Multicast method based on key dynamic negotiation and related device
A dynamic key technology, which is applied in the field of communication, can solve the problem that the key distribution negotiation cannot take into account the balance between the number of distribution keys and the amount of encryption and communication volume, so as to achieve the effect of reducing workload and taking into account the communication volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
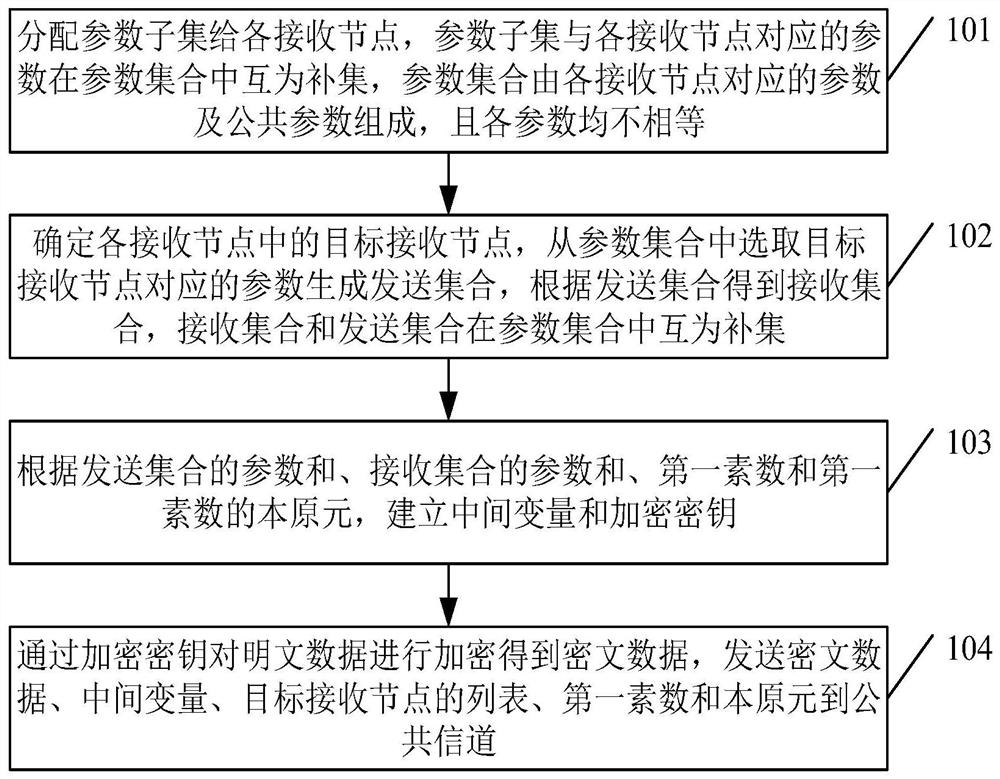
[0064] For ease of understanding, see figure 1 Embodiment 1 of a multicast method based on dynamic key negotiation provided by the present application includes:
[0065] Step 101, assign parameter subsets to each receiving node, the parameter subset and the parameters corresponding to each receiving node are complementary sets in the parameter set, the parameter set is composed of the parameters corresponding to each receiving node and public parameters, and each parameter is not equal.
[0066] It should be noted that the parameter set contains public parameters, and the public parameter is the same parameter that each node has. This parameter can be set according to the actual situation; a parameter set with unequal parameters is randomly generated according to the number of receiving nodes, that is, every Each receiving node has corresponding parameters, and the parameter set is composed of the parameters corresponding to each receiving node and the public parameters; the ...
Embodiment 3
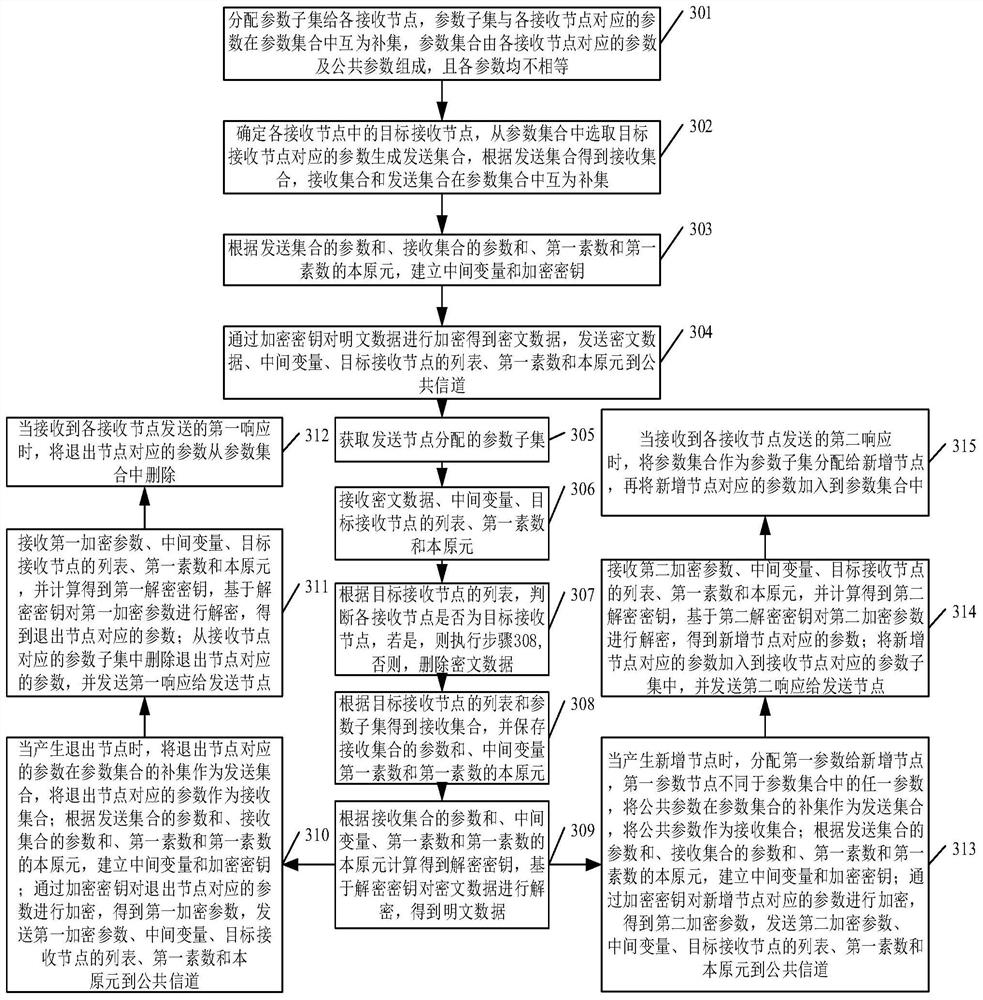
[0096] see image 3 , an embodiment three of a multicast method based on dynamic key negotiation provided by the present application, including:
[0097] Step 301, assign parameter subsets to each receiving node, the parameter subset and the parameters corresponding to each receiving node are complementary sets in the parameter set, the parameter set is composed of parameters corresponding to each receiving node and public parameters, and each parameter is not equal.
[0098] Step 301 is the same as the description of step 101 in Embodiment 1, please refer to the description of step 101, and details will not be repeated here.
[0099] Step 302: Determine the target receiving node in each receiving node, select the parameters corresponding to the target receiving node from the parameter set to generate the sending set, and obtain the receiving set according to the sending set, and the receiving set and the sending set are complementary sets in the parameter set.
[0100] Step...
Embodiment 3
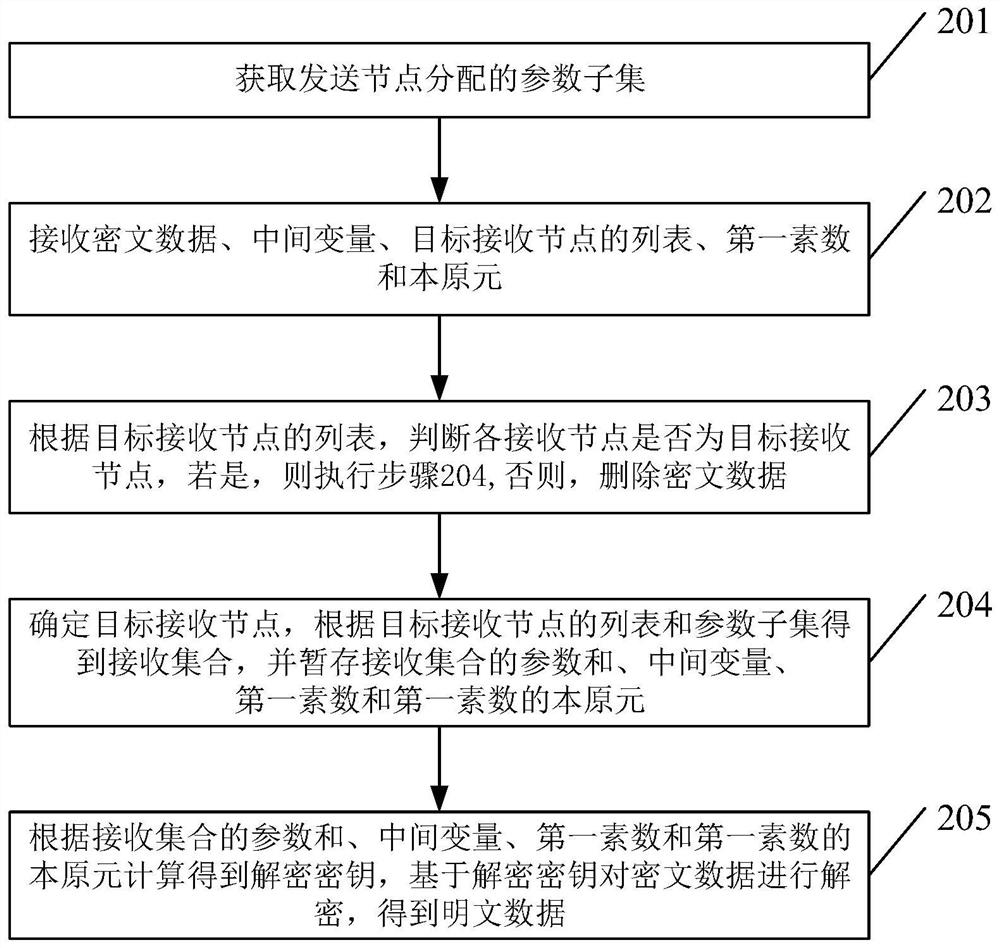
[0142] The above is the third embodiment of a multicast method based on dynamic key negotiation provided by the embodiment of this application. The following is an embodiment of a network sending node based on dynamic key negotiation provided by the embodiment of this application. Please refer to Figure 4 ,include:
[0143] The allocation unit 401 is used to allocate parameter subsets to each receiving node. The parameter subsets and the parameters corresponding to each receiving node are complementary sets in the parameter set. The parameter set is composed of parameters corresponding to each receiving node and public parameters, and each None of the parameters are equal.
[0144] The first generation unit 402 is configured to determine a target receiving node in each receiving node, select a parameter corresponding to the target receiving node from the parameter set to generate a sending set, obtain a receiving set according to the sending set, and exchange the receiving se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com