow of the vehicle is facing the front direction), and the rear direction is the rear direction. The forward direction of the vertical parking space ( Figure 9 The arrow connecting the center of the short side of the middle rectangle indicates the direction), which is set to the direction that the vehicle faces forward after parking in reverse.
[0123] Figure 9 where 0 is the position of the root node ( Figure 9 The position of a certain trisection point on the line connecting the center of the short side of the middle rectangle, the exact position of the trisection point is not required, and the nearby position is also acceptable, generally the position of the center point of the rear axle of the parked vehicle), 800 is the detection and detection distance outside the parking space. The vehicles forward detect the regions where the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com