Generation and synchronization of pulse-width modulated (PWM) waveforms for radio-frequency (RF) applications
A technology of pulse width modulation and pulse width, applied in the direction of pulse duration/width modulation, radio frequency amplifier, high frequency amplifier, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0086] Table 1 summarizes a list of acronyms employed throughout this specification to aid in understanding the described embodiments:
[0087]
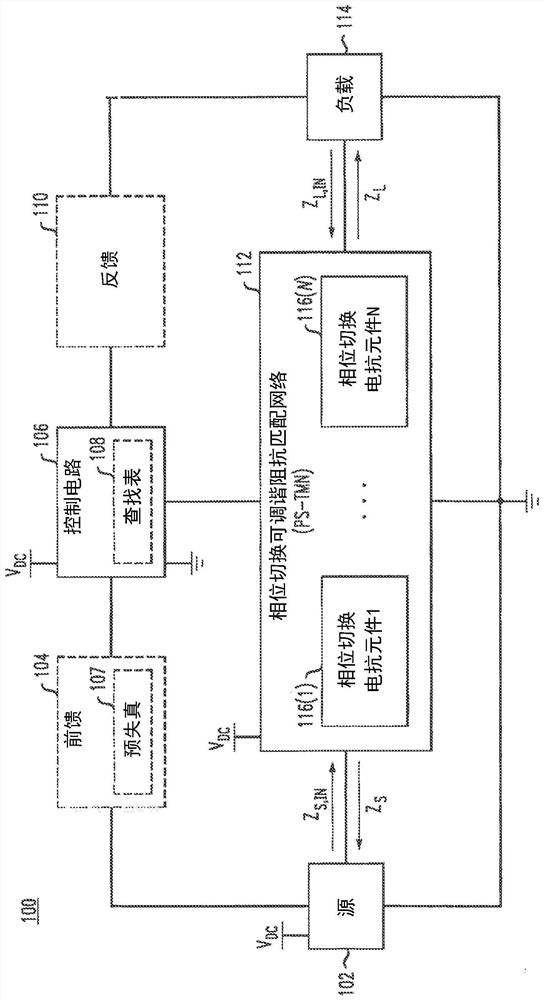
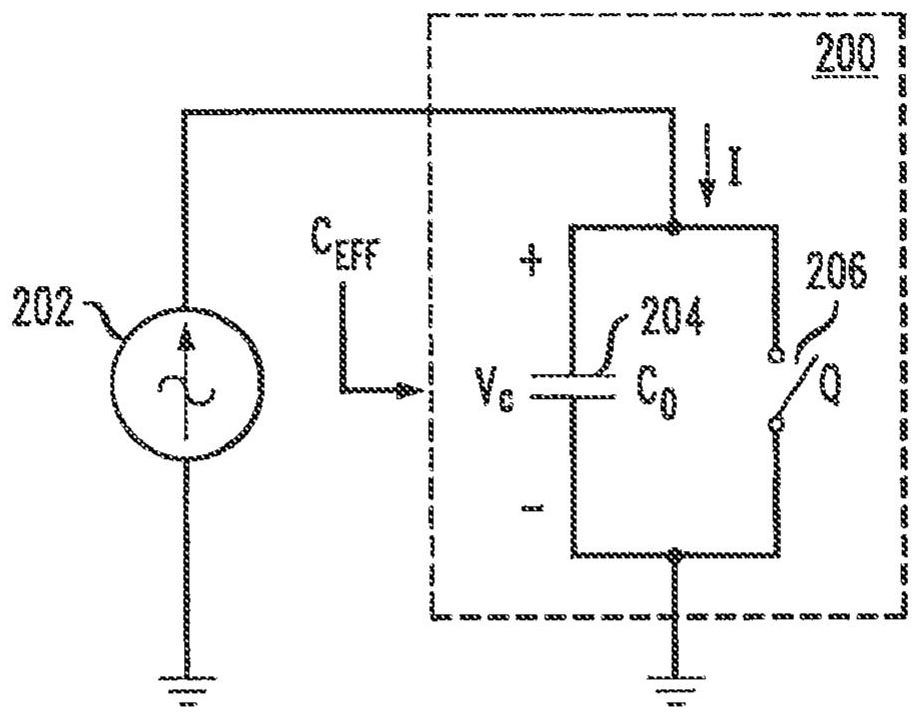
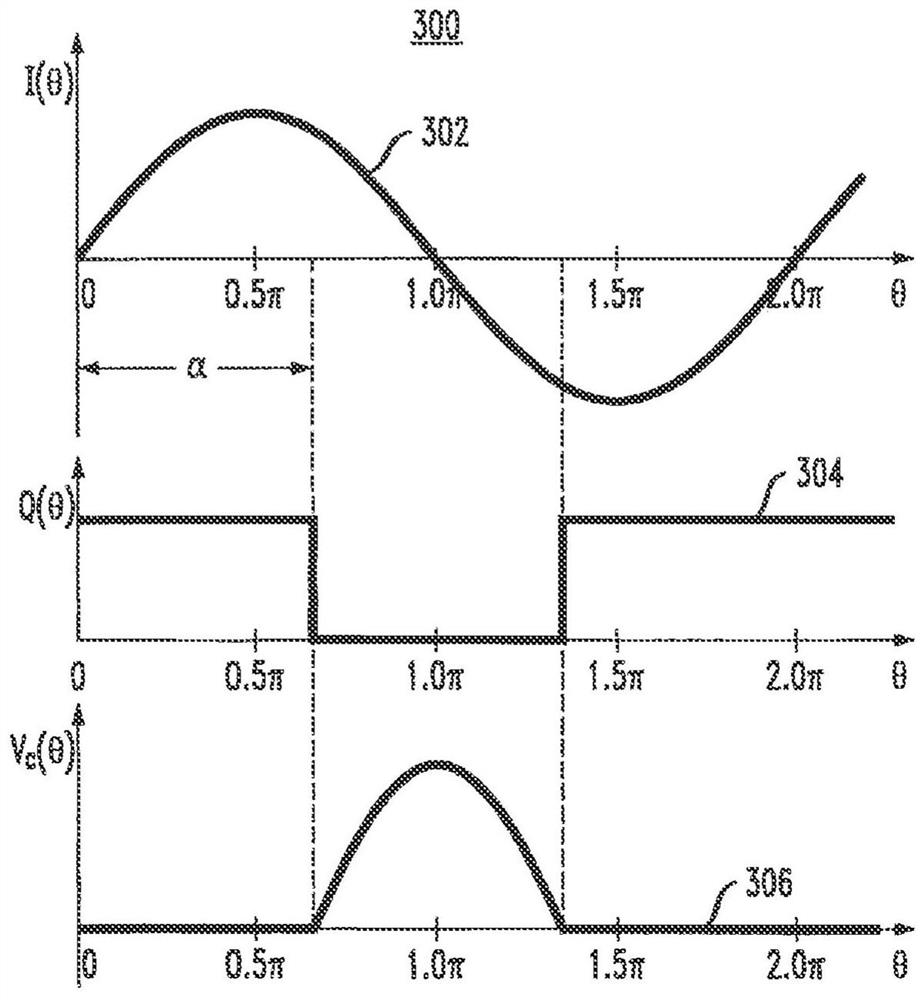
[0088] The described embodiments are directed to a phase switched tunable matching network (PS-TMN) and a phase switched impedance modulated amplifier (PSIM). Both the phase-switched tunable matching network and the phase-switched impedance modulated amplifier include phase-switched variable network reactive elements. When configured in the context of PS-TMN and phase-switched impedance-modulated amplifiers, such phase-switched variable network reactive elements provide fast, high-bandwidth, continuous impedance matching over a wide impedance range while not requiring high bias It operates efficiently at high power levels with no set voltage or current. PS-TMN can be used alone or in combination with other matching techniques such as discrete switched reactance banks.
[0089] PS-TMN can be used in a variety of reconfigurable an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com