A heat exchange structure and method for an ultra-low temperature solenoid valve
A heat exchange structure, solenoid valve technology, applied in valve heating/cooling devices, valve operation/release devices, valve details, etc. Effects of heat exchange efficiency, increased contact area, reduced height requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
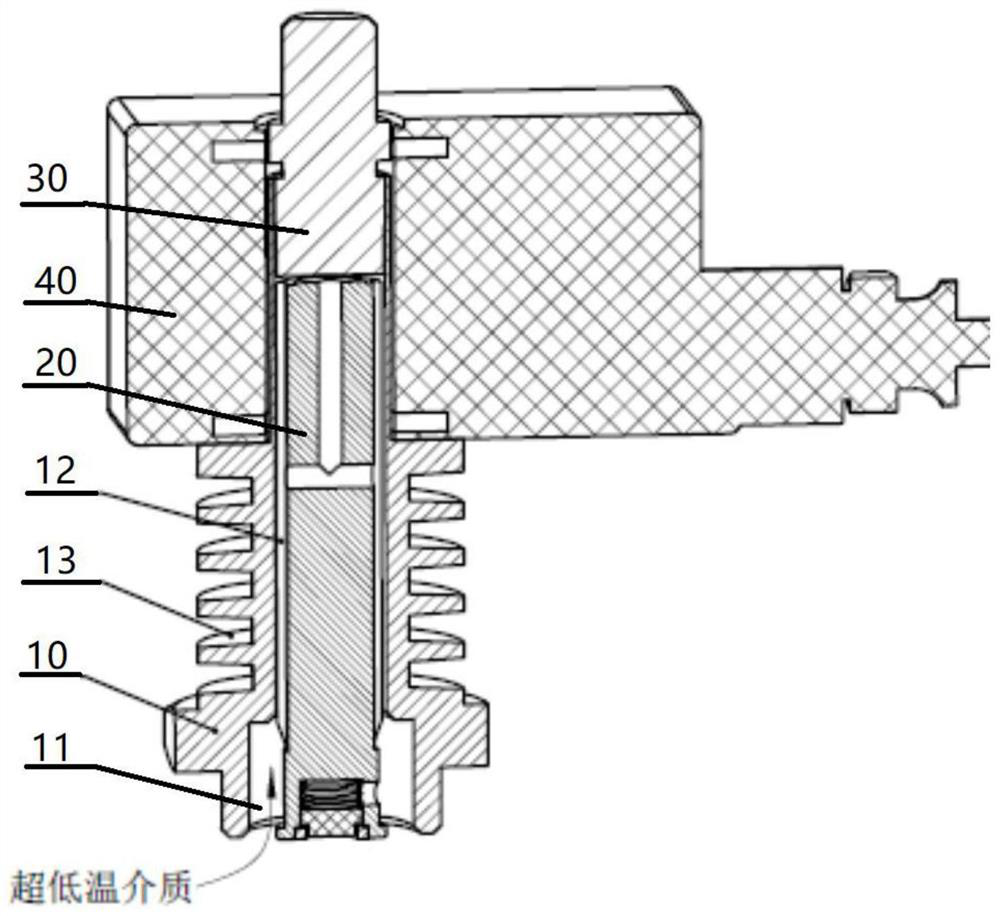
[0042] A heat exchange structure of an ultra-low temperature solenoid valve, wherein, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes: valve seat 10 , moving core 20 , static core 30 , and coil 40 .
[0043] like figure 1 As shown, the valve seat 10 has a movable cavity 11 and an annular structure 13 . The movable cavity 11 is located in the valve seat 10 . The annular structures 13 are distributed on the outer surface of the valve seat 10 , and the annular structures 13 are located on the side of the movable cavity 11 .
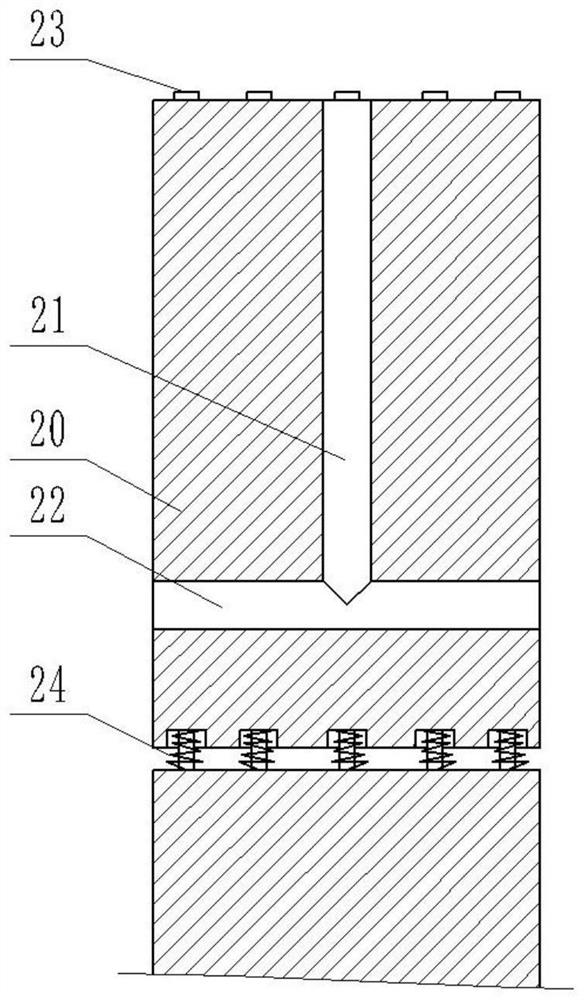
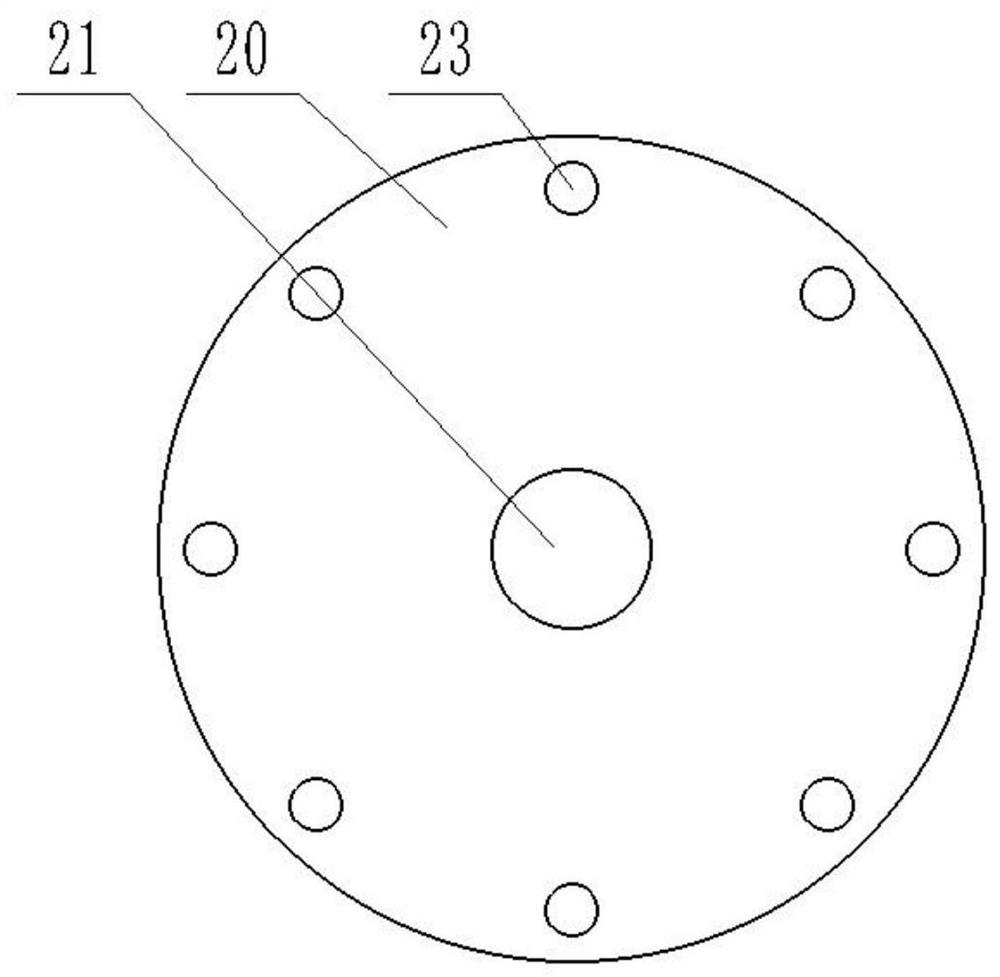
[0044] The moving core 20 is slidably arranged in the movable cavity 11 , the moving core 20 and the side wall of the movable cavity 11 form a movement gap 12 , and heat exchange with the outside air is realized through the movement gap 12 . The static core 30 is fixedly arranged on the movable cavity 11 , and the static core 30 is located on the side of the moving core 20 . There is a gap between the static core 30 and the moving core 20 , and the static core 30 a...
Embodiment 2
[0057] A heat exchange method for an ultra-low temperature solenoid valve, comprising the following steps:
[0058] When the ultra-low temperature medium gradually flows close to the coil 40 through the moving gap 12 around the moving core 20, during this process, the medium continuously exchanges heat with the outside air when it contacts the side wall of the movable cavity 11, and the ultra-low temperature medium heats up, making the coil 40 The temperature of the medium at the place rises to the extent that the coil can withstand;
[0059] At the same time, a plurality of rings of annular structures 13 are processed on the valve seat 10, so that there is a heat exchange space between each annular structure 13, and when the outside air is passed into the heat exchange space, it can be carried out with each annular structure 13. The heat exchange greatly increases the contact area with the outside air, improves the heat exchange efficiency, and realizes the temperature rise f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com