A Parallel Discrete Update Method for Heterogeneous Many-Core Processors
A technology of many-core processor and update method, applied in the field of parallel discrete update for heterogeneous many-core processors, can solve the problem of inconvenient automatic transformation of compilers, reduce program readability and portability, and increase programming burden, etc. problems, to achieve good readability and portability, increase user burden, and facilitate automatic transformation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
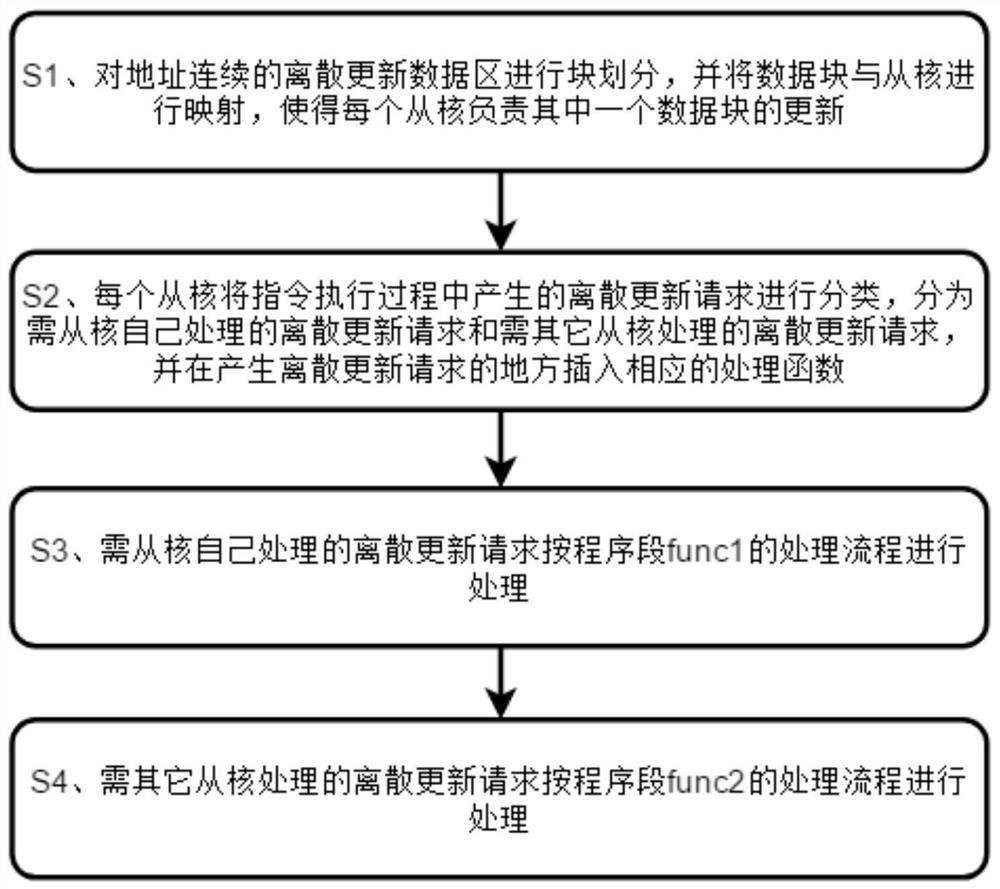
[0040] Embodiment: a parallel discrete update method for heterogeneous many-core processors, comprising the following steps:
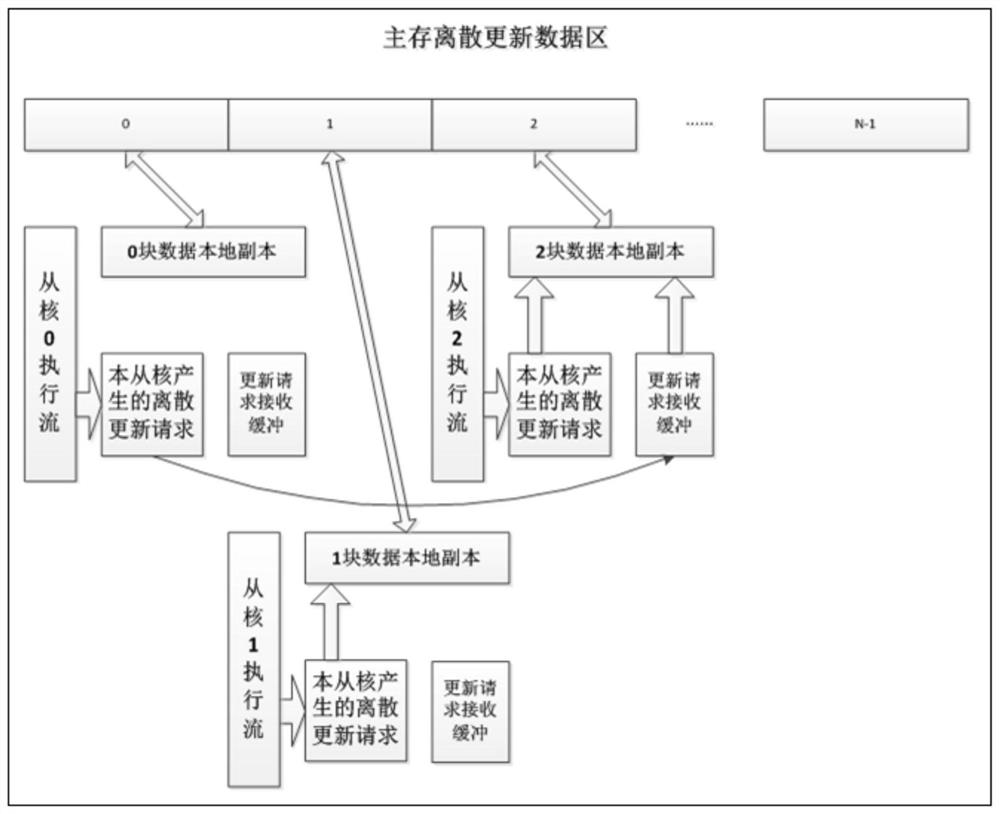
[0041] S1. Divide the discrete update data area with continuous addresses into blocks, and map the data blocks with the slave cores, so that each slave core is responsible for updating one piece of data, as follows:
[0042] In the discrete update data area with continuous addresses, the data units are continuously addressed in the main memory space, and the update operation is performed on the data unit in the discrete update data area, that is, the value of the data unit is taken out, and an operation is performed on it, for example Add a numerical value, and finally write the result back to the above data unit, and the update operation on the data unit in the discrete update data area is discrete;
[0043] S11. The method of dividing the discrete update data area with continuous addresses into blocks is: assuming that the number of slave cores is N,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com