Mobile robot path planning method based on deep reinforcement learning
A mobile robot and reinforcement learning technology, applied in the direction of instruments, non-electric variable control, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problems of limited generalization ability, poor navigation effect, and low learning efficiency in unfamiliar scenes. Achieve the effects of self-learning efficiency and motion safety improvement, short time spent, and strong action robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
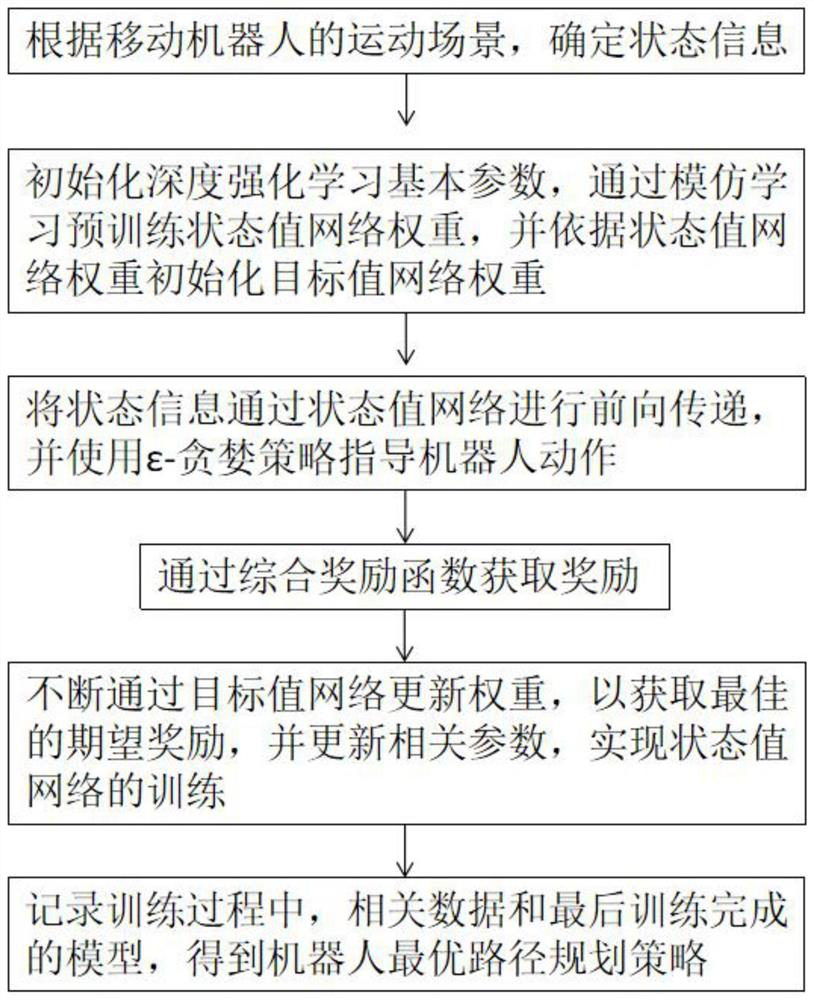
[0186] The invention utilizes the deep reinforcement learning algorithm and the artificial potential field method to improve the autonomous learning efficiency of the mobile robot, and can obtain higher action safety and action robustness under training, and the time taken to reach the target position is shorter; the present invention Take the simulation training process on the V-REP software and the testing process of the 3WD omnidirectional wheel mobile robot as examples to elaborate;
[0187] The task scenario designed in this embodiment is that the mobile robot starts from the starting position, passes through five randomly moving pedestrians, and arrives at the target position without collision;
[0188] The method for path planning of a mobile robot in a pedestrian environment based on deep reinforcement learning and artificial potential field method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
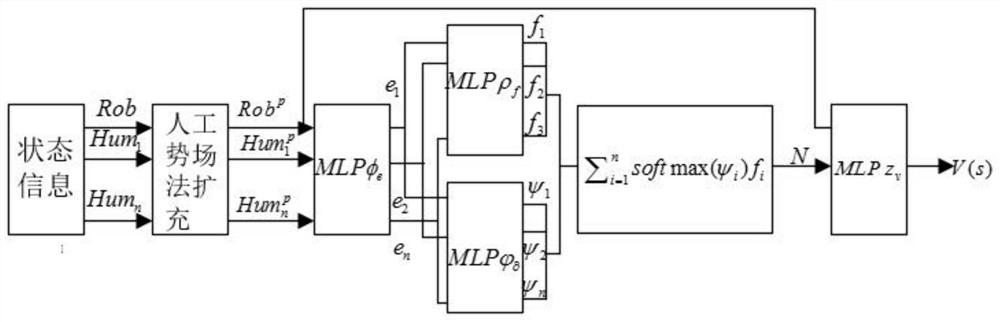
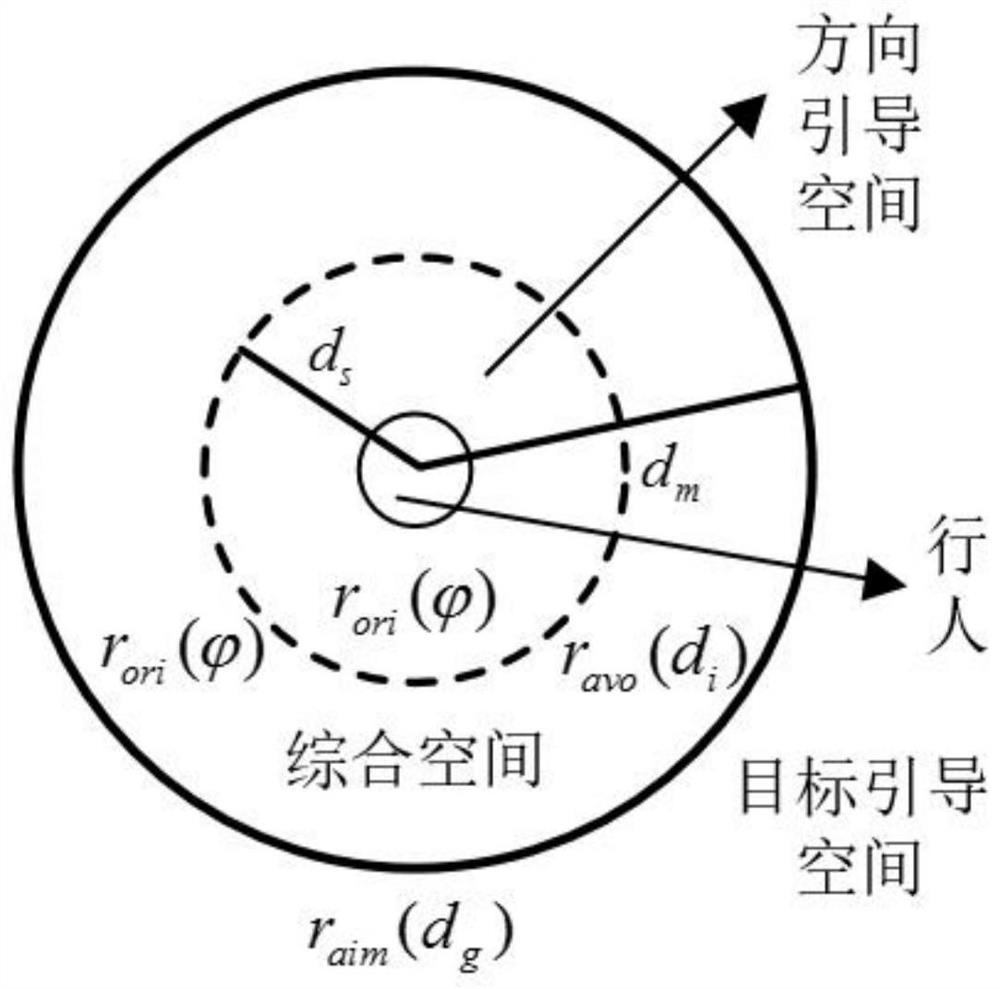
[0189] Step S1. Determine state information according to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com