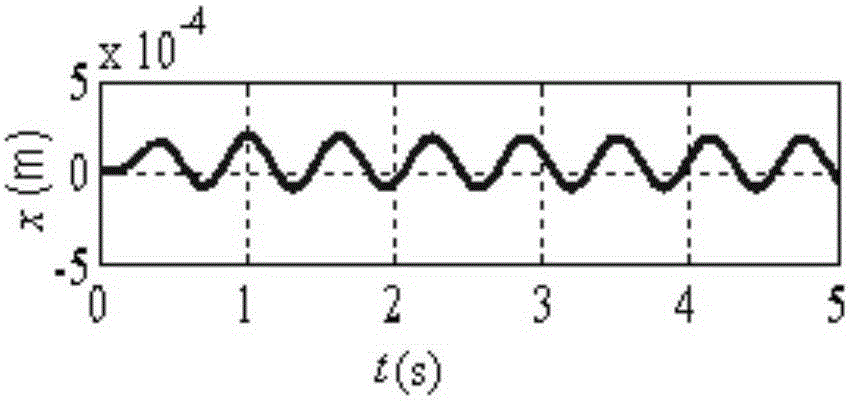
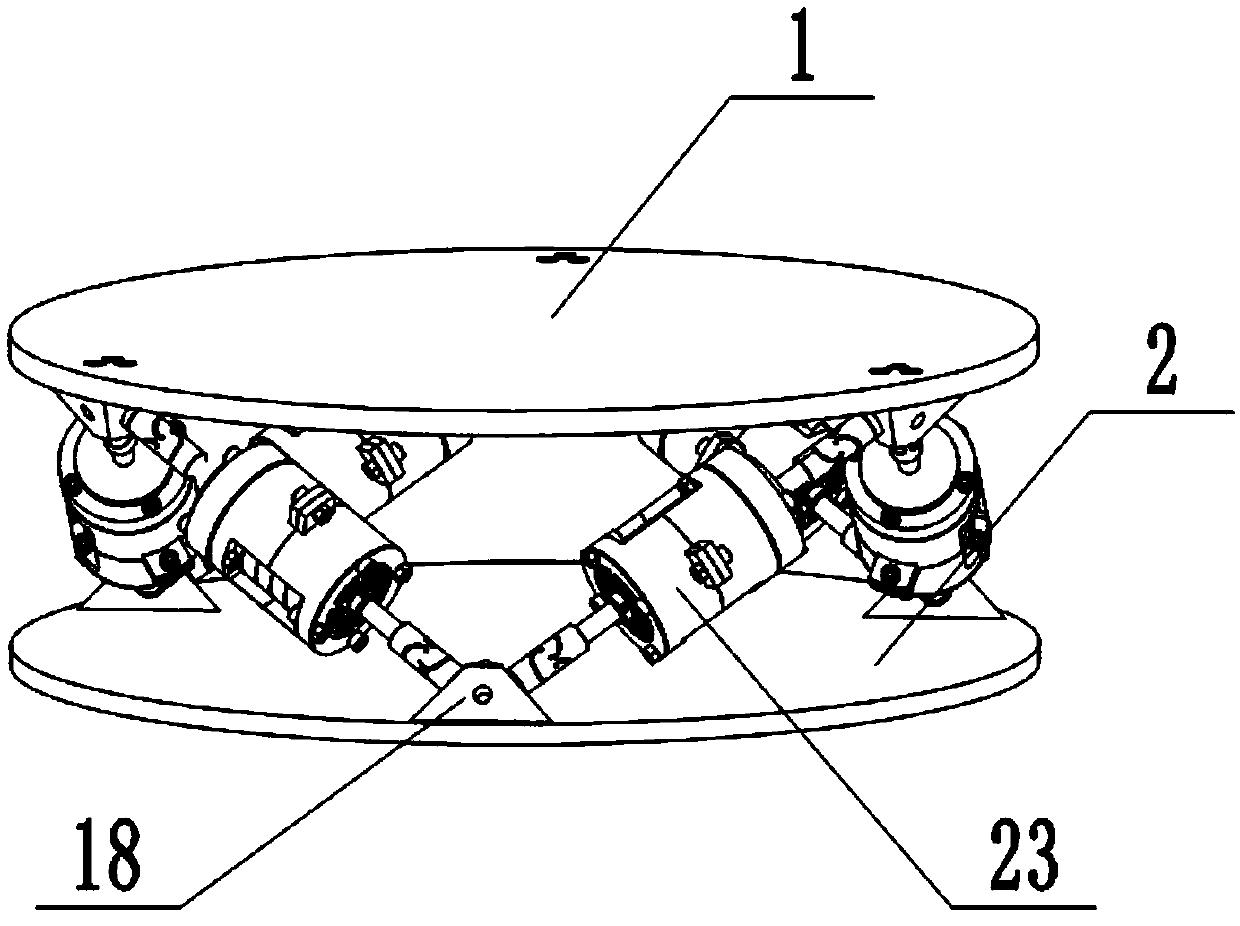
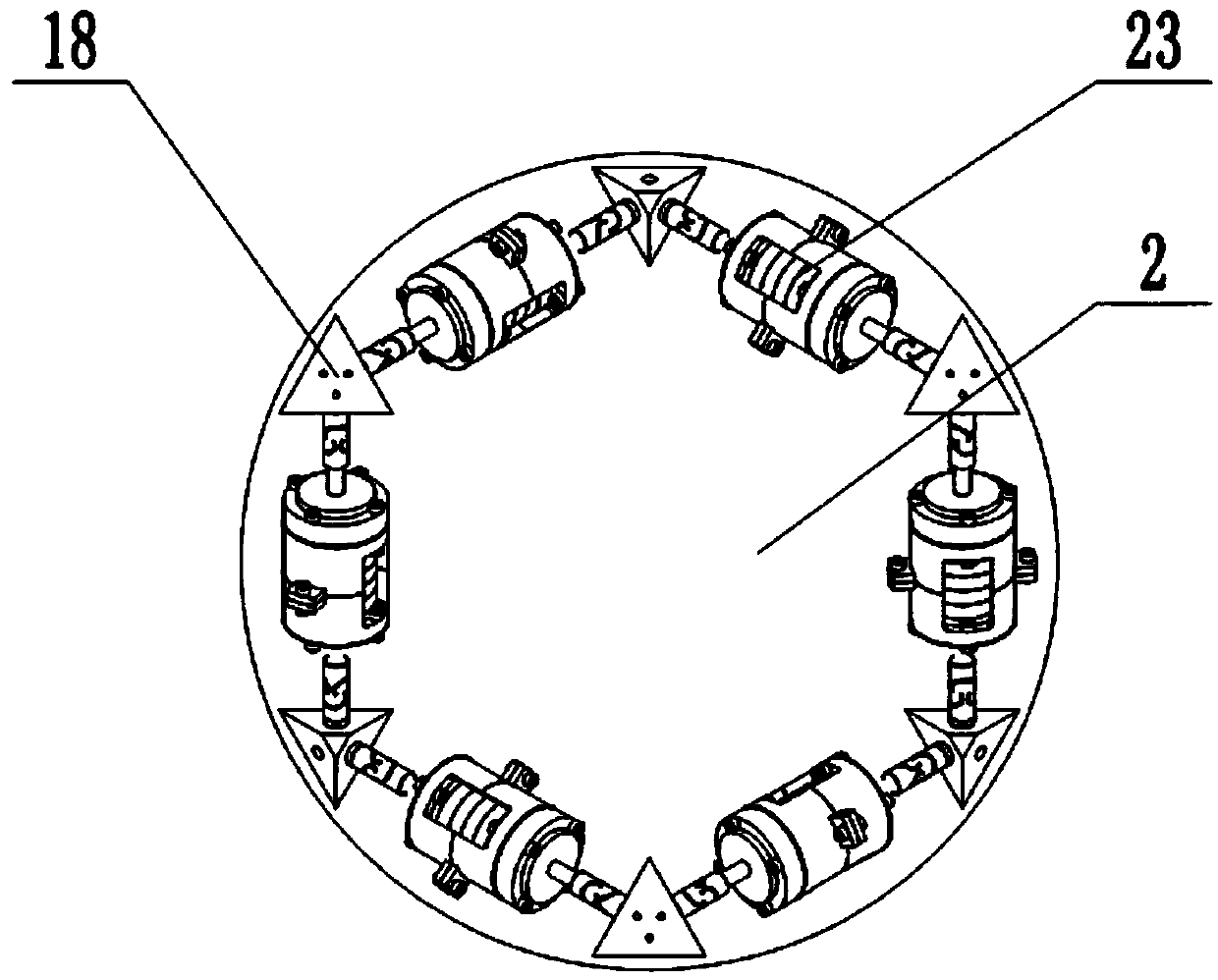
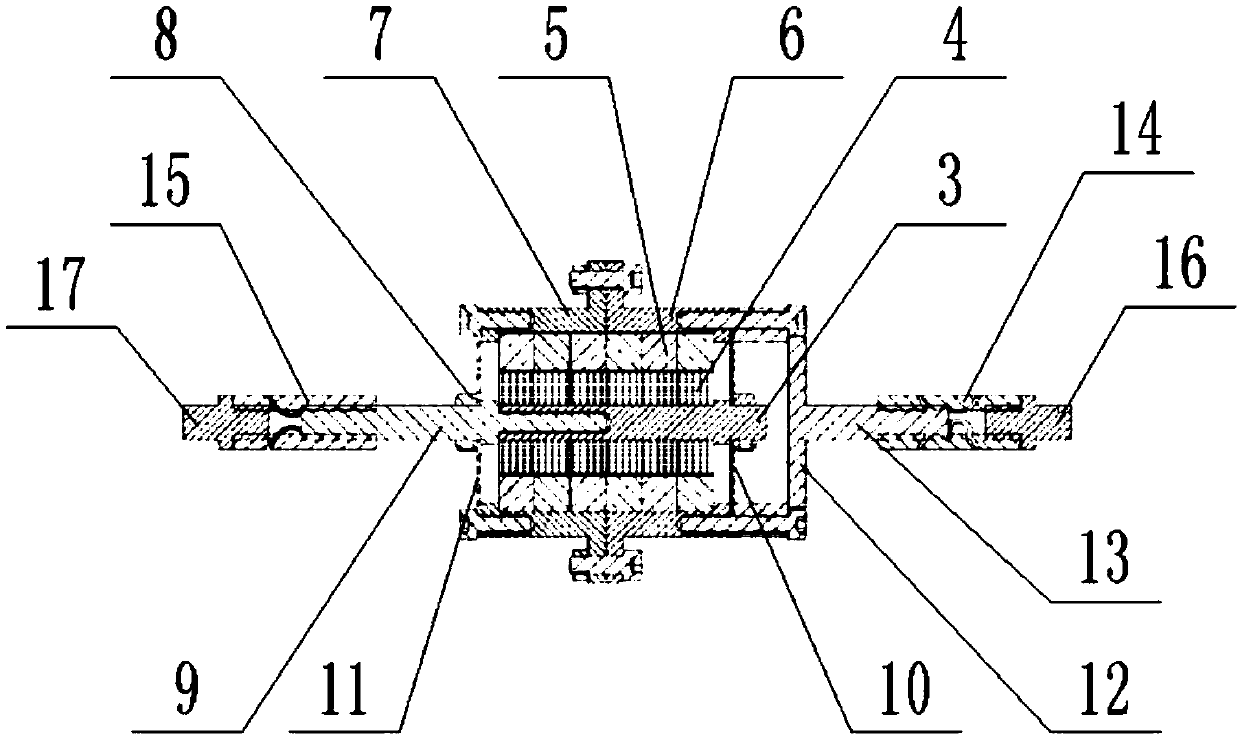
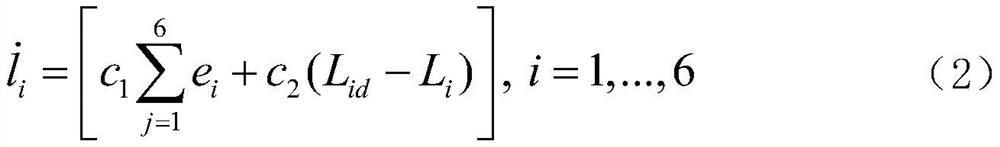Patents
Literature
105 results about "Stewart platform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
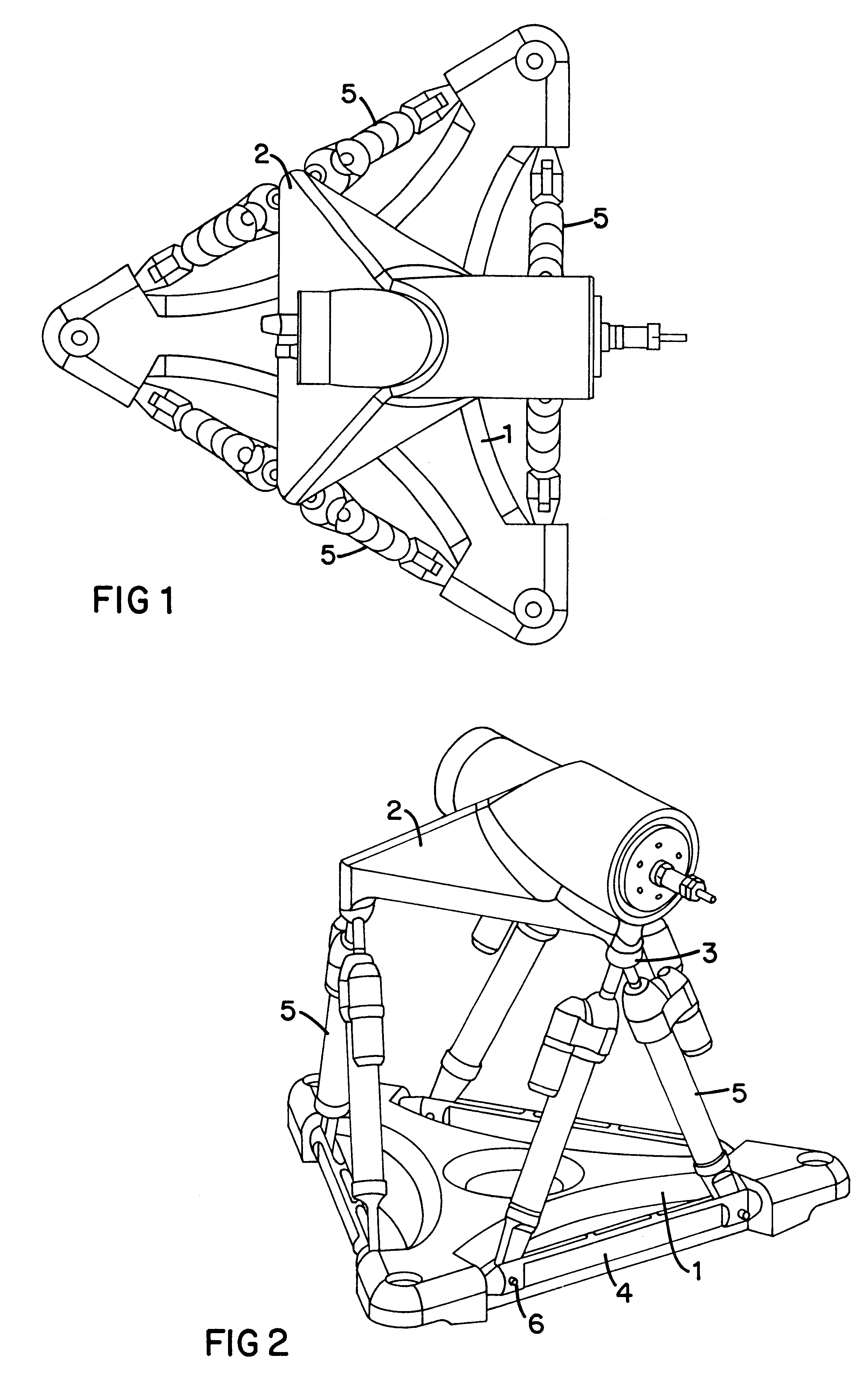
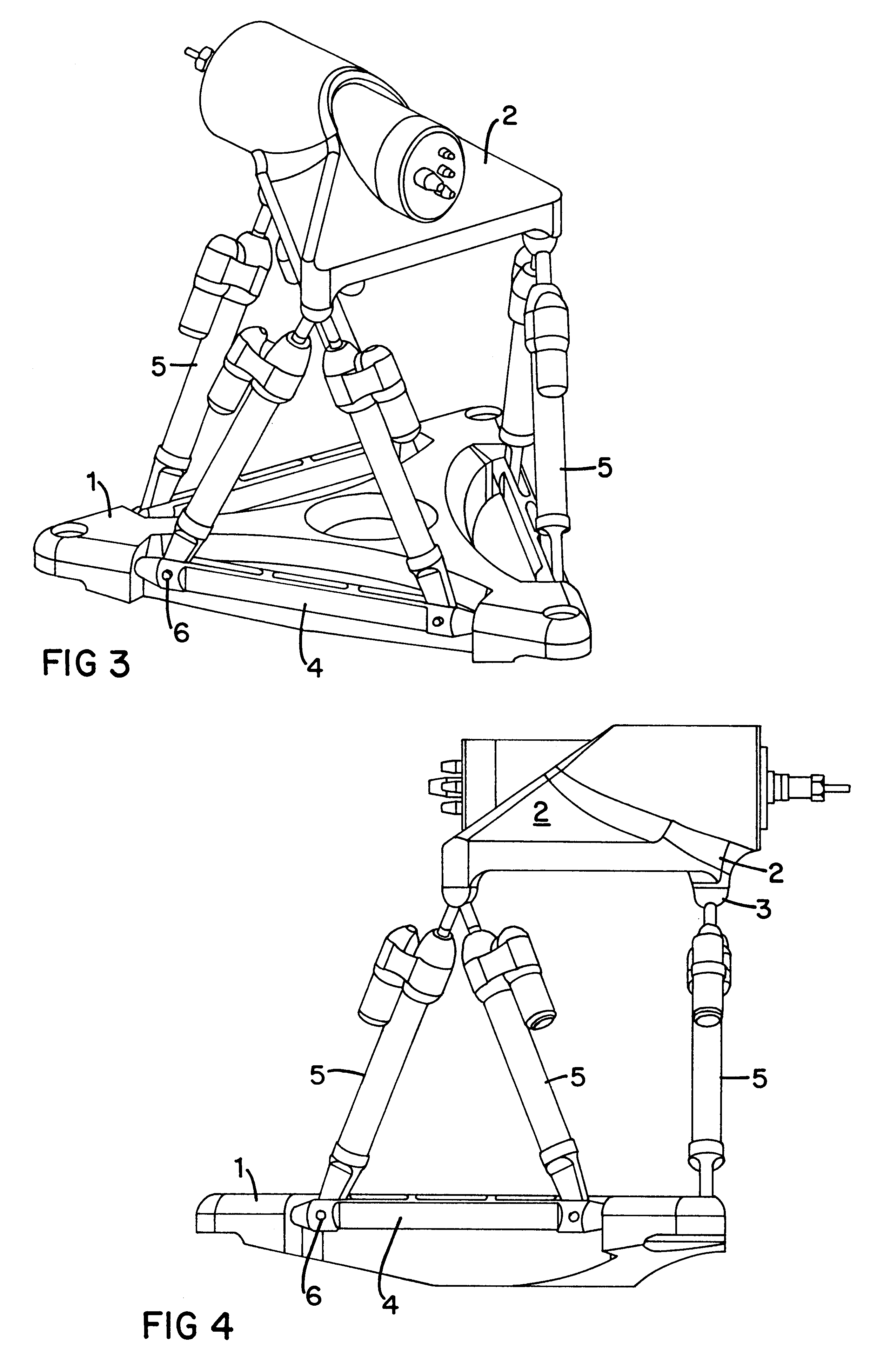
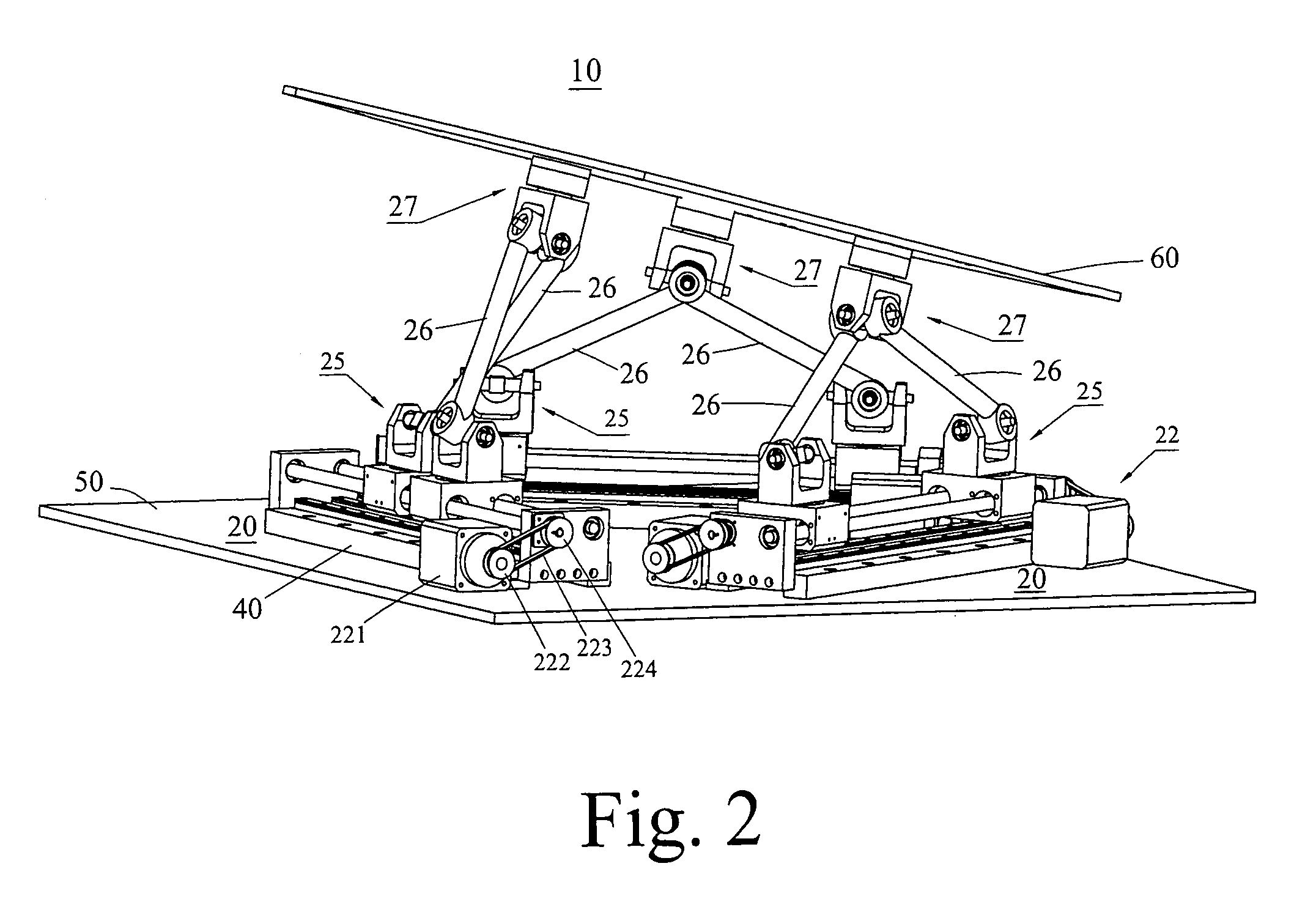
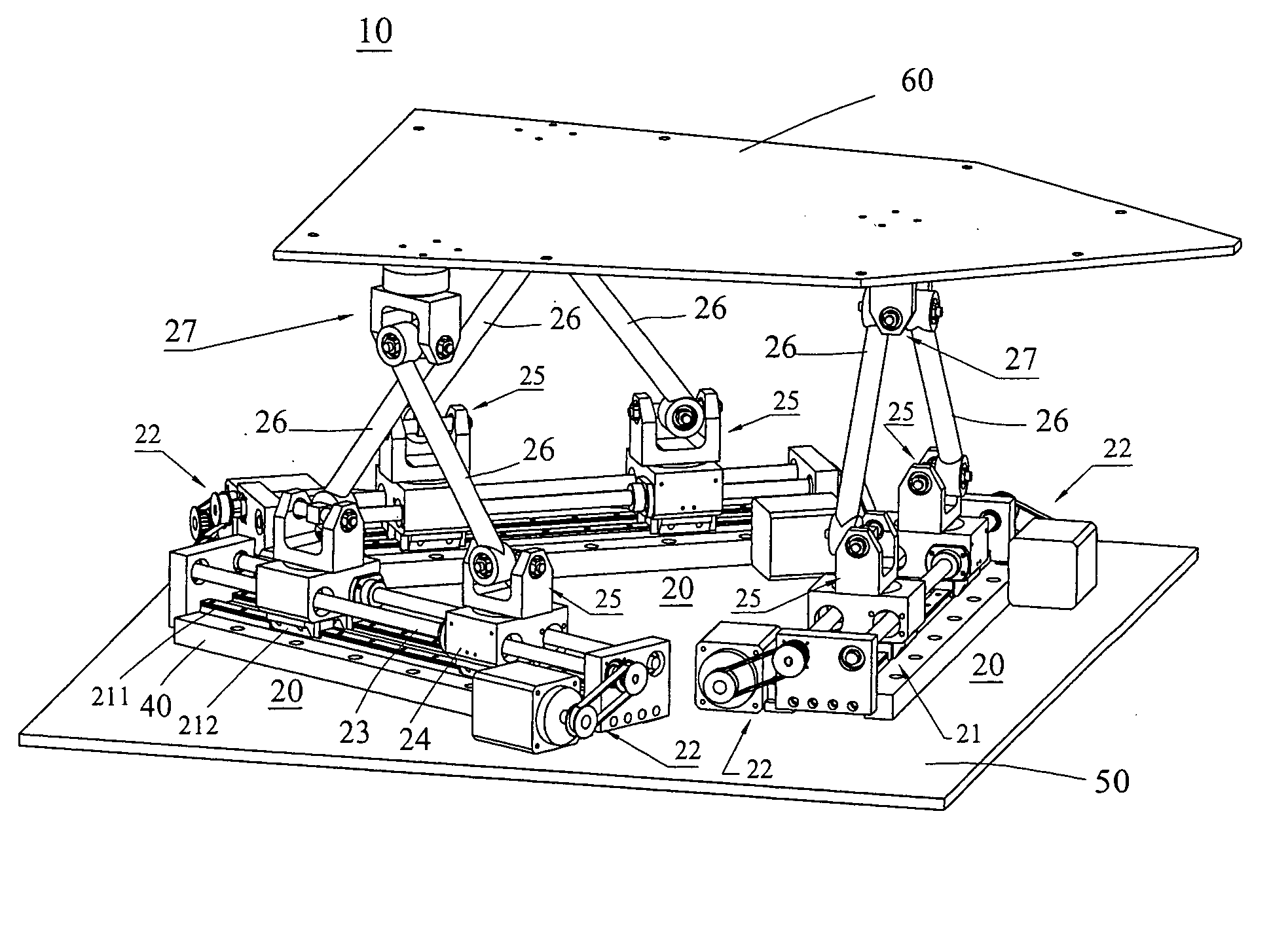
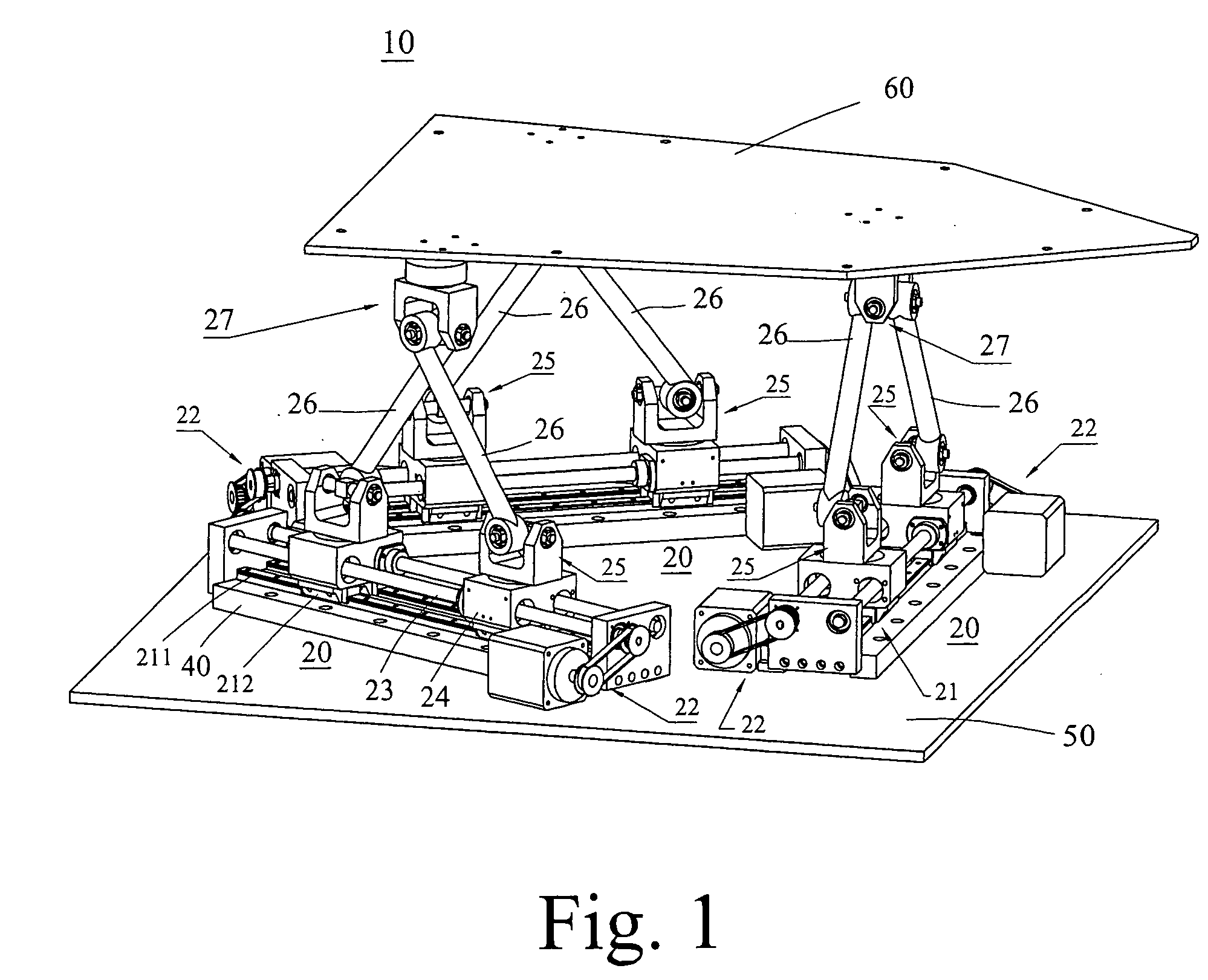
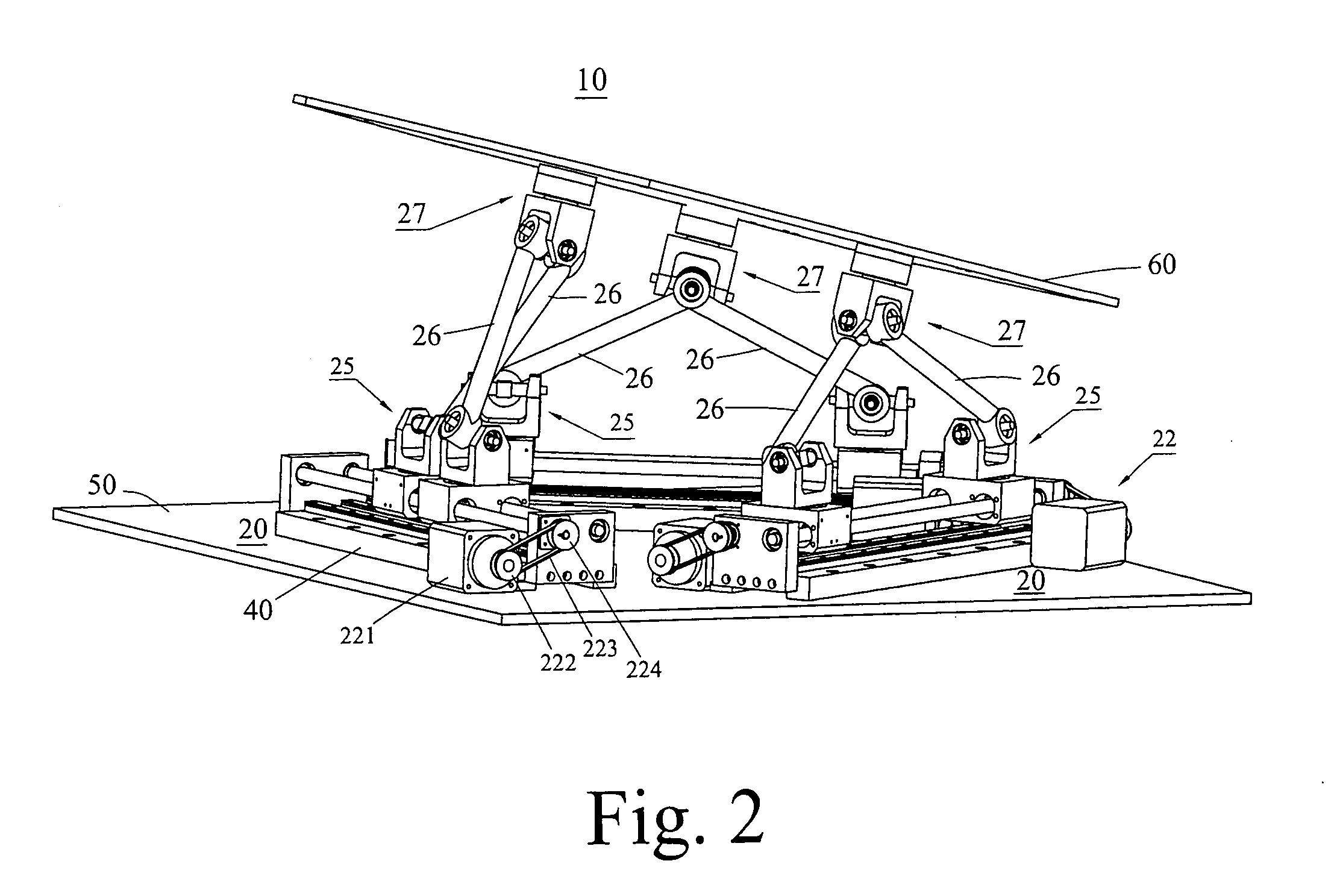
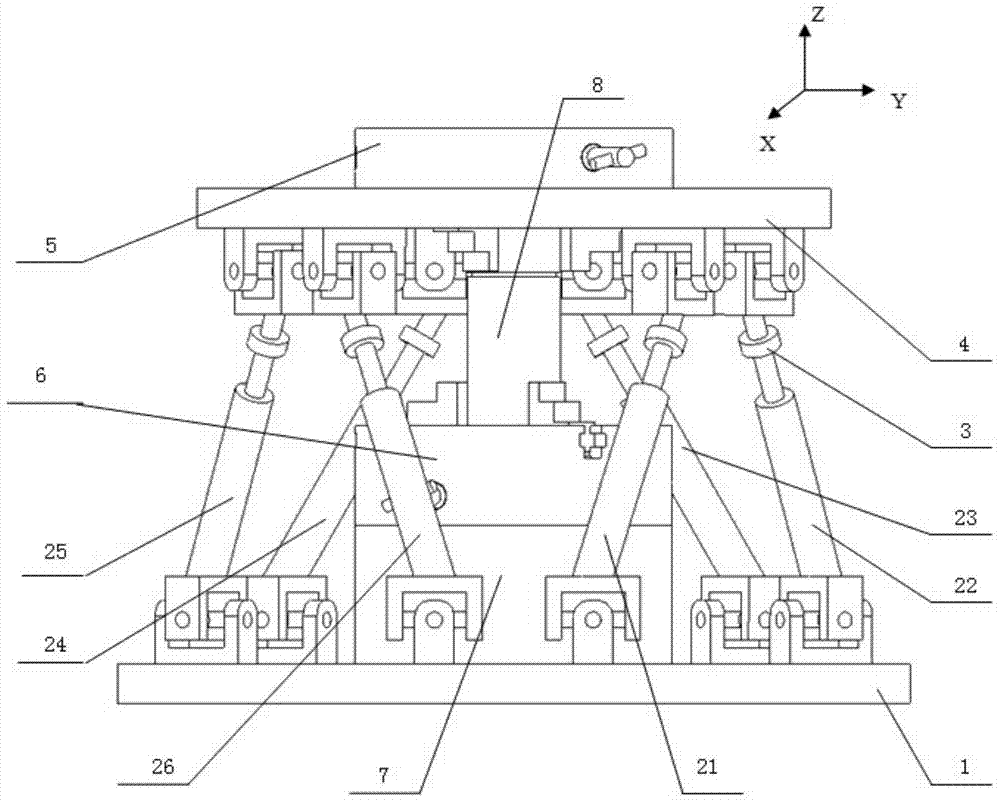
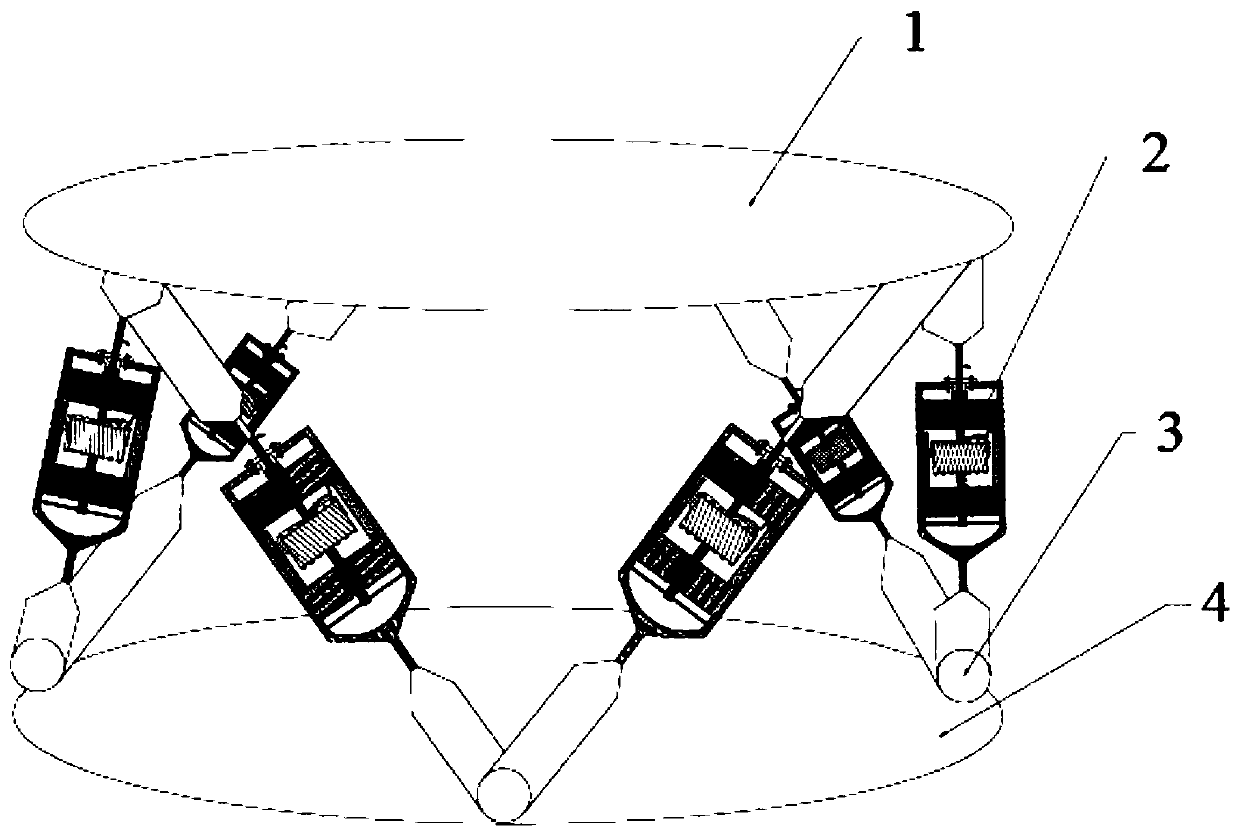
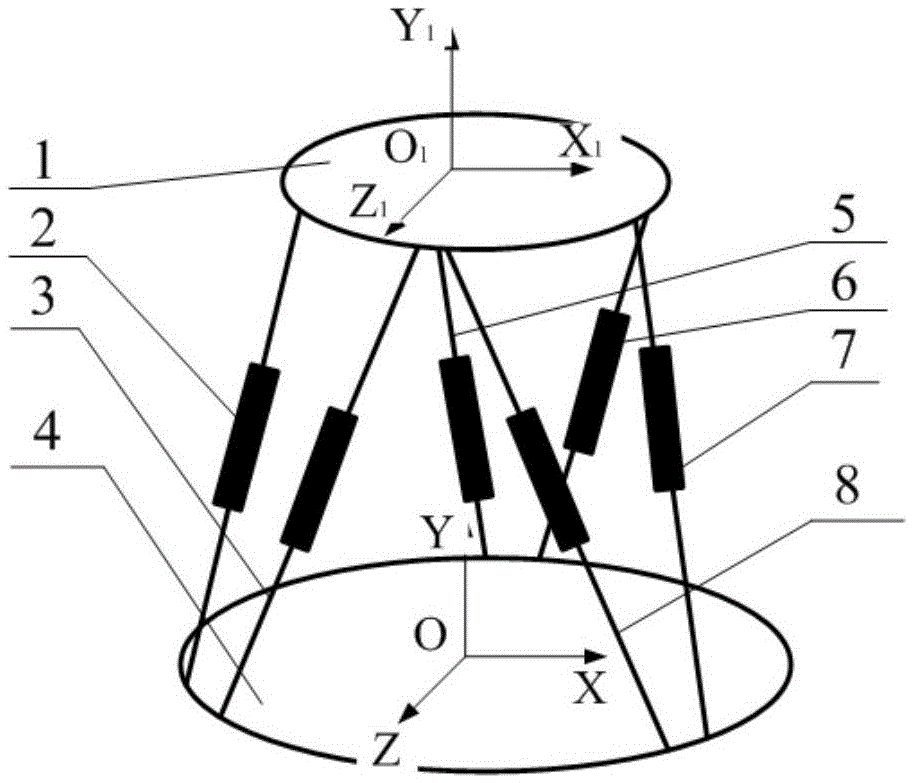
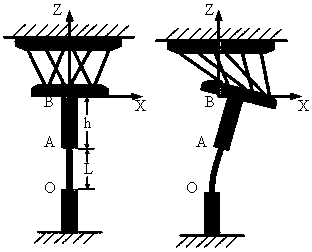
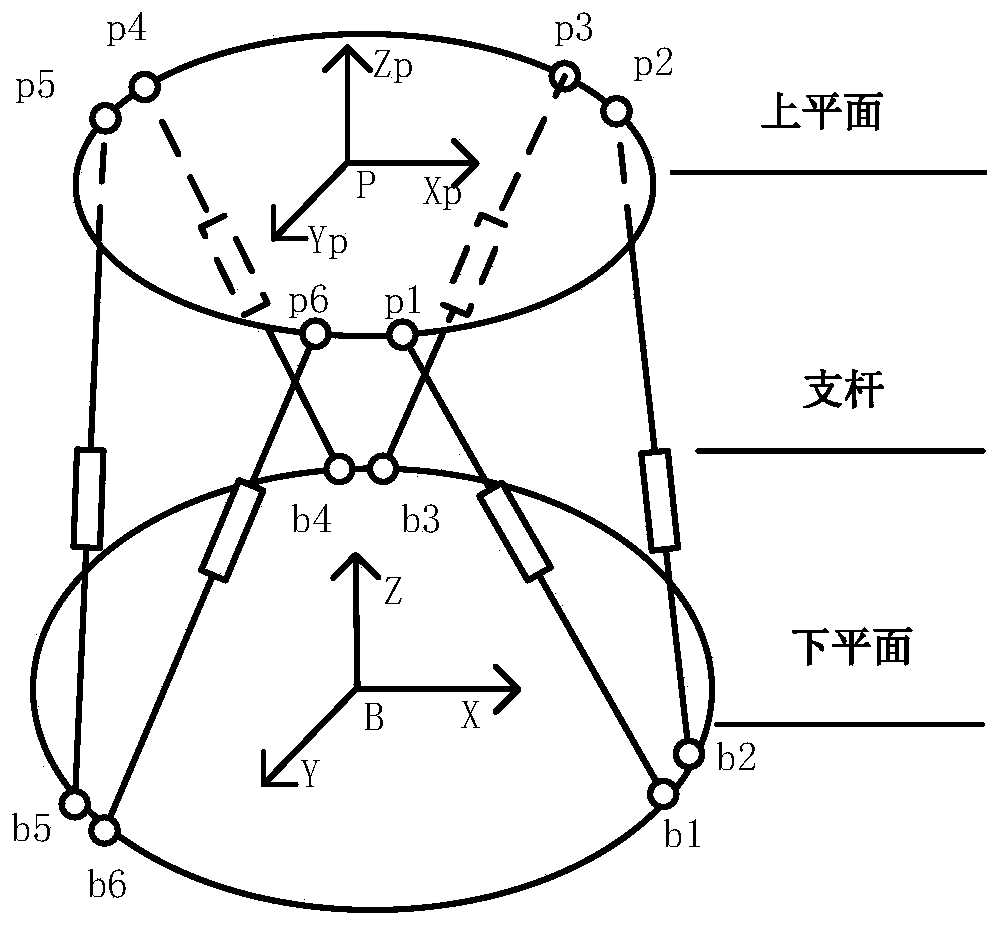
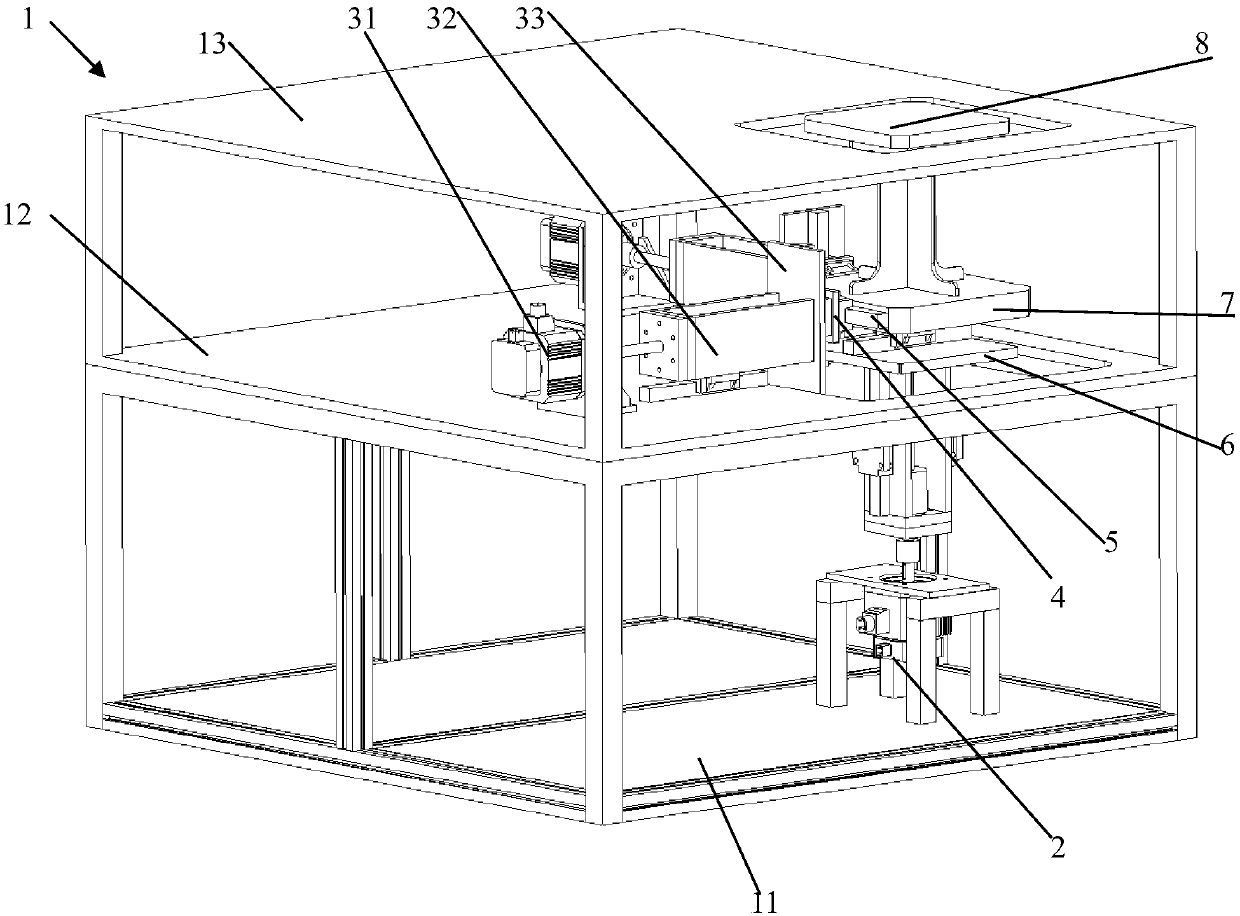
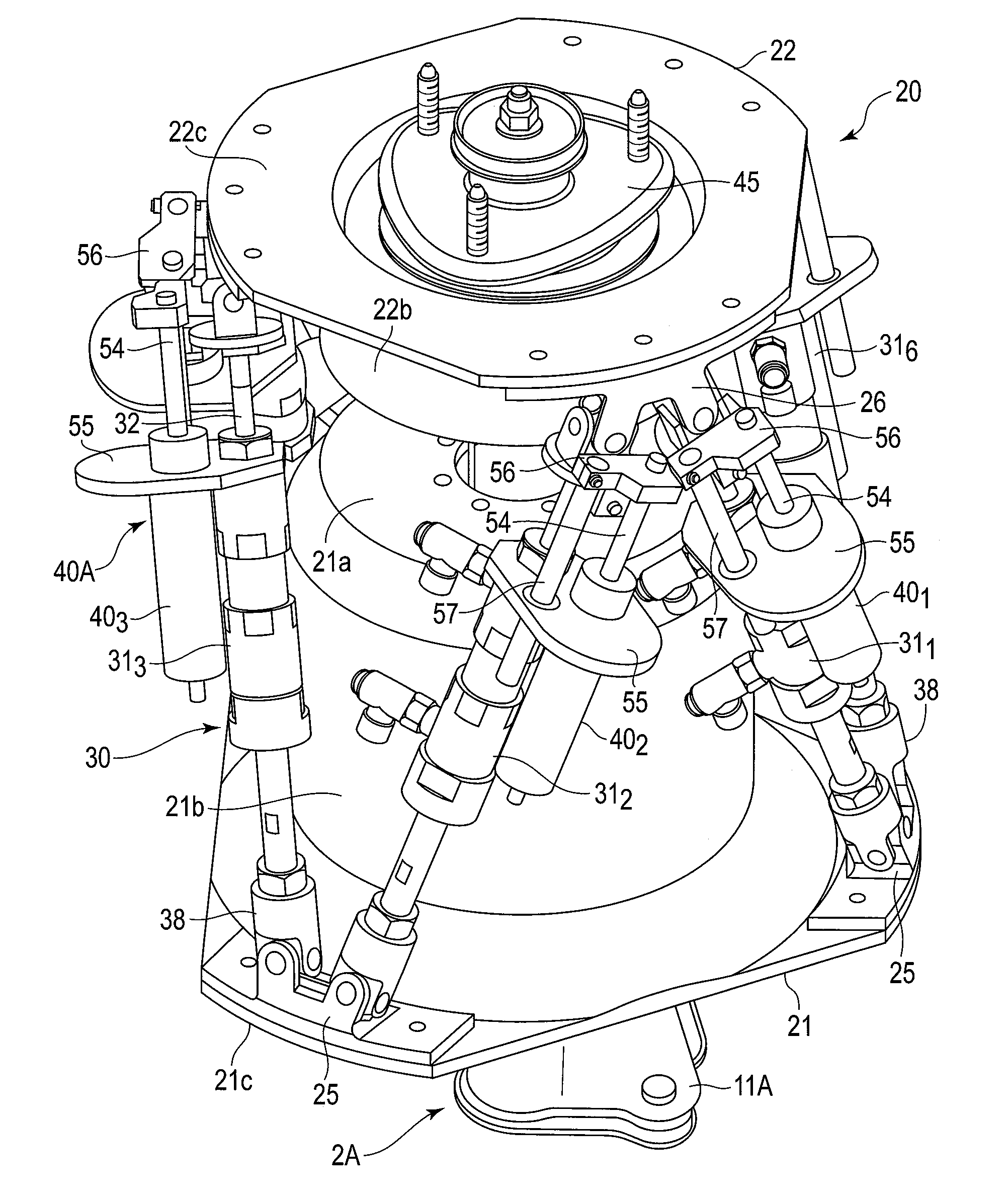
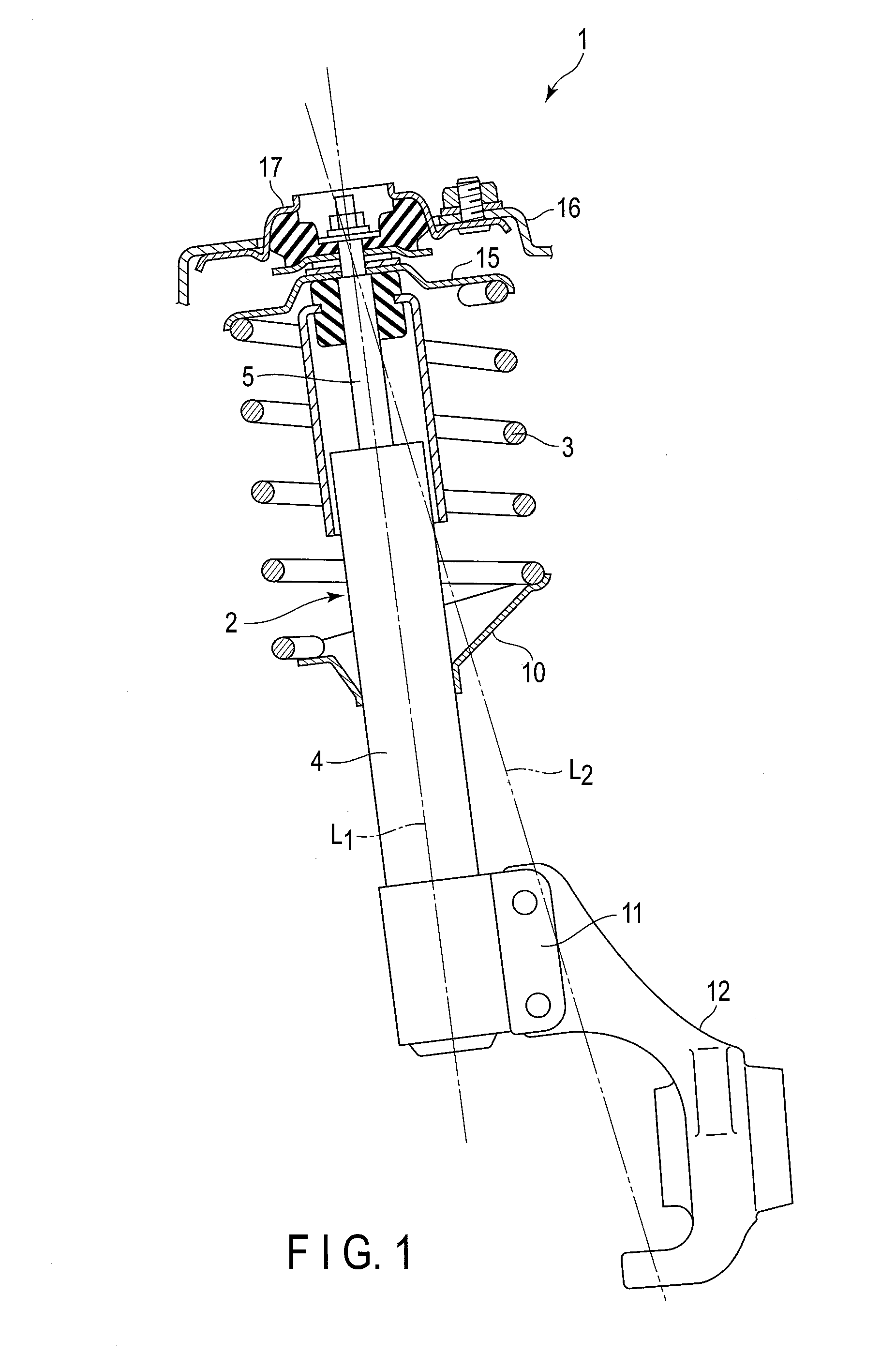
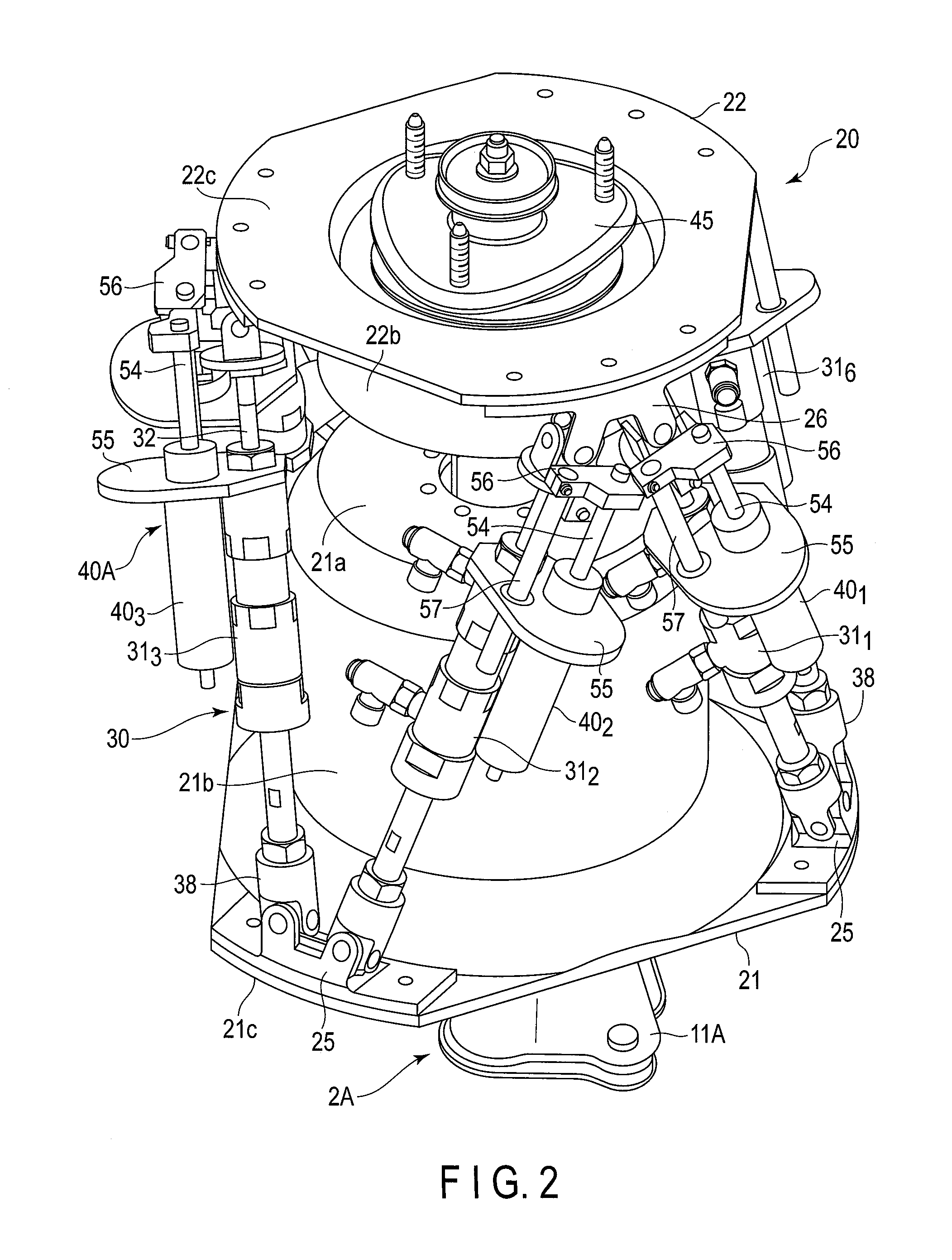
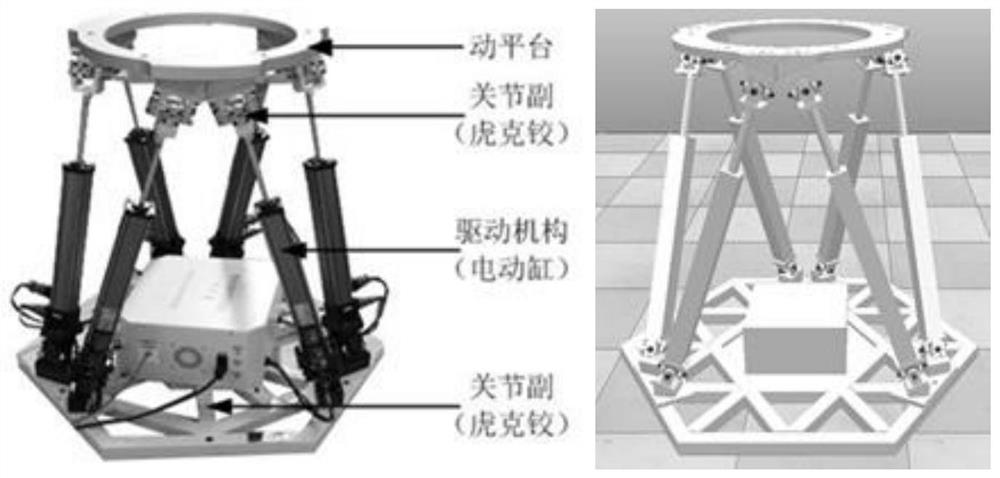
A Gough–Stewart platform is a type of parallel manipulator that has six prismatic actuators, commonly hydraulic jacks or electric linear actuators, attached in pairs to three positions on the platform's baseplate, crossing over to three mounting points on a top plate. All 12 connections are made via universal joints. Devices placed on the top plate can be moved in the six degrees of freedom in which it is possible for a freely-suspended body to move. These are the three linear movements x, y, z (lateral, longitudinal, and vertical), and the three rotations (pitch, roll, and yaw). Because of its motions, it is also called a six-axis platform or 6-DoF platform.
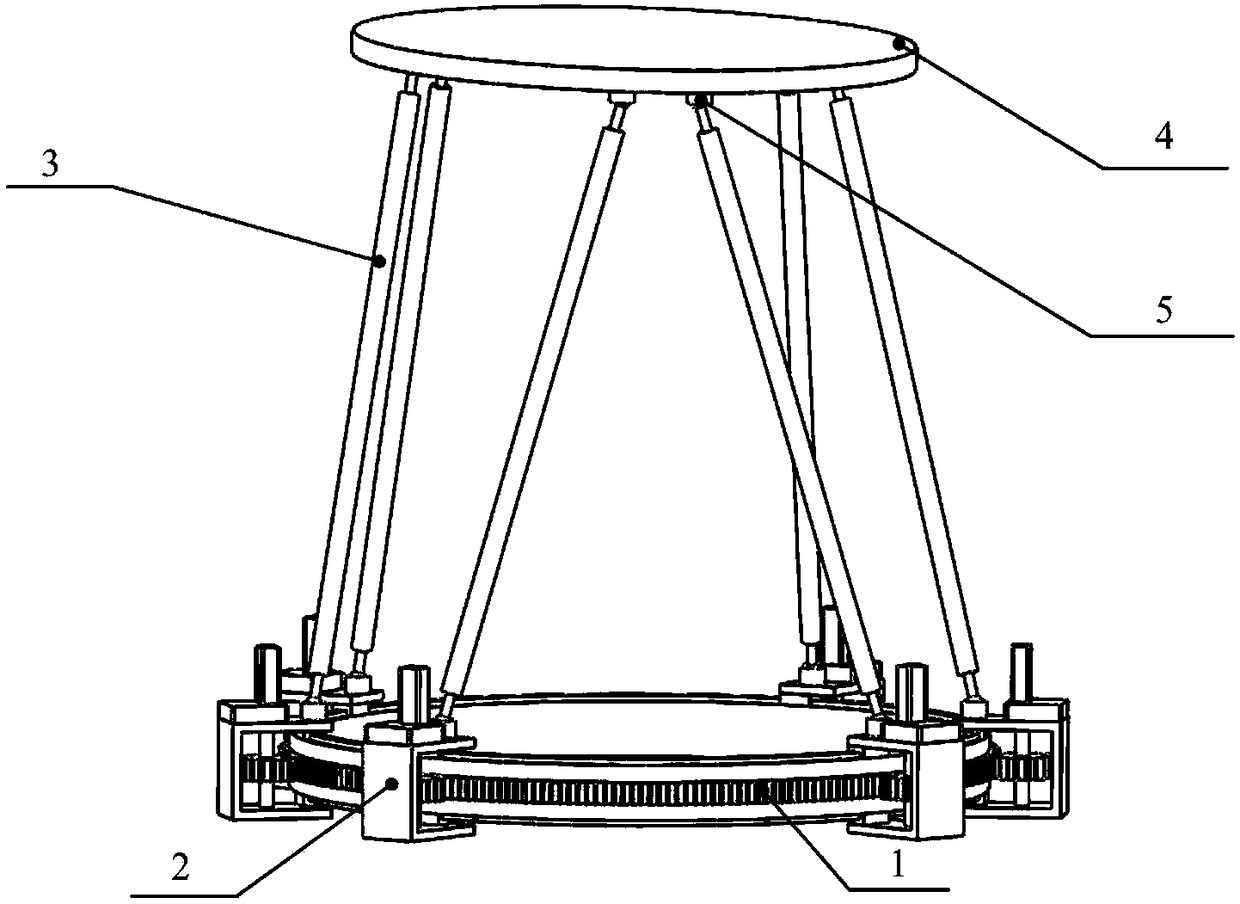
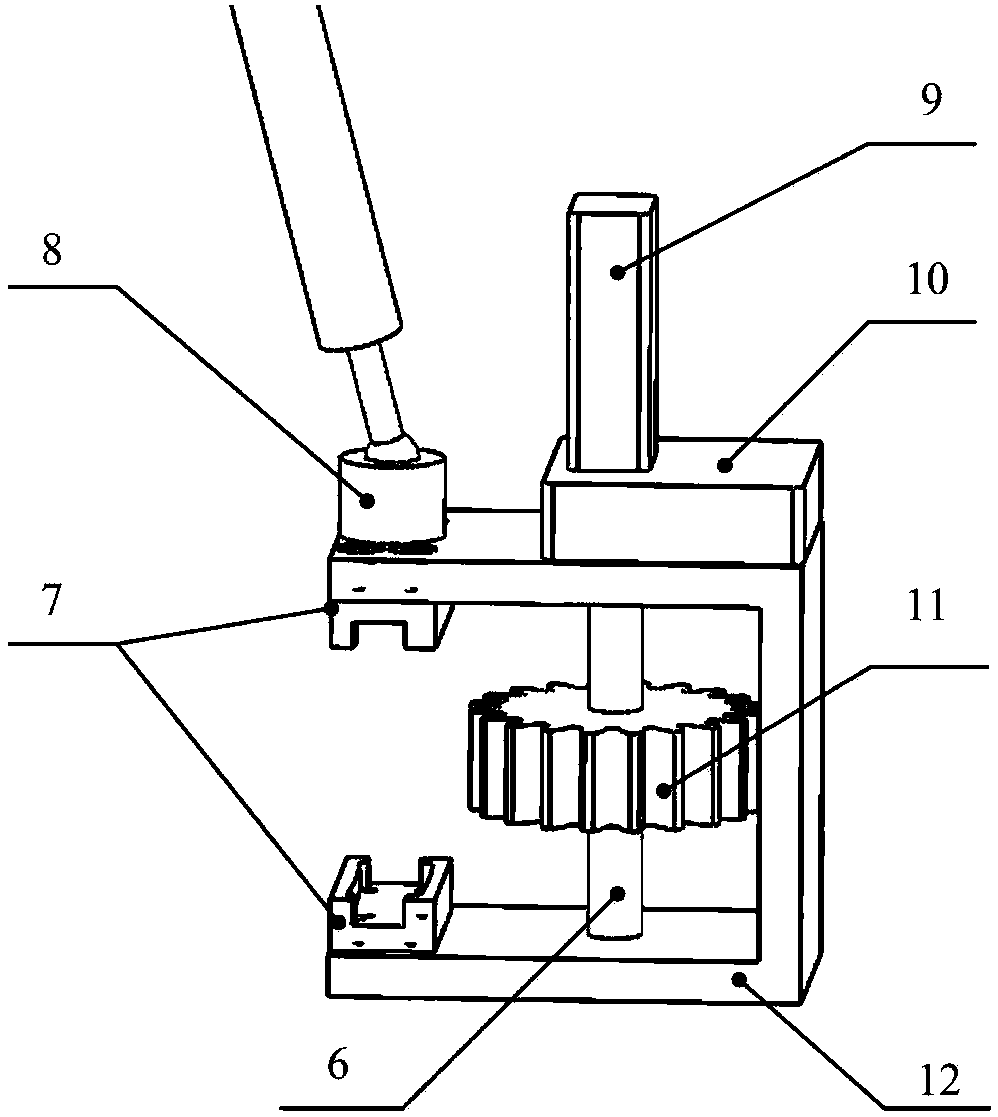
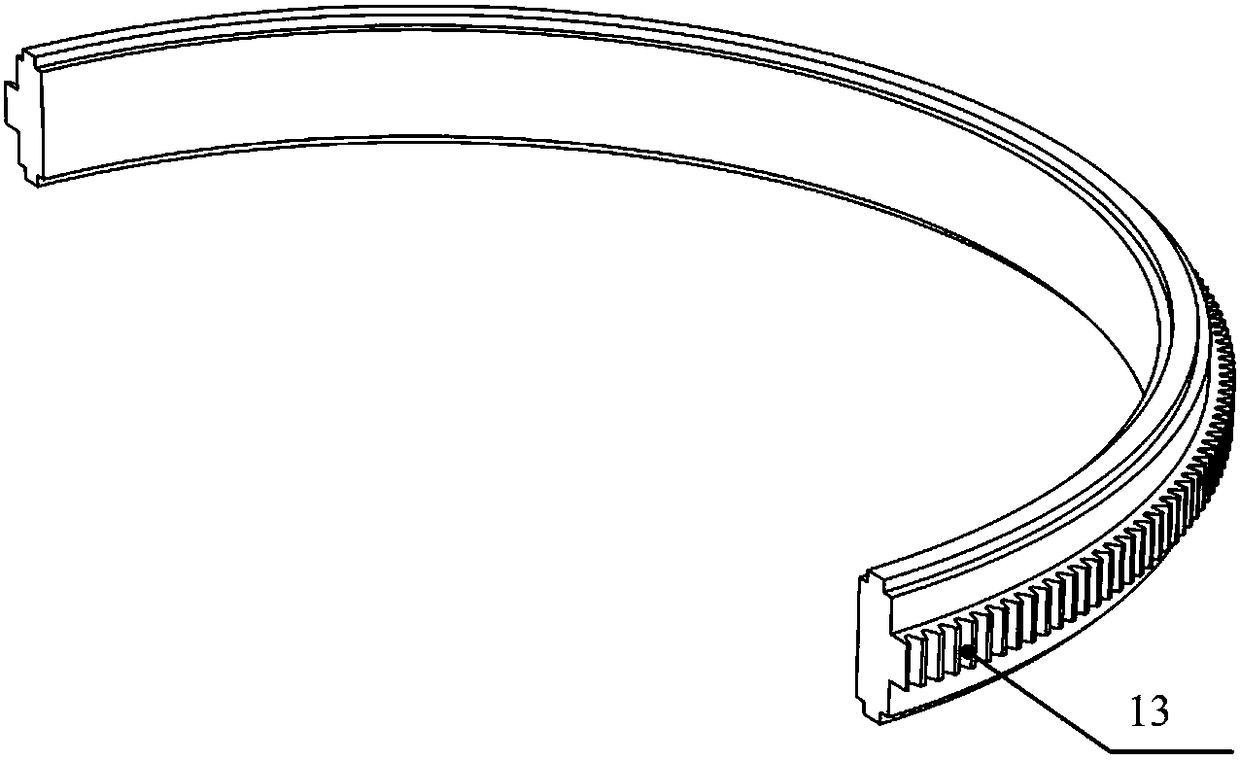
Systems and methods employing a rotary track for machining and manufacturing
InactiveUS6196081B1Low thermal expansionOptimization rangePortable framesJointsThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
The systems and methods described herein include hexapod systems, Stewart platform systems and other mechanical movement systems, in which a set of independently moveable trucks support legs that couple to a working surface capable of holding a machine tool or other end-effector, and preferably wherein the trucks travel across a reference surface, such as around the circumference of a circle or along some other pre-defined geometrical pattern or track. For example, as described herein, the systems include Stewart platform machines that have six supportive legs each of which connects to a truck that can travel independently along a track. By coordinating the movement of these six trucks, the working surface can be moved in three dimensional space and can be oriented about three axes, providing control of roll, pitch and yaw.
Owner:HEXEL CORP
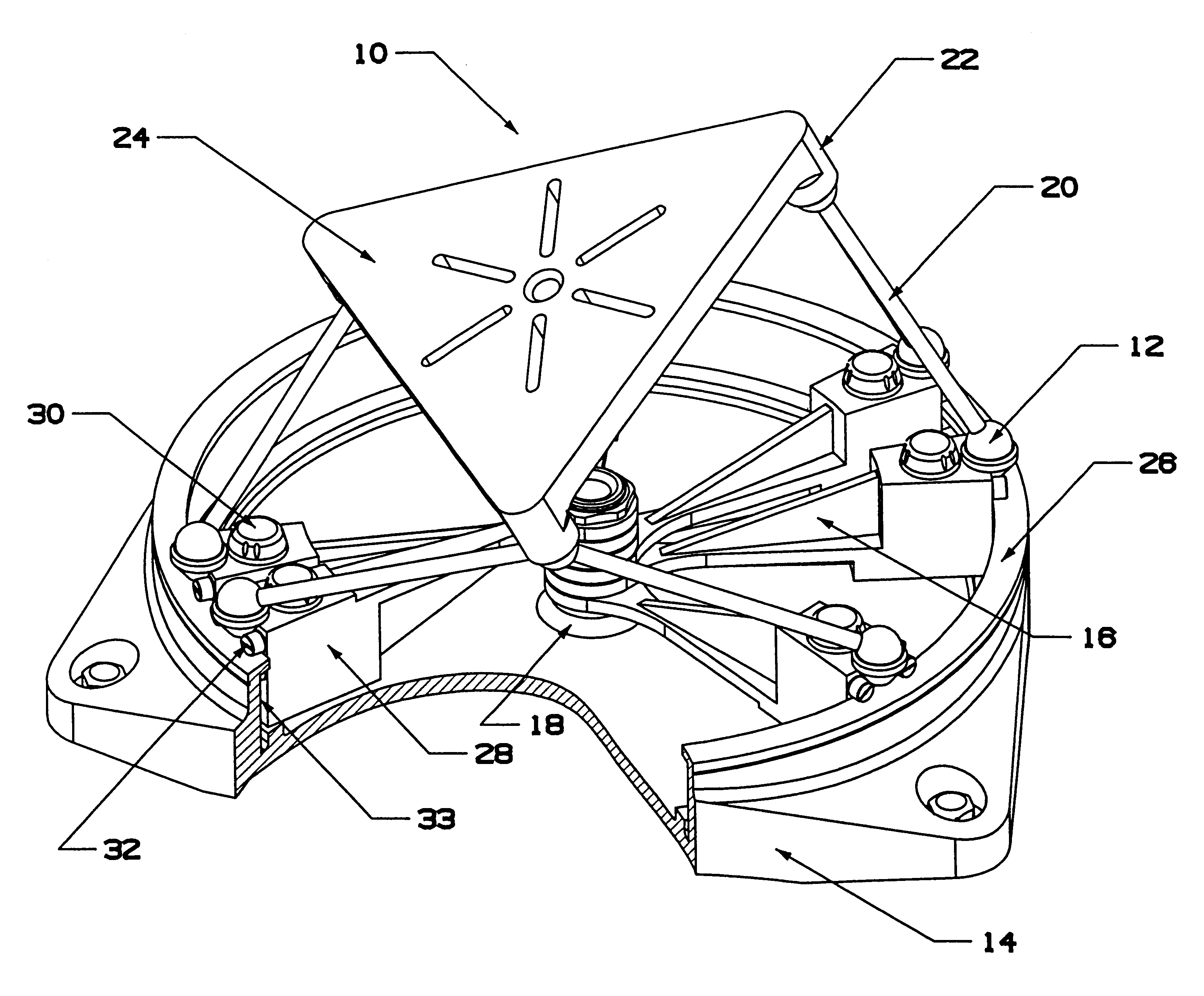
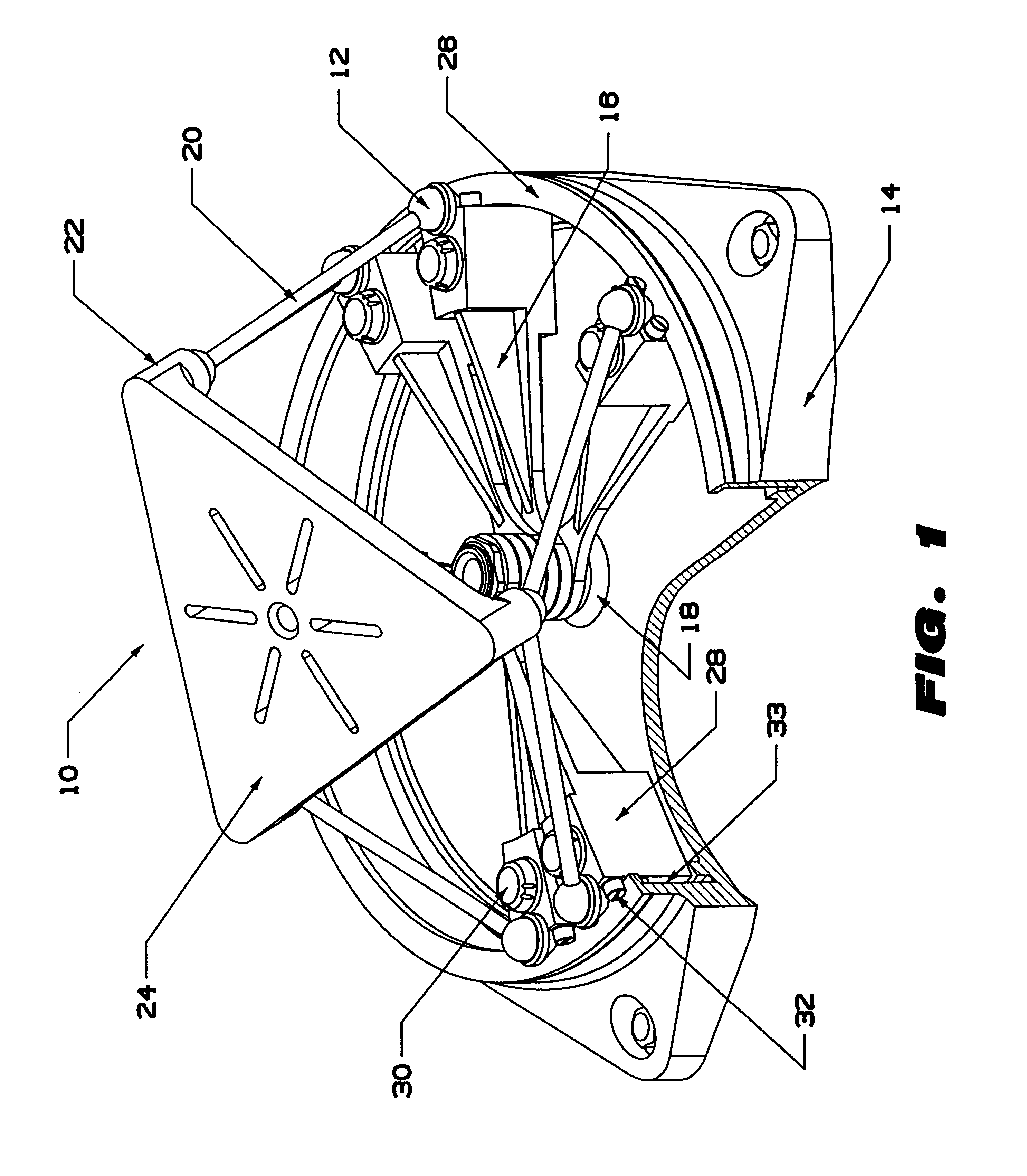
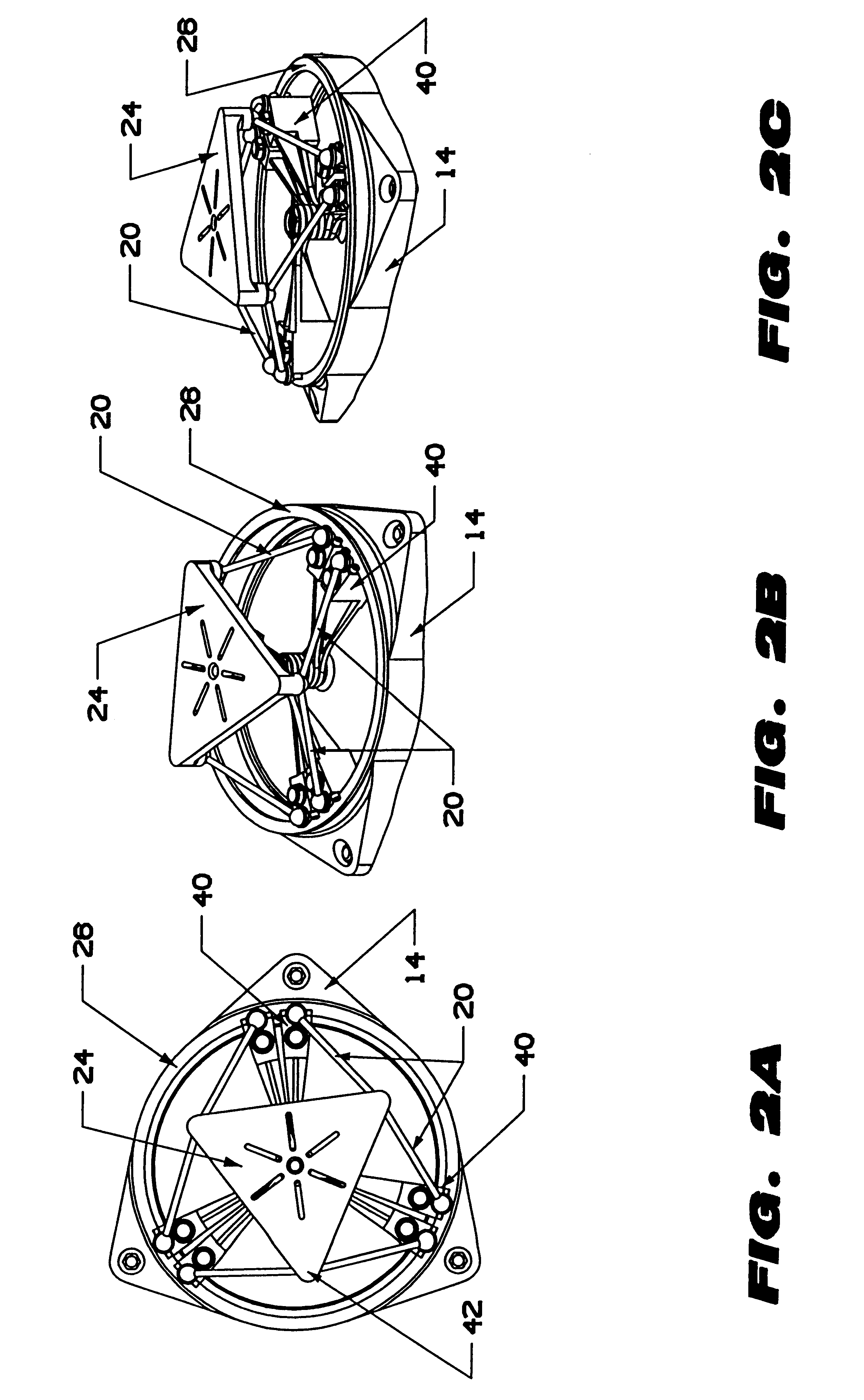
Triangular gimbal
A system and related method to enable six-axis movement of a structure. The system is related to hexapods, Stewart platforms and other mechanical movement systems. It includes a plurality of moveable supportive legs coupled to a platform. For the Stewart platform version of the system, there are six supportive legs, each of which connects to a triangular platform that acts as a base.
Owner:HEXEL CORP
Hex-axis horizontal movement dynamic simulator
InactiveUS7124660B2Move preciselyProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic condition simulationsIsoetes triquetraUniversal joint
A hex-axis horizontal movement dynamic simulator is aimed at Modular Design without hydraulic or pneumatic system but which were conventionally used in the so called Stewart Platform; this dynamic simulator comprises three sets of movement control unit with symmetrical structure located at the positions relative to each other forming three sides of an equilateral triangle, and a load-carrying platform which connected to the three movement control by means of three sets of universal-joint yoke mechanism each relative position located on the load-carrying platform are each other arranged to form as three sides of an equilateral triangle too; with this type of arrangement, this dynamic simulator have a 6-degree of freedom motion when a sets of movement control unit makes different rectilinear motion, the load-carrying platform will generate a combination of spatial translation motion and angular motion.
Owner:INTERNET MOTION NAVIGATOR CORP
Hex-axis horizontal movement dynamic simulator
InactiveUS20040144288A1Move preciselyProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic condition simulationsIsoetes triquetraUniversal joint
A hex-axis horizontal movement dynamic simulator is aimed at Modular Design without hydraulic or pneumatic system but which were conventionally used in the so called Stewart Platform; this dynamic simulator comprises three sets of movement control unit with symmetrical structure located at the positions relative to each other forming three sides of an equilateral triangle, and a load-carrying platform which connected to the three movement control by means of three sets of universal-joint yoke mechanism each relative position located on the load-carrying platform are each other arranged to form as three sides of an equilateral triangle too; with this type of arrangement, this dynamic simulator have a 6-degree of freedom motion when a sets of movement control unit makes different rectilinear motion, the load-carrying platform will generate a combination of spatial translation motion and angular motion.
Owner:INTERNET MOTION NAVIGATOR CORP
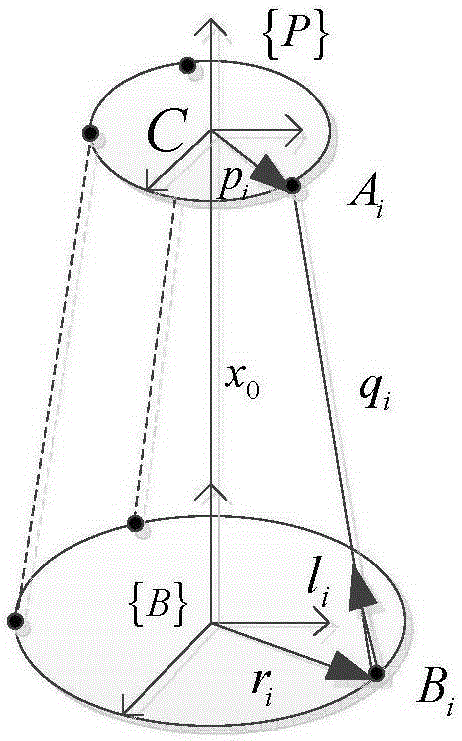
Standard pose calibration method for six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot used for Stewart platform structure
ActiveCN104390612AHigh repeat positioning accuracyStrong reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsCoordinate vectorSimulation
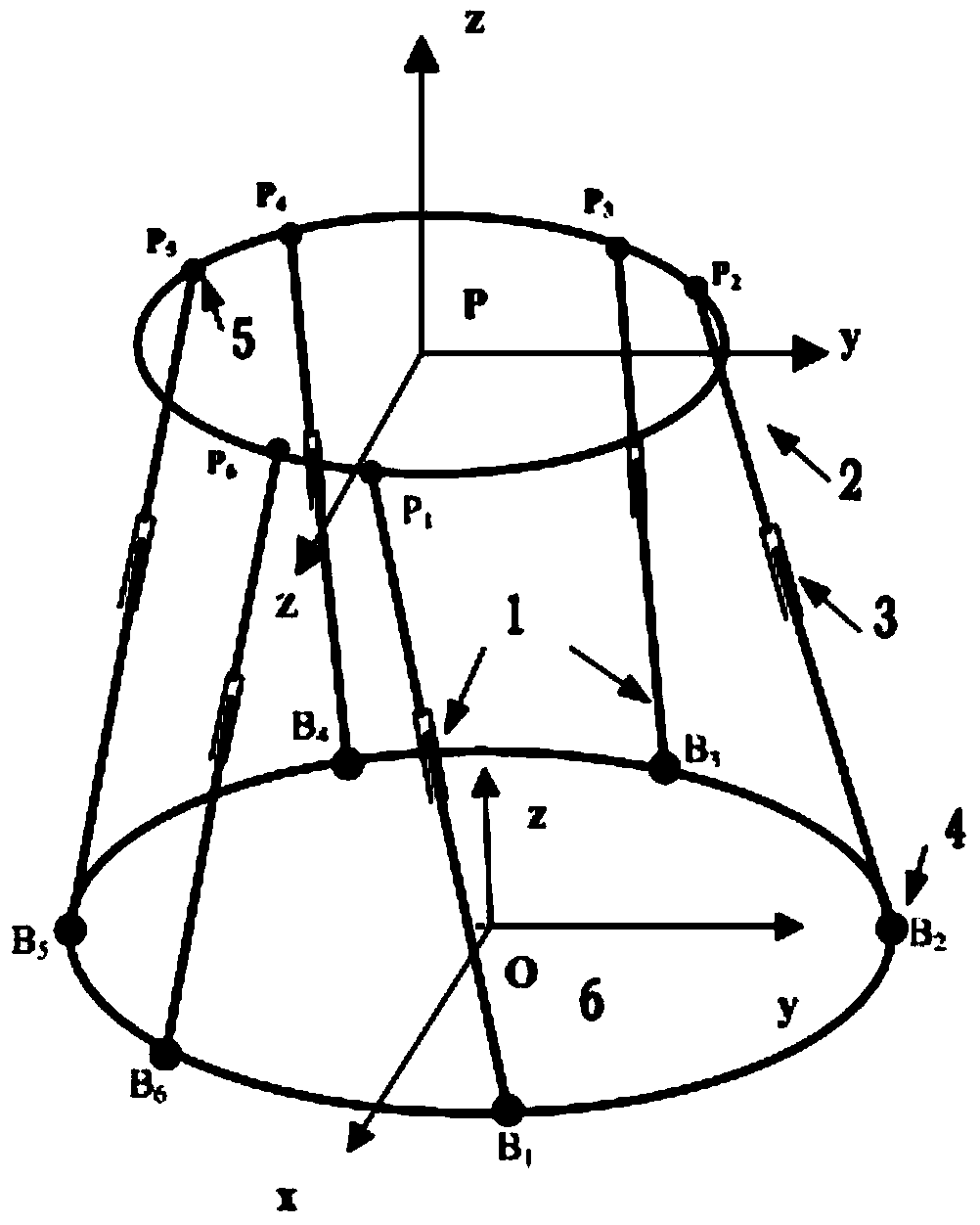
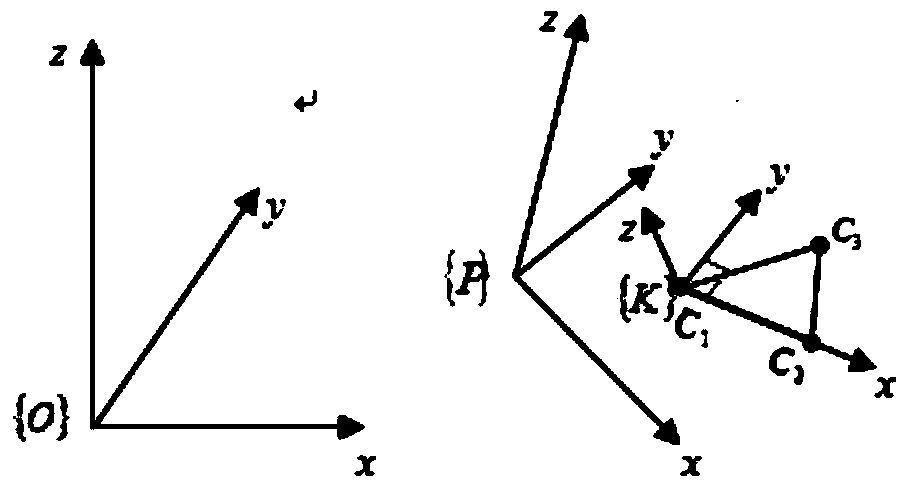
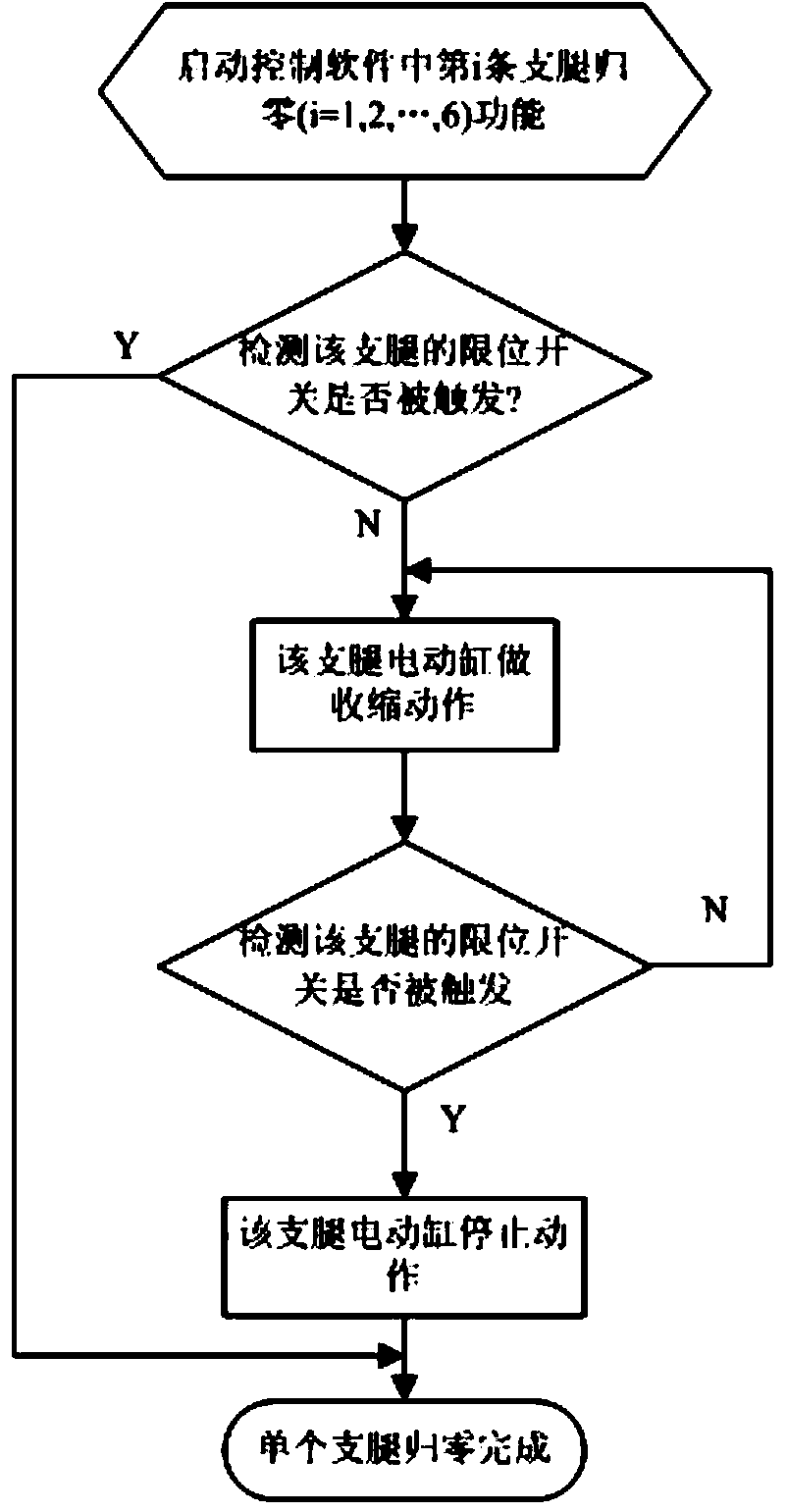
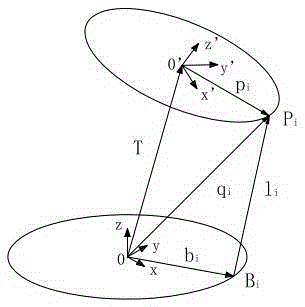
The invention discloses a standard pose calibration method for a six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot used for a Stewart platform structure. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a base coordinate system {O} and a motion platform coordinate system {P}; under the condition of six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot open chain organization, calibrating position coordinate vectors of Hooke hinge centers and spherical hinge centers of the parallel robot in the{O} and the {P} respectively; selecting three mark points on a motion platform and measuring local coordinates of the mark points in the motion platform coordinate system; installing an optocoupler limit switch at the push rod extending end of an electric cylinder of each supporting leg, and assembling the parallel robot to form a closed chain organization; controlling each supporting leg of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot to shorten slowly at a constant speed until each optocoupler limit switch is triggered and stimulates the six legs to stop moving successively, and thus the standard pose of the motion platform is generated; measuring the three mark points on the motion platform, ad calculating the standard pose of the parallel robot; and calculating the initial length of the supporting leg corresponding to the standard pose according to the standard pose. With the method, repeated positioning accuracy is high and reliability is high.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-degree-of-freedom vehicle dynamics test platform
InactiveCN101968403ARealize simulationRealize researchVehicle testingMeasurement of force componentsVehicle dynamicsRoad surface
The invention discloses a multi-degree-of-freedom vehicle dynamics test platform which comprises a double-rod vertical loading hydraulic cylinder with an axial force sensor, a measurement and control system, a roller, a rotating disk, a position servo hydraulic cylinder, a six-degree-of-freedom Stewart platform, an outer rotor motor, a six-force-component sensor and the like. The use of the multi-degree-of-freedom vehicle dynamics test platform can simulate the changes of geometrical shape and mechanical properties of a road pavement and the incentive role of the changes to wheels, the exertion of any one-dimensional or multi-dimensional force in six-dimensional pavement incentive force on the wheels can simultaneously carry out pavement simulation, static load simulation and dynamic load simulation, and the wheels can change the direction relative to the roller, thereby realizing the simulation of large tire sideslip angle caused by turning of a vehicle, being capable of measuring steering angles of the wheels and six-dimensional force born on the wheels, carrying out better simulation and testing on the practical driving working status of the vehicle, realizing the comprehensive research of the multi-degree-of-freedom vehicle dynamics and providing the vehicle dynamics test platform with more excellent performances.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
Robot single-leg assembly control development performance test platform and method
The invention discloses a robot single-leg assembly control development performance test platform and method. The platform comprises a gantry three-coordinate mechanical arm assembly, a robot leg connection bracket, a Stewart platform, a six-dimensional force sensor, a robot single-leg assembly and a five-dimensional force measurement platform, wherein a servo controller and a displacement sensor are integrated in the Stewart platform; the Stewart platform is invertedly arranged on a base of the robot leg bracket; the five-dimensional force measurement platform is arranged at the center of the ground below the robot single-leg assembly; and the robot leg connection bracket is fixed on a Z-axis-direction mobile supporting frame assembly of the gantry three-coordinate mechanical arm assembly. The test platform is suitable for single-leg movement and quick gait control during bionic gait generation of a four-foot or multi-foot hydraulic driving robot as well as development and research on multiple control strategies for robot load distribution, control force distribution, single-leg force feedback control and 'discrete gait and continuous force control' attitude stabilization control.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Structural dimension parameter adjustable Mecanum wheel type mobile robot
The invention discloses a structural dimension parameter adjustable Mecanum wheel type mobile robot. The robot is composed of a structural dimension parameter adjustable Stewart platform and a Mecanum wheel type mobile platform, wherein the Stewart platform comprises a Stewart movable platform, a Stewart static platform and a linkage mechanism. The Stewart platform is a parallel robot which has six freedom degrees and is applicable to heavy load; the Mecanum wheel type mobile platform has the characteristics of heavy load and all-direction movement; a mobile parallel robot formed by combination of the Mecanum wheel type mobile platform and the Stewart platform has the characteristics of being movable in all directions, high in positioning precision, capable of being heavily loaded and flexible in adjustment of tail end posture, and is applicable to industrial demands of flexible processing, overloading transportation and the like. By respectively changing the structural dimension parameters of the Stewart movable platform and the Stewart static platform, the robot disclosed by the invention is correspondingly changed in overall height, tail end motion space range and bearing capacity so as to adapt to work demands, so the applicability of the Mecanum wheel type mobile parallel robot is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
6-PSS parallel mechanism and position forward and inverse solution method
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots and discloses a 6-PSS parallel mechanism and a position forward and inverse solution method. A circular rail is arranged and provided with six sliding modules which move actively and precisely along the rail. The sliding modules are connected with the lower ends of connecting rods of a fixed length through spherical hinges correspondingly. Theupper ends of the connecting rods are connected with a motion platform through spherical hinges correspondingly. According to the 6-PSS parallel mechanism and the position forward and inverse solution method, six-degree-of-freedom motion of the motion platform can be achieved, the mechanism is remarkably characterized in that the motion platform can rotate at any angle around the vertical axis, the motion flexibility of the mechanism is improved, and the posture adjustment work space is expanded; and the mechanism can be applied to multiple occasions including light radar antenna pedestals, radiotelescope feed source supporting platforms, motion simulators and the like. The mechanism and method provided by the invention are easy to operate, and the problem that a Stewart platform traditional six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot is limited in work space is effectively relieved; and the motion platform moves by driving the six parallel sliding modules, and the motion speed of the motionplatform is increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
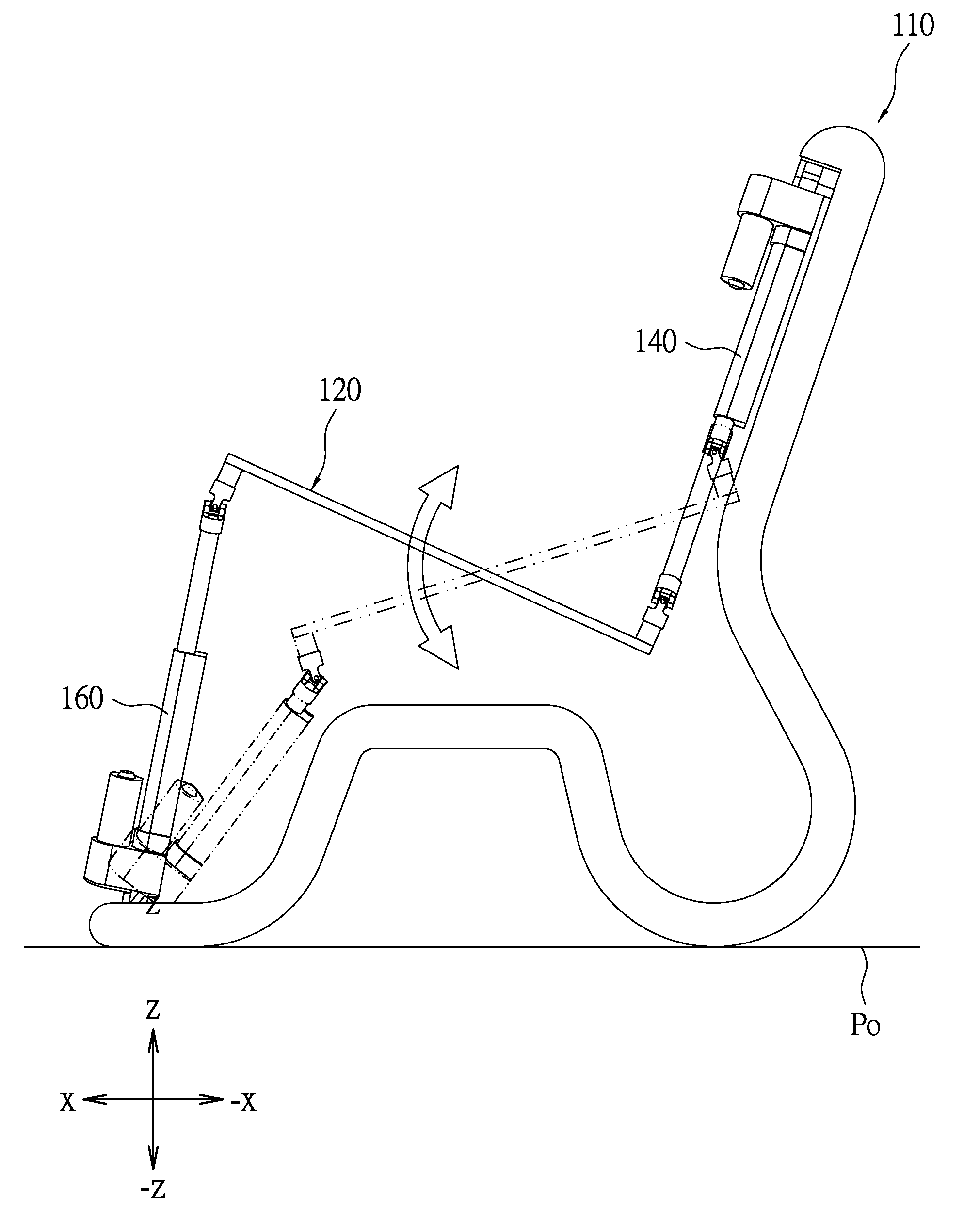
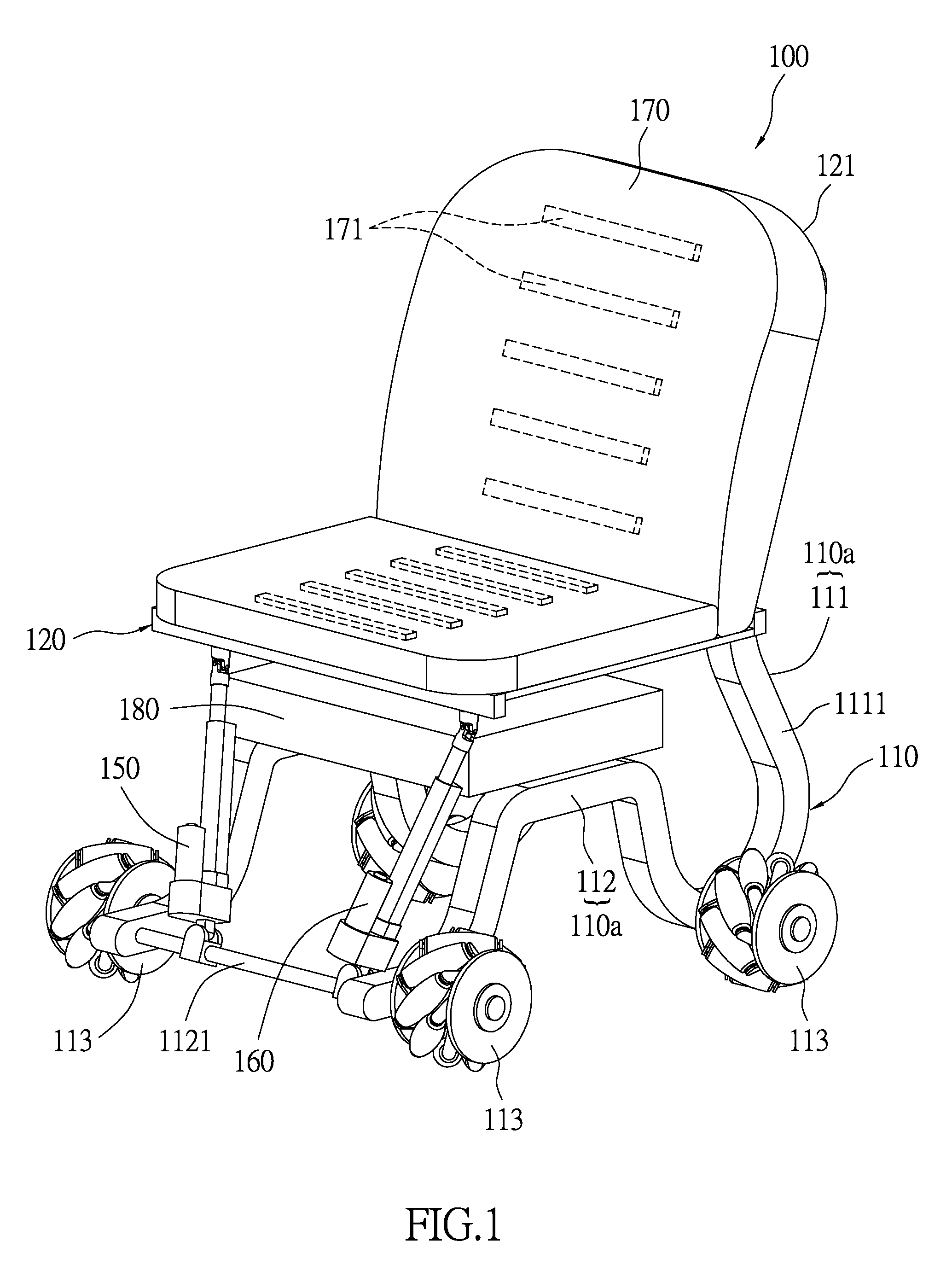
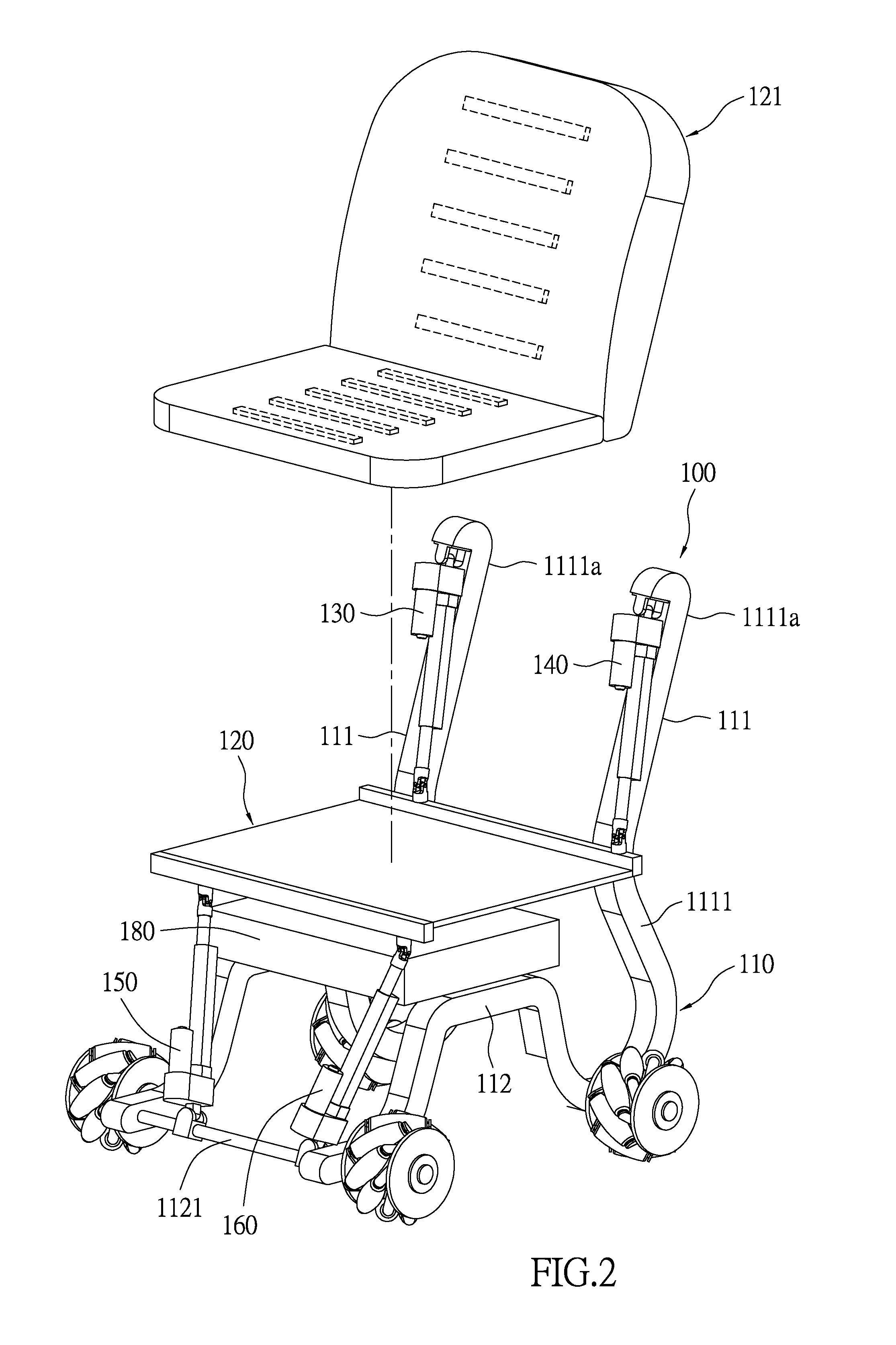
Movement device having a stewart platform
ActiveUS20140339391A1Reduce control complexityWheelchairs/patient conveyanceStands/trestlesVertical projectionClassical mechanics
A movement device having a Stewart platform has a supporting body disposed on a horizontal plane, a movable platform, and four extensible links rotatably connected between the supporting body and the platform. The extension directions of the upper extensible links are in parallel with one another. When the movement device is in an equilibrium condition, the upper extensible links lie in a first common plane. When the movement device is in an equilibrium condition, vertical projections of the extension directions of the extensible links on a normal plane slant toward the horizontal plane; the vertical projection of the extension direction of the first bottom extensible link slants toward a first direction whereas the vertical projections of the extension directions of the other three extensible links slant toward a second direction, which is opposite to the first direction.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
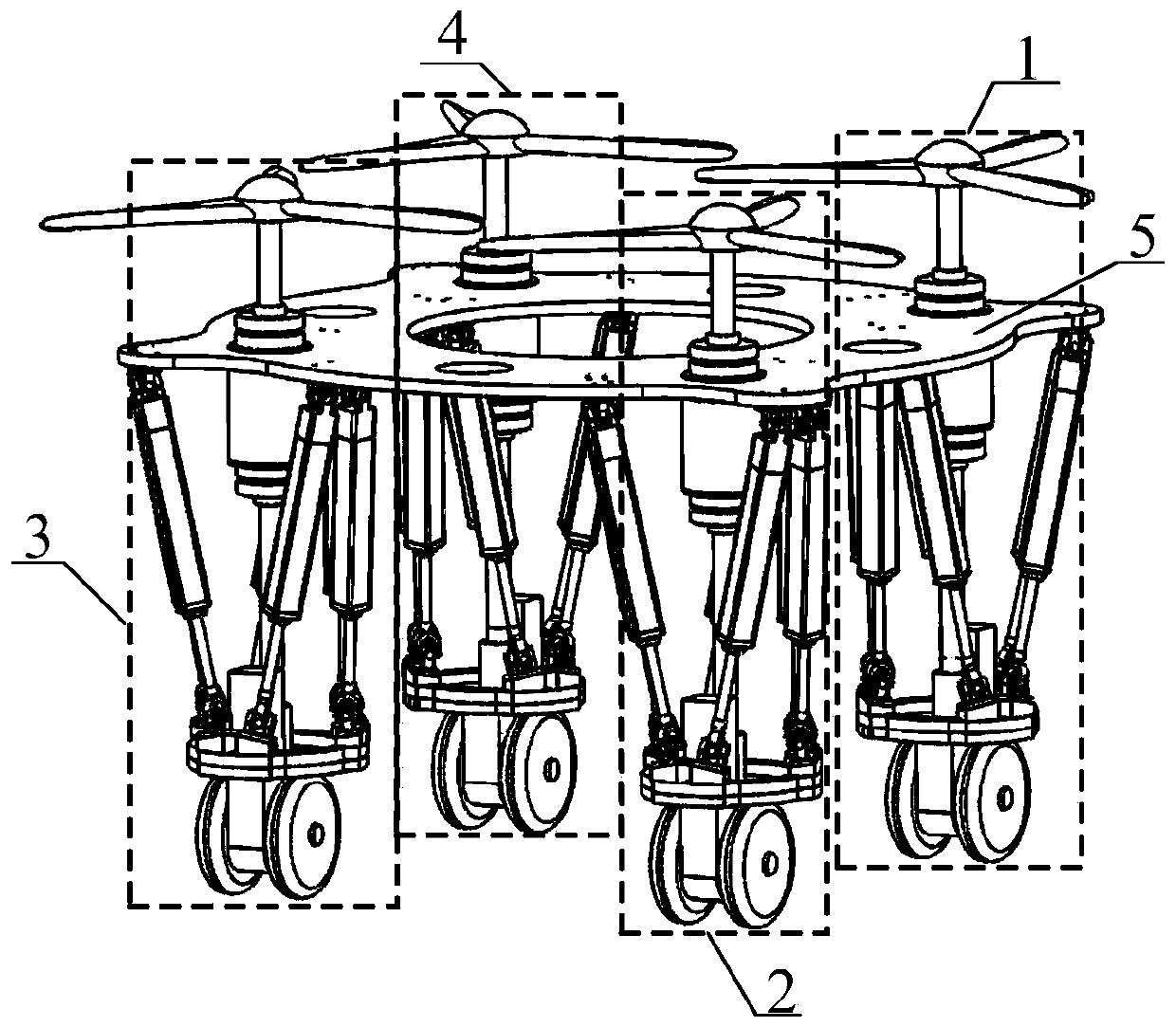
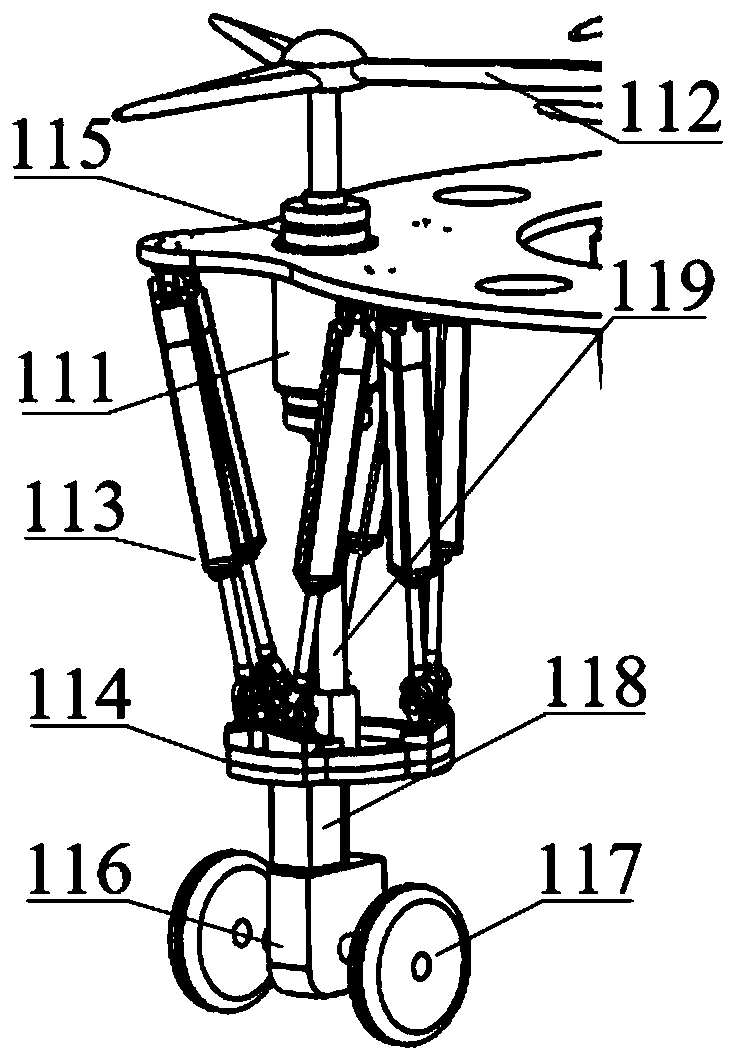
Air-ground integrated electric parallel-connection type wheel-foot driving mechanism
ActiveCN110126562AImprove athletic abilityPass efficientlyAircraft convertible vehiclesConnection typeRoad surface
The invention discloses an air-ground integrated electric parallel-connection type wheel-foot driving mechanism. The air-ground integrated electric parallel-connection type wheel-foot driving mechanism comprises a fuselage, a Stewart platform, flight driving modules, wheel-foot driving modules and transmission connecting rods; the flight driving modules can realize flight movement, and the wheel-foot driving modules can be switched to be in foot-type movement or wheel-type movement or wheel-foot composite movement by locking and unlocking idler wheels; the Stewart platform is reversely arranged, the fuselage is fixedly connected with a lower platform of the Stewart platform, the flight driving modules are mounted on the fuselage, the wheel-foot driving modules are mounted on an upper platform of the Stewart platform, and the flight driving modules are connected with the wheel-foot driving modules through the transmission connecting rods to constitute driving devices; and the four driving devices are evenly arranged around the fuselage, the flight driving modules and the wheel-foot driving modules are controlled to be connected and disconnected with the transmission connecting rodscorrespondingly to realize switching of the flight movement, the foot-type movement, the wheel-type movement and the wheel-foot composite movement. According to the air-ground integrated electric parallel-connection type wheel-foot driving mechanism, the defect that a conventional robot cannot pass on the complex road surface and the road surface with obstacles and even in the extreme environmentcan be avoided.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
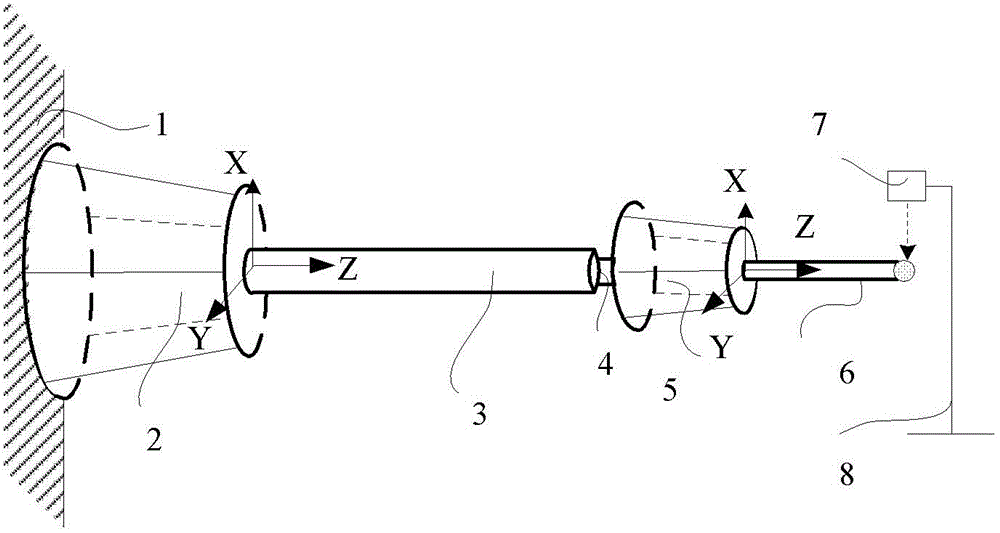
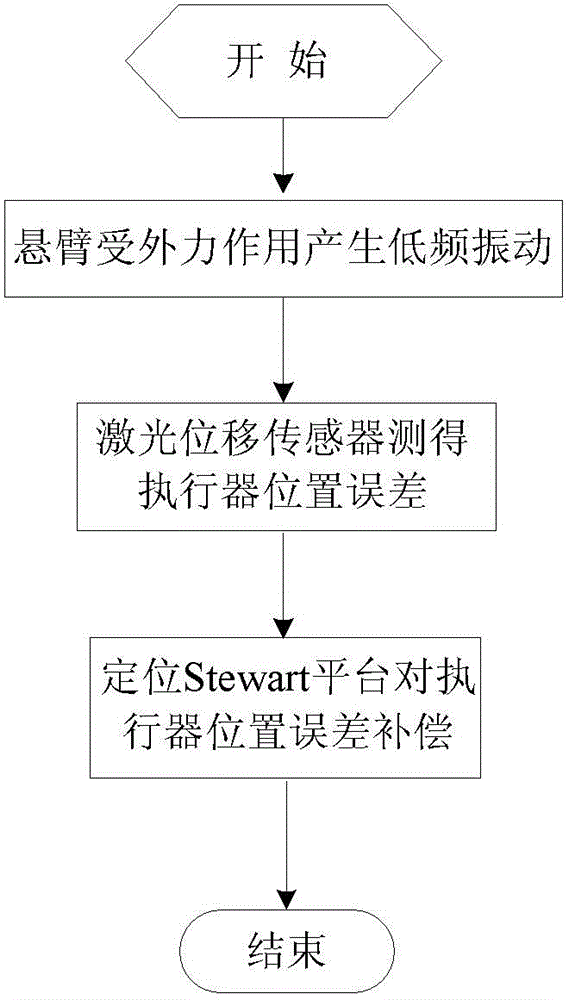
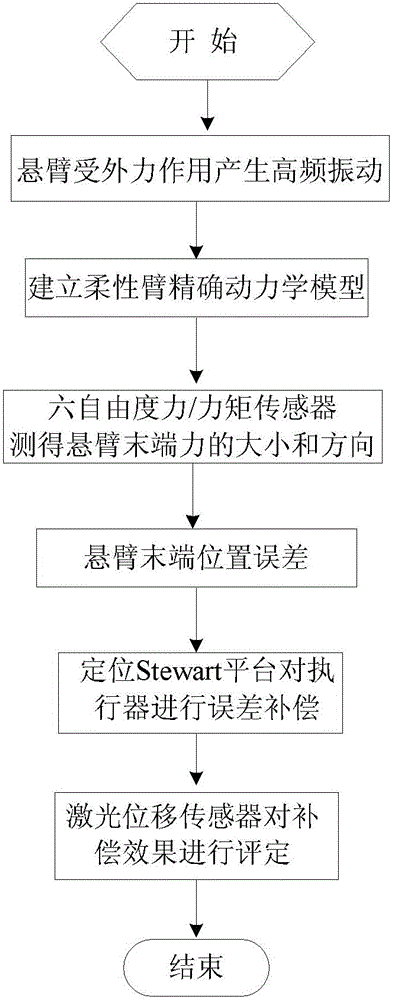
Cantilever tail end vibration analysis and error compensation method
InactiveCN103144110AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorDynamic modelsCompensation effect
The invention discloses a cantilever tail end vibration analysis and error compensation method, which comprises the following steps: simulating low-frequency vibration of the cantilever by a base body Stewart platform, and compensating the space error of an actuator tail end by a positioning Stewart platform based on the value measured by a laser displacement transducer; and simulating high-frequency vibration of the cantilever by a scaled-down cantilever based on the parameterized standard excitation, measuring the space error of the actuator tail end based on a cantilever distribution parameter dynamic model and a force sensor, and compensating the space error by the positioning Stewart platform based on the measuring, wherein the compensation effect is assessed by the laser displacement transducer. According to the invention, the space error of the cantilever tail end is measured based on a cantilever precise dynamic model and the force sensor, which improves the error compensation precision and efficiency of the positioning Stewart platform; and meanwhile, based on the space error caused by the positioning Stewart platform in compensating high / low-frequency vibration, the static and dynamic positioning accuracy of the actuator can be improved.
Owner:天津中科智能技术研究院有限公司
Six-dimensional force transducer calibration device
InactiveCN104236794ARealize the loadReduce calibration errorForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingEngineeringSpatial movement
The invention discloses a six-dimensional force transducer calibration device which comprises a base, a sensor fixing platform, a calibration operation platform, an upper three-jaw chuck, a lower three-jaw chuck, electric push cylinders, standard one-way force sensors and universal hinges. The calibration operation platform, the electric push cylinders, the universal hinges and the base form a Stewart platform structure. By the adoption of the Stewart platform structure, a Stewart platform can perform any spatial movement in the Stewart structure, loading of any spatial force can be realized, sensors or loading force sources do not need to move, and calibration error generated from moving of the sensors or the loading force sources is decreased. The electric push cylinders serve as the loading force sources, and automatic, continuous and highly accurate loading can be realized. Date measured by the six standard one-way force sensors and data outputted by calibration sensors are subjected to comparative analysis, and the standard one-way force sensors are high in accuracy and can accurately calibrate performance of the six-dimensional force sensors.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and methods of positioning a subsea object
InactiveUS20120282064A1Easy to installEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureOcean bottomMarine engineering
A manipulator tool for installing and retrieving objects from a fixed or floating structure in a subsea tidal environment includes an articulated arm attached to the fixed or floating structure. The tool may be configured to compensate for movement of the objects due to tidal forces. In one embodiment, a stewart platform is used as a compensator to maintain the objects in a substantially stationary position in the tidal environment.
Owner:HALLIN MARINE SINGAPORE PTE
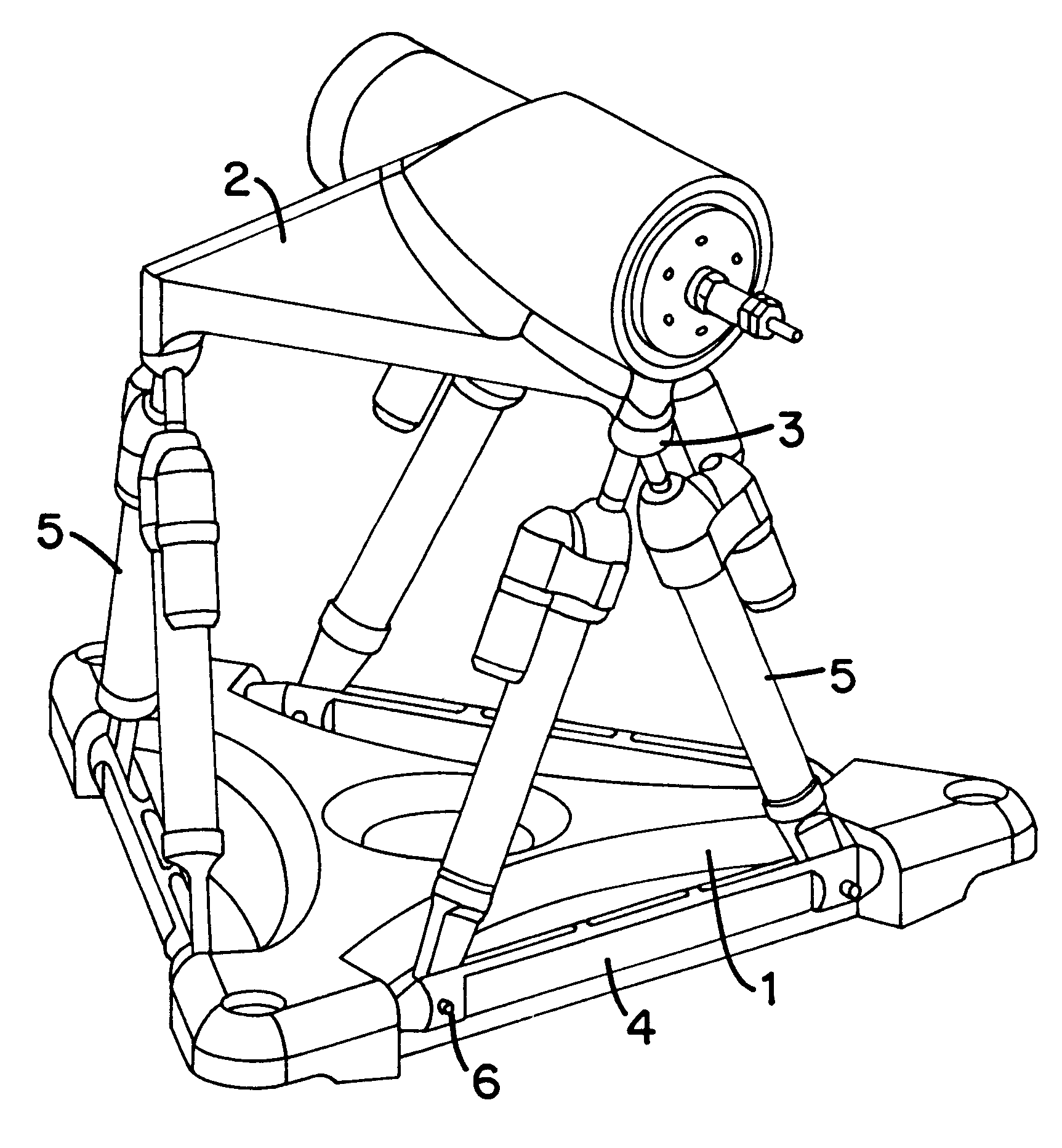
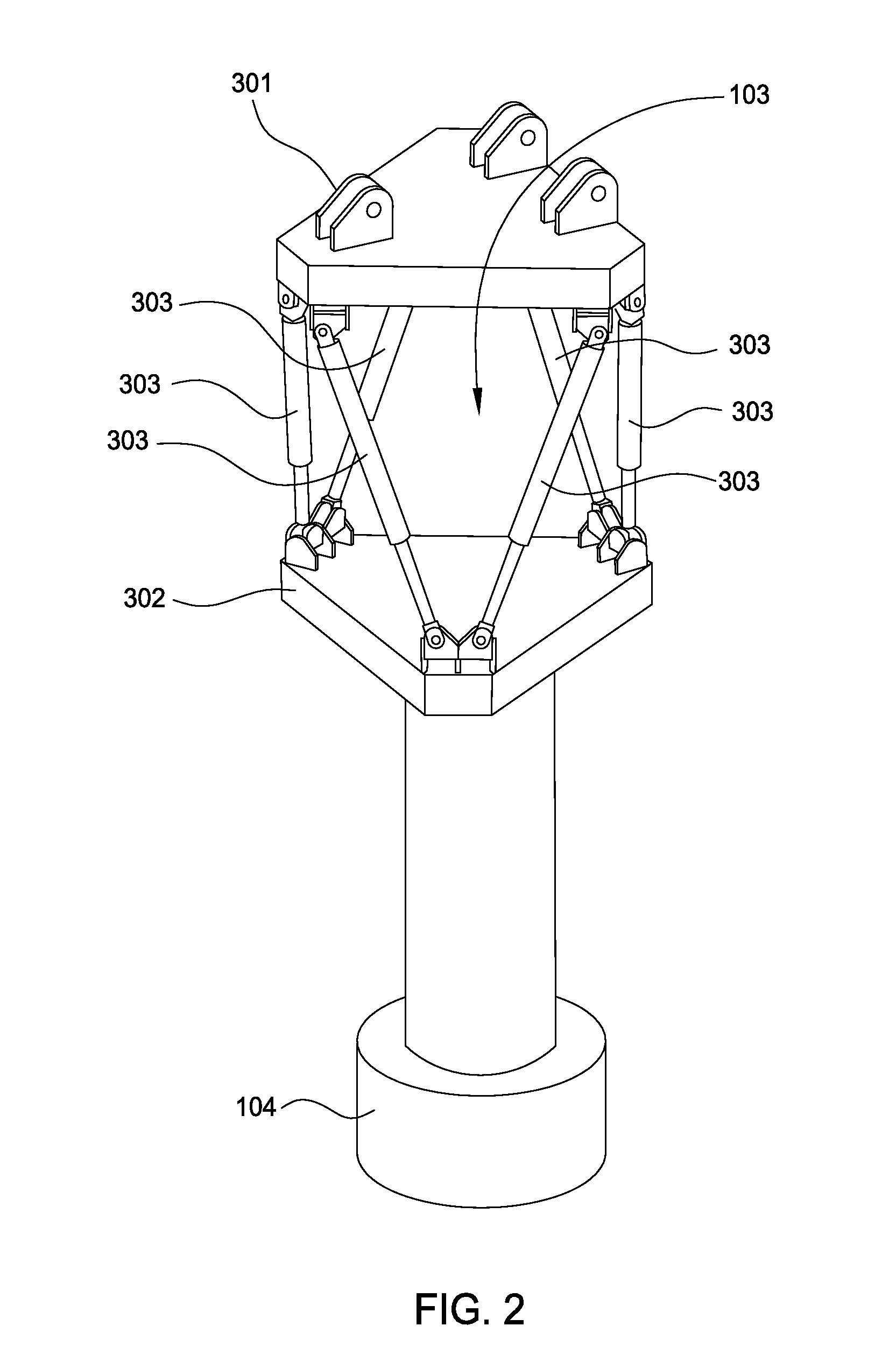
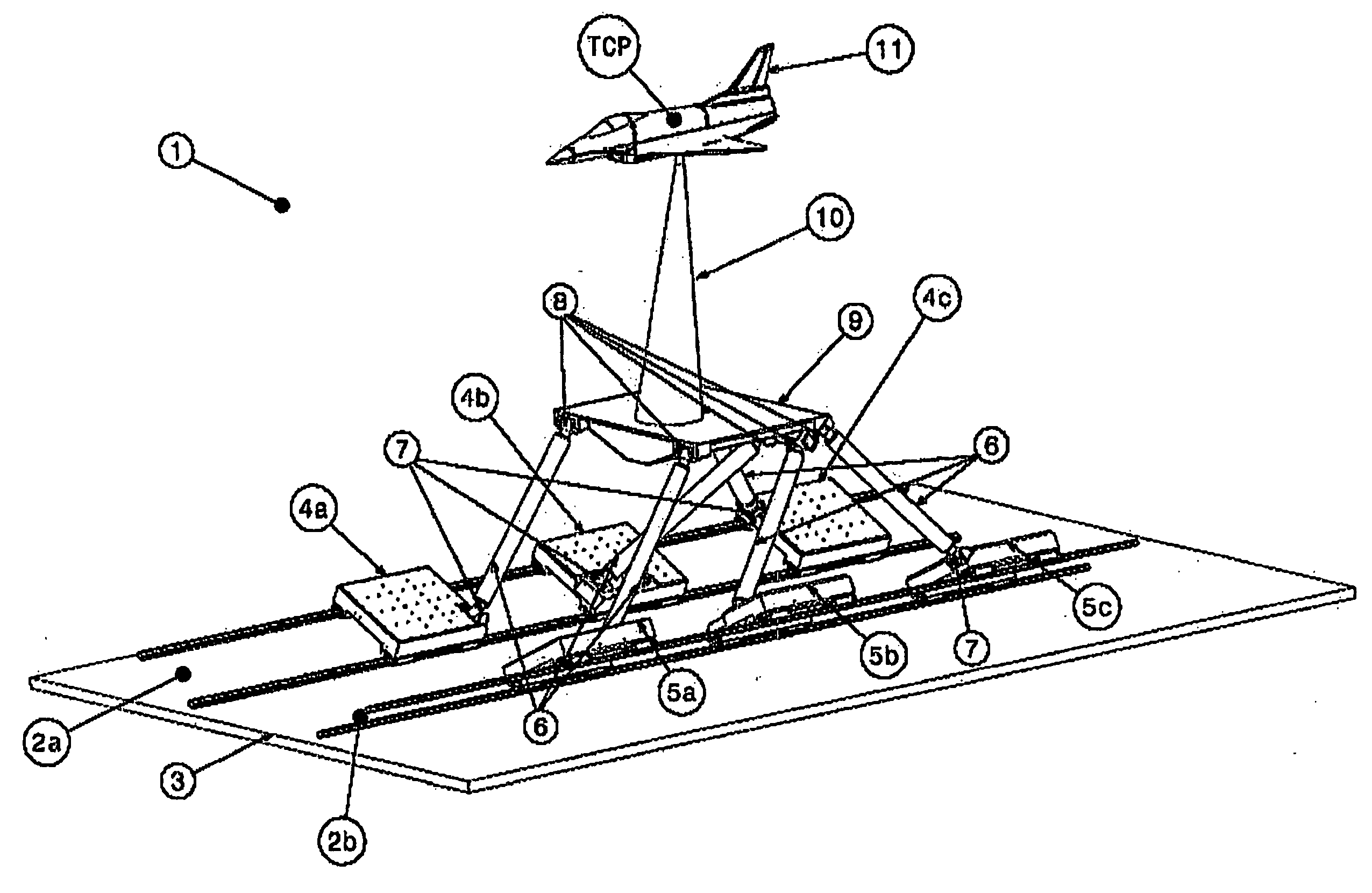
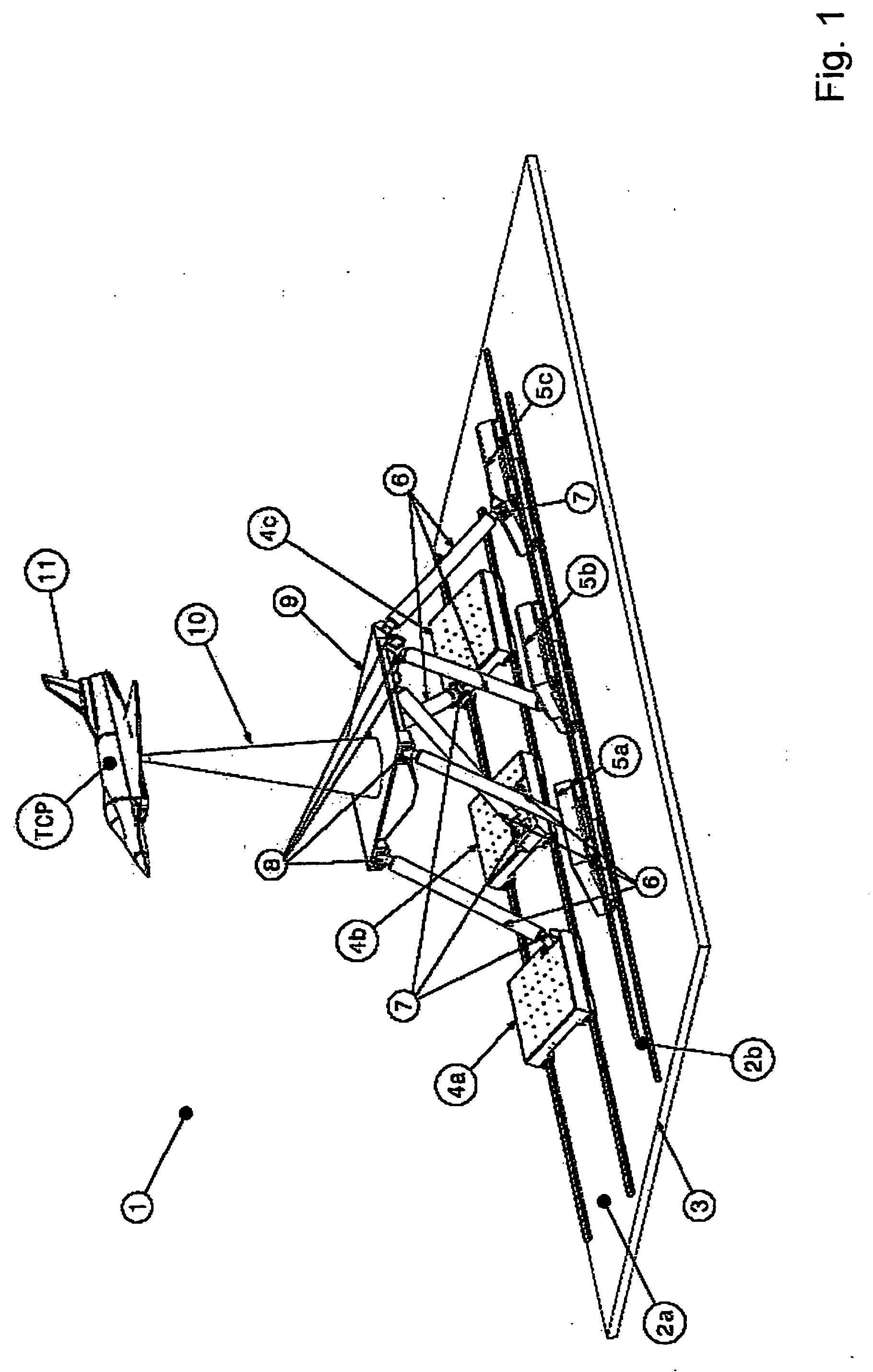
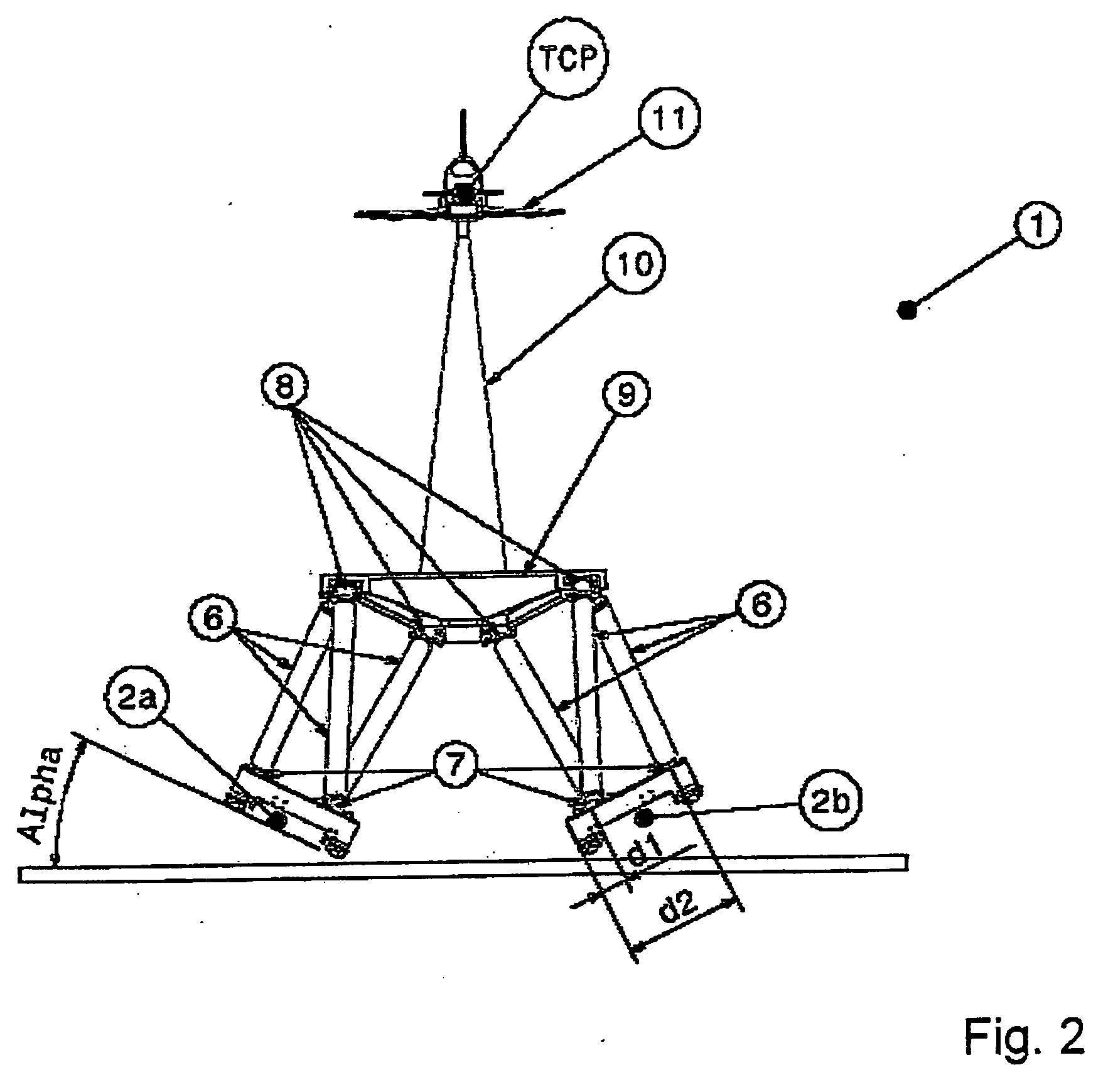
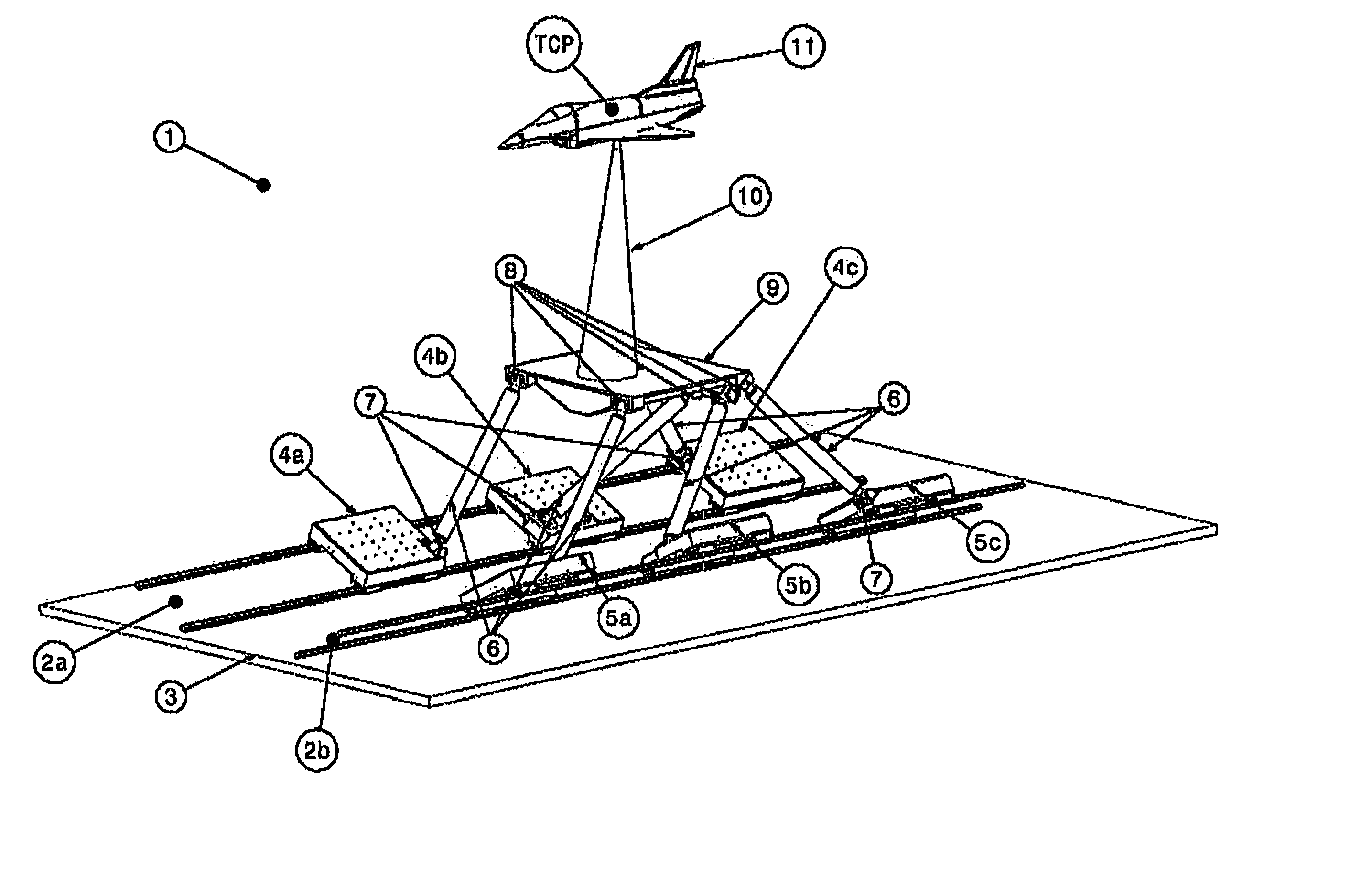
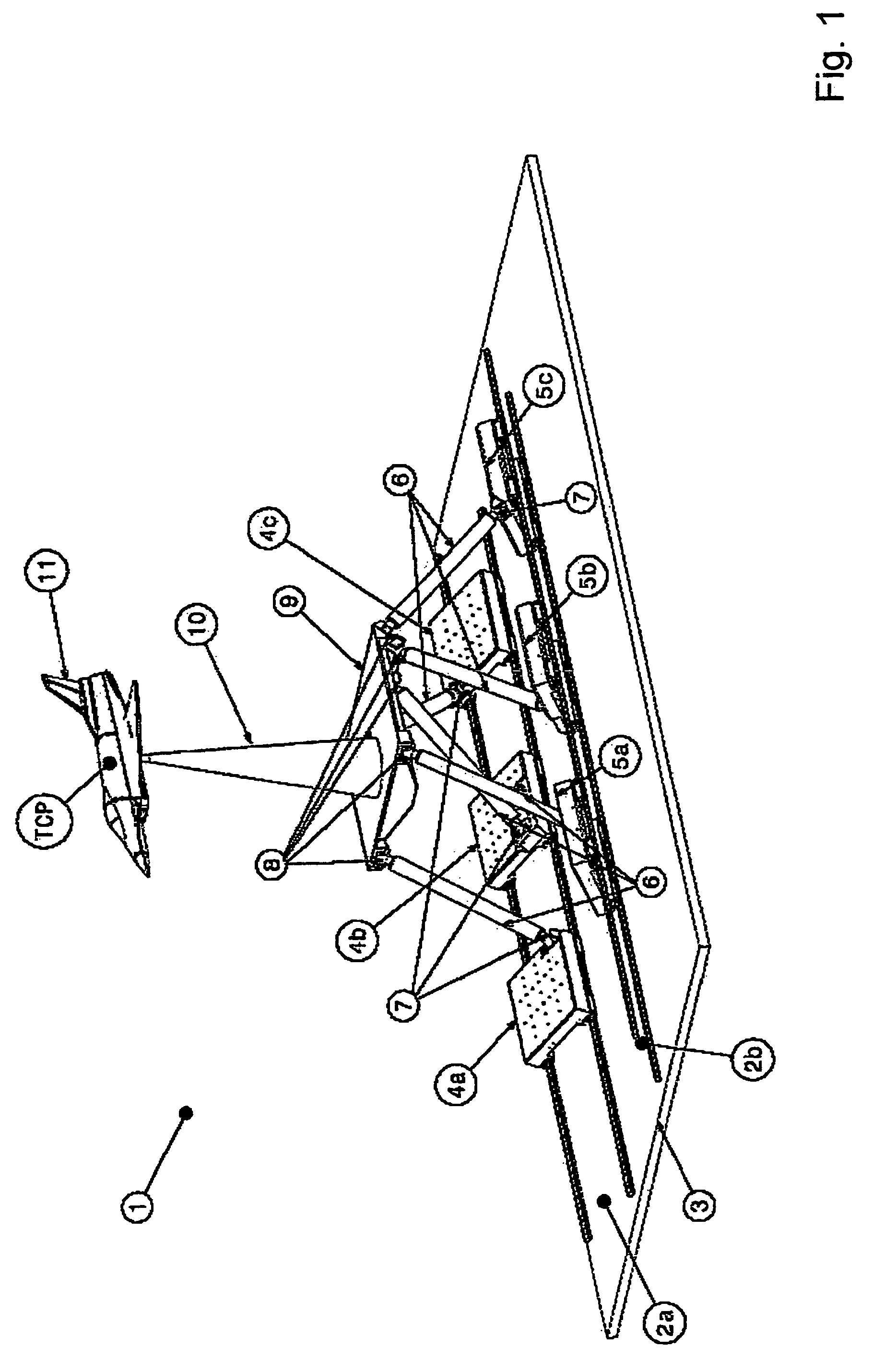
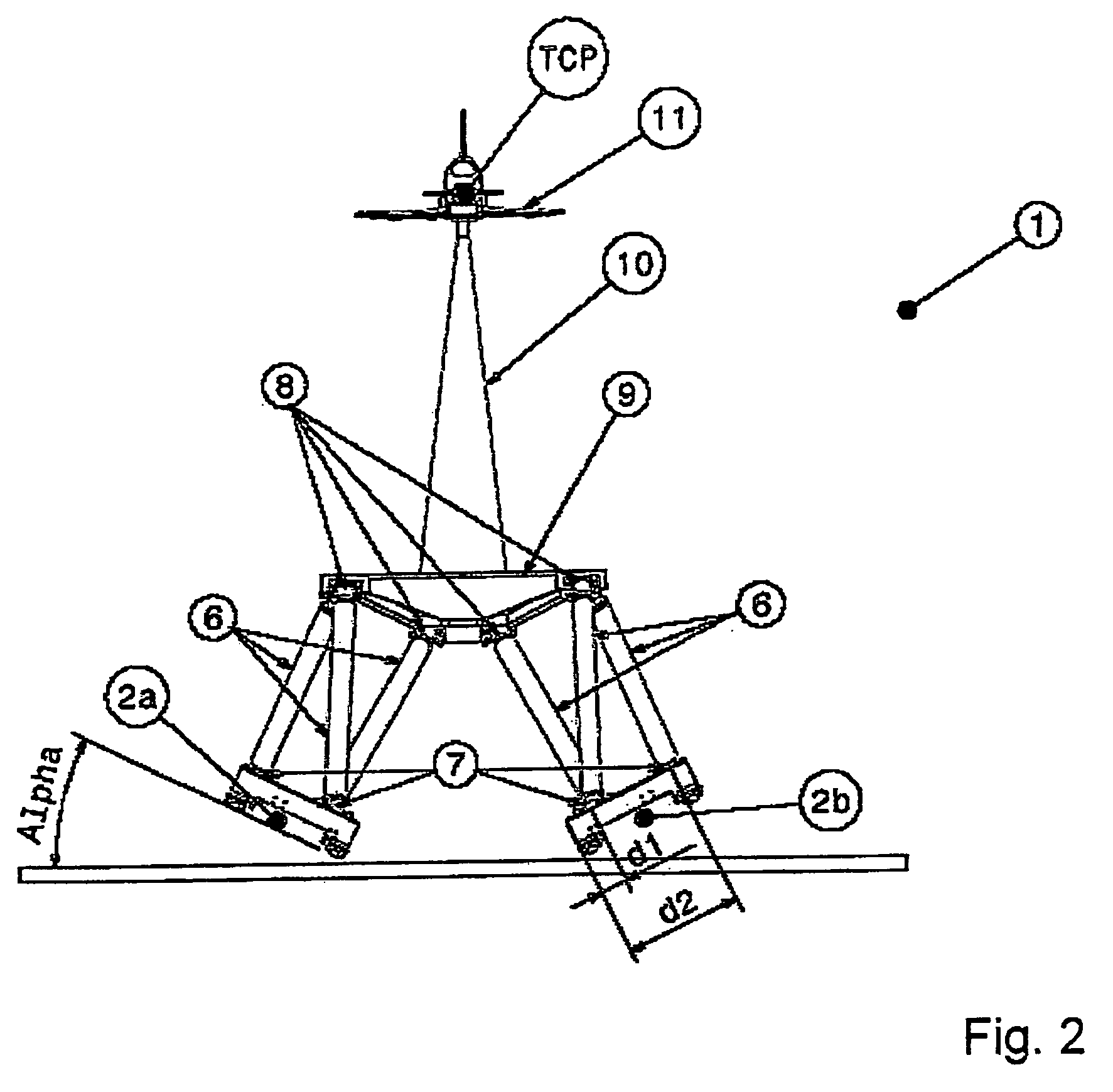
Movement device
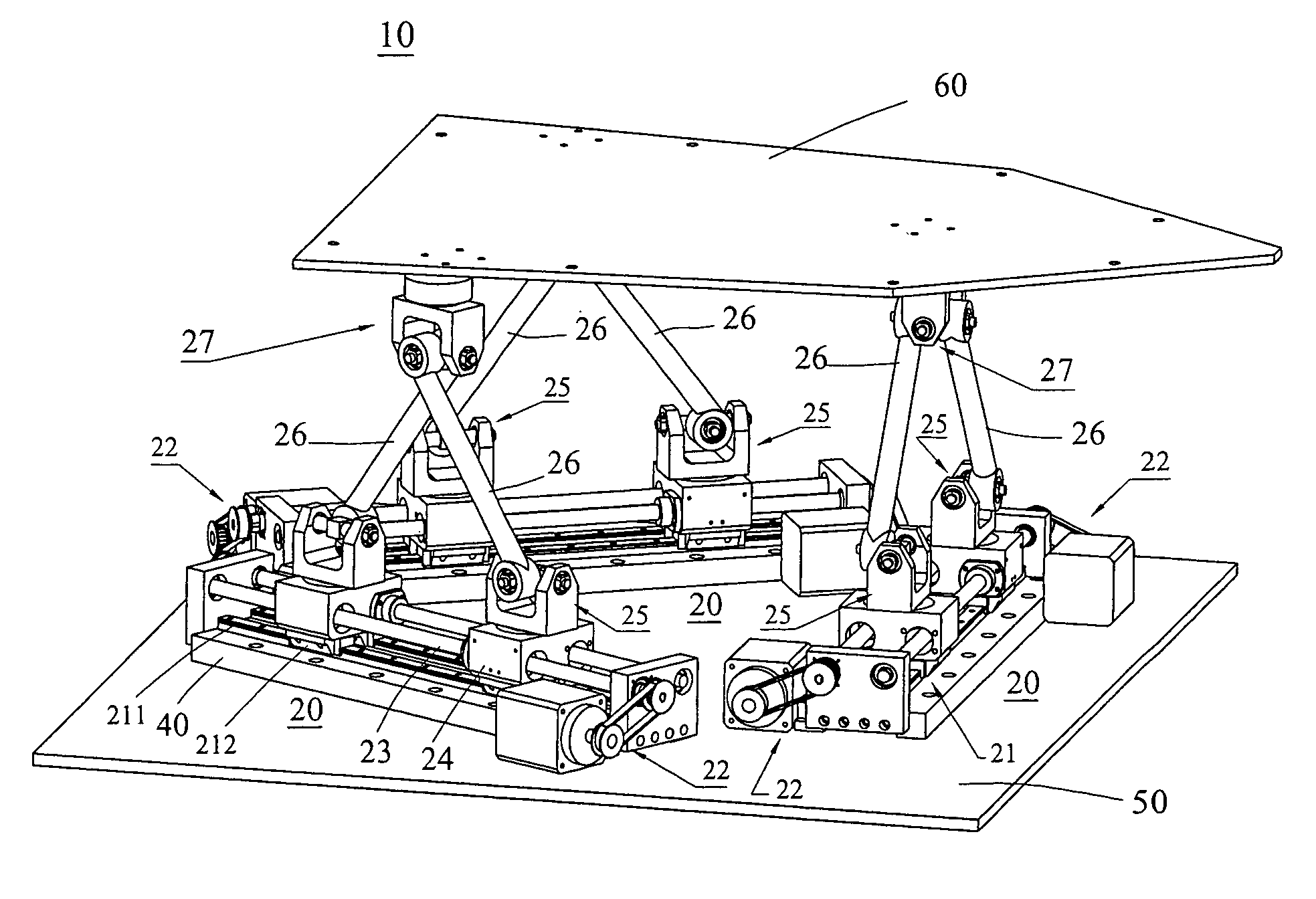
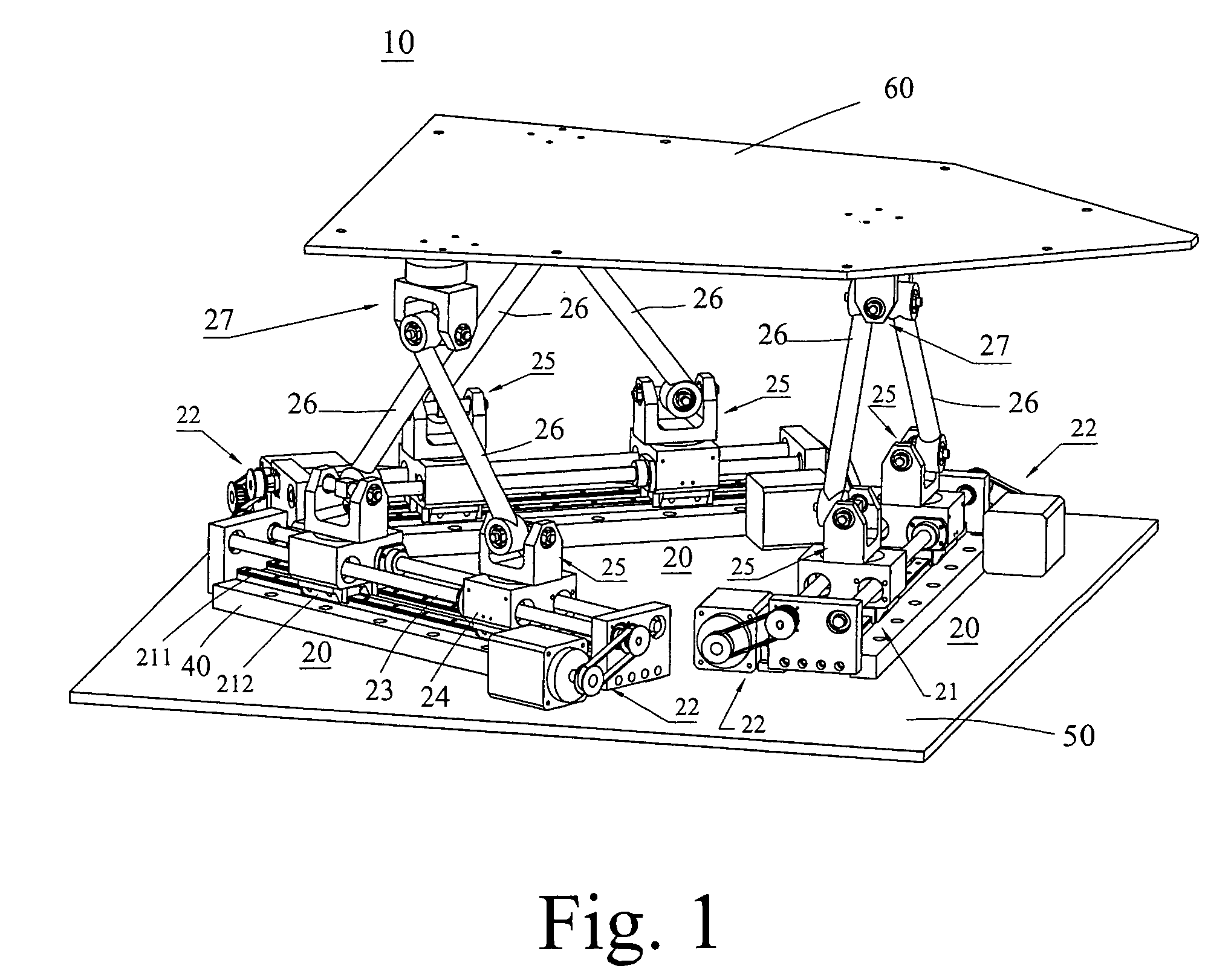
A movement device (1) having a Stewart platform includes a movable platform (9) that has platform joints (8) connecting it in an articulated manner by at least six rods (6) to a base (3). The rods (6) have base joints (7) resting in an articulated manner on carriages (4, 5) that can be displaced in the longitudinal direction on rails (2a, 2b) that are fixed to the base. Each carriage (4, 5) has a dedicated drive, and the carriages (4, 5) can be moved independently of one another. Exactly two rails (2a, 2b) are provided, and each rail (2a, 2b) supports at least three carriages (4a, 4b, 4c and 5a, 5b, 5c).
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV +2
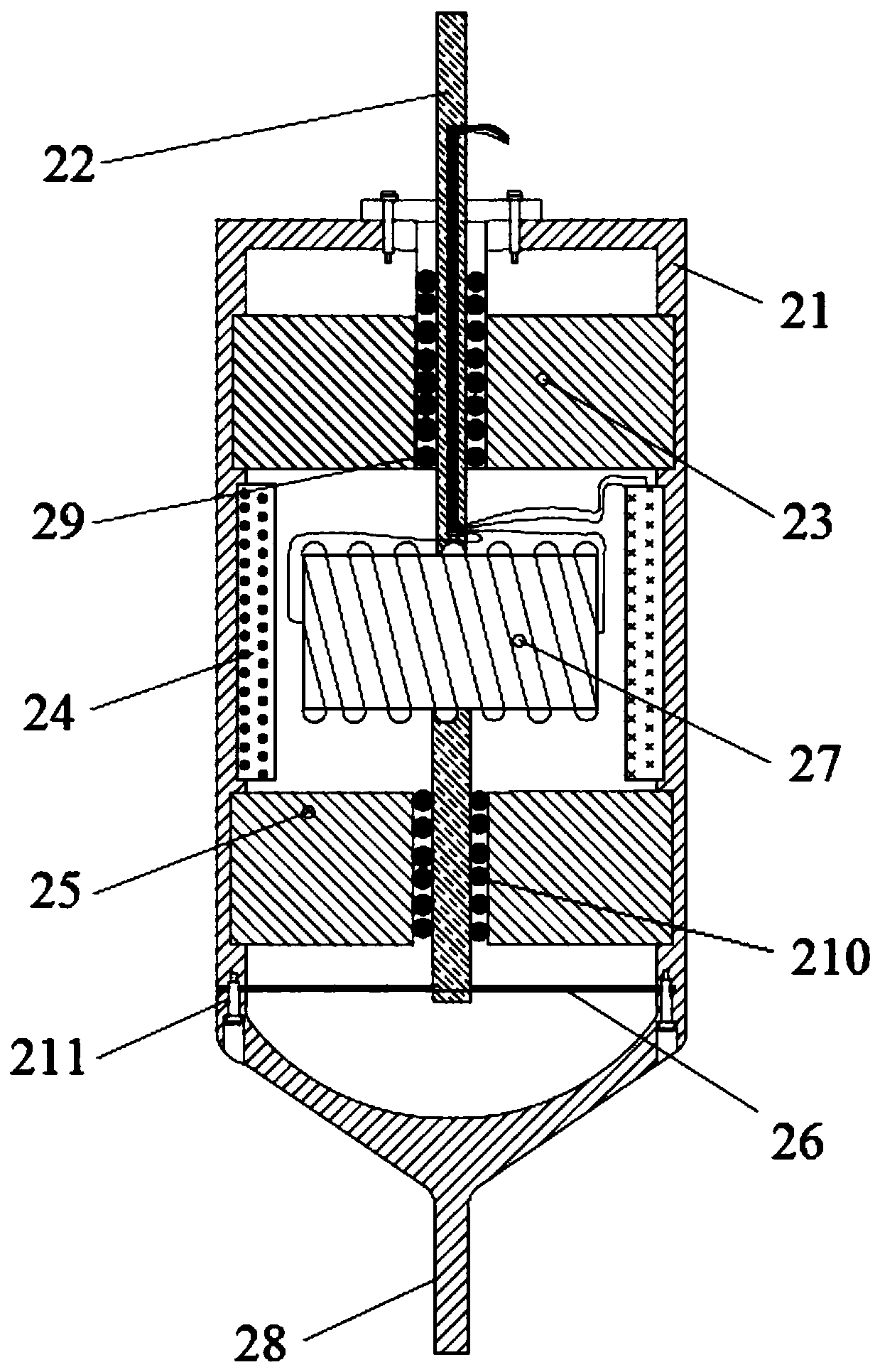
Quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolation and energy collection system based on Stewart platform
ActiveCN110365249ARealize integrationVibration isolation frequency band increasedPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower network operation systems integrationCollection systemEngineering
The invention discloses a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolation and energy collection system based on a Stewart platform and relates to the technical field of vibration isolation. The system devicecomprises an upper platform, a lower platform and six supporting legs. Each supporting leg comprises an outer sleeve, a connecting rod, a guide rod, an electromagnet, a first annular permanent magnet, a coil, a second annular permanent magnet and a diaphragm spring, wherein the first annular permanent magnet, the coil, the second annular permanent magnet and the diaphragm spring are up-down successively fixed in the outer sleeve. A first guide part is arranged in the first annular permanent magnet. A second guide part is arranged in the second annular permanent magnet. The guide rod is sleeved in the first guide part and the second guide part. The lower end of the guide rod is fixedly connected with the diaphragm spring. The electromagnet is fixed to the guide rod and arranged in a spaceformed by enclosing the first annular permanent magnet, the second annular permanent magnet and the coil. The upper end of the guide rod is connected with the upper platform through a hinge piece. Thelower end of the connecting rod is connected with the lower platform through a hinge piece. According to the system, rigidity is adjustable, low-frequency vibration can be well restrained, energy collection is achieved, and energy can be input to the outside.
Owner:苏州天工测试技术有限公司
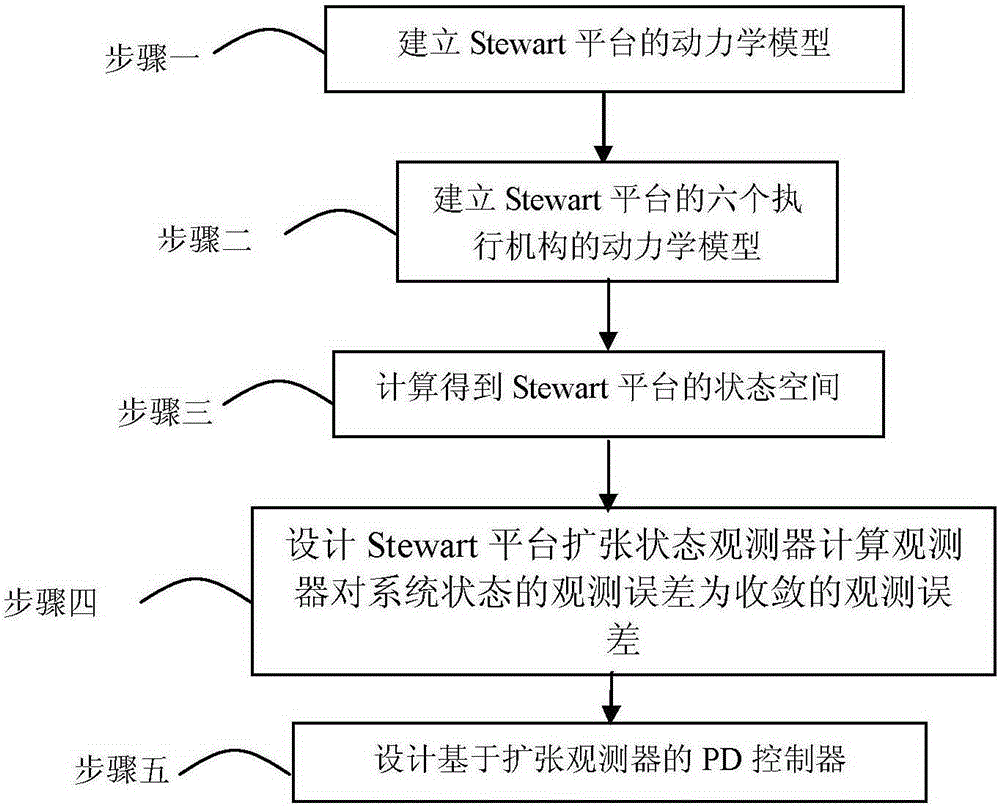
Method for controlling PD (proportion differentiation) of active vibration isolation of Stewart platform based on extended state observer
ActiveCN105182801AImprove the vibration isolation effectReduce in quantitySimulator controlDynamic modelsState observer
The invention provides a method for controlling the PD (proportion differentiation) of active vibration isolation of a Stewart platform based on an extended state observer, relates to a PD controlling method, and aims to solve the problems that formulation of a control strategy is relatively simple, the control accuracy should be improved, the influence of uncertain flexible accessories of a system is not taken into consideration, and the designing process which does not take structural linearity and control algorithm of the platform into consideration is arbitrary. The method is implemented by the following steps: 1, establishing a dynamic model of the Stewart platform; 2, establishing dynamic models of six actuation mechanisms of the Stewart platform; 3, acquiring a state space of the Stewart platform; 4, determining that observation error of the observer on the system state is a convergent observation error. The method is applied to PD control methods.
Owner:严格集团股份有限公司
Electromagnetic quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolation system based on Stewart platform
ActiveCN109630602ALower natural frequencySimple structureSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringNegative stiffness
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Six-freedom parallel control self-correction return apparatus for space vector force loading
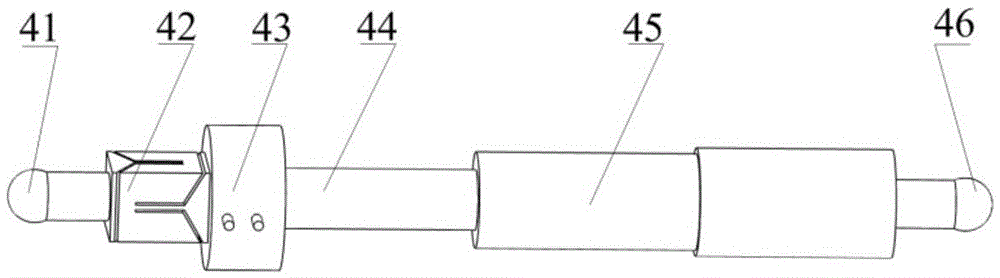
The invention discloses a six-freedom parallel control self-correction return apparatus for space vector force loading. The apparatus comprises a loading point 32, a loading part 33, a moving platform 1, a fixed platform 4 and six self-correction return parts, wherein the moving platform 1 and the fixed platform 4 are connected through the six self-correction return parts, and connection relations are arranged according to six-freedom parallel Stewart platform structure. Each self-correction return part comprises a first ball hinge 41, a universal flexible element 42, a force transducer 43, a telescoping rod 44, a driving mechanism 45 and a second ball hinge 46, wherein the universal flexible element 42 is an elastic element only transmitting axial forces and is connected with the moving platform 1 through the first ball hinge 41, the other end of the universal flexible element 42 is connected with a telescoping rod driving mechanism through the force transducer 43, the telescoping rod driving mechanism comprises the telescoping rod 44 and the driving mechanism 45, and the other end of the driving mechanism 45 is connected with the fixed platform 4 through the second ball hinge 46.
Owner:CHINA GAS TURBINE ESTAB
Active compliance control strategy of Stewart platform
The invention relates to an active compliance control strategy of a Stewart platform and belongs to the control field of a Stewart platform. The strategy is the active compliance control strategy of aStewart platform that takes a six-dimensional force transducer as a collection element through a neural network. Through combination of a track plan and the neural network, a relation model between the movement track of the platform and an output load can be obtained under a condition that platform design parameters are unknown. After an expected load applied a test piece is input into the model,a movement track of the platform, which enables the test piece to reach the expected load, can be obtained, and then a control method enabling the Stewart platform to take the load as a parameter canbe realized by means of displacement control. Compared with the prior art, the active compliance control strategy avoids conventional complex decoupling and coupling problems in control of the Stewart platform. Moreover, the design of the control strategy needs no prior information of equipment, is high in fault tolerance rate, and is not disturbed by the assembly errors, measurement errors and other factors.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for improving primary positioning precision of receiver of radio telescope
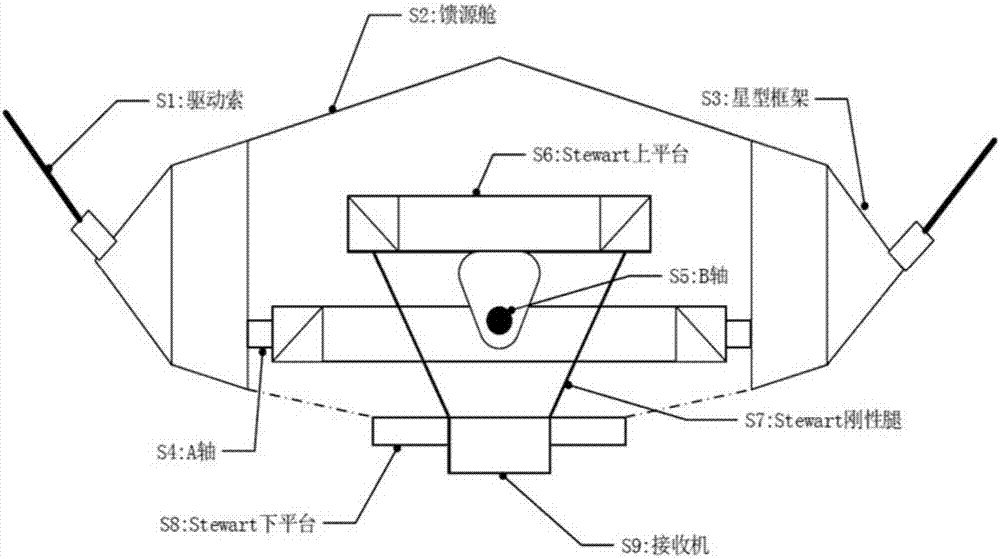
ActiveCN107369908AImprove the positioning accuracy onceExtended service lifeControl using feedbackAntennasSupporting systemMeasuring instrument
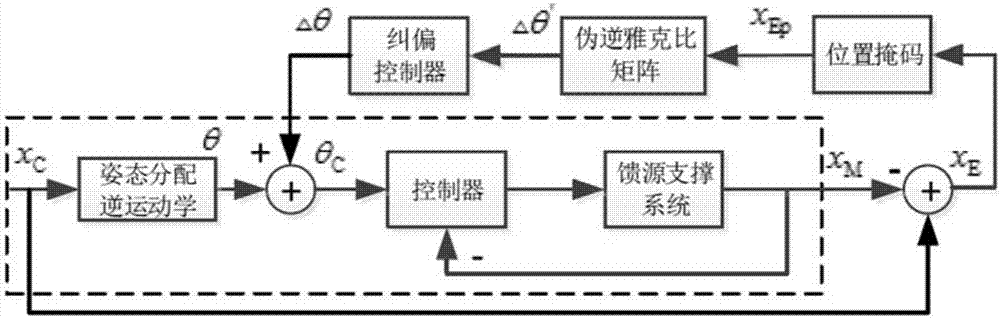
The invention provides a method for improving primary positioning precision of a receiver of a radio telescope. The method includes steps of S1, utilizing a measurement instrument for measuring poses of the receiver and obtaining a measurement value *M; S2, obtaining a joint deviation correction control volume Delta Theta by utilizing a deviation correction process in a deviation correction control model; S3, applying an input volume Theta C of a controller obtained after adding a joint deviation correction control volume Delta Theta to a joint spatial expected value Theta obtained through inverse kinematics conversion to the controller so as to acting on a feed source support system; S4, repeating the S1 to S3 and compensating position errors of primary positioning of the receiver in a receiver pose error allowable range. According to the invention, position errors of the primary positioning of the receiver can compensated in a high level, so that position error compensation load of a Stewart platform fine tuning mechanism is reduced and related precision requirements can be met even without controlling a Stewart platform in conditions with comparatively small original primary positioning errors.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Movement device
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV +2
Six-freedom-degree automobile racing simulator
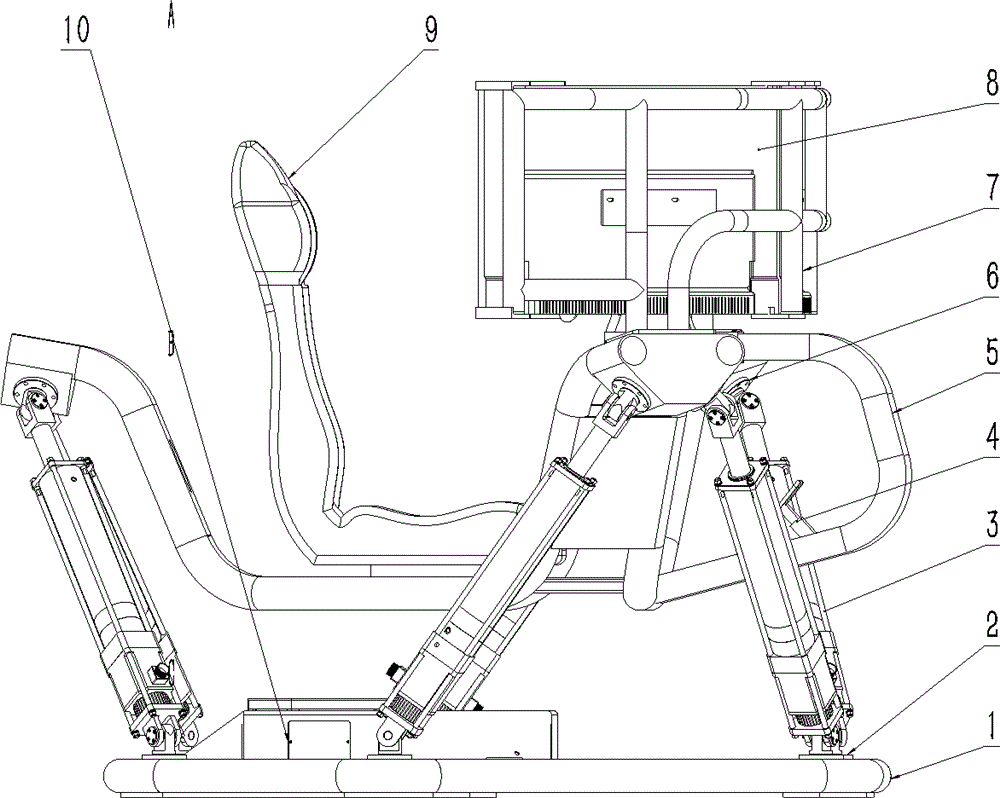
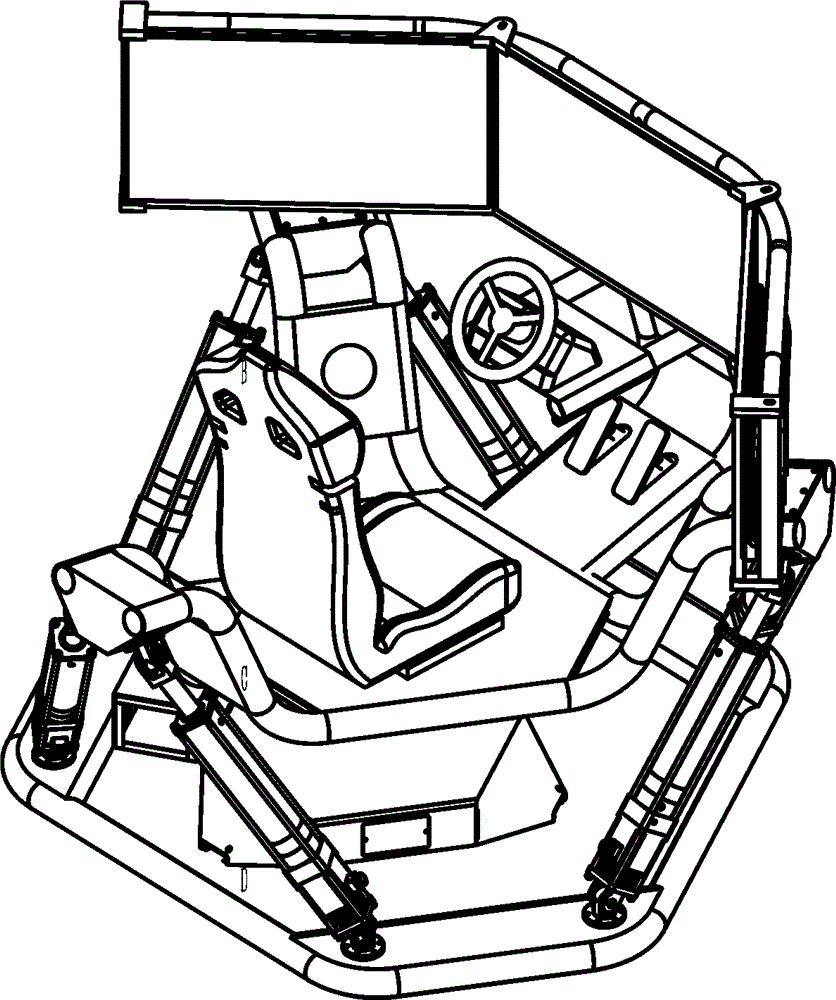
InactiveCN105013178AIncrease stiffnessImprove carrying capacityVideo gamesSteering wheelLiquid-crystal display
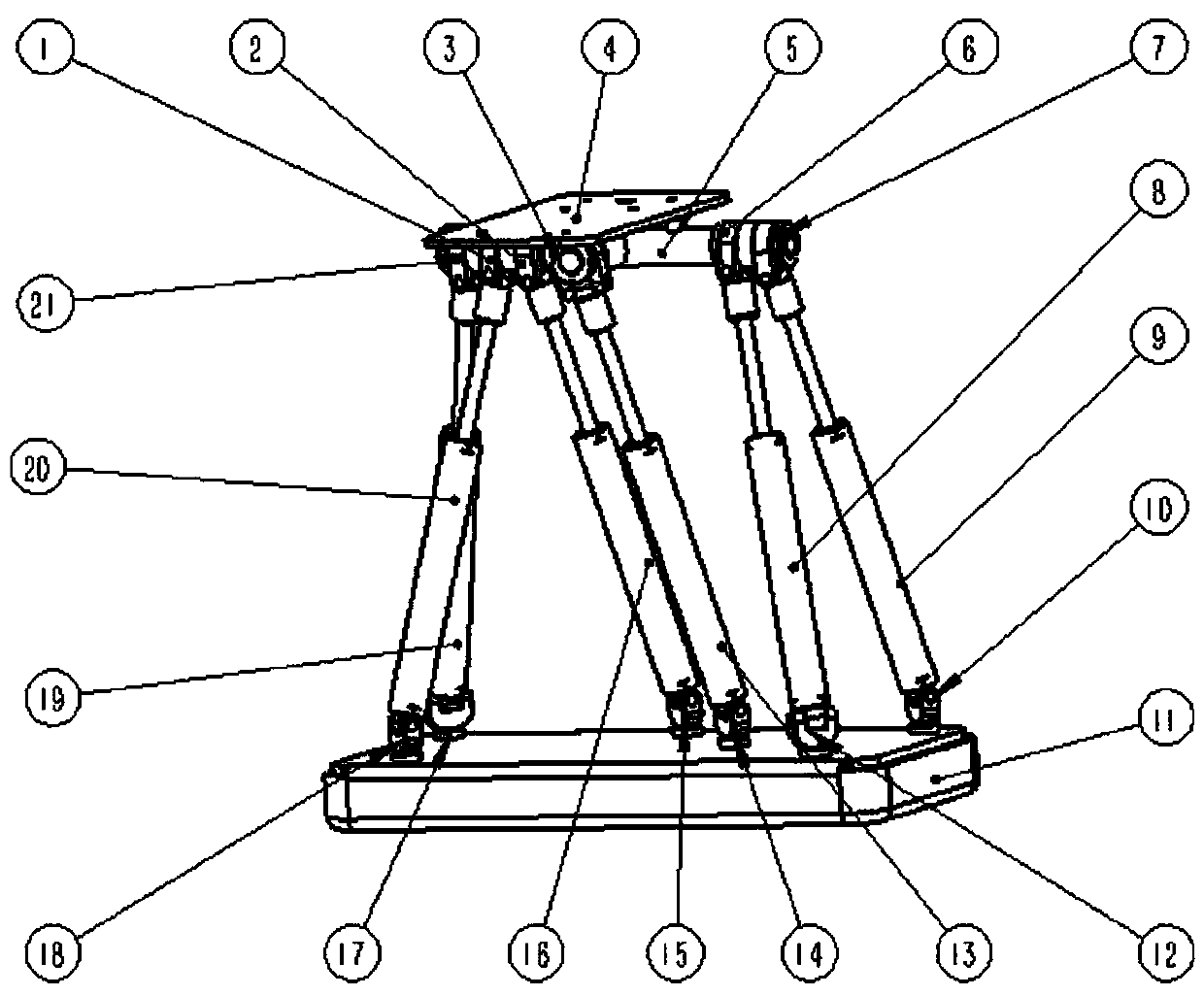
Disclosed is an automobile racing simulator capable of achieving six space freedom degrees. On the basis of a classic Stewart platform, an automobile racing seat, a displayer fixing frame assembly, pedals and a steering wheel are connected to an automobile body, a person sits on the automobile racing seat, the steering wheel and the pedals are controlled according to game scenes displayed in liquid crystal displayers, and the person can have the acceleration, deceleration, sudden turning, impacting and other true experience feelings. The automobile body, a base and a displayer support are formed by bending and welding seamless polished pipes, the appearance is attractive and fashionable, the three liquid crystal displayers are fixed easily, rapidly and conveniently, and maintenance is convenient.
Owner:MOTUS TECHNOLOGIES INC
Improved ankle rehabilitation mechanism based on Stewart platform
InactiveCN109662867AMeet functional requirementsWide range of motionChiropractic devicesLinear motionReduction drive
The invention discloses an improved ankle rehabilitation mechanism based on a Stewart platform. The improved ankle rehabilitation mechanism based on the Stewart platform comprises six telescopic branch chains; the telescopic branch chains are composed of motors, speed reducers and lead screws, and are symmetrically distributed relative to an intermediate plane at initial positions, and the motorsdrive the speed reducers and the lead screws to convert the rotational motion of the motors into linear motion; the telescopic branch chains are connected with a static platform and a movable platformthrough hinges respectively. The improved ankle rehabilitation mechanism based on the Stewart platform has the advantages that a parallel mechanism is improved based on the Stewart platform accordingto working space required for the rehabilitation of the ankle, the accessible working space is space formed by translating and scaling a prismatic section in the direction perpendicular to the staticplatform, the skillful working space has a wide range of angular motion, and the functional requirements of the ankle rehabilitation robot can be better met.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
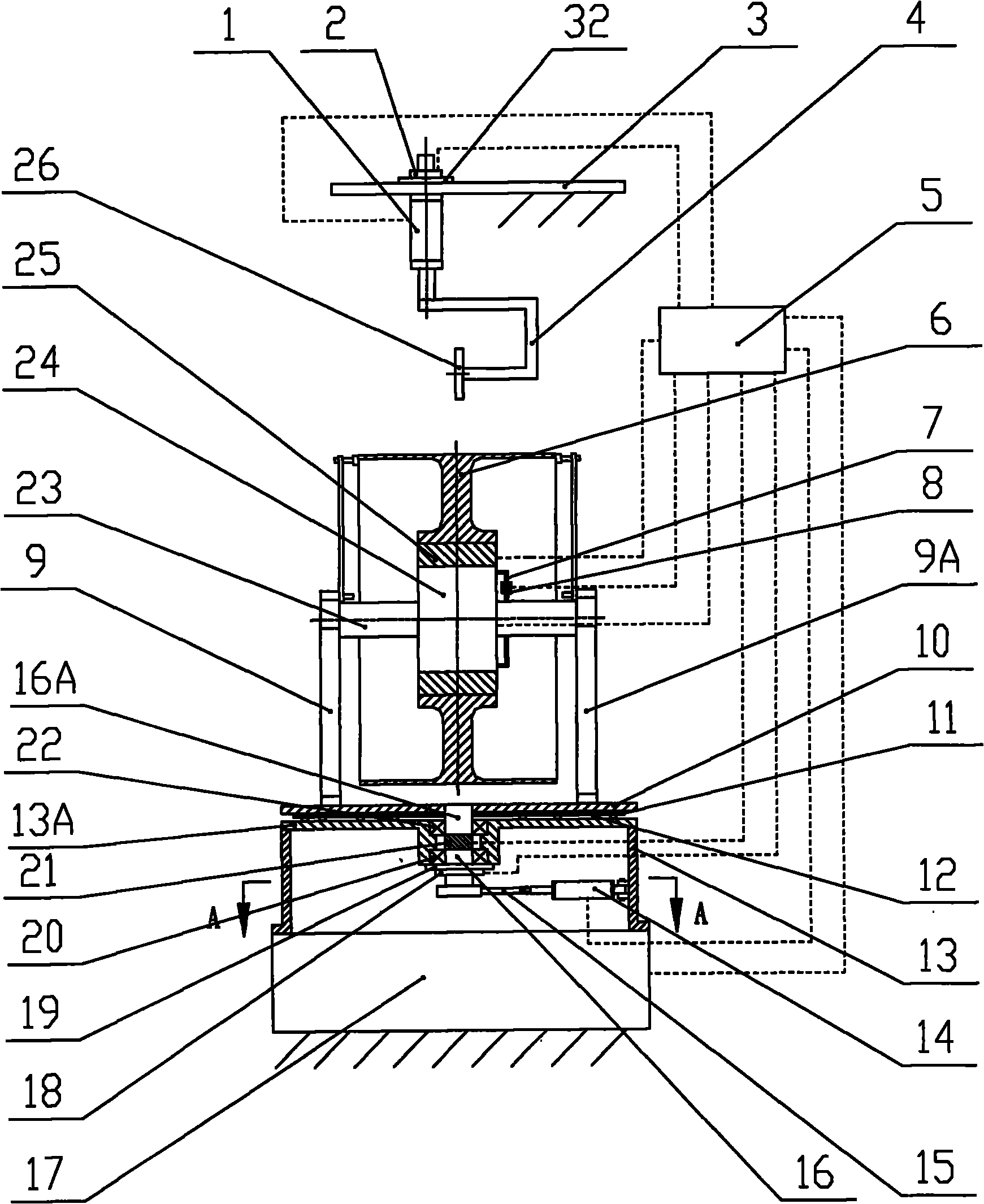
Stewart platform parallel mechanism limiting measurement and control apparatus and measurement and control method thereof
The invention discloses a Stewart platform parallel mechanism limiting measurement and control apparatus, and a measurement and control method thereof. The apparatus comprises a base. A hook joint is arranged on the base. A first attitude sensor is fixedly arranged on the base. A second attitude sensor is fixedly arranged on the inner ring of the hook joint. A third attitude sensor is fixedly arranged on a motion platform. An absolute value type stay wire encoder is further fixedly arranged on the inner ring of the hook joint. The stay rope of the absolute value type stay wire encoder is linearly connected with one point on the center line of the motion platform and the point where the axial line of the hook joint outer ring shaft and the axial line of the hook joint inner ring shaft intersect. A data processing module is further arranged. The Stewart platform parallel mechanism limiting measurement and control apparatus, and the measurement and control method thereof are simple and reliable.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Stewart stable platform control method based on RBF neural network
InactiveCN110597051AOvercoming Assembly ErrorsOvercoming Model ErrorsControllers with particular characteristicsAdaptive controlPid control algorithmDynamic models
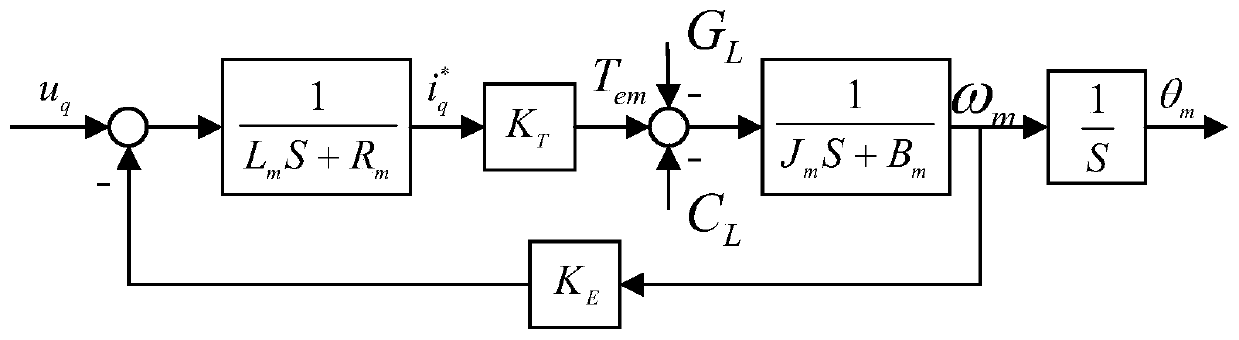
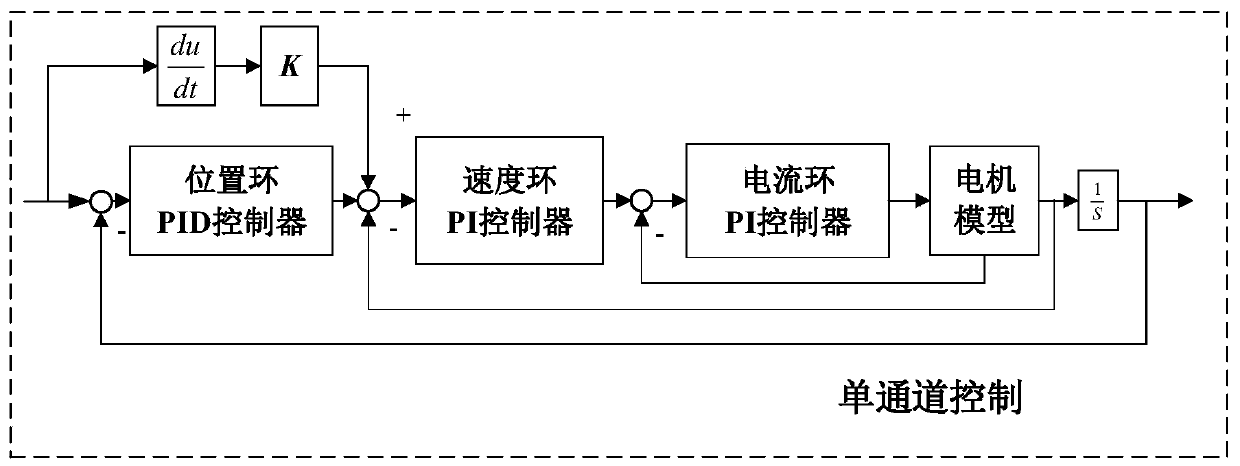
The invention discloses a Stewart stable platform control method based on an RBF neural network, and the method comprises the following contents of establishing a kinematic model of the Stewart stableplatform according to the principle of robot kinematics, and obtaining a Jacobian matrix of the Stewart stable platform about the posture through total differentiation; establishing a dynamic model of the Stewart stable platform by using the Lagrange's equation method and combined with the Jacobian matrix; mathematically modeling the single channel of Stewart according to the dynamic model to obtain a transfer function, and then adopting a PID control algorithm and a series control strategy to control the position of the single channel; constructing a posture control strategy of the Stewart stable platform, and stably controlling the Stewart platform by using the strategy. The method provided by the invention can effectively overcome the assembly error and model error of the Stewart stable platform, and improves the tracking accuracy and anti-interference ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-axis vibration test table and control method
The invention discloses a three-axis vibration test table and a control method. The three-axis vibration test table comprises a frame body, a bottom carrier board, a top carrier board, a test platformand a cross guide mechanism, wherein the bottom carrier board is driven to take a translational motion up and down; the top carrier board is arranged above the bottom carrier board and can be drivento take a translational motion relative to the bottom carrier board; the test platform is fixedly arranged on the top carrier board; the cross guide mechanism comprises two groups of linear guide parts correspondingly and perpendicularly arranged at an interval, a middle plate positioned between the two groups of linear guide parts and guide parts respectively arranged on two lateral surfaces of the middle plate and correspondingly matched with the linear guide parts; and the cross guide mechanism is arranged between the bottom carrier board and the top carrier board. The three-axis vibrationtest table is high in expansibility; and when the three-axis vibration test table is used as a vibration source, a workpiece can be additionally and randomly arranged on a vibration platform and for example, a high-frequency vibrator is additionally arranged, so that application of the three-axis vibration test table is further expanded.
Owner:天津格特斯检测设备技术开发有限公司
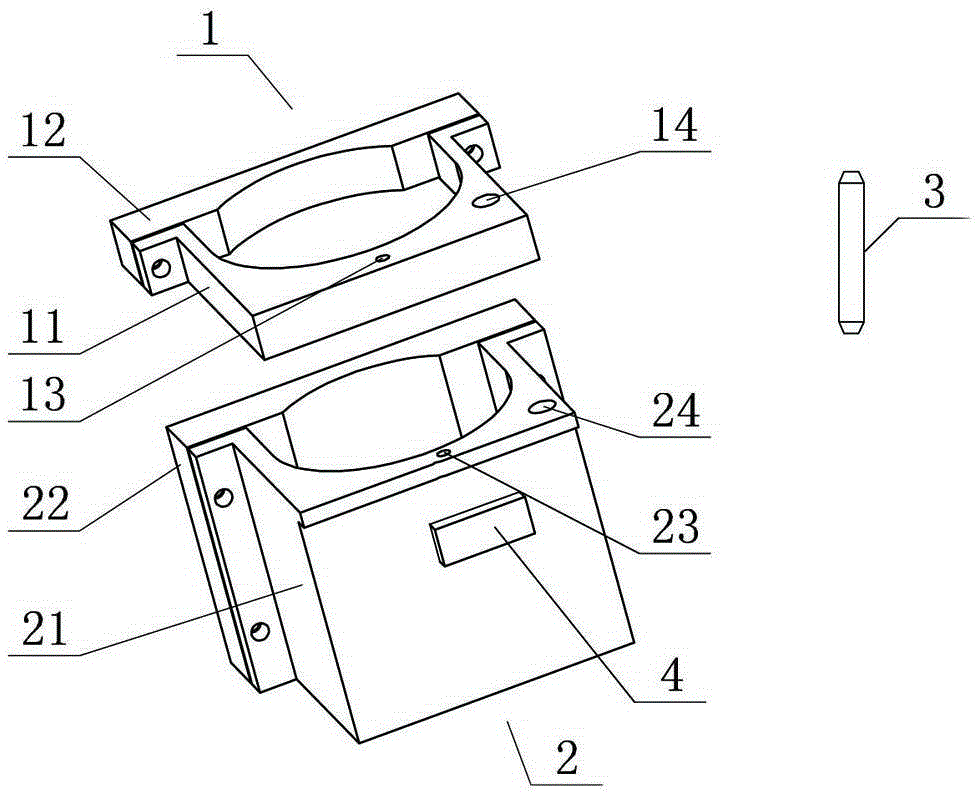
Stewart platform supporting leg length-measuring apparatus, and Stewart platform pose-testing system and method
The invention discloses a Stewart platform supporting leg length-measuring apparatus, and a Stewart platform pose-testing system and method. The Stewart platform supporting leg length-measuring apparatus comprises a fixing clamp and a displacement sensor for measuring the telescoping amount of a supporting leg. The fixing clamp comprises a first clamping portion fixed on a supporting leg piston and a second clamping portion fixed on a supporting leg sleeve; and the displacement sensor is fixed on the second clamping portion. The Stewart platform supporting leg length-measuring apparatus can measure real-time lengths of supporting legs in the movement process of a Stewart platform, and has the advantages of simple structure and high cost performance, thereby being applied to measurement of the telescoping amount of the supporting legs of the Stewart platform at a certain time point. The Stewart platform pose-testing method can solve a real-time pose of the Stewart platform in the movement process according to measured lengths of the supporting legs by use of a value calculation method, thereby being suitable for measurement of the real-time pose of the Stewart platform in the movement process.
Owner:PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY ORDNANCE ENG COLLEGE
Coil spring modeling apparatus and method of the same
ActiveUS20160238098A1Accurate measurementAccurate detectionSimulator controlSprings/dampers design characteristicsHydraulic cylinderLinear variable differential transformer
A coil spring modeling apparatus includes a first attachment member disposed on a lower spring seat, a second attachment member disposed on an upper spring seat, an actuator unit formed of a Stewart-platform-type parallel mechanism, a hydraulic pressure supply device, a torsion detection mechanism, and a controller. The torsion detection mechanism is constituted of displacement gauges such as a linear variable differential transformer. The displacement gauges are provided on hydraulic cylinders, and detect amounts of displacement relative to the reference lengths of the hydraulic cylinders, respectively. The controller calculates a relative torsional angle between the first attachment member and the second attachment member based on the detected displacement.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
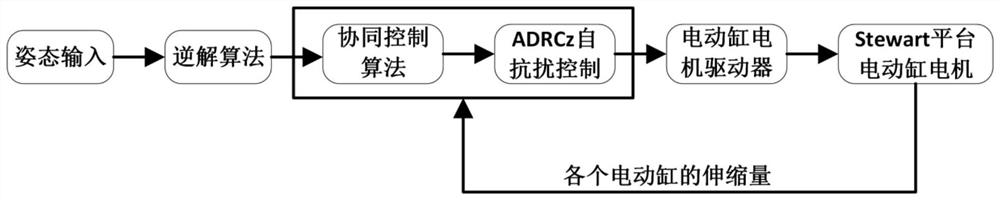
Cooperative control method of Stewart platform
ActiveCN112847303AImprove inconsistenciesHigh control precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl signalSimulation
The invention relates to a cooperative control method of a Stewart platform, and belongs to the technical field of parallel robot control. In an upper computer controller, a cooperative control algorithm is adopted, non-interactive control signals in each independent controller are coordinated as a whole, and the problems of position mismatching and over-fitting of electric cylinders in parallel platform pose control caused by different loads or other factors are solved. Meanwhile, an ADRC is adopted, the uncertainty of internal modeling is estimated, external disturbance is compensated, the control precision is improved to a certain degree, and the high-performance pose control requirement is met. According to the cooperative control method of the Stewart platform, the control precision can be improved, the cooperative effect of the electric cylinders in the transition process is improved, the problems of deformation and the like caused by unbalanced load distribution among the electric cylinders are reduced, the joint burden of the electric cylinders is relieved, the service life of the electric cylinders is prolonged, and economic benefits are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com