Method, device, medium and computer equipment for initial value estimation of image points in a sub-region
A technique of seed area and sub-area, applied in the field of initial value estimation of image points in the sub-area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
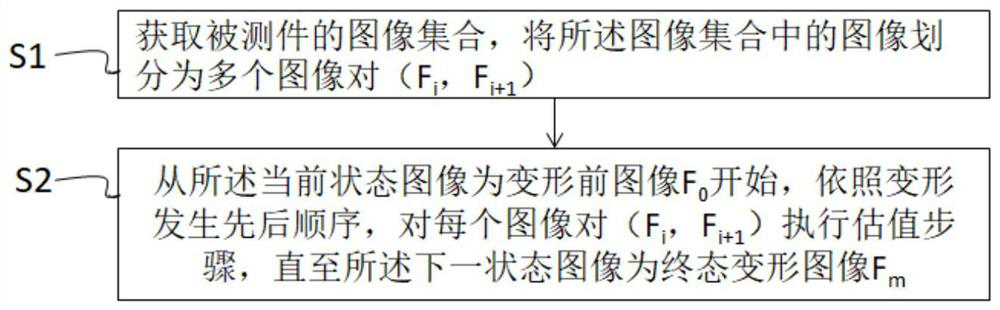
[0075] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention discloses a method for estimating an initial value of an image point in a sub-region, comprising the following steps:
[0076] S1 acquires the image collection of the object under test, and divides the images in the image collection into multiple image pairs (F i , F i+1 ), where, 0≤ii is the current state image, F i+1 is the next state image, F O is the image before deformation, F m is the final deformed image;
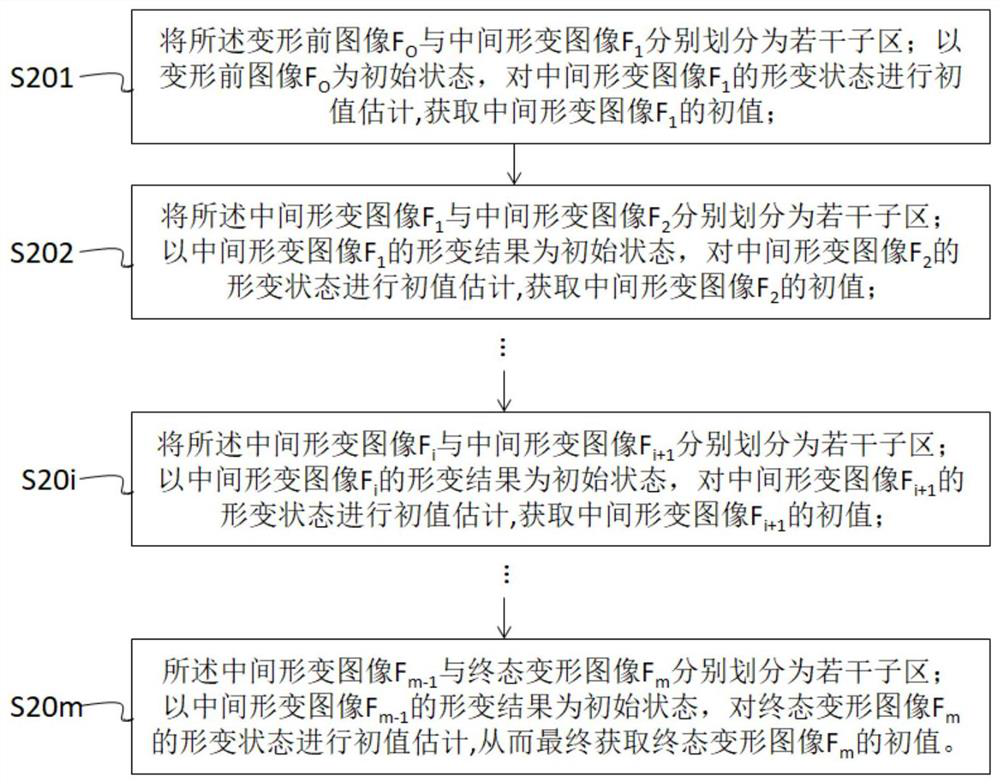
[0077] S2 from the current state image to the pre-deformation image F O At first, according to the order of deformation occurrence, for each image pair (F i , F i+1 ) perform the following steps until the next state image is the final state deformation image F m :
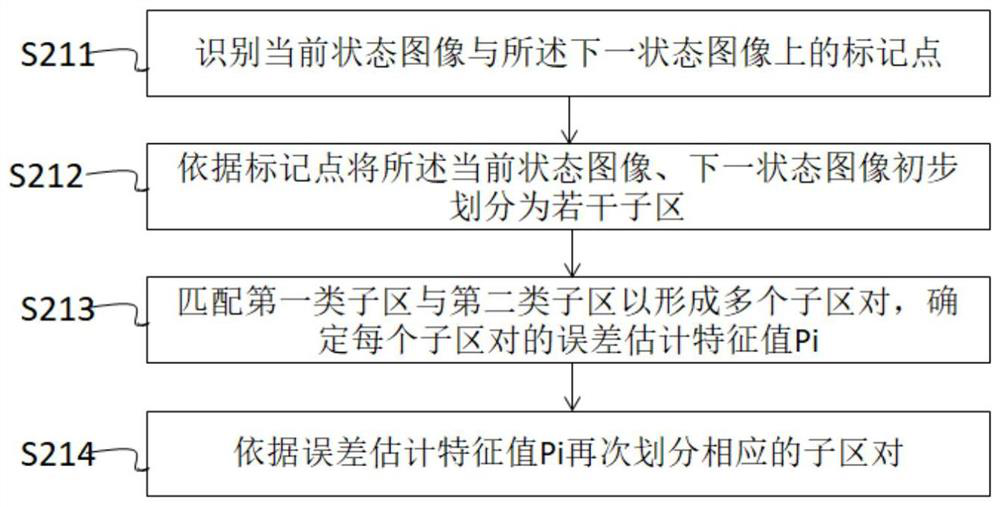
[0078] S21 each of the current state images F i with the next state image F i+1 respectively divided into several sub-areas, wherein the current state image F i The sub-area is the first type of sub-area, and the next state image F i+1 T...
Embodiment 2
[0154]Such as Figure 12 As shown, the present invention also discloses an initial image point estimation device 10 in a sub-region, including:
[0155] Image acquisition and pairing module 11 is used to obtain the image set of the test piece, and the images in the image set are divided into a plurality of image pairs (F i , F i+1 ), where, 0≤ii is the current state image, F i+1 is the next state image, F O is the image before deformation, F m is the final deformed image;
[0156] The initial value estimation module 12 is used to convert the image F from the current state image to the image F before deformation O At first, according to the order of deformation occurrence, for each image pair (F i , F i+1 ) perform the following steps until the next state image is the final state deformation image F m :
[0157] The sub-regions are divided into sub-modules, which are used to convert each of the current state images F i with the next state image F i+1 respectively div...
Embodiment 3
[0192] Figure 13 Shown is a schematic structural diagram of a computer device provided by an embodiment of the present invention, such as a smart phone, a tablet computer, a notebook computer, a desktop computer, a rack server, a blade server, a tower server or a cabinet server that can execute programs (including independent servers, or server clusters composed of multiple servers), etc. The computer device 20 of this embodiment at least includes but is not limited to: a memory 21 and a processor 22 that can communicate with each other through a system bus, such as Figure 13 shown. It should be pointed out that, Figure 13 Only computer device 20 is shown having components 21-22, but it should be understood that implementing all of the illustrated components is not a requirement and that more or fewer components may instead be implemented.
[0193] In this embodiment, the memory 21 (that is, a readable storage medium) includes a flash memory, a hard disk, a multimedia ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com