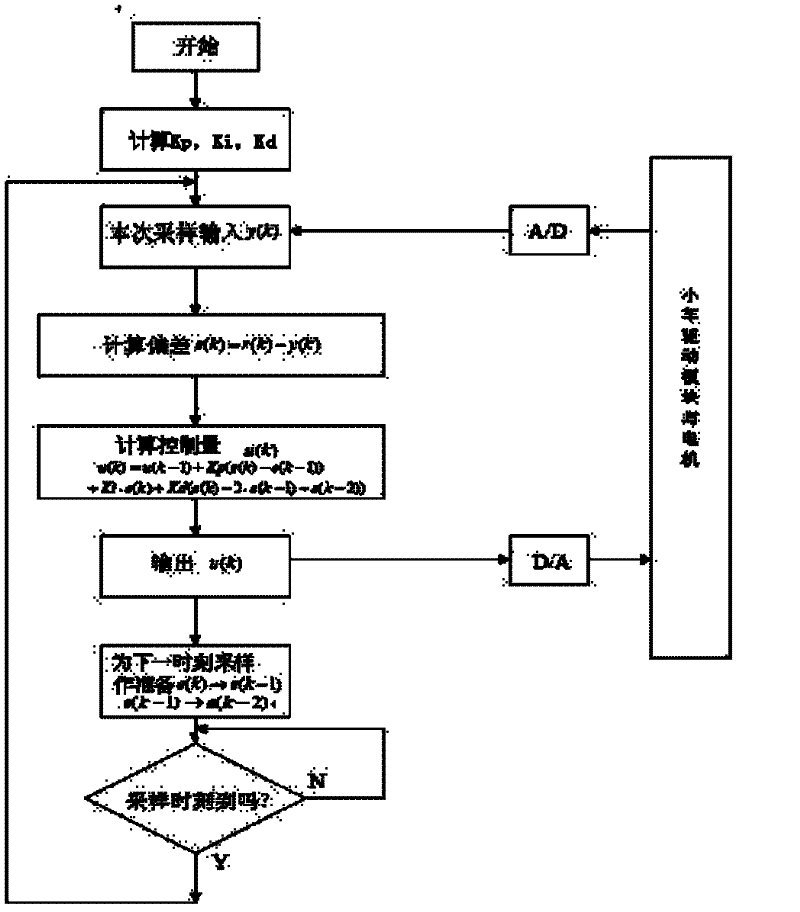
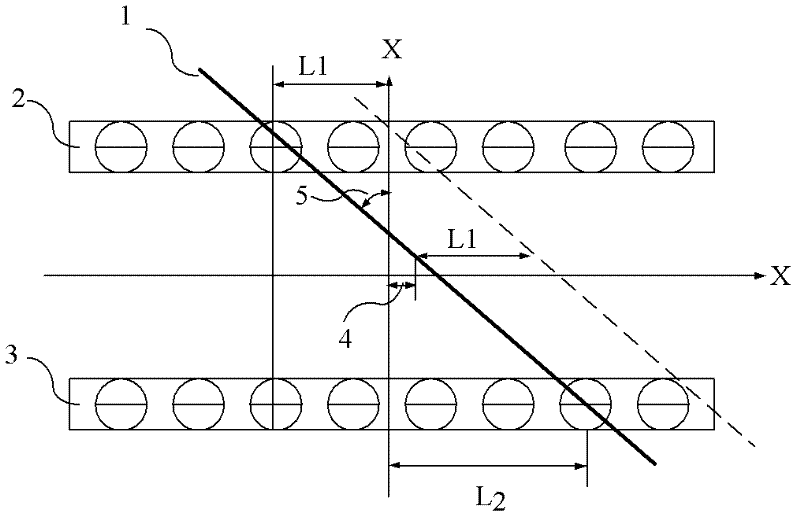
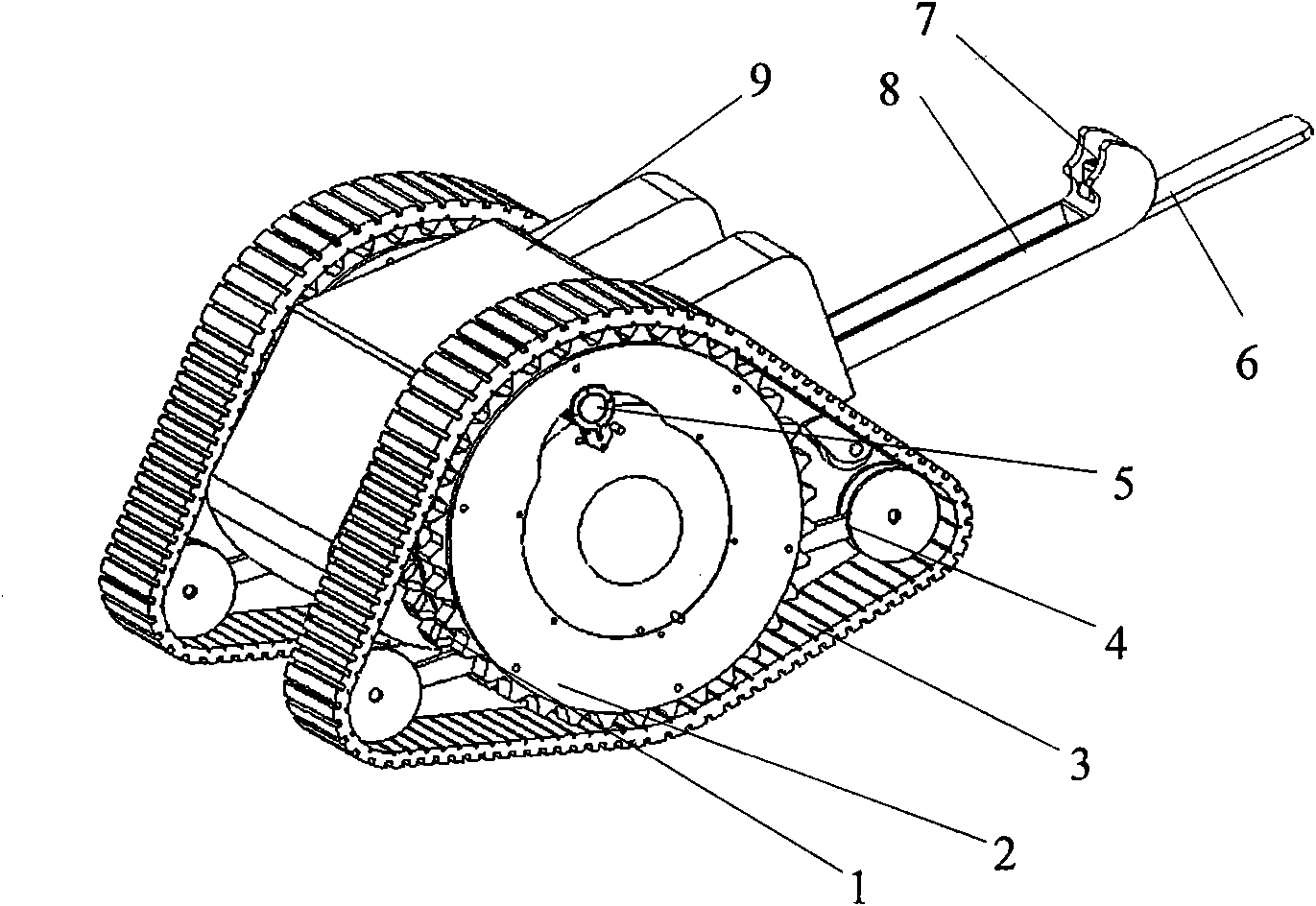
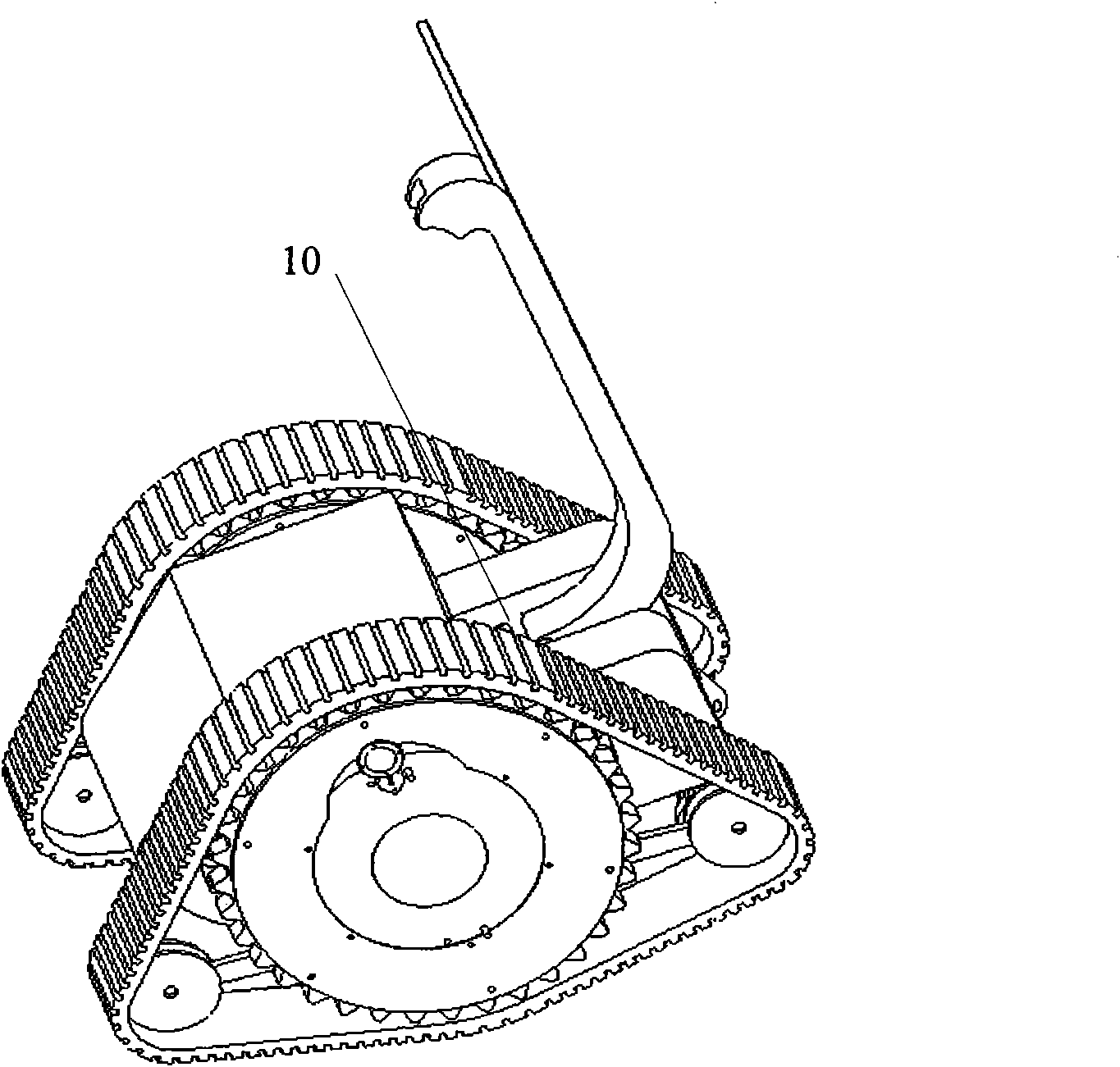
Patents
Literature
196 results about "Wheel mobile robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Robot system
InactiveUS7066291B2Good flexibilityEasy to operateProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectric devicesRobotic systemsCommunications system
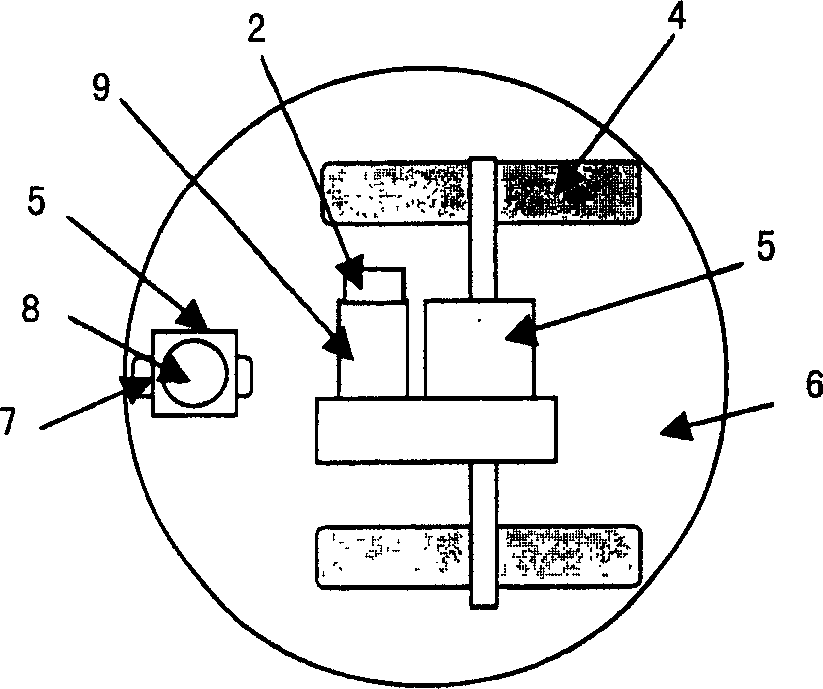
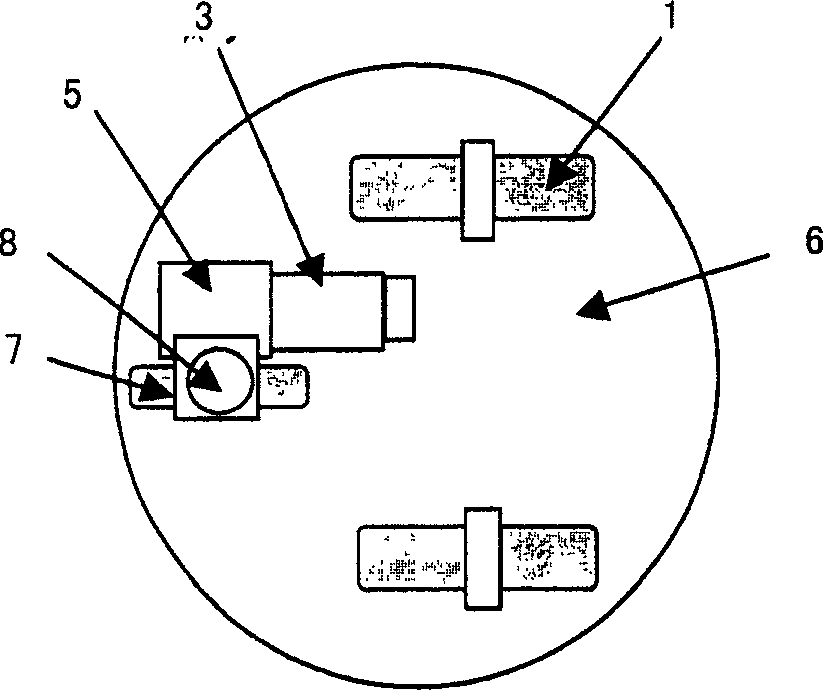
A mobile robot system for performing a plurality of separate operations, and including at least one autonomous wheeled mobile robot having at least one wheel-driving motor, an on-board computer, a system for navigation, orientation, and maneuvering in an environment with moving obstacles, a sensor system, a wireless communication system operative to receive and send signals, and a plurality of dockable operation modules and operative to be selectively coupled to the autonomous mobile robot to form an operation unit, wherein the autonomous wheeled mobile robot autonomously docks to the dockable operation modules.
Owner:UNIBAP AB
Robot system
InactiveUS7082350B2Good flexibilityEasy to operateVehicle fittingsSpeed/accelaration controlRobotic systemsCommunications system
An autonomous wheeled mobile robot (1) comprising at least one wheel-driving motor, an on-board computer, means for navigation, orientation, and maneuvering in an environment with moving obstacles; a sensor system; and a wireless communication system for receiving and sending.
Owner:UNIBAP AB
Wheel-foot combined obstacle detouring non-contact magnetic absorption type wall climbing robot system
InactiveCN101947777ASimple structureIncrease load capacityManipulatorVehiclesVehicle frameDrive motor
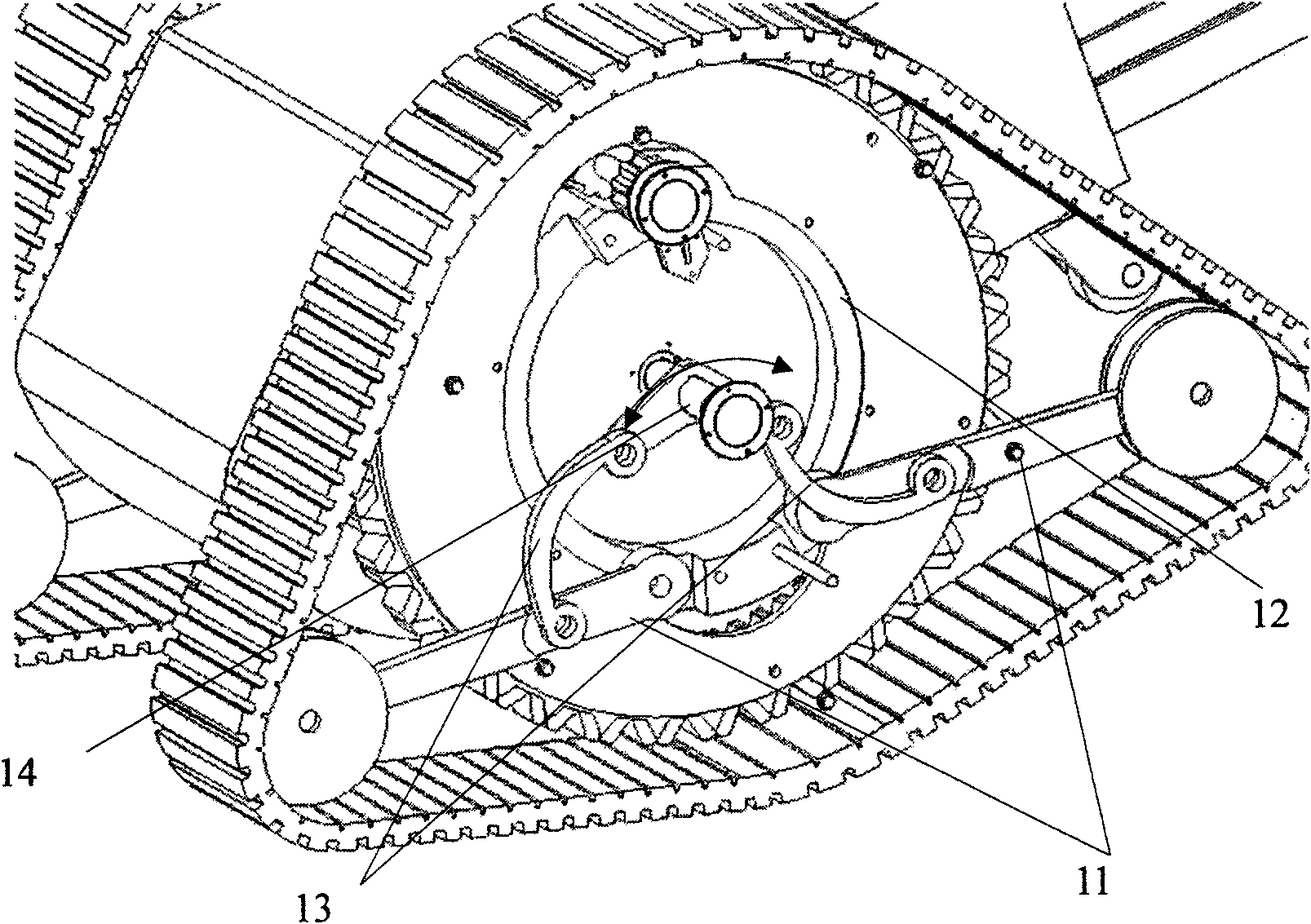
The invention discloses a wheel-foot combined obstacle detouring non-contact magnetic absorption type wall climbing robot system, belonging to the technical field of robots and comprising a robot frame, a 5-DOF (degree of freedom) robot arm, three groups of mobile absorption mechanisms, linear sliding rails, screws and drive motors, wherein the linear sliding rails, the screws and the drive motors respectively correspond to the three groups of mobile absorption mechanisms; the five-DOF robot arm is arranged above the robot frame; the three groups of linear sliding rails and screws are vertically arranged below the robot frame and two ends thereof are connected with the robot frame and the mobile absorption mechanism respectively; and the drive motor is fixedly connected with the mobile absorption mechanism. The invention solves the technical defects of the existing wall climbing robot in vertical wall surface operation, enables the robot to have the advantages of rapid speed and flexible steering of a wheeled mobile robot and have the characteristics of large magnetic absorption force and good load capacity as well as obstacle detouring capacity, and can satisfy the requirements of motion and operation in complicated environments.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Trajectory tracking sliding mode control system and control method for spraying mobile robot
InactiveCN103019239ANon-linearWith couplingPosition/course control in two dimensionsDrive motorAngular acceleration
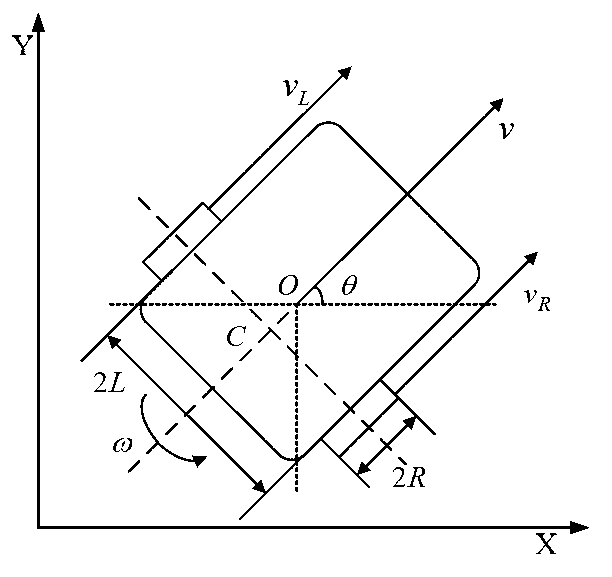
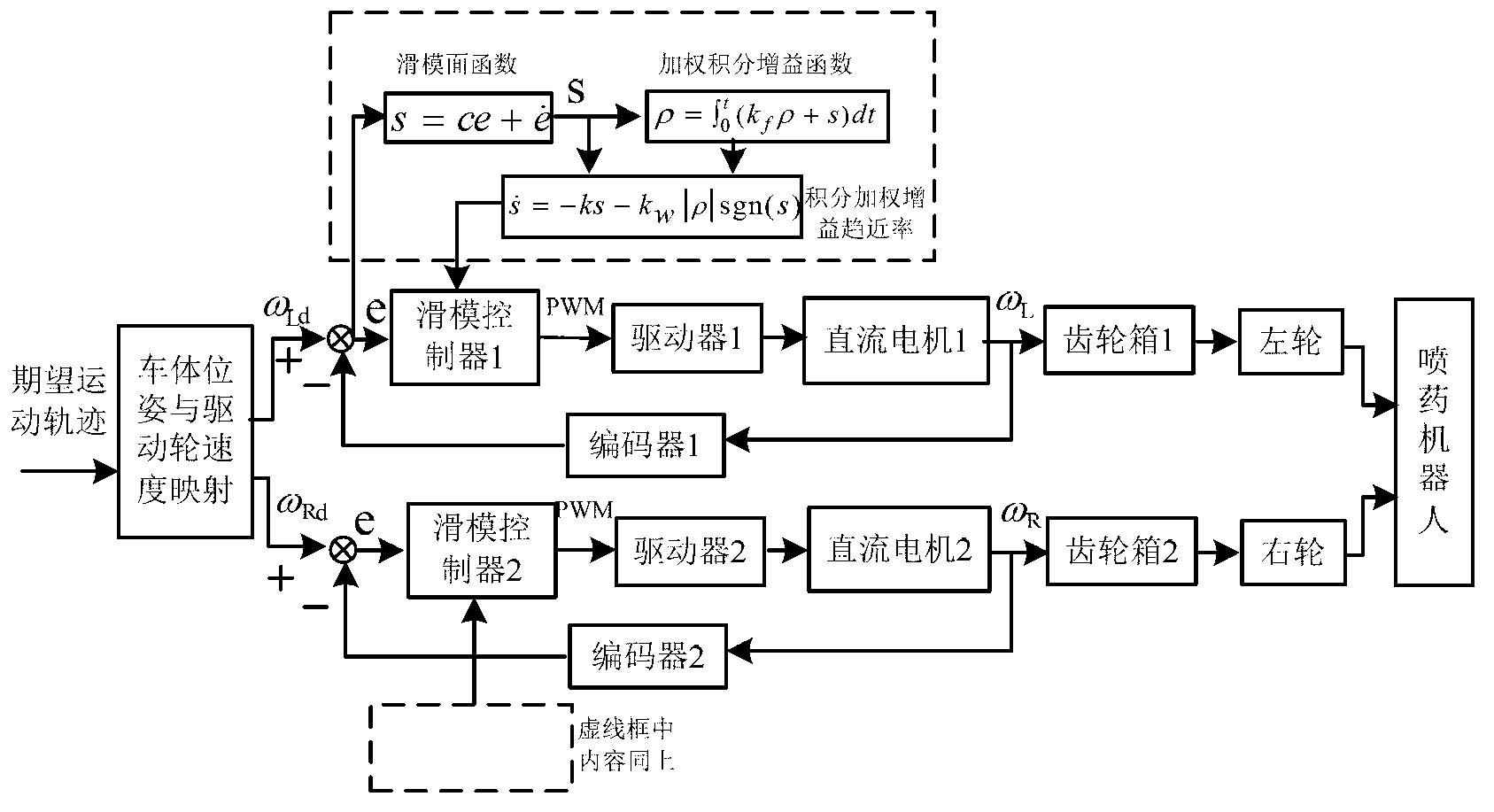
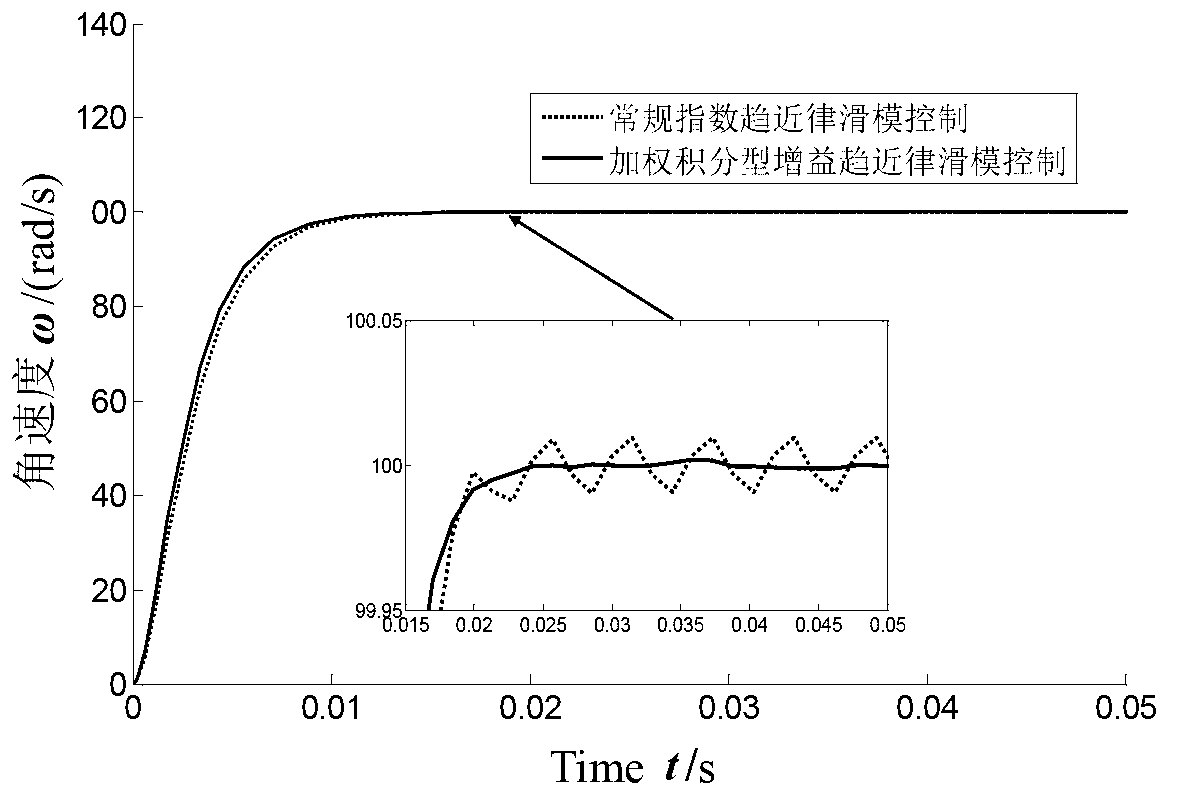
The invention discloses a trajectory tracking sliding mode control method for a spraying mobile robot. The method comprises the following steps of: performing mechanism analysis on a mobile robot, and establishing a mobile robot kinematic model with non-integrity constraint; establishing a controlled object mathematical model of each branch controller of a wheeled mobile robot provided with a motor driving shaft disturbance term; identifying a traveling path by utilizing a computer vision system, and determining an expected motion track of each branch driving motor according to the kinematic model deduced in the previous step; detecting the rotating speed of the motor, calculating the actual motion angular velocity and actual motion angular acceleration of left and right driving motors of the mobile robot, and calculating the deviation and deviation derivative between the expected angular velocity and the actual angular velocity of each driving motor; establishing a sliding mode switching function which meets the speed control requirement of the driving motor; determining the sliding mode controller control quantity of the left and right driving motors of the mobile robot on the basis of the sliding mode surface function s; and respectively transmitting the control quantity of the motor of the mobile robot to the left and right driving motors.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Mixed control method based on trace tracking of wheeled mobile robot
ActiveCN104317299AReduce the amount of controlGuaranteed stabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsKinematicsAngular velocity
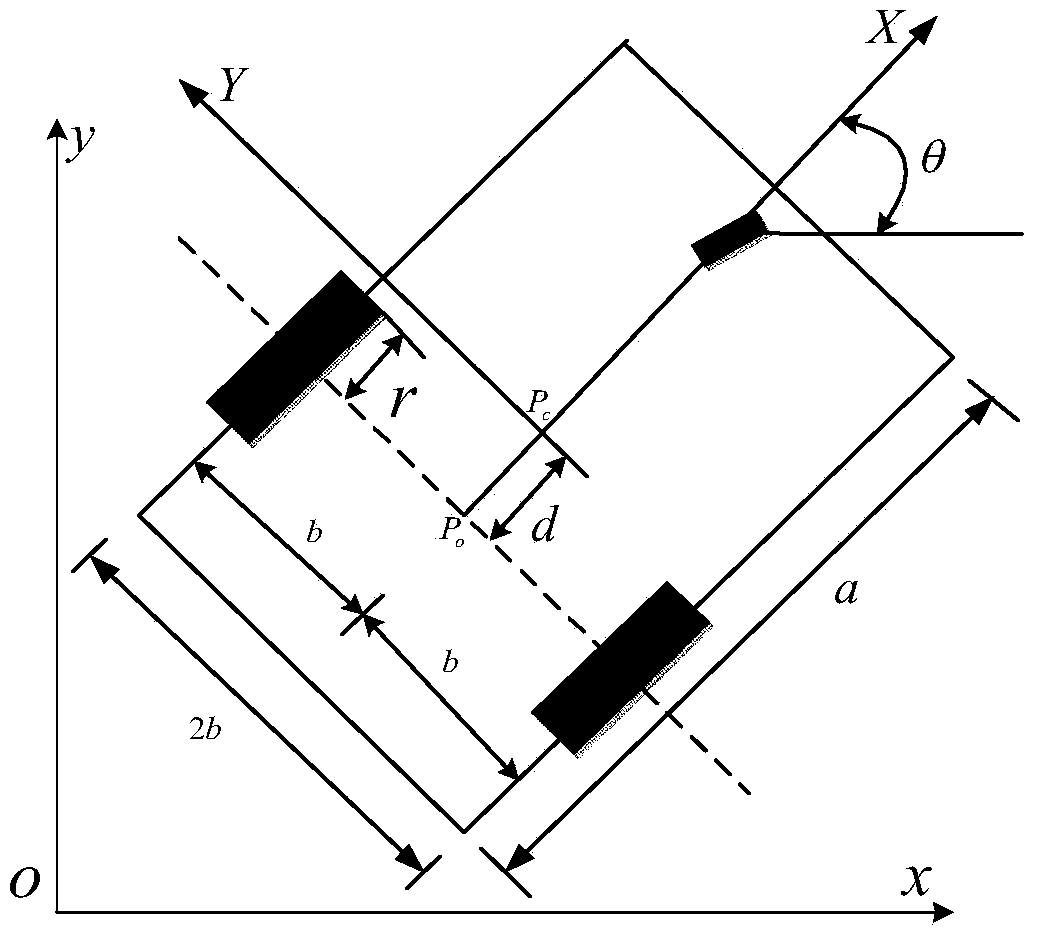
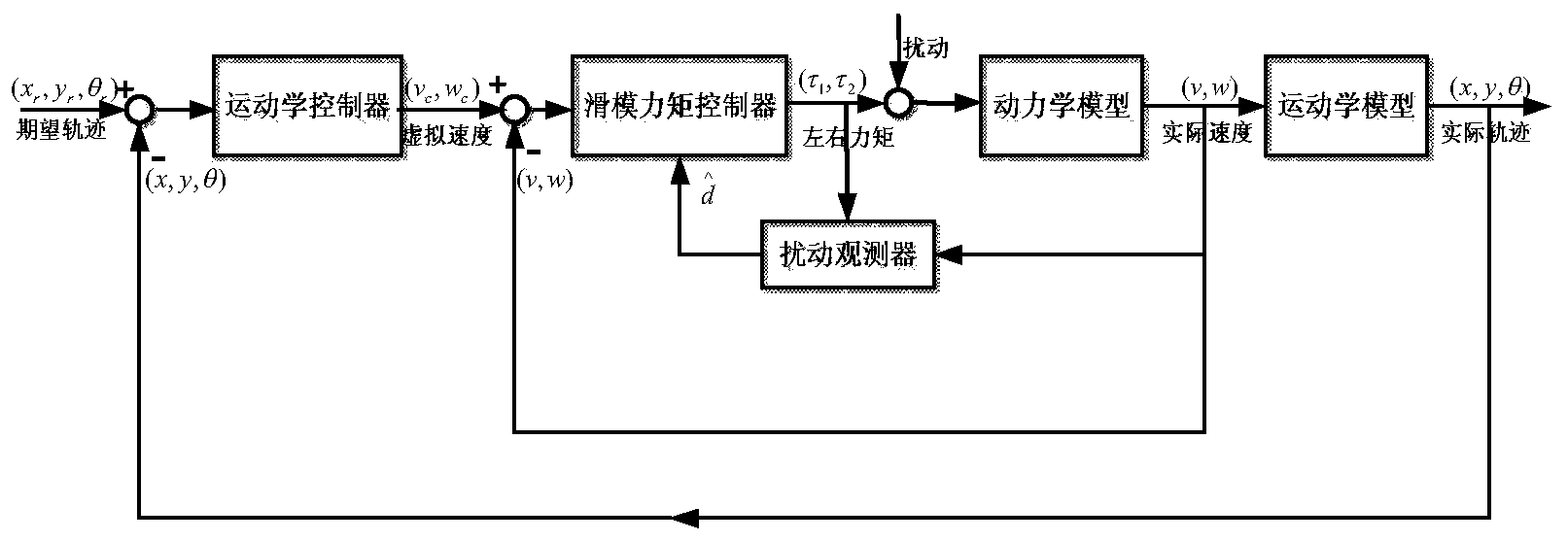
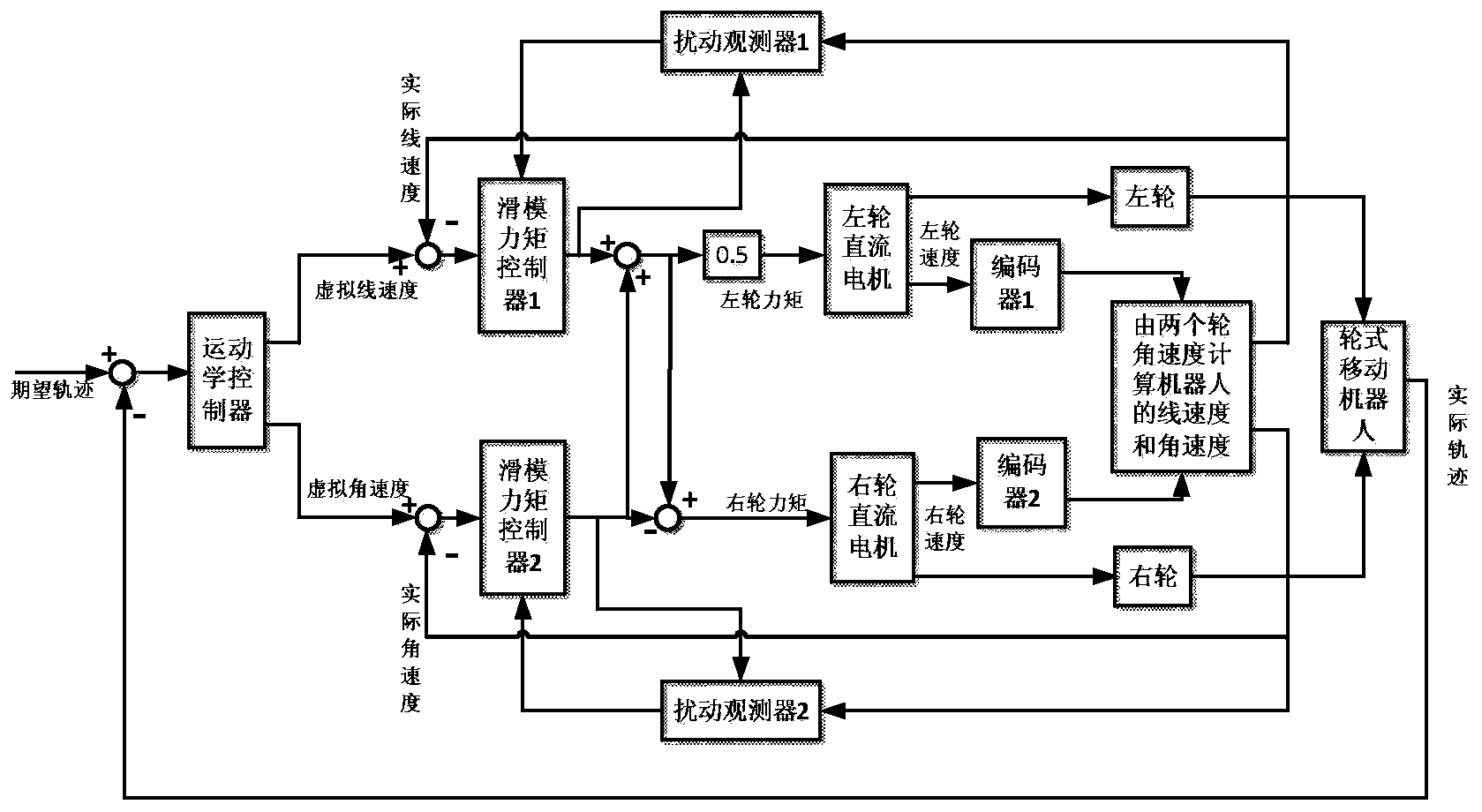
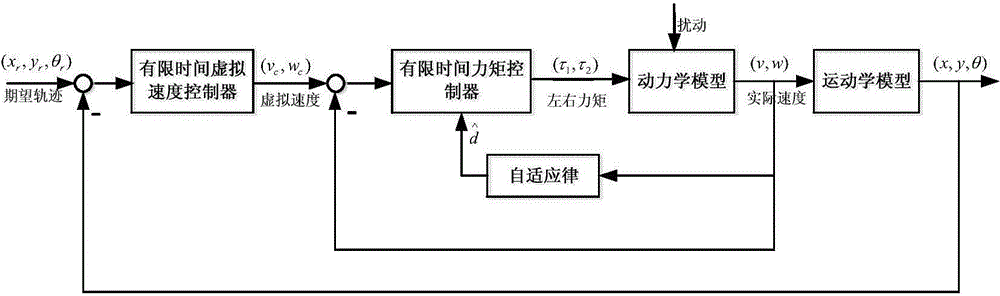
The invention discloses a mixed control method based on trace tracking of a wheeled mobile robot. A kinematic virtual velocity controller, a sliding mode torque controller and a disturbance observer are involved in the mixed control method, wherein the sliding mode torque controller and the disturbance observer are based on dynamics. The virtual velocity controller is used for designing the linear velocity and the angular velocity of the robot; the sliding mode torque controller is used for designing a sliding mode face and a sliding mode control law, and the disturbance observer is used for observation of the external disturbance of a system to reduce the control quantity of the sliding mode controller and is introduced as a feedforward term. By means of the mixed control method, control over the trace tracking of the robot is achieved by the system under the condition that external change and external disturbance happen to a parameter. It is shown upon simulation experiments that by means of the mixed control method, chatter output by sliding mode control and output of the control quantity can be effectively reduced, and good robustness is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Variable structure control method of wheeled mobile robot
InactiveCN102269995AImprove motion control performanceEnhance and improve motion control performancePosition/course control in two dimensionsMobile robot controlLinear motion
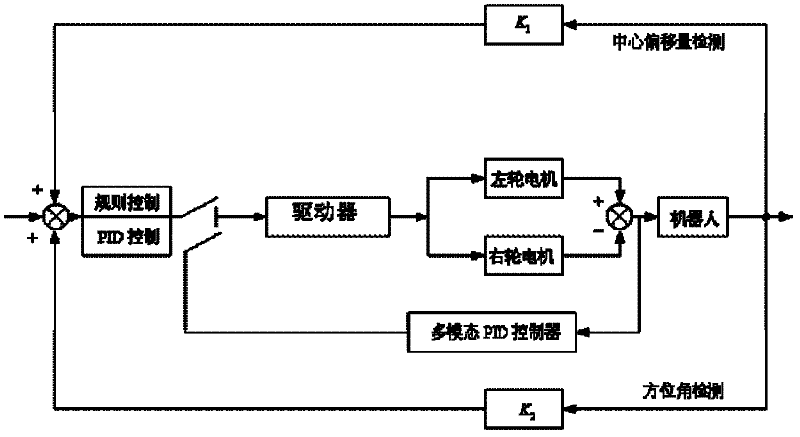
The invention discloses a variable structure control method of a wheeled mobile robot. according the method, the linear motion of a robot is controlled by using a multimodal PID (proportion integration differentiation) control method; and a forward direction of a trolley is corrected by using the combination of a control method and a PID control and a rule control; the two control modes are switched through the changes of a directional angle and a centre offset; the robot is controlled to turn in an in-situ right angle turning mode according to turning direction information and position information; by using the multimode PID control and the combination of the rule control and the PID control, the algorithm can use different control algorithms and corresponding control parameters according to different states of the robot to effectively improve the robot motion control performance; the control mode is divided according to the error change condition so as to reasonably simulate the control behavior of a human; compared with the traditional PID control method, the variable structure control method has a certain intelligence and improves the walking motion control quality of the robot.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Minitype wheel/caterpillar structure-variable mobile-search reconnaissance robot
InactiveCN101570216AReduce volumeSmall all-terrain abilityEndless track vehiclesMobile searchLocking mechanism
The invention relates to a minitype wheel / caterpillar structure-variable mobile-search reconnaissance robot, which mainly comprises a case, road wheels, an electric motor, an interconversion mechanism that can carry out mobile interconversion between the wheel type and caterpillar type, an elastic caterpillar, a running gear, a reconnaissance device, a mobile driving mechanism, a self-locking mechanism and a robot case, wherein, the rear part of the robot case is provided with a universal wheel, the robot case and the reconnaissance device are connected through a live shaft to form a robot. The robot has the characteristics of both the quick movement of a wheel type mobile robot and good through-obstacle capability of a caterpillar type mobile robot, namely that the robot adopts the wheel type movement to get fast-moving performance under good ground condition, and can change the motion mode of the motion mechanism into the caterpillar type movement that has favorable through-obstacle capability under poor ground conditions such as meeting with obstacles, stairway or non-hard road surface.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
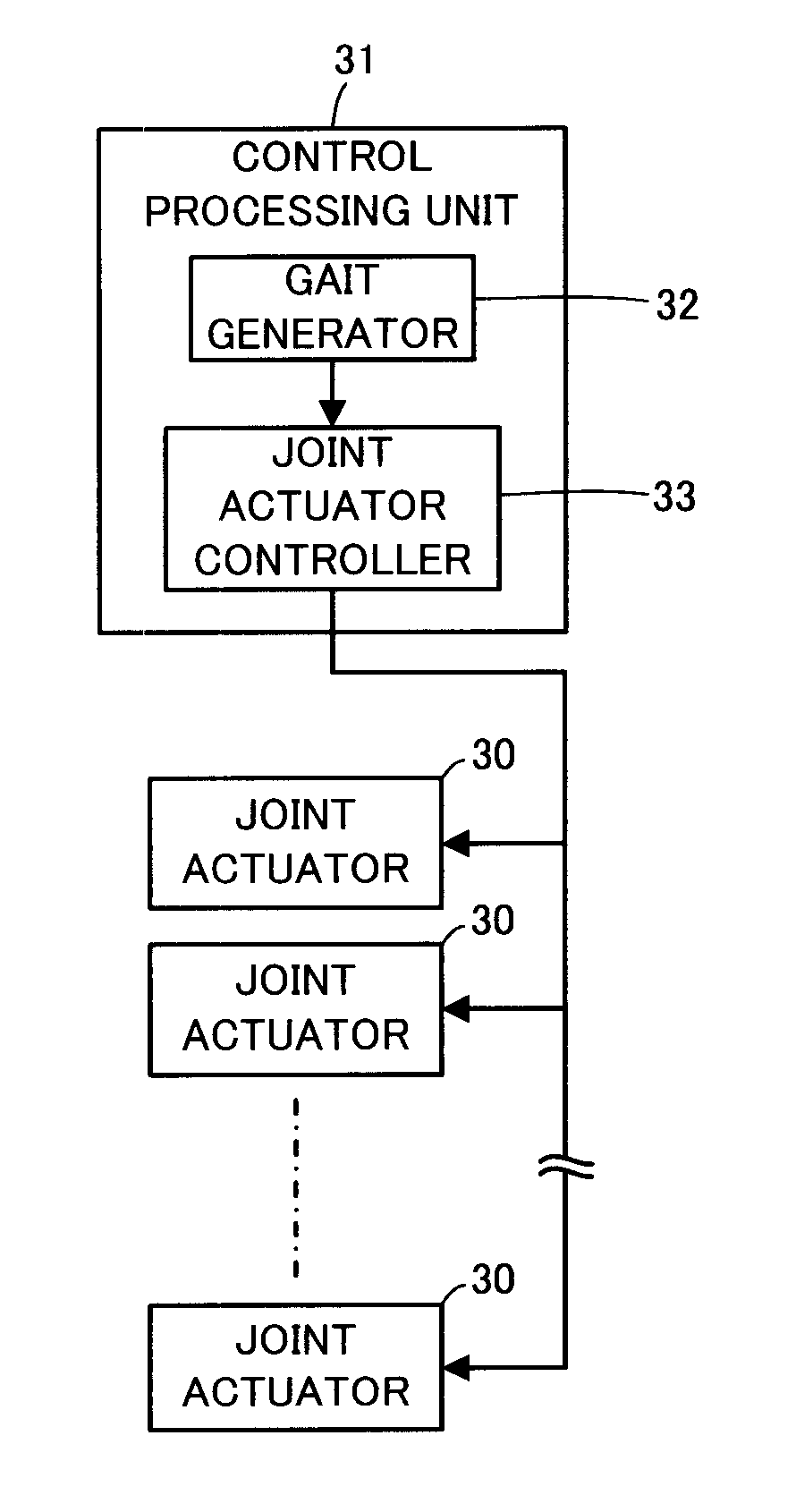
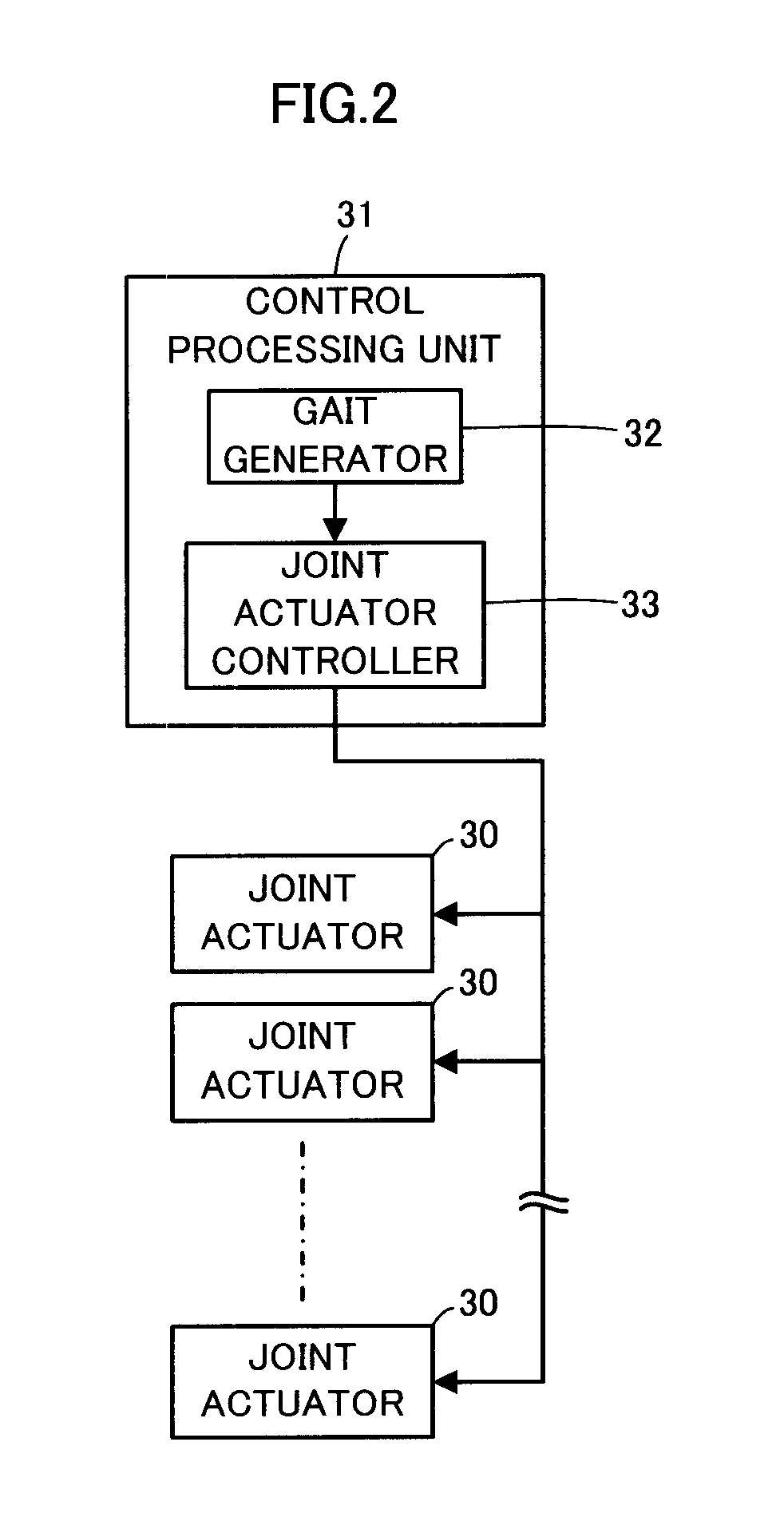
Control device for legged mobile robot
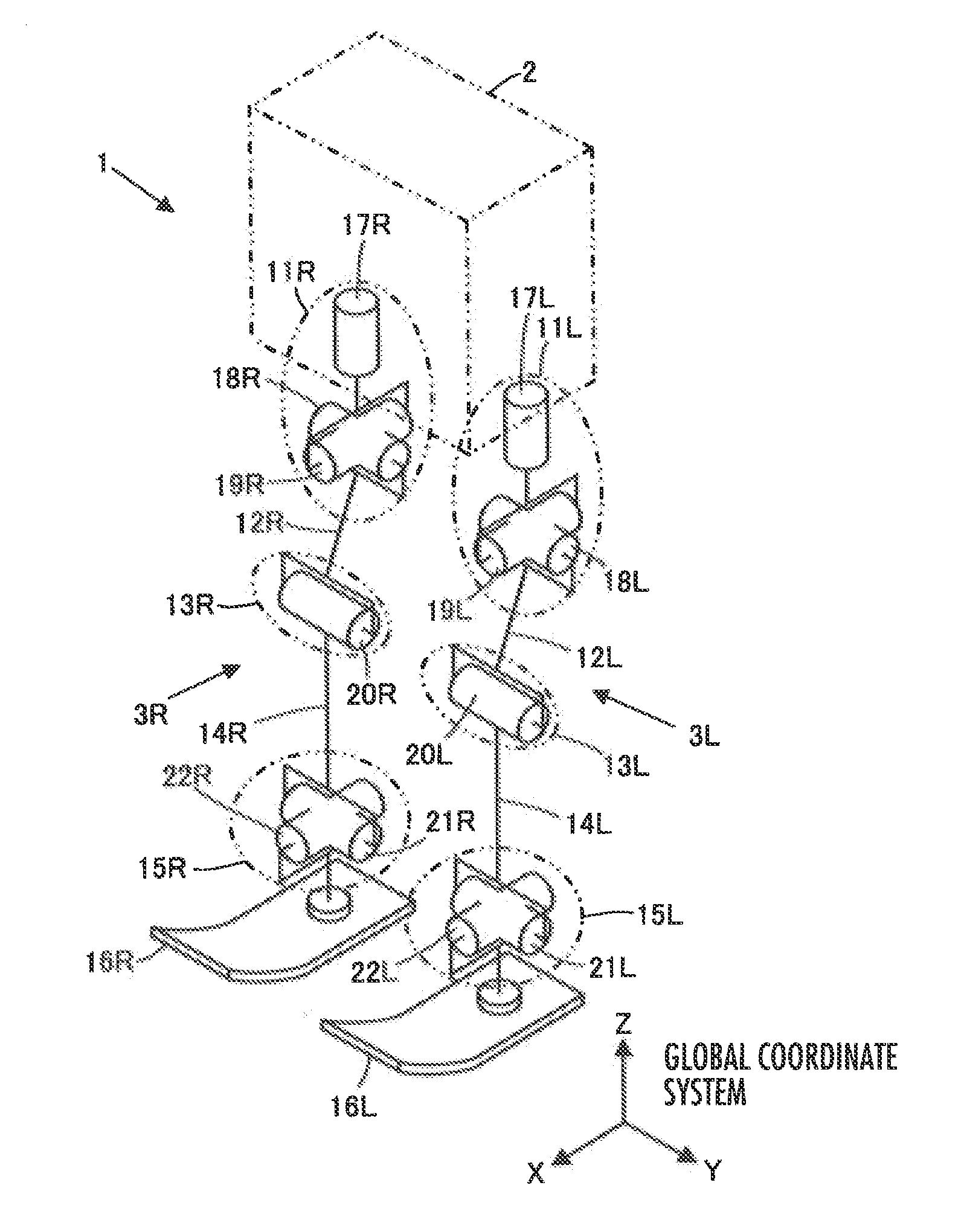
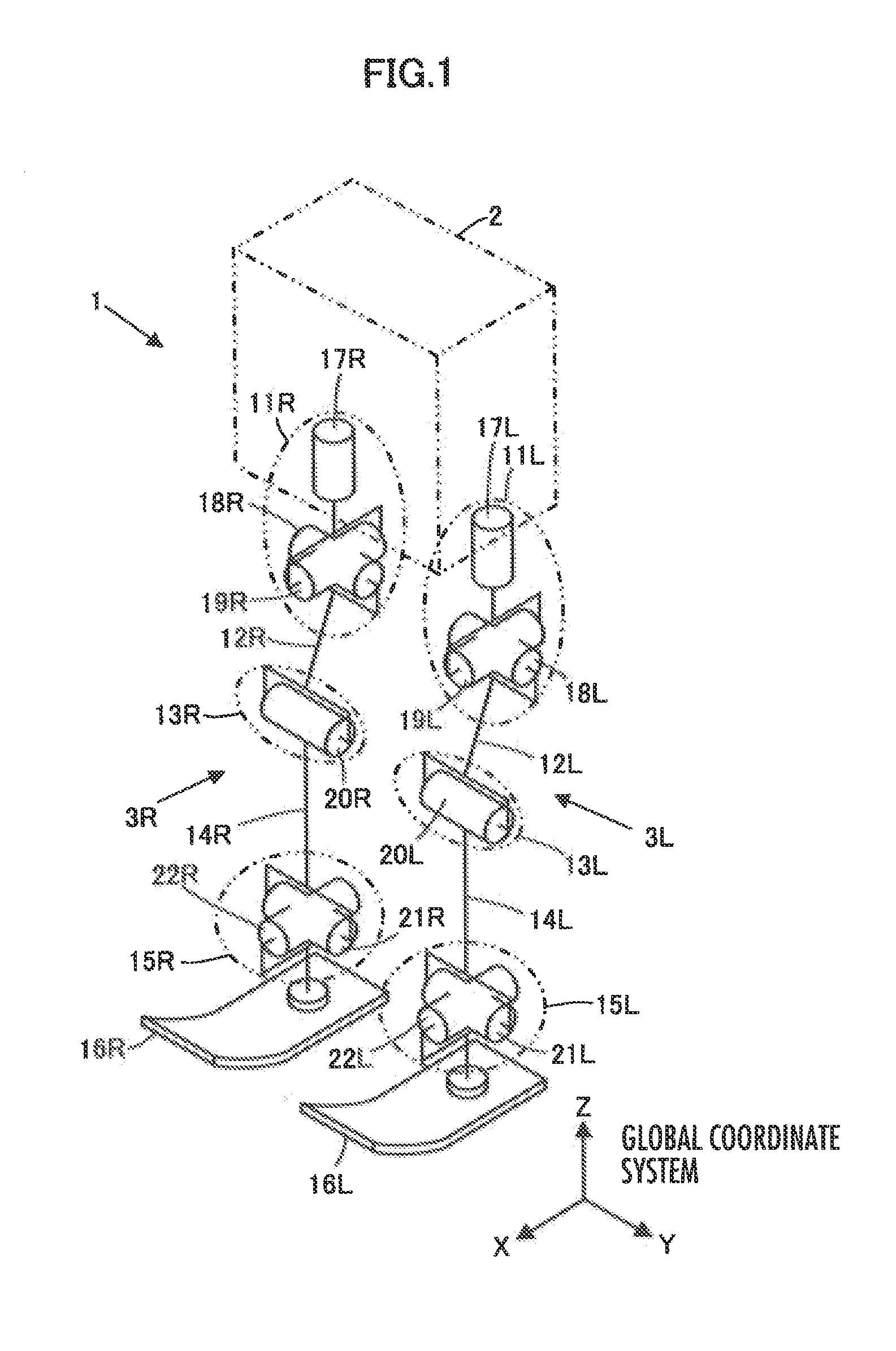
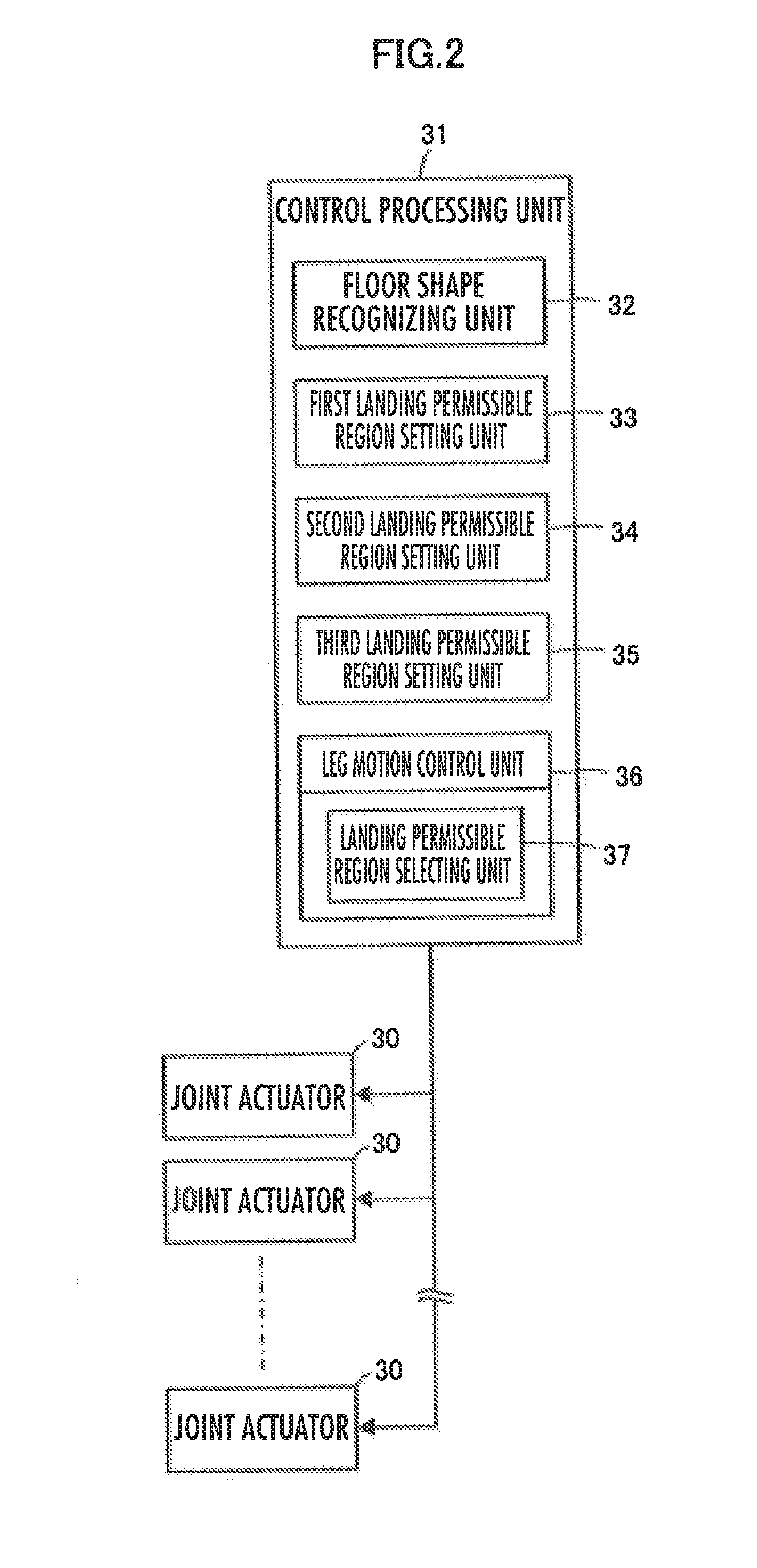
ActiveUS20150073592A1Increasing sizeIncreasing weightProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotMobile robot controlEngineering
A setting unit 33 configured to set a first landing permissible region in order to ground a free leg side foot 16 within an upper tread surface or a lower tread surface of a step existing ahead of a legged mobile robot 1 in a traveling direction, and a setting unit 34 configured to set a second landing permissible region in order to ground the free leg side foot 16 on an edge of the upper tread surface or the lower tread surface are provided to switch landing permissible regions for movement control of the robot 1 according to a step height.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Trajectory tracking control method for four-wheel-driven wheeled mobile robot
ActiveCN106125728AImprove stabilityImprove effectivenessAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsKinematic controllerBackstepping
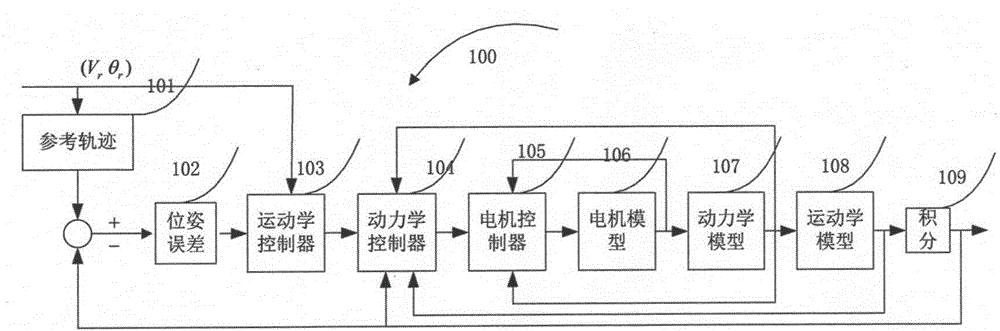
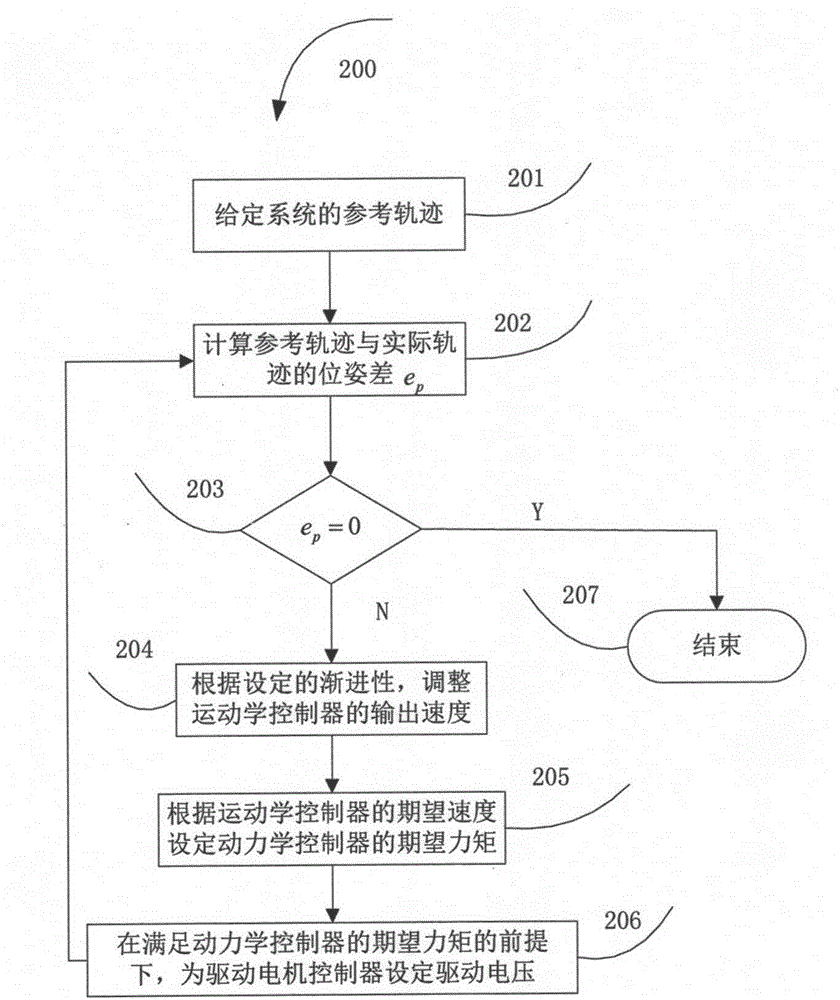
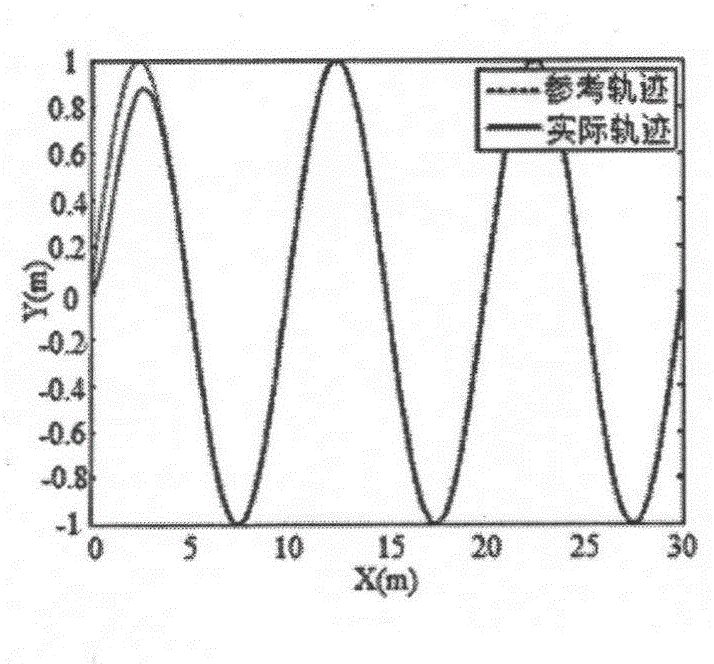
The invention provides a trajectory tracking method for a four-wheel-driven wheeled mobile robot. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a kinematic model, a dynamic model and a driving motor model of a system; then designing a kinematic controller for adjusting speed of the system according to a given reference trajectory based on the kinematic model; operating the kinematic controller for obtaining the anticipated torque of a motor according to the speed of a to-be-adjusted system based on the kinematic model; designing a driving motor controller for designing an appropriate driving voltage of the system for satisfying the anticipated torque of the motor based on the driving motor model; and finally performing trajectory tracking control on the four-wheel-driven wheeled mobile robot according to a backstepping robustness trajectory tracking control method. The trajectory tracking method according to the invention realizes a purpose of improving stability of a four-wheel-driven wheeled mobile robot control system in a complicated uncertain environment and furthermore improves system controlling effectiveness on the condition with uncertain factors.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
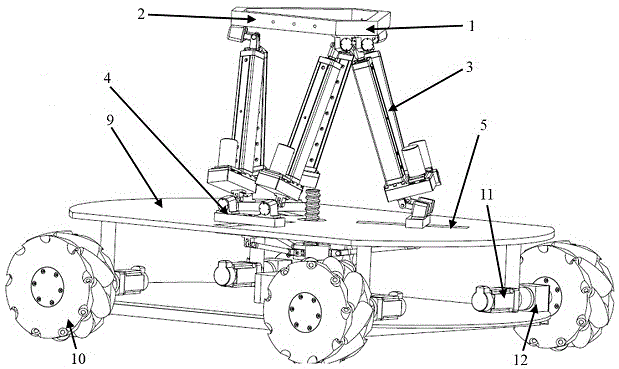
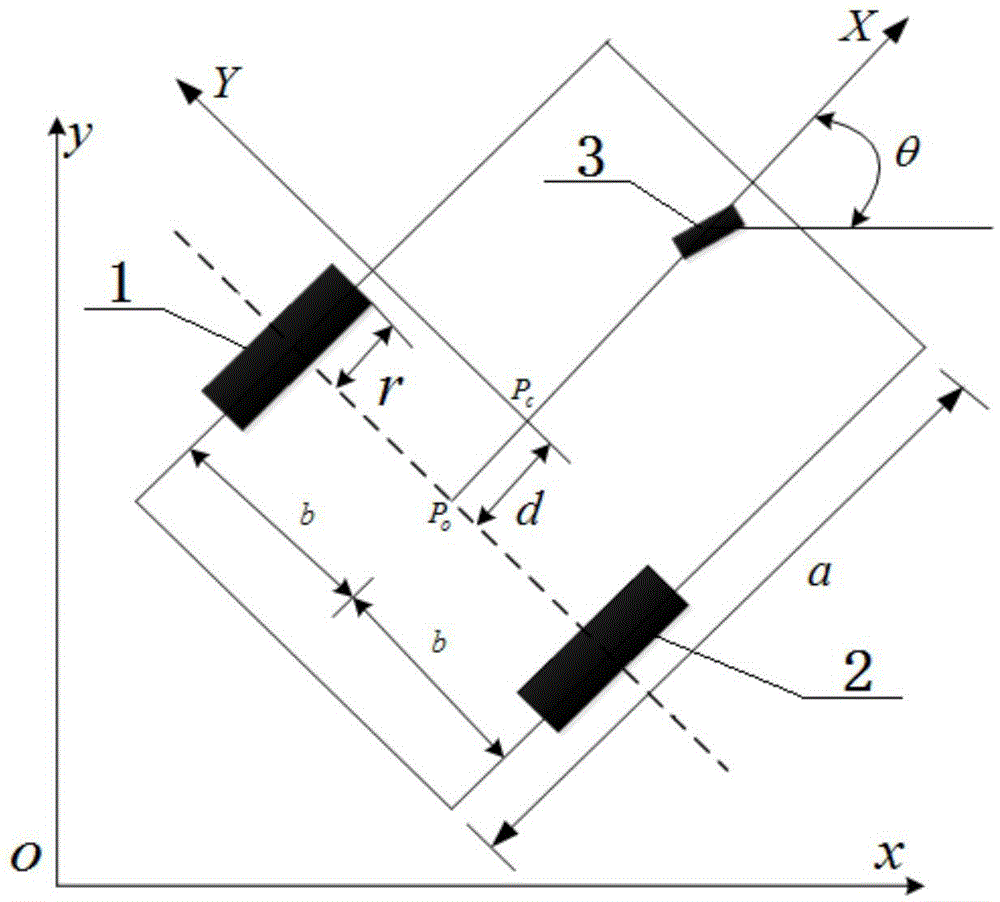
Structural dimension parameter adjustable Mecanum wheel type mobile robot
The invention discloses a structural dimension parameter adjustable Mecanum wheel type mobile robot. The robot is composed of a structural dimension parameter adjustable Stewart platform and a Mecanum wheel type mobile platform, wherein the Stewart platform comprises a Stewart movable platform, a Stewart static platform and a linkage mechanism. The Stewart platform is a parallel robot which has six freedom degrees and is applicable to heavy load; the Mecanum wheel type mobile platform has the characteristics of heavy load and all-direction movement; a mobile parallel robot formed by combination of the Mecanum wheel type mobile platform and the Stewart platform has the characteristics of being movable in all directions, high in positioning precision, capable of being heavily loaded and flexible in adjustment of tail end posture, and is applicable to industrial demands of flexible processing, overloading transportation and the like. By respectively changing the structural dimension parameters of the Stewart movable platform and the Stewart static platform, the robot disclosed by the invention is correspondingly changed in overall height, tail end motion space range and bearing capacity so as to adapt to work demands, so the applicability of the Mecanum wheel type mobile parallel robot is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Movement subdivision control method of wheeled mobile robot
InactiveCN103926839AEasy to controlMeet various application needsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsSimulation
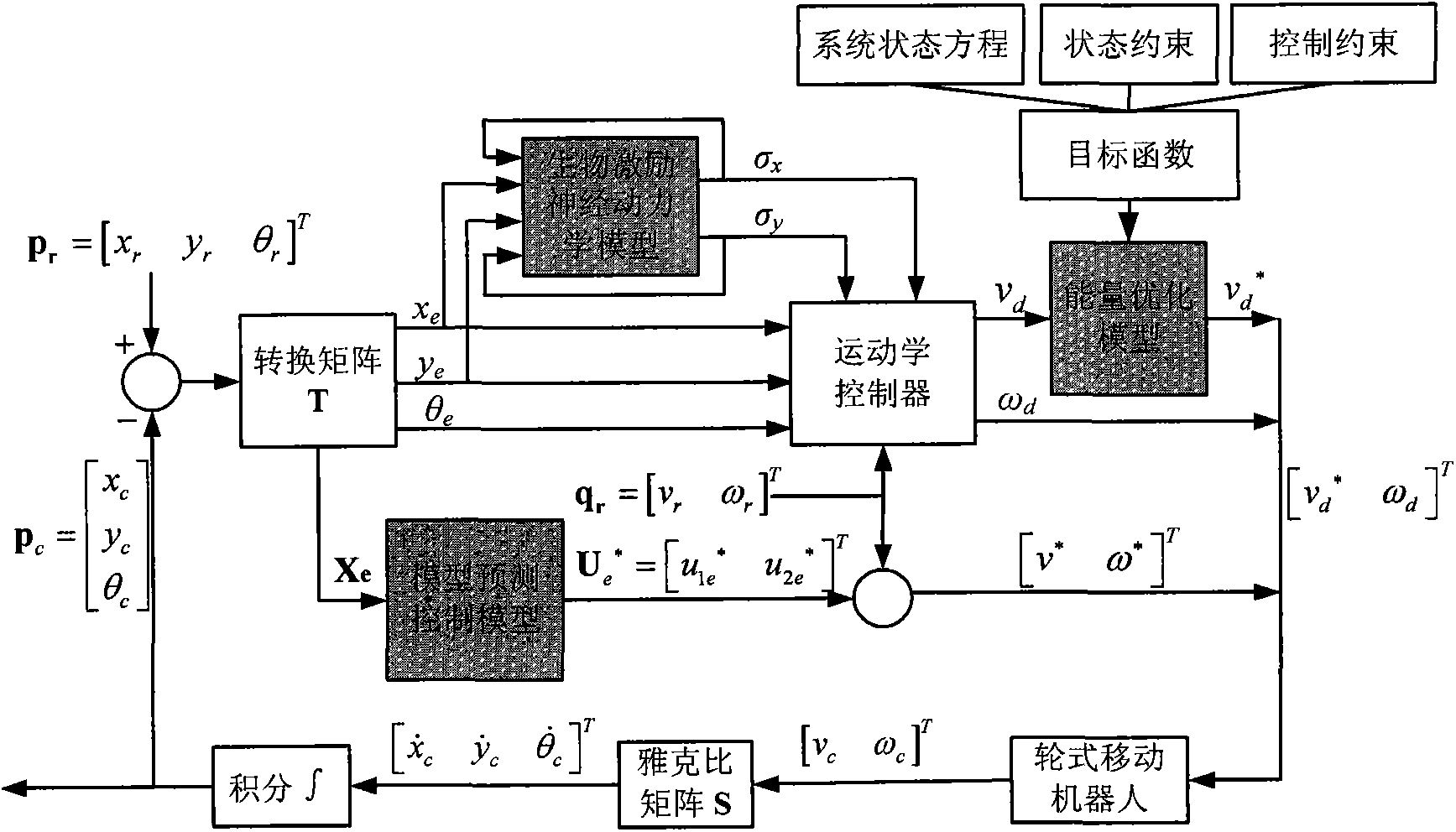
The invention discloses a movement subdivision control method of a wheeled mobile robot. The movement subdivision control method of the wheeled mobile robot comprises the steps that (1) three trajectory tracking movement control strategies based on a biologically inspired neural dynamic model, an energy optimization model and a model predictive control model are integrated; (2) a current posture error vector is worked out according to a current actual posture obtained through feedback and a reference posture given by a route planning algorithm; (3) the control strategy is selected according to the stage where the mobile robot is located, if it is in an early tracking period, the trajectory tracking movement control strategy based on the biologically inspired neural dynamic model is selected; if it is in a medium tracking period, the trajectory tracking movement control strategy based on the energy optimization model is selected; if it is in a later tracking period, the trajectory tracking movement control strategy based on the model predictive control model is selected. The movement subdivision control method of the wheeled mobile robot can achieve the best control over the whole process of the wheeled mobile robot, and achieve robustness, energy saving performance and stability while carrying out accurate trajectory tracking.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Wheel type moving robot track tracking method based on fast terminal sliding mode
ActiveCN104932506AEasy to trackImprove robustnessPosition/course control in two dimensionsTracking modelAngular velocity
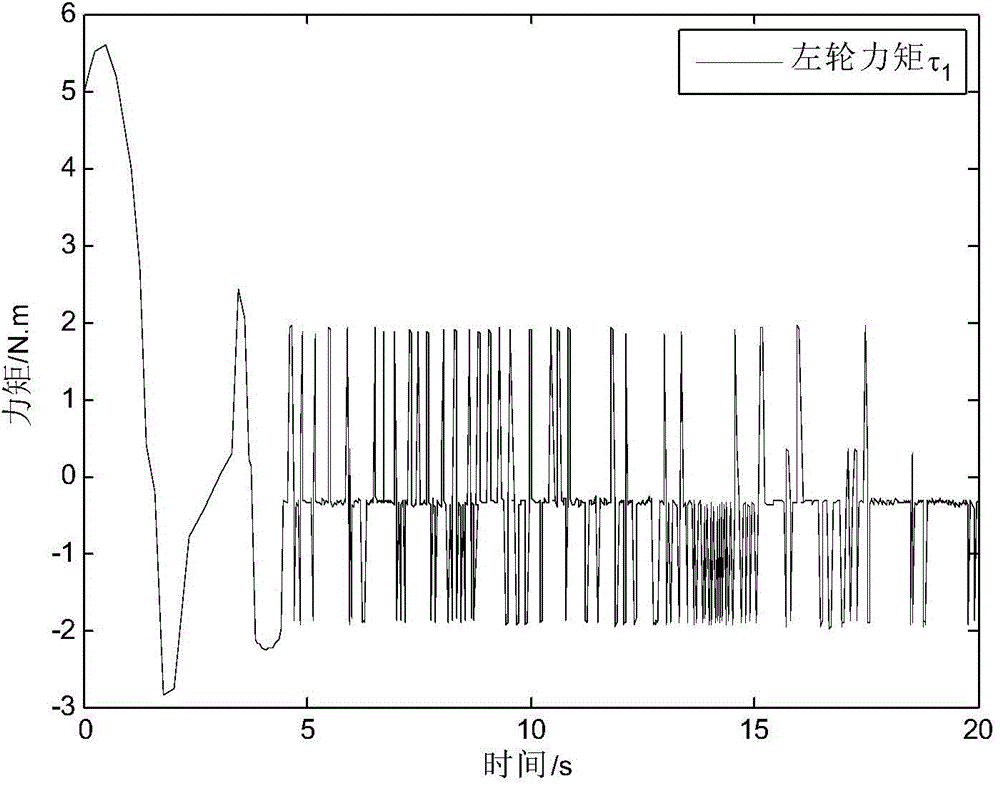
The invention discloses a wheel type moving robot track tracking method based on a fast terminal sliding mode. The wheel type moving robot track tracking method comprises steps of (1) establishing a kinematic model of the wheel type moving robot and an expectation track model and establishing an error model according to the kinematic model and the expectation track model, (2) introducing an appropriate sliding mode surfaces s1, s2, designing a virtual feedback amount according to the error model <~ > theta e<->, (3) obtaining a linear speed deviation signal <~ > Upsilon and a angular velocity deviation signal <~ >Omega, (4) constructing the wheel type moving robot kinematic model and substituting the linear speed deviation signal <~ > Upsilon and the angular velocity deviation signal <~ >Omega into the kinematic model, and designing a left-and-right-wheel torque controller Tau, an unknown parameter estimator <^>Phi and an external interference disturbance estimator. The wheel type moving robot track tracking method based on a fast terminal sliding mode can track the expectation track in the limited time under the disturbance complicated working condition of the unknown parameters and the external disturbance, has a good tracking effect and has a strong robustness for the unknown parameters and the external disturbance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
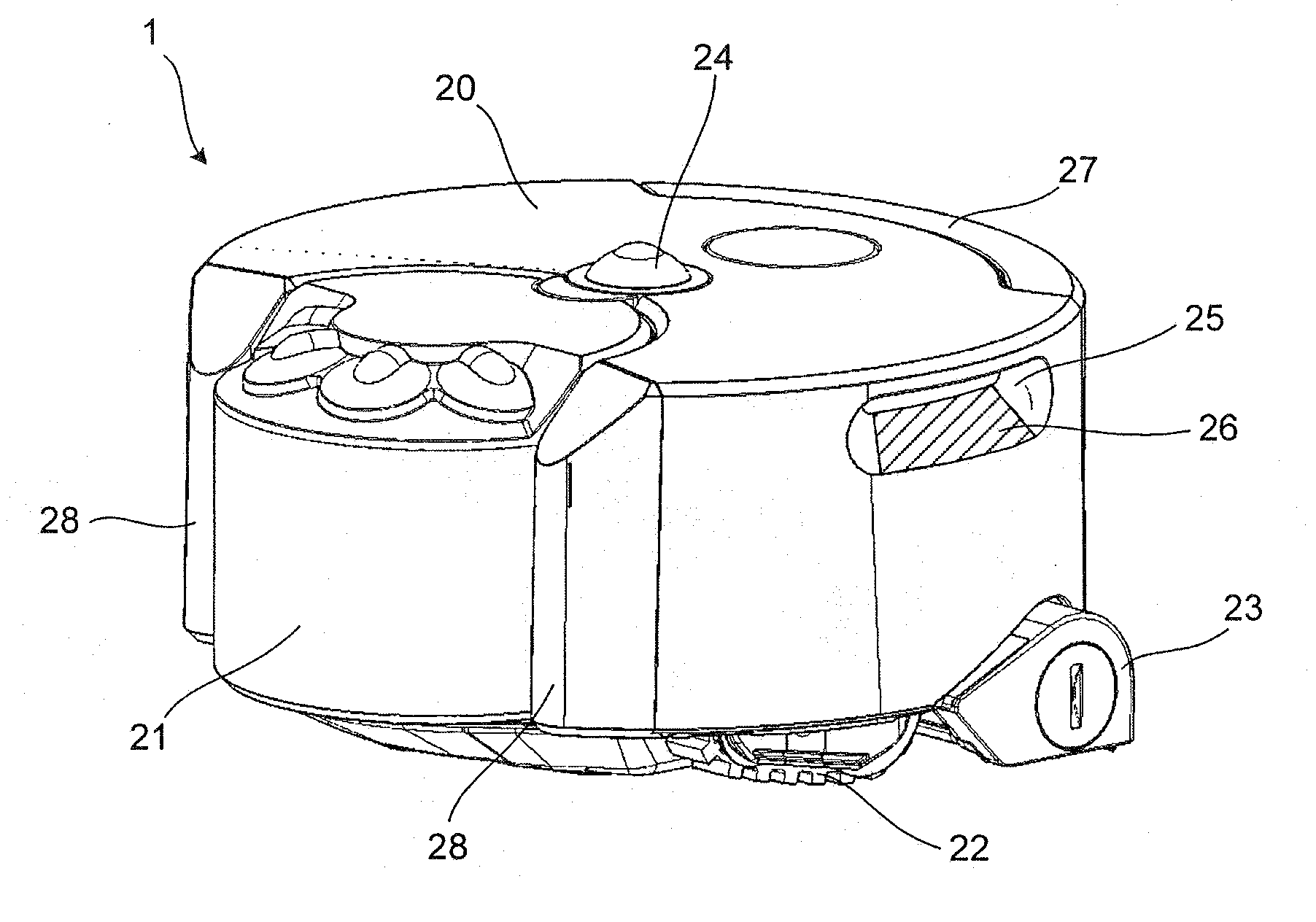
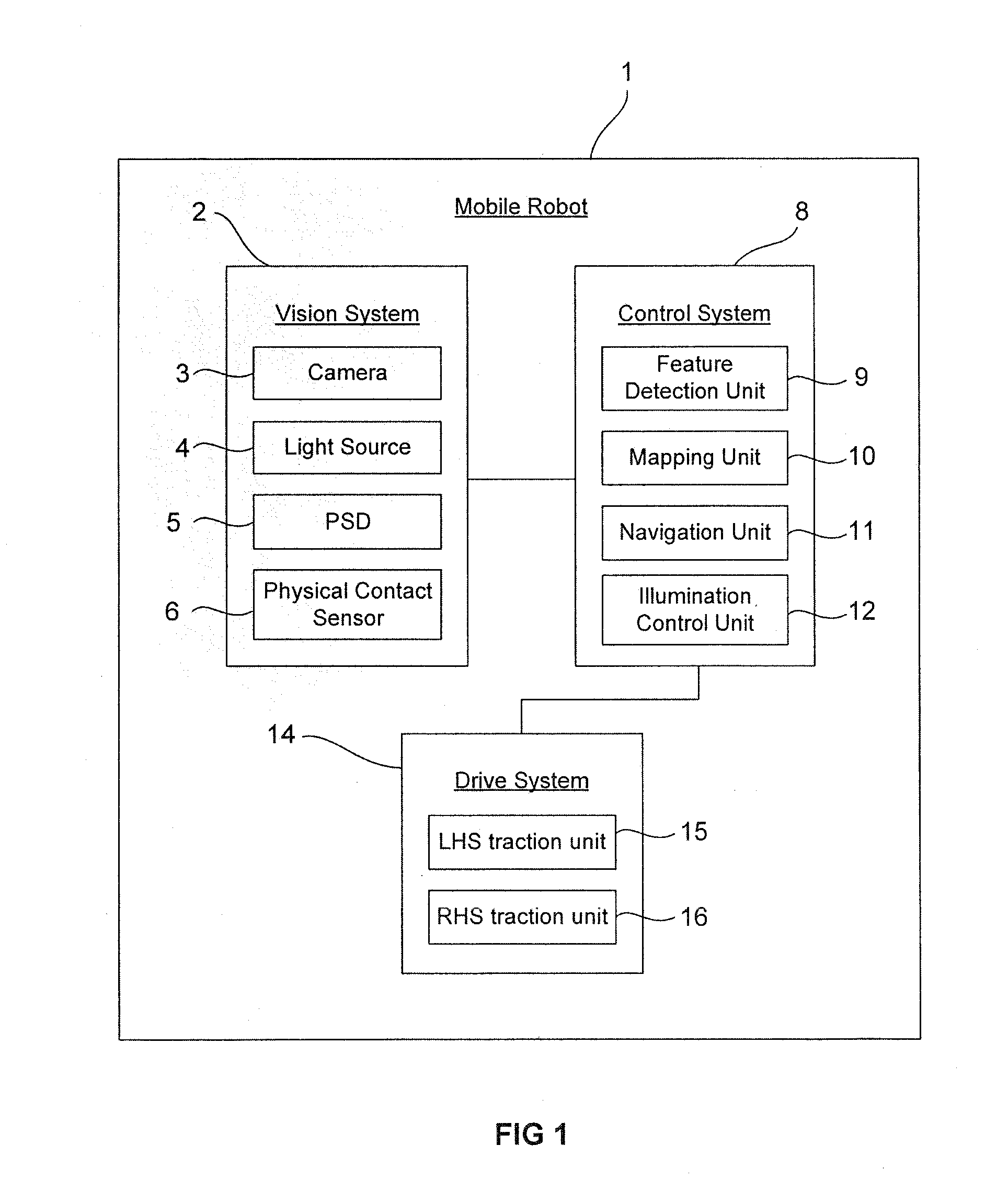
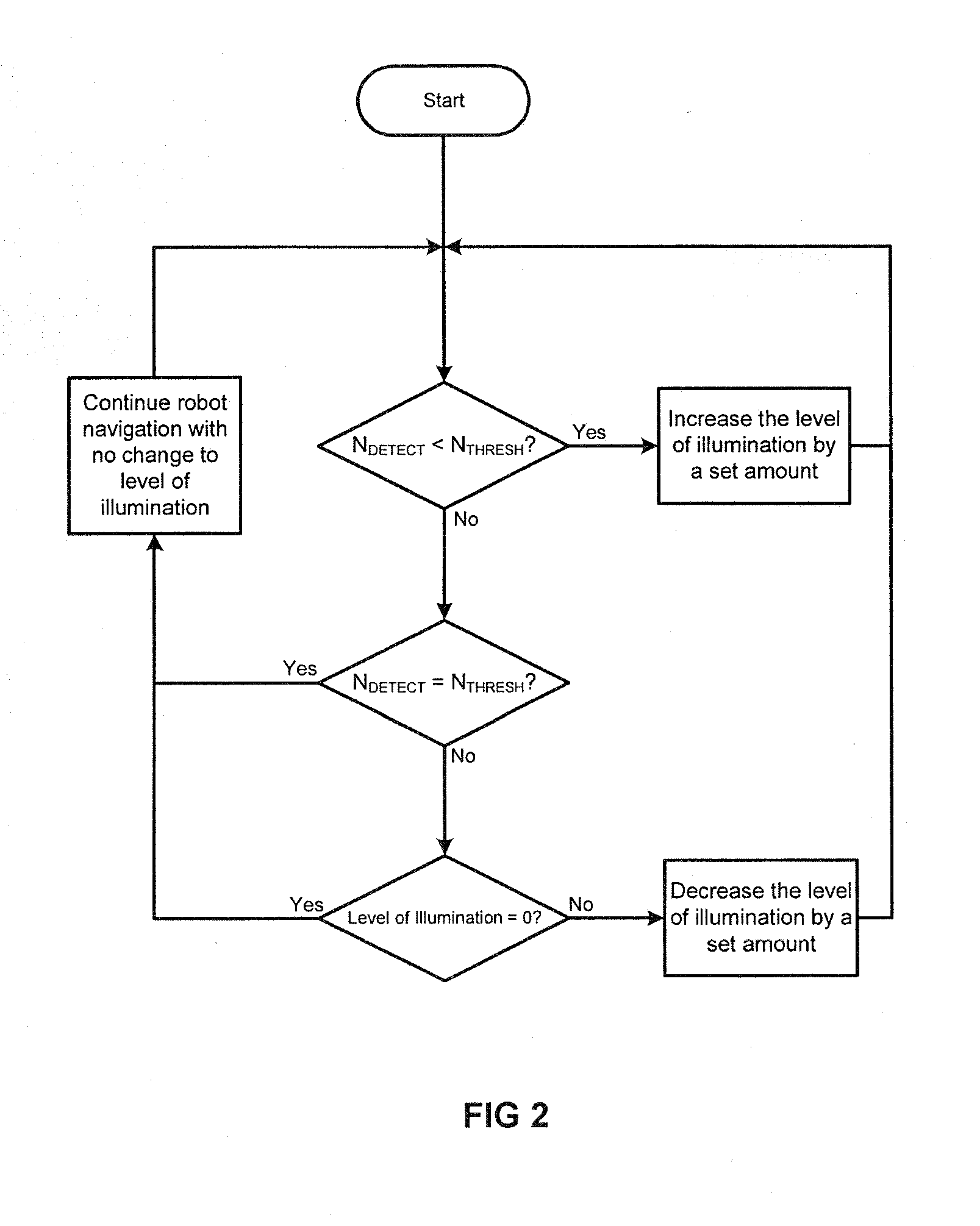
Mobile robot
InactiveUS20160059770A1Extend battery lifeReducing power providedProgramme-controlled manipulatorTelevision system detailsEngineeringImage capture
A mobile robot comprising: a vision system, the vision system comprising a camera and two or more light sources each arranged to provide a level of illumination to an area surrounding the mobile robot; wherein the two or more light sources are arranged to illuminate separate areas surrounding the robot corresponding to different sections of an image captured by the camera, and the level of illumination provided by each of the light sources is independently adjustable.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
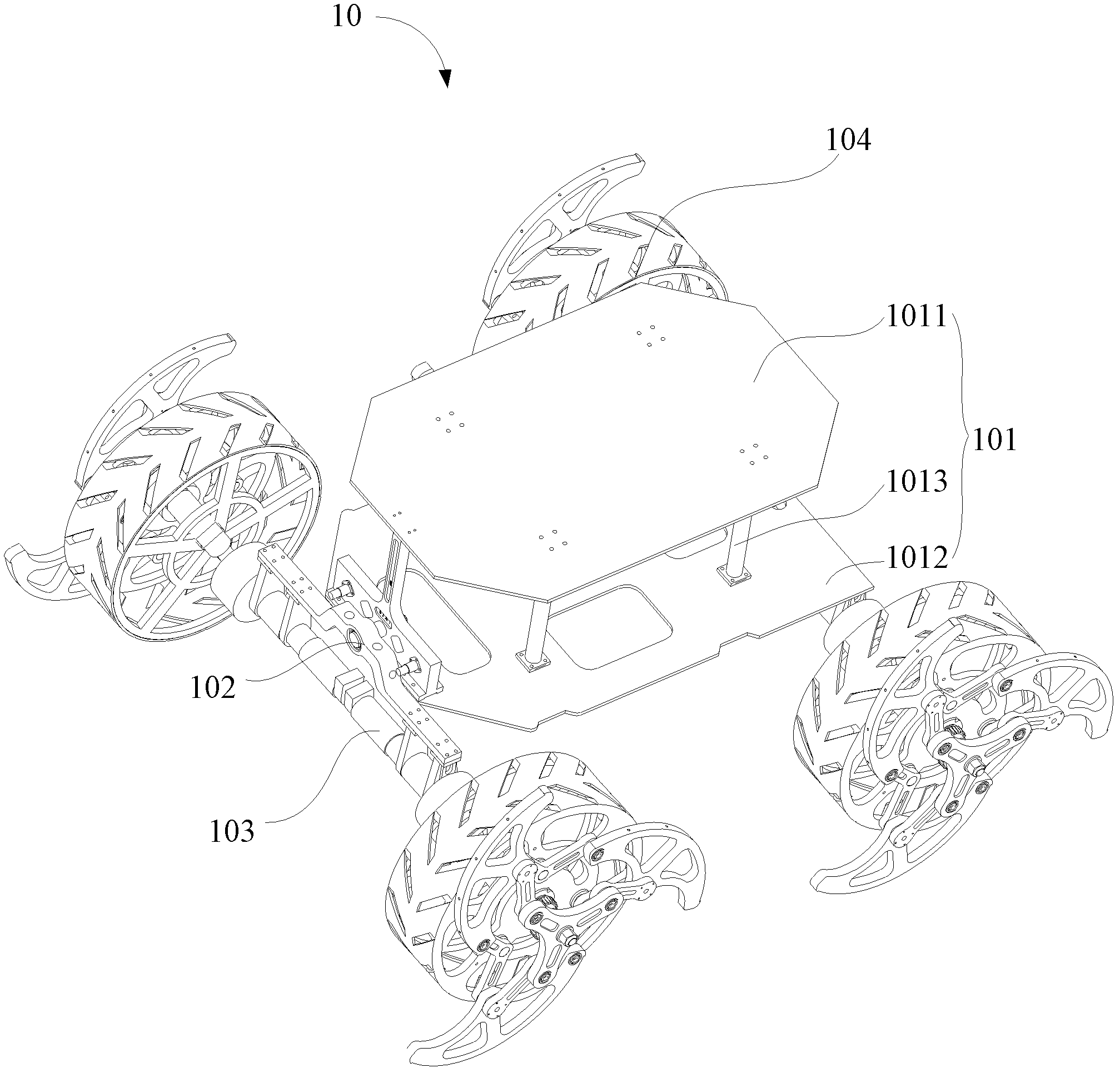
Extendable wheeled mobile robot
The invention relates to an extendable wheeled mobile robot. The robot comprises a frame, a swing suspension component which can swing relative to the frame, four driving shaft components which are connected to two ends of the swing suspension component in a rotatable mode, and four wheel groups which are fixedly connected to the four driving shaft components and can rotate relative to the frame,wherein each wheel group comprises a cylindrical normal wheel, three extendable wheel rims, three binary rods and a driving piece; each extendable wheel rim is bow-shaped and is provided with two bearing holes; the three binary rods are arranged around the axis of the normal wheel; each binary rod is provided with two free ends and a bending part; the bending part is connected to the outer side of the normal wheel in the rotatable mode; the two free ends of each binary rod are connected with the middle bearing hole of one extendable wheel rim and the edge bearing hole of the adjacent wheel rim in the rotatable mode; and the driving piece drives the three binary rods to rotate around the centers of the respective bending parts. The extendable wheeled mobile robot has high obstacle-surmounting capability.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intelligent autonomous wheel type mobile robot
InactiveCN1513645AWith voice human-computer interaction functionManipulatorVision sensorHuman–computer interaction
An autonomous wheel type movable intelligent robot with such functions as dynamic target tracking, target recognization, and man-machine interaction by speed is composed of the camera for providing ambient information, industrial control computer able to communicate via CAN bus to motor driver / controller, ultrasonic ring and infrared ring, and the moving mechanism controlled by motor driver / controller. The ultrasonic, infrared and visual sensors are used.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-joint series wheeled mobile robot
InactiveCN101973028AGuaranteed work efficiencyThe control system is stableProgramme-controlled manipulatorArmsControl systemEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-joint series wheeled mobile robot. A middle box body is arranged on a middle axle of the robot, a control system is arranged above the middle box body, a pitching joint is fixed in the middle box body, each pitching joint is symmetrical to the middle axle and is respectively connected with a torsion joint, each torsion joint is respectively connected with a swinging joint which is respectively connected with a front axle and a rear axle, both ends of the front axle, the rear axle and the rear axle are provided with wheels, the torsion joint of the rear end is connected with a mechanical arm installing bracket, a mechanical arm is arranged on the mechanical arm installing bracket, and the front part of the robot is provided with a navigation system. The whole structure of the robot is in central axis symmetry by taking the middle axle as a symmetrical central axis. The gravity is evenly distributed on the wheels to furthest exert the work efficiency of a direct current motor. The multi-joint series wheeled mobile robot can measure and regulate the posture of the middle box body in real time, ensures the relative stabilization of the control system and has simple structure and light weight.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
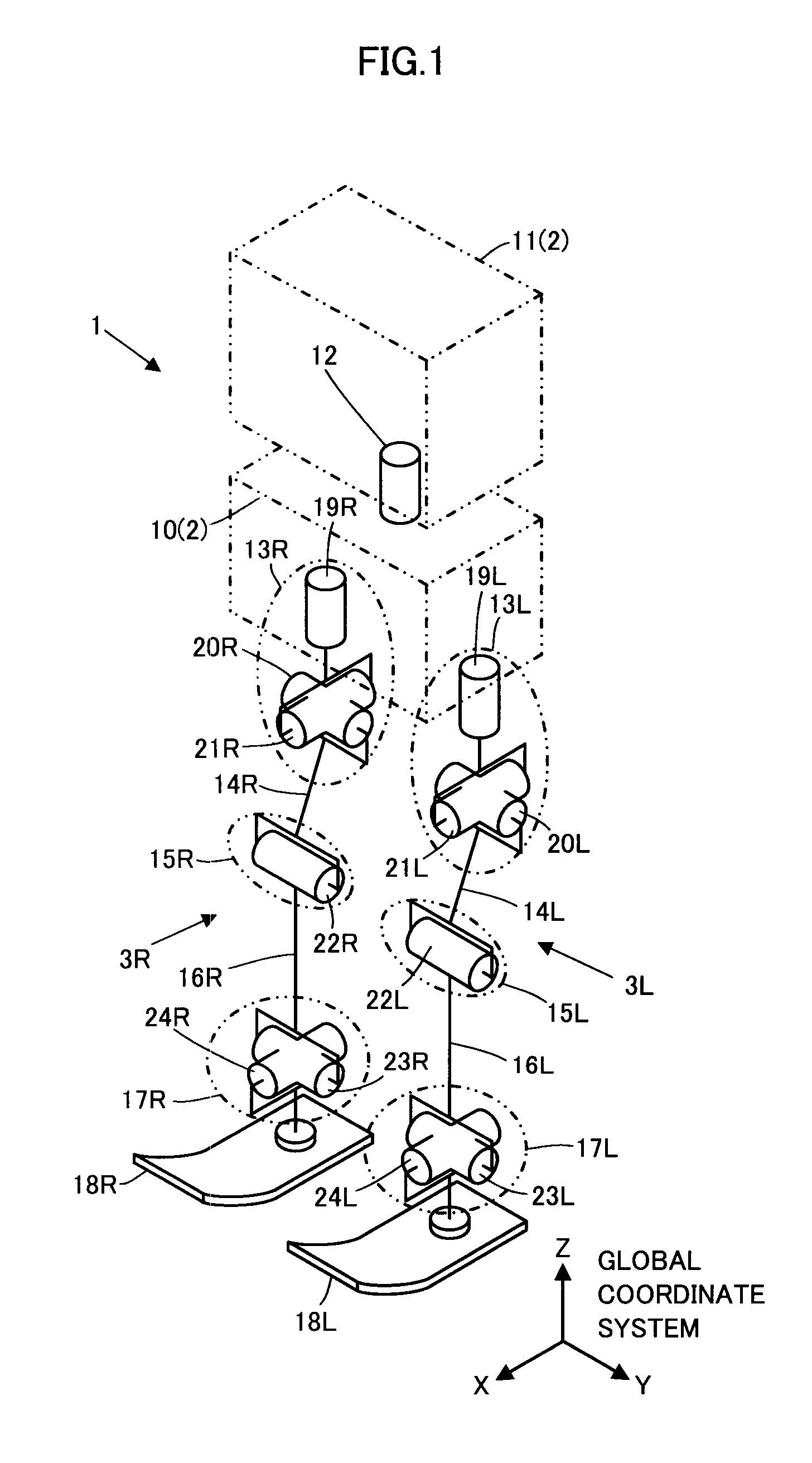
Gait generating device for legged mobile robot and operational target generating device for robot
ActiveUS20130144441A1Minimizes valueProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDistal portionEngineering
A gait generating device 32 includes a desired particular-site motion velocity value determining unit 45 that uses a quadratic evaluation function having a particular-site motion velocity vector ↑Vb as a variable and a linear matrix inequality having ↑Vb as a variable to sequentially determine, as a desired value ↑Vb_cmd2 of ↑Vb, a value of ↑Vb that can minimize the value of the evaluation function within a range in which a restriction condition that the linear matrix inequality holds is satisfied, by arithmetic processing according to a solution method for a quadratic programming problem. The device then integrates ↑Vb_cmd2 to sequentially determine desired values of the position and posture of the particular site (the body) 2 of the robot 1. The linear matrix inequality is set to satisfy a condition restricting the operations of the joints between the particular site 2 and the distal portion of each leg link 3.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Shrimp-shaped six-wheel mobile robot
InactiveCN101380978AAutomatically overcome obstaclesRealize the use of turningVehiclesShrimpGyration
The invention relates to a shrimp-shaped six-wheeled moving robot which can fit for complex road conditions automatically, has stronger capacity for crossing obstacle and belongs to the mechanical field. The shrimp-shaped six-wheeled moving robot consists of a head part, an abdomen part, lateral wings and a tail part, and the shape likes a shrimp; the head part is articulated with the front wall of the abdomen part; the left lateral wing and the right lateral wing are respectively articulated with the left side and the right side of the abdomen part; the tail part is articulated with the back wall of the abdomen part; the head part is a four bar mechanism; the end of a connecting rod is equipped with a wheel which is driven by a drive motor and realizes the turning by a turning motor; each lateral wing is a parallelogram mechanism, and each parallelogram mechanism is provided with two legs; two wheels are respectively installed at the ends of the legs and are respectively driven by a drive motor; and the end of the abdomen part is equipped with a wheel which is driven by a drive motor and realizes the turning by a turning motor. The shrimp-shaped six-wheeled moving robot can cross the vertical stage 1.5 and 2 times higher than the diameter of the wheel, has stronger bearing capacity and higher mechanism efficiency and can make the turning movement with the gyration radius which is zero approximately.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Independent steering driving wheel for mobile robot
ActiveCN105691131AHigh precisionEasy to installMotor depositionElectrical steeringDrive wheelOptical axis
The invention discloses an independent steering driving wheel for a mobile robot. The independent steering driving wheel for the mobile robot comprises a hub motor, a wheel frame, a hollow shaft and the like, wherein the wheel frame is installed on the hub motor; the hollow shaft is installed on the wheel frame; the interior of the hollow shaft is hollow and is used for wiring of the motor; a lower flange disc is coaxially installed on the hollow shaft; a bearing seat is coaxially installed on the lower flange disc; two angular contact bearings are coaxially installed in the bearing seat; three optical axes are uniformly installed on the lower flange disc with the hollow shaft as the center, penetrate through a middle flange disc and are fixed with an upper flange disc; a spring is coaxially installed on the outer edge of the bearing seat; one end of the spring is embedded in the lower surface of the middle flange disc; the other end of the spring is arranged against the upper surface of the lower flange disc; and a steering mechanism is installed on the upper flange disc and is composed of a worm and worm wheel reduction gearbox, a stepping motor and a photoelectric encoder. The independent steering driving wheel for the mobile robot has a compact structure, is rapid and convenient in installation and good in practicability and can wholly rotate within a large range in the horizontal direction.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Two-wheel differential wheel type mobile robot experimental platform with adjustable gravity center
InactiveCN103196685AReduce weightGuaranteed reliabilityStructural/machines measurementControl engineeringGravity center
The invention discloses a two-wheel differential wheel type mobile robot experimental platform with an adjustable gravity center. The two-wheel differential wheel type mobile robot experimental platform with the adjustable gravity center is characterized by comprising a base plate, wherein a driving system is arranged on the base plate, three supporting rods are evenly distributed in the upper direction of the base plate, three cross rods which transversely extend towards the center and then are connected and fixed into a whole are respectively arranged at the tops of the three supporting rods, a lifting mechanism is arranged in the middle of the cross rods, a two-dimensional platform is arranged in the middle of the supporting rods, a balance weight and a two-dimensional moving mechanism used for driving the balance weight to move along the level plane of the two-dimensional platform are arranged on the two-dimensional platform, and the lifting mechanism is used for driving the two-dimensional platform to do lifting movement. The two-wheel differential wheel type mobile robot experimental platform with the adjustable gravity center has the advantages that the structure is simple, the gravity center moves rapidly, sensitively, accurately, and controllably in the three-dimensional direction, and is particularly suitable for being used for researching the influence relationship between the moving condition of the gravity center of a robot and the moving condition of the robot.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Driving structure and driving method of mobile orbot platform
A drive structure using the coordinative drive mode for the movable wheel-type robot platform is composed of an active steering wheed driven by a low-power motor with high reduction rate, two back drive wheels driven respectively by two low-precision motors, and a drive controller. Its drive method includes decomposing the movement requirement into the control commands of three motors by said drive controller according to a coordination algorithm, and controlling three wheels. Said back wheels move in differential modes.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dual tracked mobile robot for motion in rough terrain
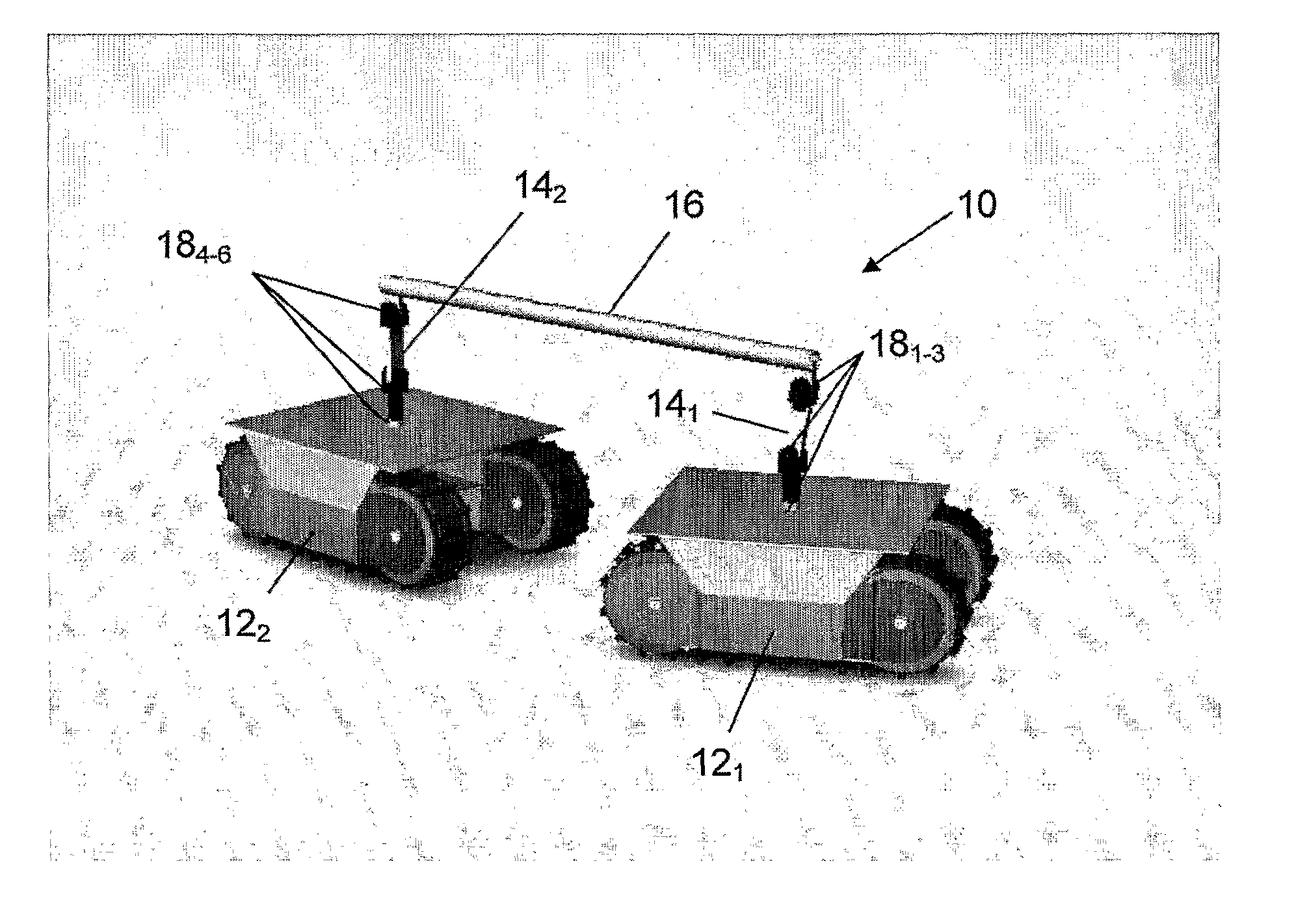
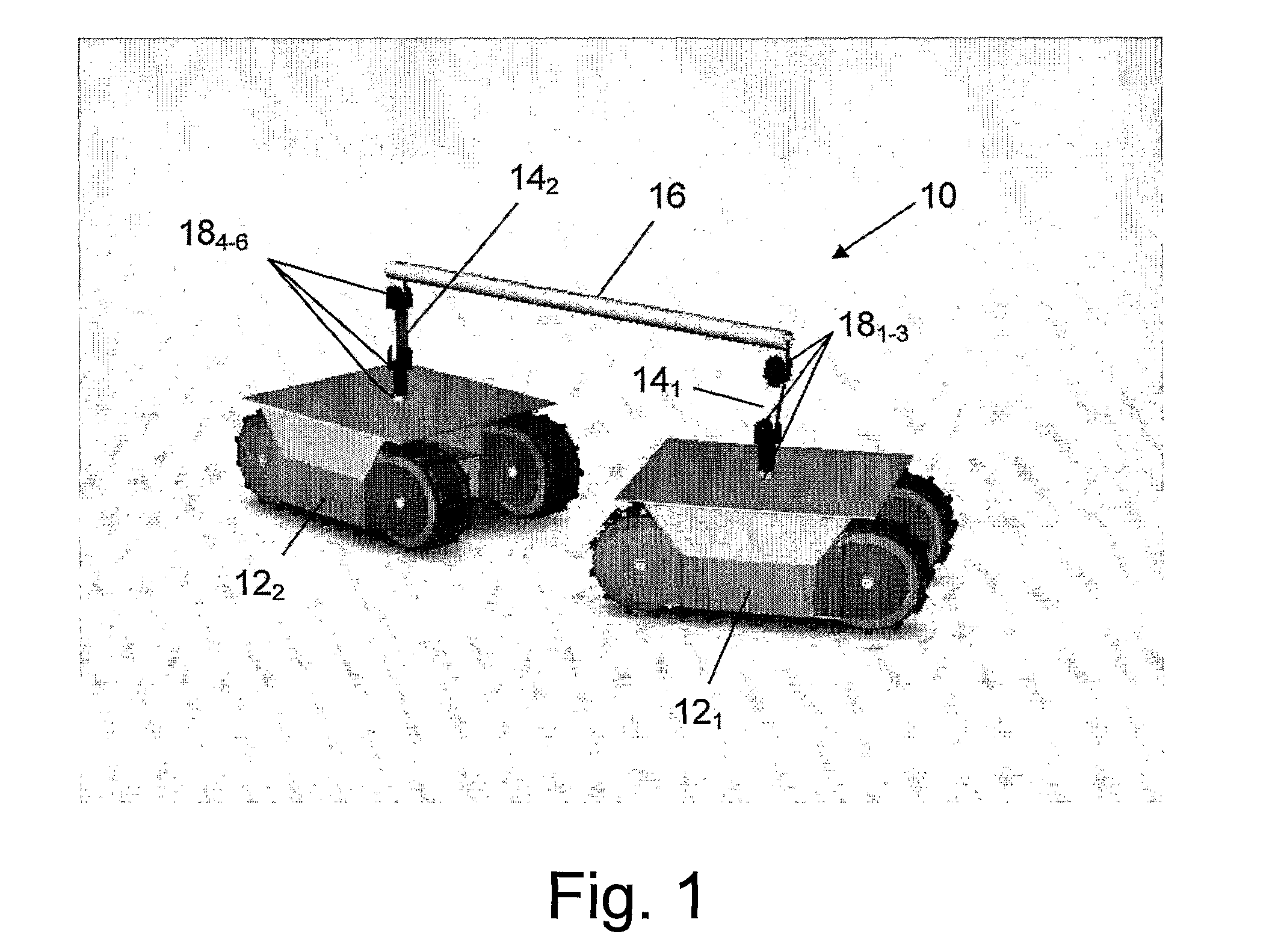
InactiveUS7946372B2Agricultural machinesTractor-trailer combinationsTerrainElectric power transmission
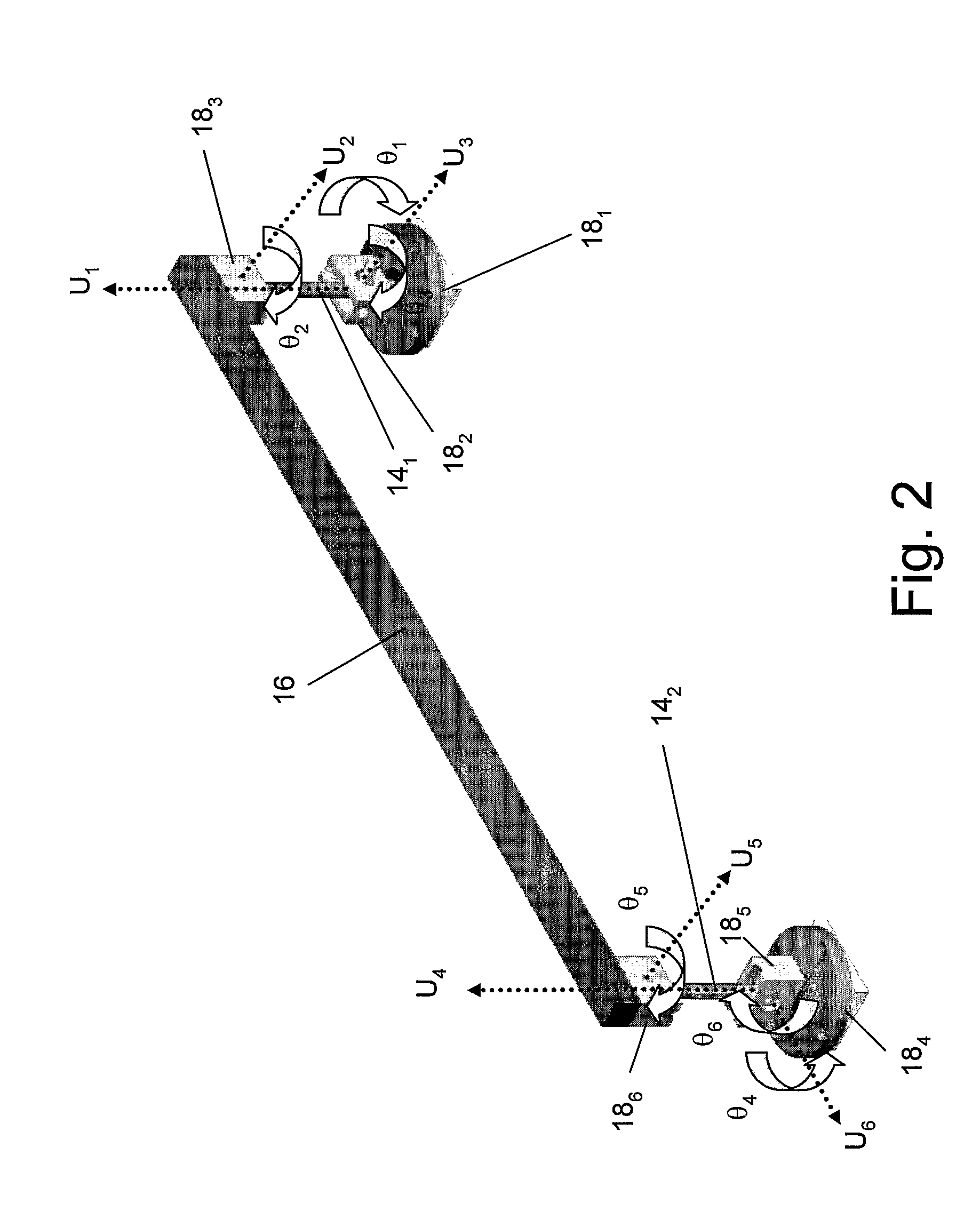
The invention is an autonomous dual tracked mobile (10) robot system comprising two or more tracked driving units (12x) configured to travel in tandem and a separate mechanical linkage (16), which joins each of the mobile units to the unit immediately preceding and following it, and enables efficient power transmission between the two driving units. Each of the mechanical linkages comprises one connecting bar (14) and three revolute joints (18y) located on each of the adjacent units and a connecting beam that connects the connecting bar on one of the units with the connecting bar on the adjacent unit.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV +1
Wheel-type detection mobile robot control system and method
InactiveCN106444754AGuaranteed uptimeEnsure safetyPosition/course control in two dimensionsOperation modeControl theory
The invention provides a wheel-type detection mobile robot control system and method and relates to the field of robot control technologies and safety. The invention overcomes the problem that the conventional wheel-type detection mobile robot can be damaged when operating in a complex environment as topographic relief is large. A wireless signal input or output end of a remote control operation unit is connected with the output or input end of an external communication unit, the external communication unit is connected with a master control unit, two paths of communication signal input or output ends of the master control unit are connected with two paths of communication signal output or input ends of a sensor unit respectively, the input or output end of the master control unit is connected with the output or input end of a movement control unit, the output end of the movement control unit is connected with the input end of a drive control unit, and the input end of the movement control unit is connected with the output end of the drive control unit. The robot can be used in an operation environment where the topographic relief is large, and selects the operation mode according to change in real-time parameters of vehicle body operation collected by a vehicle-mounted sensor, so that the safety operation of a vehicle body is ensured.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Wheel type mobile robot trajectory tracking method based on disturbance observer
ActiveCN109597310AGood tracking effectAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsKinematic controllerKinematics
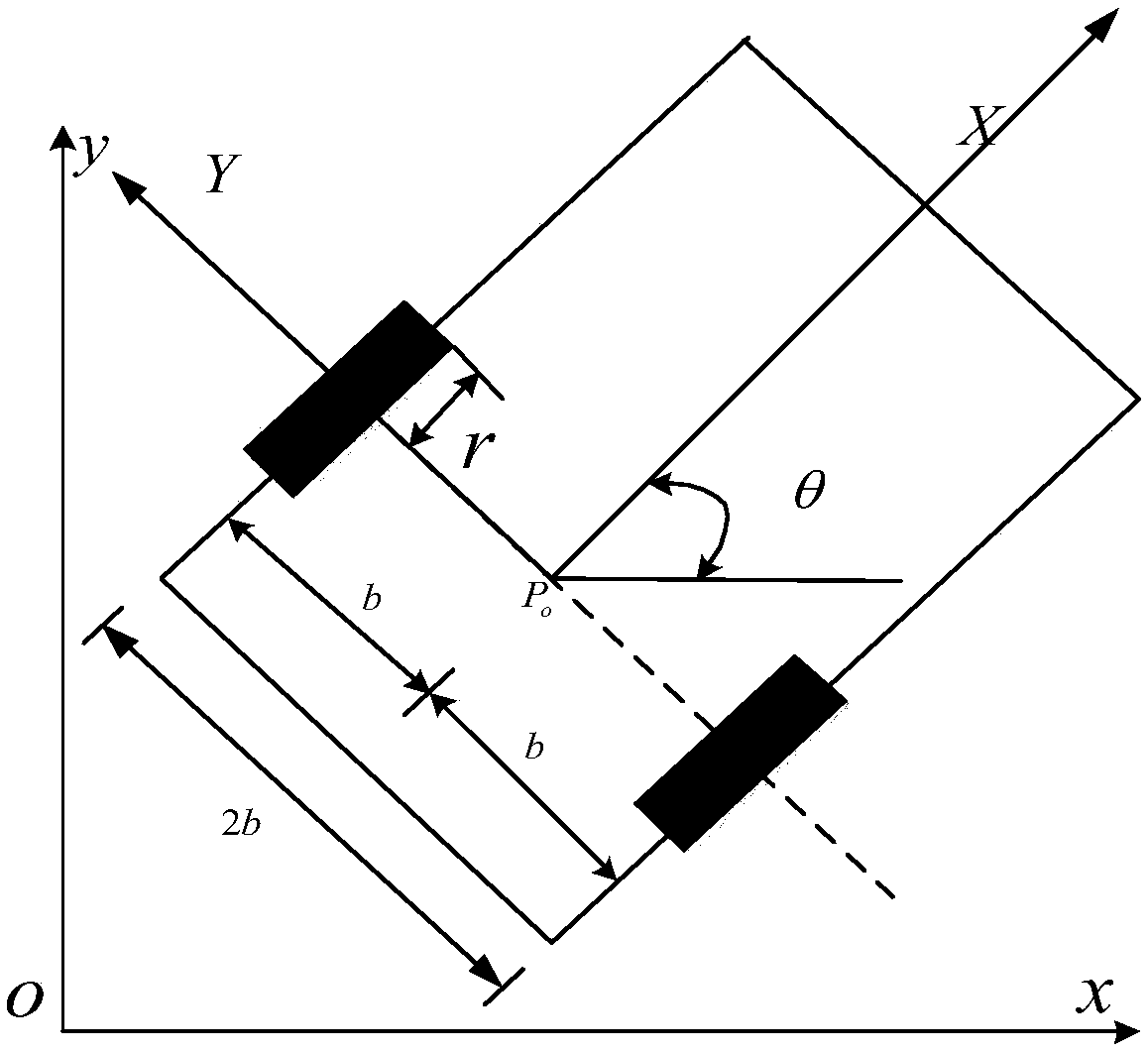
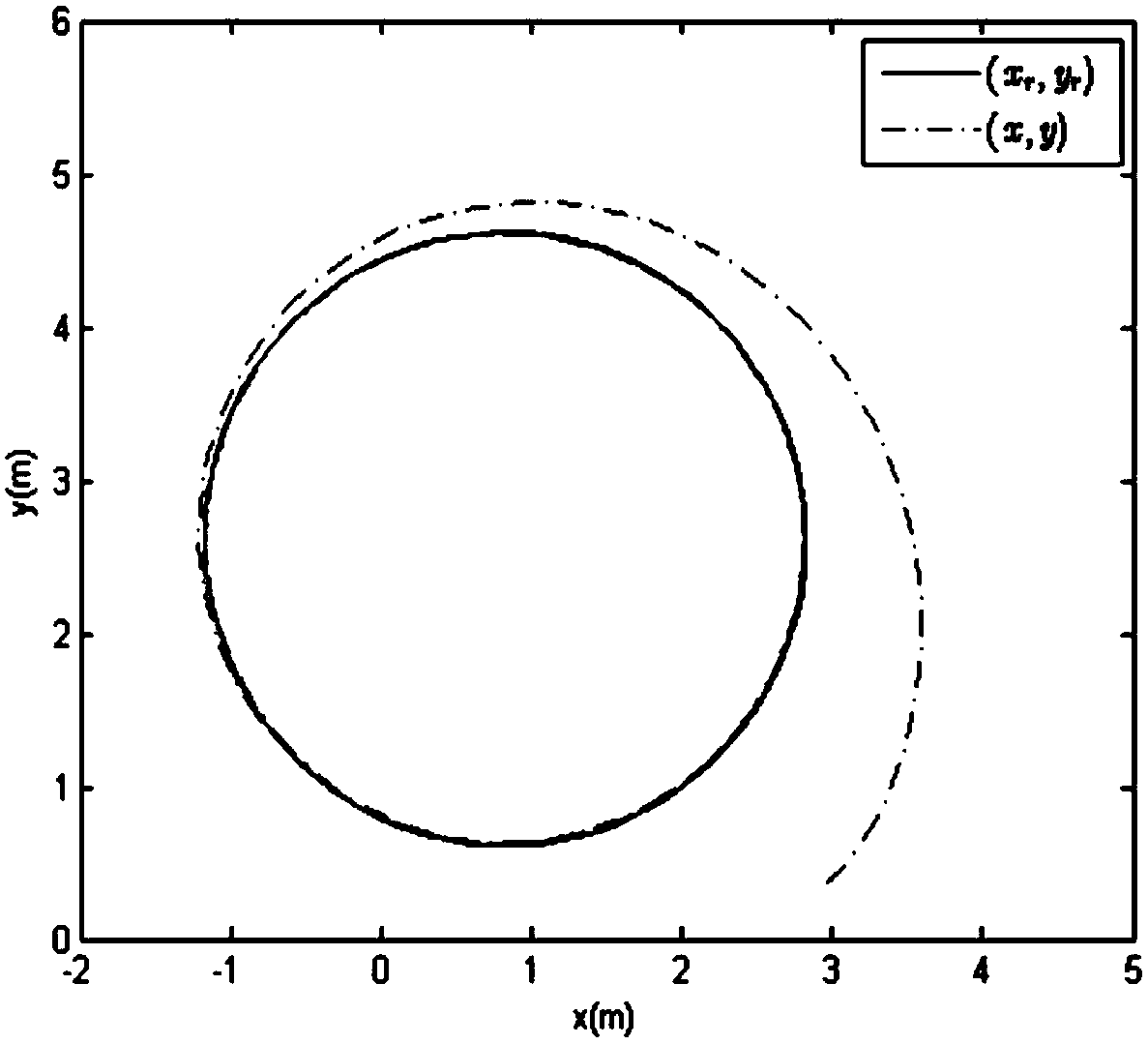
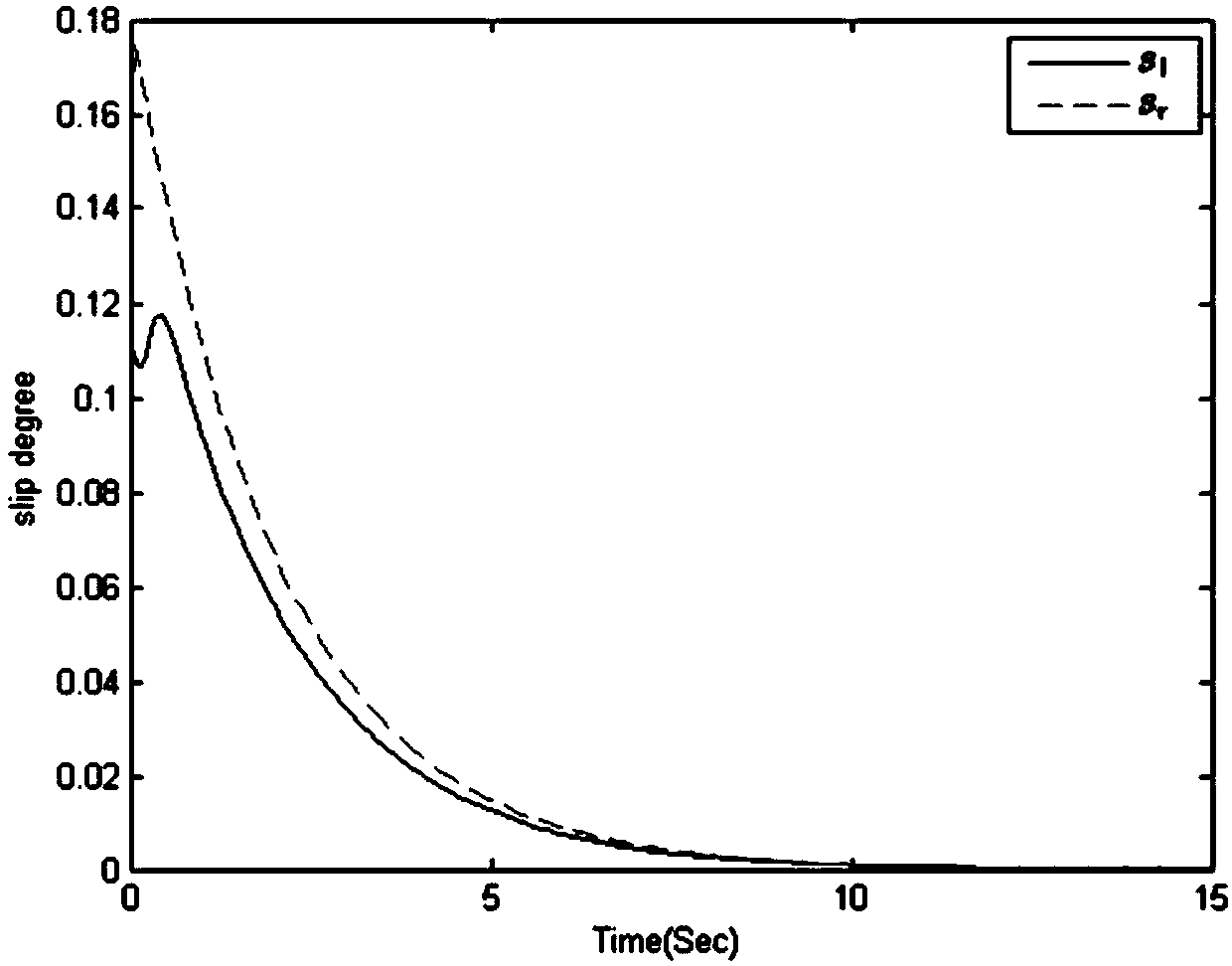
The invention discloses a wheel type mobile robot trajectory tracking method based on a disturbance observer. The slip degree is introduced in the design of a kinematics controller; the difference between an actual pose and an expected pose is expressed; if a wheel type mobile robot can be stabilized in a limited time, namely, an actual movement trajectory and an expected movement trajectory can be coincided in the limited time, based on this, a kinematics linear velocity controller and an angular velocity controller are designed; in the design of a dynamics torque controller, firstly, lumpeddisturbance is introduced, the observer is designed for estimation, and based on this, the dynamics torque controller is designed; and the stability is proved by a Lyapunov function. According to themethod, the problem of how to track the trajectory in the presence of slip, external interference and the like of the wheel type mobile robot can be solved, so that the robot can be subjected to trajectory tracking control.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
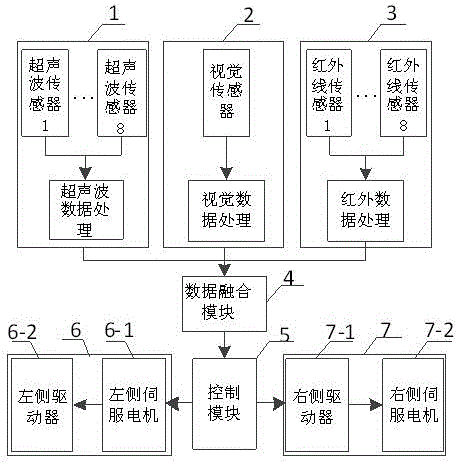
Wheel-type moving robot obstacle-avoiding control system based on multi-sensor information fusion
InactiveCN106383515AEnsure safetyEnsure reliabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsData informationData acquisition
The invention discloses a wheel-type moving robot obstacle-avoiding control system based on multi-sensor information fusion, and the system mainly comprises a vision sensor module, a supersonic sensor module, an infrared sensor module, a data fusion module, a control module, and an execution module. Each sensor module carries out the processing of the collected surrounding and obstacle information, and the data fusion module receives the data collected by each sensor module, and carries out the fusion of the data collected by all sensor modules according to a certain fusion rule. The data is transmitted to a processor of the control module after fusion. The processor carries out the behavior operation judgment and control decision making according to the data information, and completes the obstacle-avoiding operation of a wheel-type robot through the execution module. The system carries out the data collection through the plurality of sensors, and carries out the parallel processing of data through a plurality of data processors, thereby increasing the speed of data processing, meeting the requirements of obstacle-avoiding real-time performance and precision of the robot, and enabling the robot to avoid an obstacle more flexibly and reliably.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A step wheel combined mobile robot
InactiveCN101157372AImprove obstacle performanceFlexible movementEndless track vehiclesLeg typeRotation function
The invention relates to a leg-wheel-caterpillar compound mobile robot; the centers of front and rear wheels and a car body are connected by a telescopic rod and the lateral wing of a caterpillar; a power on the car body is connected with a wheel via a reducer by a bearing on the car body; two ends of the telescopic rod are respectively connected with spherical pairs fixed on the car body and the lateral wing of the caterpillar; the rotating function of the robot can be realized by the power and the reducer, which are fixed on the car body; the stretching function of the robot can be realized by a gear-rack mechanism or by hydraulic pressure; the caterpillar can realize the moving function by the power fixed on the caterpillar via the reducer; the mobile robot of the invention takes a wheel-type robot as a carrier, and combines the leg-type and the caterpillar-type mobile mechanisms into a whole; the invention can adapt to the surface curve of the ground by changing the grounding curve in the system, which has multiple movement modes and strong obstacle-climbing capacity; in addition, the invention can adjust the gravity center by changing the postures of the lateral wing of the caterpillar and the car body; the invention has the advantages of flexible movement and compact structure.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Calibration algorithm for wheel encoder for four-wheel mobile robot
The invention belongs to the field of mobile robot positioning technologies and discloses a calibration algorithm for a wheel encoder for a four-wheel mobile robot. The algorithm includes the following steps that: the robot moves along a specific trajectory, and the measured values of the wheel encoder are collected; in each time period, an iterative closest point algorithm operates, so that the pose estimated values of the origin of a laser radar sensor coordinate system are obtained, and the measured values and estimated values constitute the data samples of each time period; linear parameter estimation is carried out: a linear parameter pair J21 and J22 is constructed on the basis of the left wheel radius rL, the right wheel radius rR and the wheelbase b of the robot, and linear estimation is performed; and calibration parameter estimation is carried out: calibration parameters are determined as b, lx, ly, and ltheta, wherein l is a relative pose relationship between the sensor coordinate system and a robot body coordinate system, a log likelihood function obtained in calibration problem description is established, and calibration parameters are calculated. With the calibrationalgorithm of the wheel encoder of the invention adopted, the parameters of a sensor and an actuator and the parameters of pose relationships can be accurately obtained in various environments with nomanual intervention required.
Owner:成都天富若博特科技有限责任公司
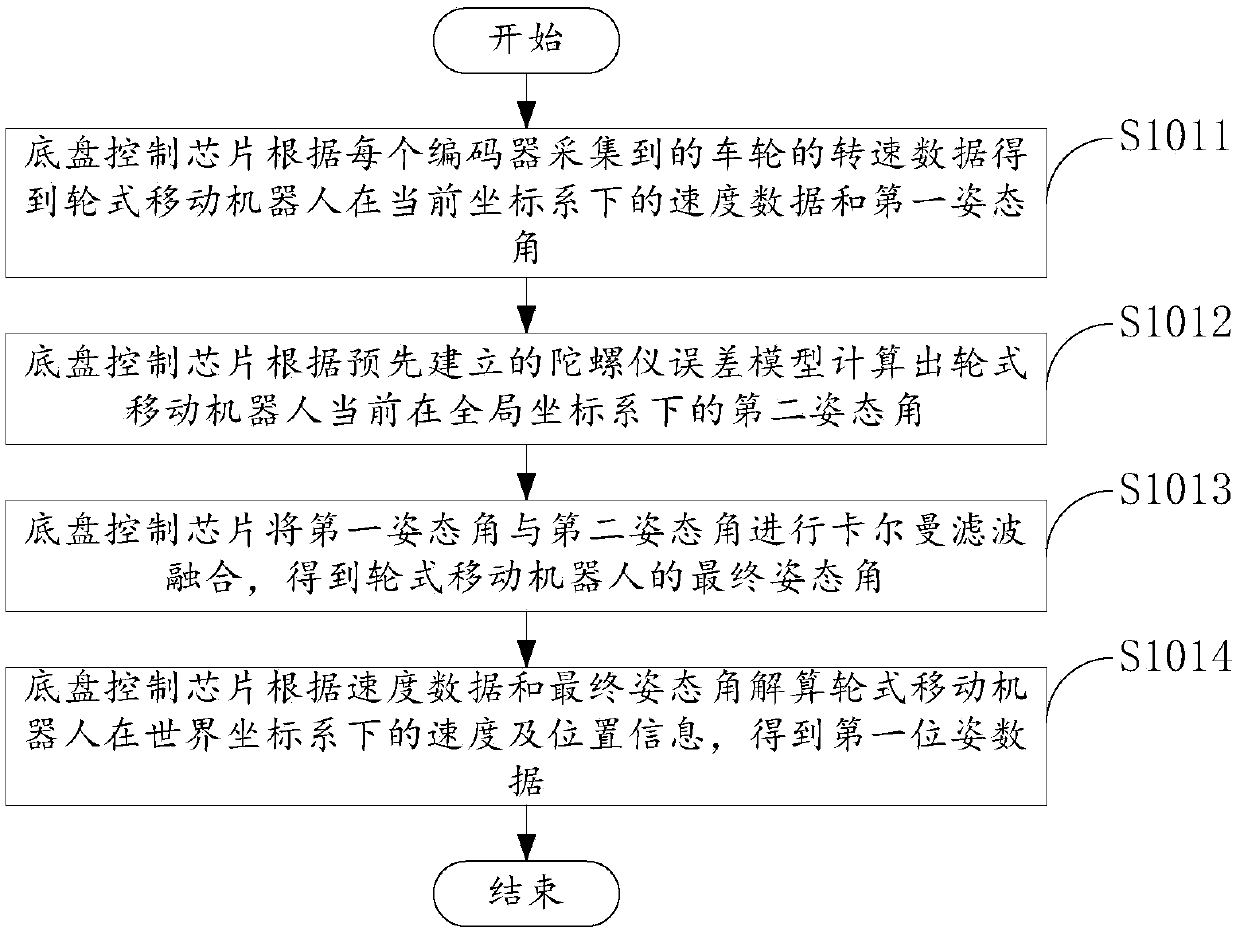
Positioning method and system
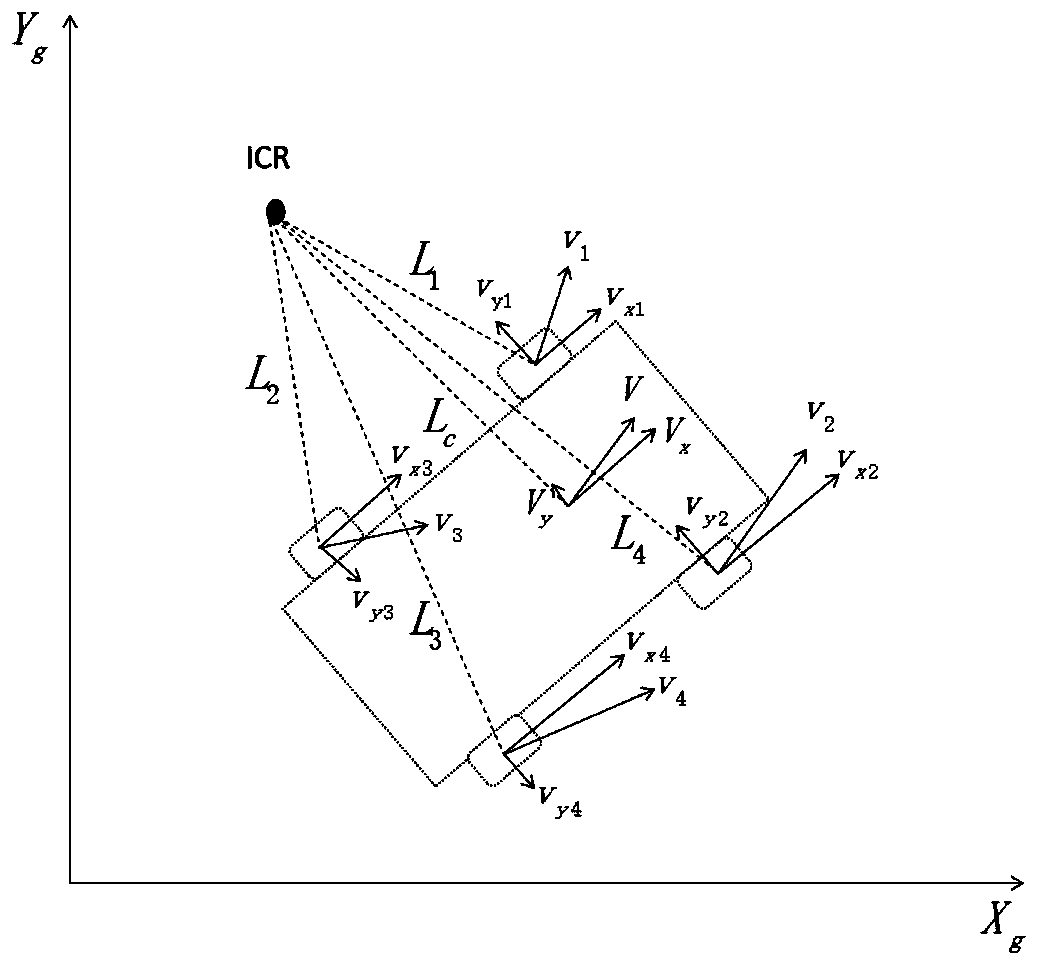
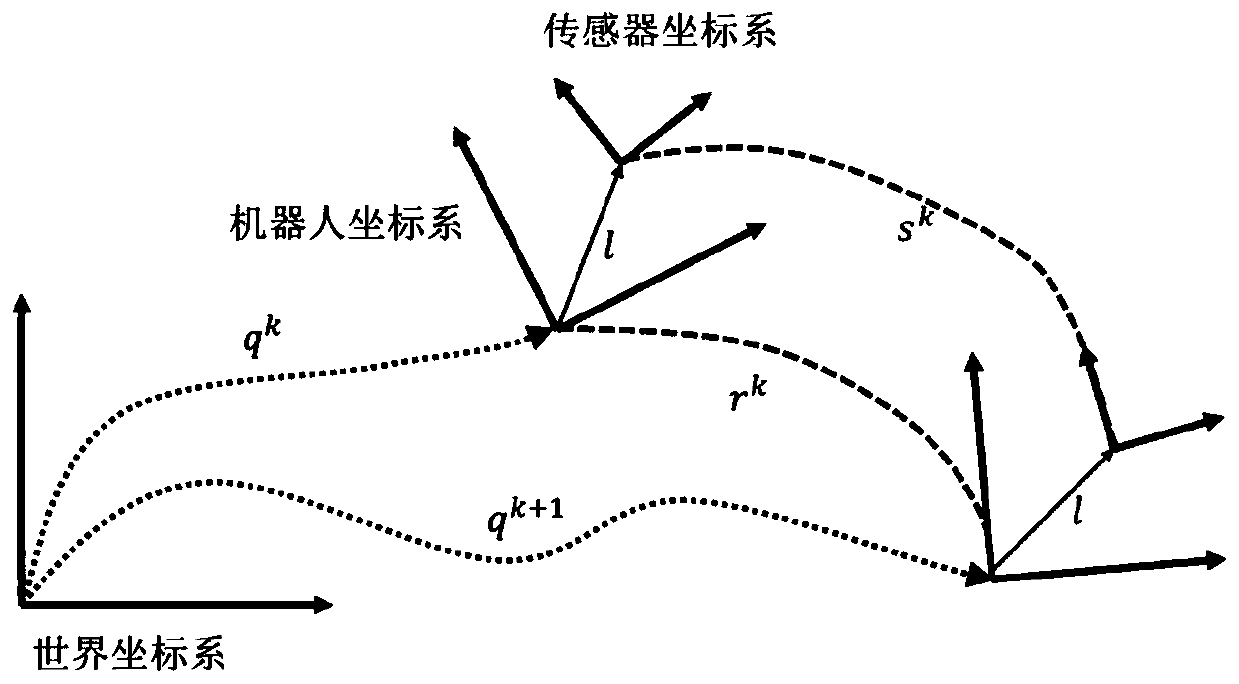
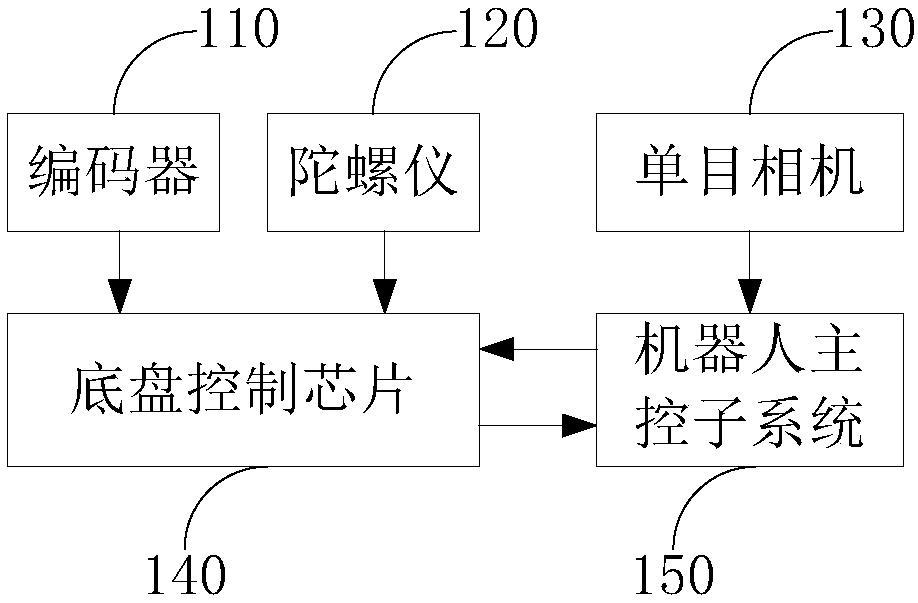
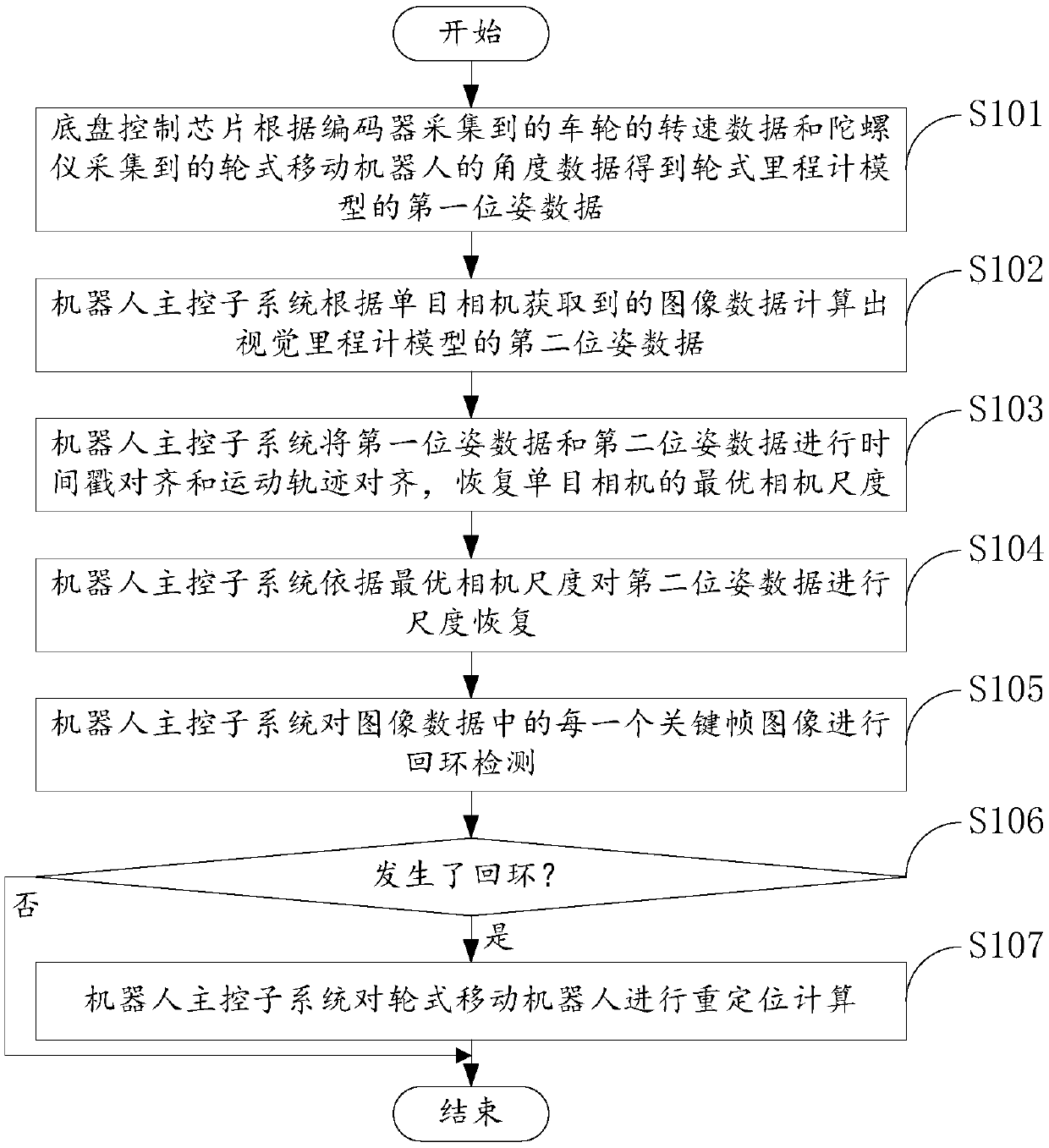
PendingCN109579844AAvoid Cumulative ErrorsOvercome no scaleNavigational calculation instrumentsPattern recognitionTimestamp
The invention discloses a positioning method and system, and relates to the technical field of robot positioning. The positioning method comprises the steps: a chassis control chip obtains first posedata of a wheeled speedometer model according to rotating speed data and angle data; a robot main control subsystem calculates second pose data of a visual speedometer model according to image data obtained by a monocular camera; the robot main control subsystem conducts timestamp alignment and movement track alignment on the first pose data and the second pose data, and the optimal camera scale of the monocular camera is recovered; the robot main control subsystem conducts scale recovery on the second pose data according to the optimal camera scale; and the robot main control subsystem fusesthe first pose data with the second pose data which are subjected to scale recovery, and final pose data of a wheeled mobile robot are obtained. According to the positioning method and system, the problems that the monocular camera has no scale and is poor in robustness in the positioning process can be avoided, and the problems of accumulative errors of a wheeled speedometer and slip of wheels ofthe robot can also be solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wheeled mobile robot target tracking control method based on point stabilization
ActiveCN105929849ASimple structureLow hardware requirementsTarget-seeking controlVirtual targetLyapunov stability
The invention discloses a wheeled mobile robot target tracking control method based on point stabilization. The method is characterized by, to begin with, establishing a wheeled mobile robot kinematic model, obtaining relative position of a target through an external sensor and establishing a virtual tracking target; and then, designing a linear velocity and angular velocity controller, and proving that the designed controller can enable the virtual target trajectory to be converged to a real target through lyapunov stability theory and LaSalle invariance principle, which represents that a wheeled mobile robot tracks the target. The tracking control method can enable a wheeled mobile robot system to be asymptotically stable; the robot tracks the target effectively; and simulation and experiment results prove reasonability of the control method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Artificial potential field obstacle avoidance method for omnidirectional-wheel mobile robot
InactiveCN108614561AImprove obstacle passing abilityImprove practicalityPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesFuzzy ruleRadar
The invention discloses an artificial potential field obstacle avoidance method for an omnidirectional-wheel mobile robot. The method comprises: S1, acquiring an initial position and a final target position of a mobile robot; S2, carrying out clustering on laser radar environment data and completing local environment modeling based on a least squares method; S3, acquiring a current time position of the mobile robot and a local target point within a laser radar scanning range; S4, establishing a fuzzy rule library by combining fuzzy controlling, selecting a marching mode, and quantifying the speed of the mobile robot based on a force size and a deflection degree; S5, controlling the robot to walk; and S6, detecting whether the mobile robot reaches the final target point; if not, returning to the S2 and carrying out cyclic execution; and if so, ending the marching process. Therefore, the omnidirectional-wheel mobile robot is able to select an own marking mode adaptively and takes different passing paths according to different obstacles; the advantage of the omnidirectional wheel is utilized fully; and the obstacle passing ability of the robot is enhanced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com