Representation Method of Optical Freeform Surface Based on Gaussian Radial Basis Function
A Gaussian radial basis and function technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as the influence of Gaussian radial basis function characterization effect, and achieve the effect of strong surface adaptability, high-precision characterization, and simple calculation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
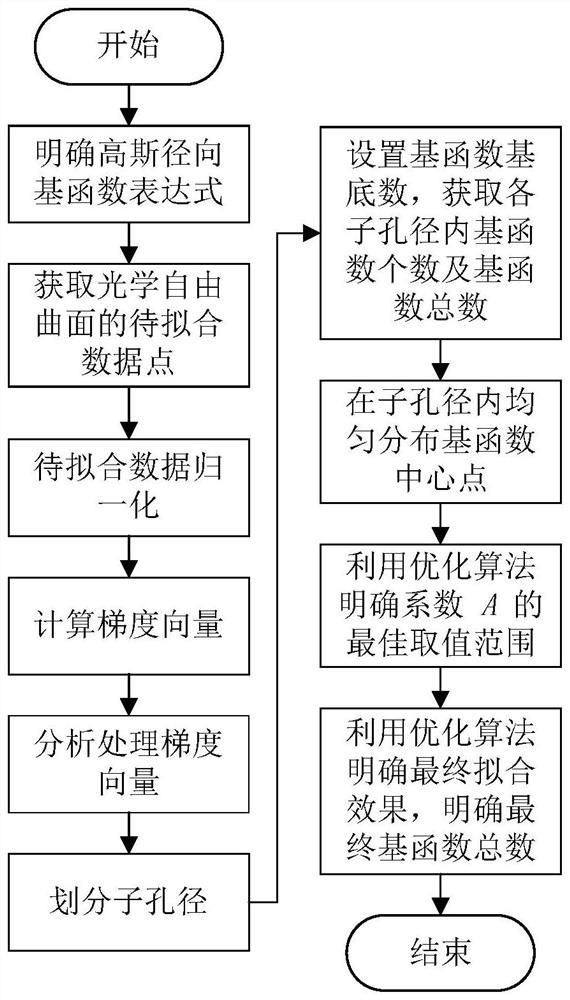
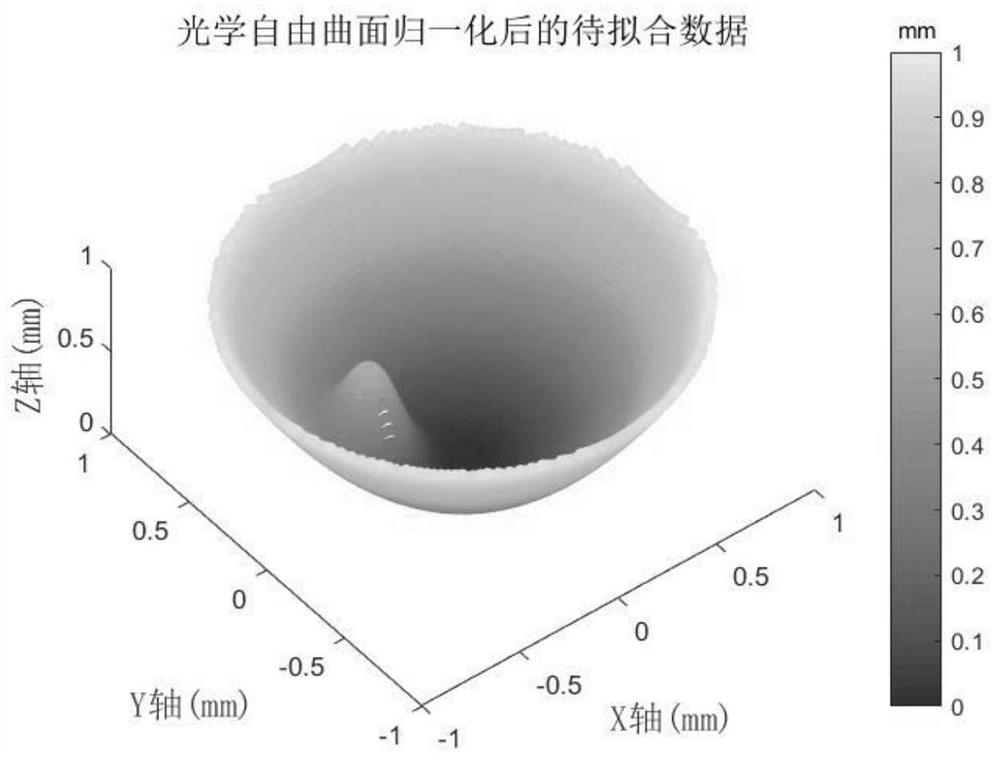
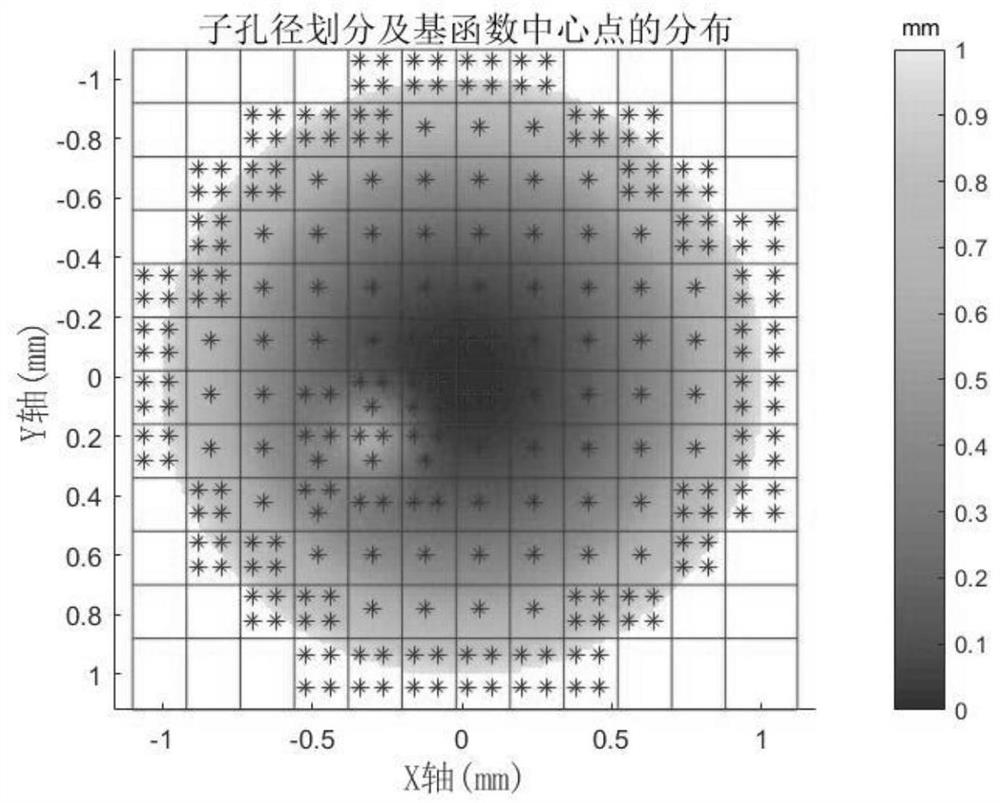
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, this optical free-form surface characterization method based on Gaussian radial basis function includes the following steps:
[0034] (1) It is clear that the expression of Gaussian radial basis function is formula (1):
[0035]
[0036] Among them, Z(X i ,Y i ) is the sagittal height of the optical free-form surface to be fitted, w j is the coefficient, (X i ,Y i ) is the Cartesian coordinate system coordinates, where ε j is the shape factor of the jth Gaussian radial basis function, (x 0j ,y 0j ) is the center point of the jth Gaussian radial basis function, m is the number of data points to be fitted, and n is the total number of Gaussian radial basis functions;
[0037] When fitting an optical free-form surface, if Z(X i ,Y i ), ε j and (x 0j ,y 0j ) is known, according to formula (1) to get w j , the fitting result is formula (2):
[0038]
[0039] The fitting deviation is formula (3)
[0040] Z error (X i ,Y i )=...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com