Traffic violation analysis method based on knowledge graph and block chain
A knowledge graph and analysis method technology, applied in special data processing applications, unstructured text data retrieval, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as inability to obtain driver photos, insufficient monitoring clarity, and reduction of illegal processing efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
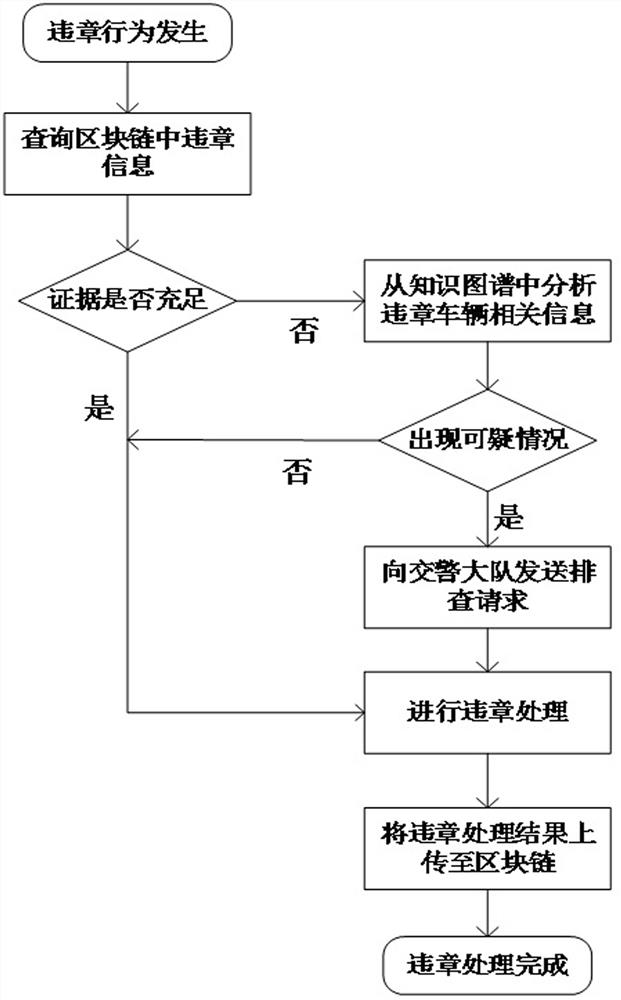
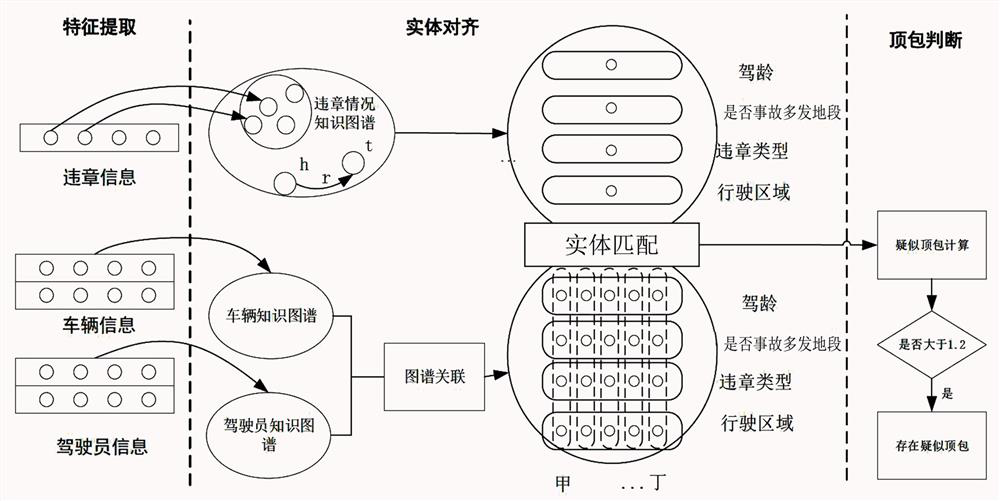
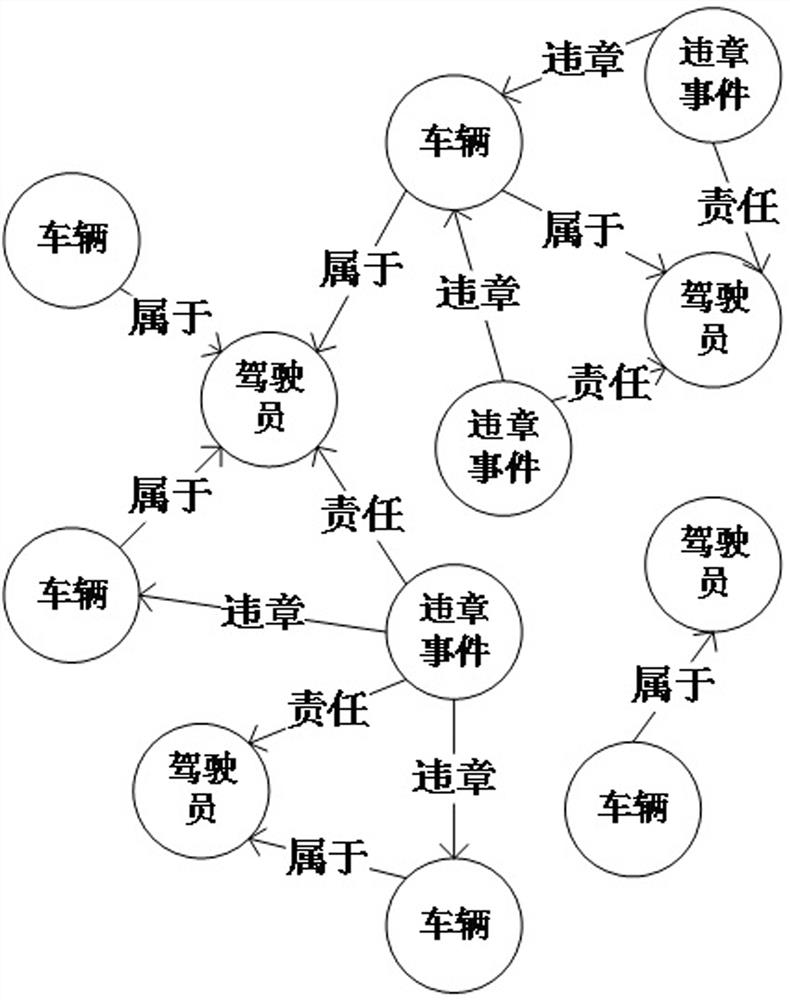
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: When a violation occurs, 3 drivers A, B, and C are associated from the knowledge map according to the license plate number, and it is the driver D who goes to the traffic control department to receive punishment, not any of the 3 drivers. Then it is directly judged that the driver Ding is suspected of topping the bag, and he will check and confirm with the traffic control department.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: When a violation occurs, 3 drivers A, B, and C are associated from the knowledge map according to the license plate number. The driver who goes to the traffic control department to receive punishment is driver A. It is an accident-prone area, and the information of drivers A, B, and C is analyzed separately. Driver A has a driving experience of more than 6 years and has run red lights, but the daily driving area is B; while driver B has a shorter driving experience and has just obtained Driver license, often driving near area A, and has repeatedly violated regulations by running red lights; driver C is also relatively short in driving experience, often driving near area C, and rarely violates regulations. Combined with Table 1-4, the above three drivers Suspected top bag calculation through knowledge graph, suspected top bag calculation: A=0.1+0.1+0.5+0.1=0.8, B=0.5+0.1+0.5+0.6=1.7, C=0.5+0.1+0.1+0.1=0.8, Finally, it is judged that driver A is suspected to be...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: A violation occurs. According to the license plate number, 3 drivers A, B, and C are associated from the knowledge graph. Driver A is the one who goes to the traffic control department to receive punishment. It is not an accident-prone area. After analyzing the driver information separately, it is found that driver A has a driving experience of more than 6 years, and his daily driving area is B, and the most common type of traffic violation is speeding; while driver B has a shorter driving experience and just With a driver's license, he often drives near Area A, and has repeatedly committed violations of running red lights; Driver C is also relatively short in driving experience, often drives near Area A, but rarely commits violations. Combined with Table 1-4, the above The three drivers performed suspected top bag calculations through knowledge graphs.
[0035] Suspected top bag calculation: A=0.1+0.5+0.1+0.1=0.8, B=0.5+0.5+0.5+0.6=2.1, C=0.5+0.5+0.1+0.1=1.2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com