Reducing fratricide of immune cells expressing nkg2d-based receptors
A technology of immune cells and receptors, applied in the field of immunotherapy, can solve problems such as poor cell yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0186] Example 1. NKR-2 CAR T cells undergo killing of killers, which drive the phenotype of engineered T cell populations and amplification.
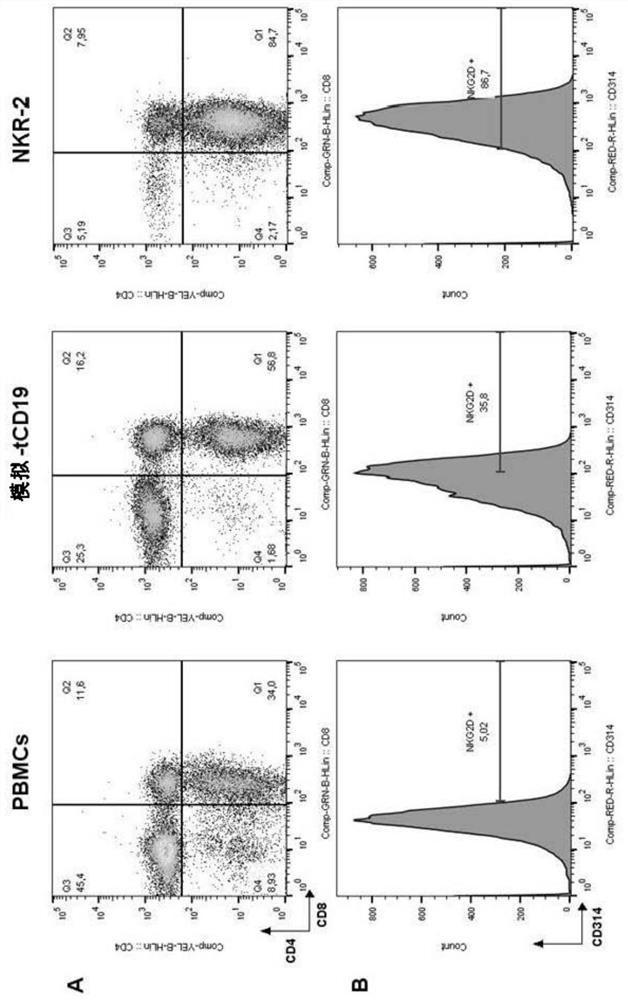
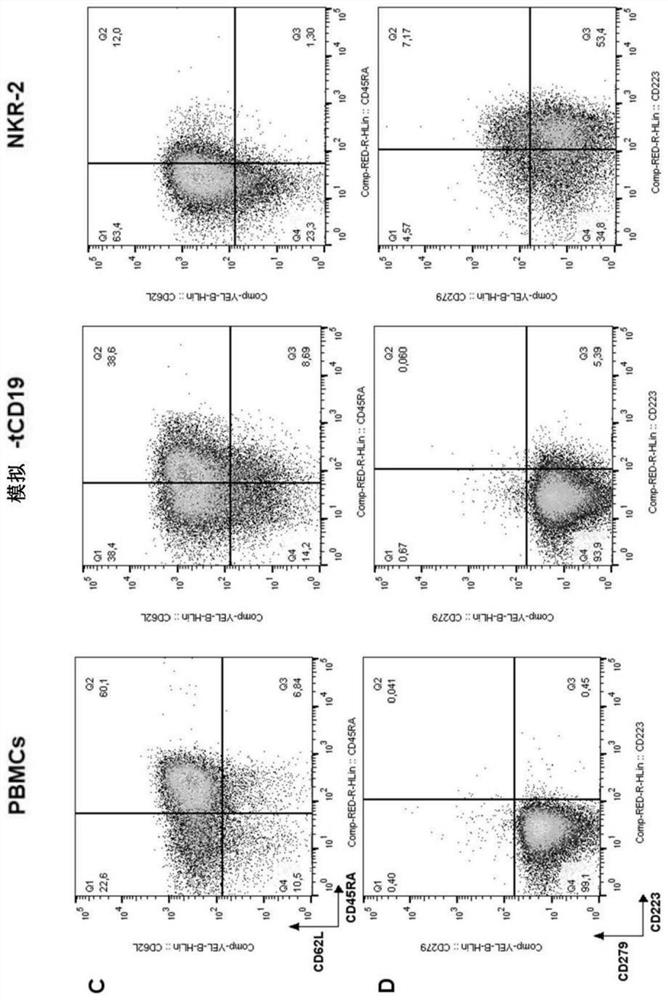
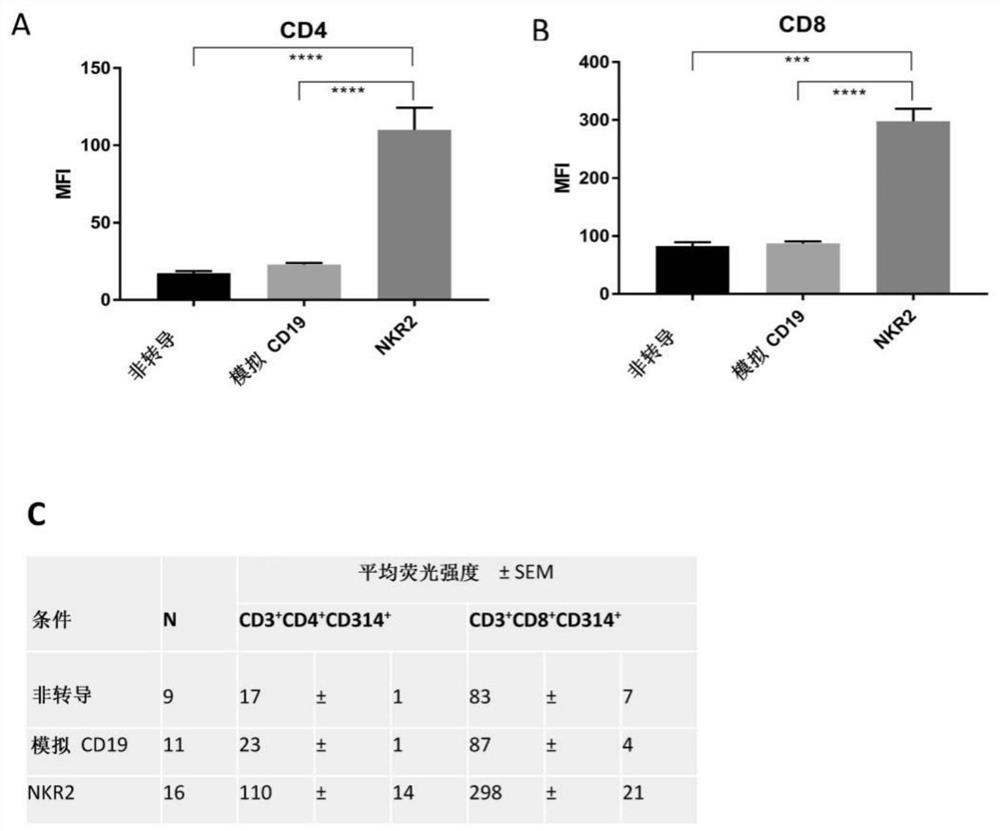
[0187] Following transduction and in vitro culture, NKR-2 T cell populations display predominant CD8 compared to T cells transduced with control vectors in the absence of means to control for killer + T cell subset composition (truncated CD19 (tCD19), figure 1 A). NKG2D expression was not restricted to NKR-2 T cells but was also clearly seen on control tCD19 T cells, although engagement of endogenous NKG2D failed to generate therapeutic responses in CAR T cells (32). However, the relative cell surface expression of NKG2D was highly increased in the NKR-2 T cell population, suggesting that T cells were transduced with the CAR construct (Figure 1B). The mean fluorescence intensity of NKG2D(CD314) was in CD4 + and CD8 + NKR-2 in both subpopulations was significantly higher in T cell populations, confirming CAR expression in both s...
Embodiment 2
[0194] Example 2. PI3K inhibition improves NKR-2 T cell viability and drives NKR-2 antigen during cryopreservation Increased production of specific cytokines and increased memory phenotype.
[0195] Following ligand binding, NKG2D and its associated DAP10 initiate signaling through the PI3K pathway in a manner similar to CD28 (25, 26). We therefore questioned whether inhibition of PI3K signaling could abrogate NKR-2-mediated killing during T cell culture. To this end, increasing concentrations of LY294002 (as a broad PI3K inhibitor) were added to the transduction and amplification phases of NKR-2 production.
[0196]The addition of LY294002 led to several observations. First, the cell surface expression of NKR-2T on NKR-2 T cells decreased in a dose-dependent manner, reaching the level of control tCD19 T cells at 10 μM ( Figure 4 A and Figure 5 ). This reduction was reversible, as removal of LY from cultures resulted in increased NKG2D expression up to the level of u...
Embodiment 3
[0199] Example 3. Antibody-mediated NKG2D blockade prevents NKR-2 CAR T cell killing.
[0200] Initial experiments including an anti-NKG2D antibody (clone 1D11) during NKR-2 T cell culture showed that NKR-2 T cell yields at the end of culture were comparable to control T cells (2.6-fold expansion of NKR-2 T cells, NKR- 2 T cells have a 13.8-fold expansion of antibody blocking ability ( Figure 8 ). This suggests that antibody blockade can abolish NKG2D target-driven killers. Dose titration experiments showed that antibody concentrations of 2.5 μg / mL and above could protect tCD19 T cells358 from NKR-2 T cell-targeted killing ( Figure 4 E). Anti-NKG2D antibody can also effectively block the release of IFN-γ in the process of target cell participation ( Figure 4 F), thereby confirming the specificity of NKR-2 T cells. Efficient killing of killers using anti-NKG2D antibodies is further supported by the fact that the observed IFN-γ release during NKR-2 T cell generation, l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com