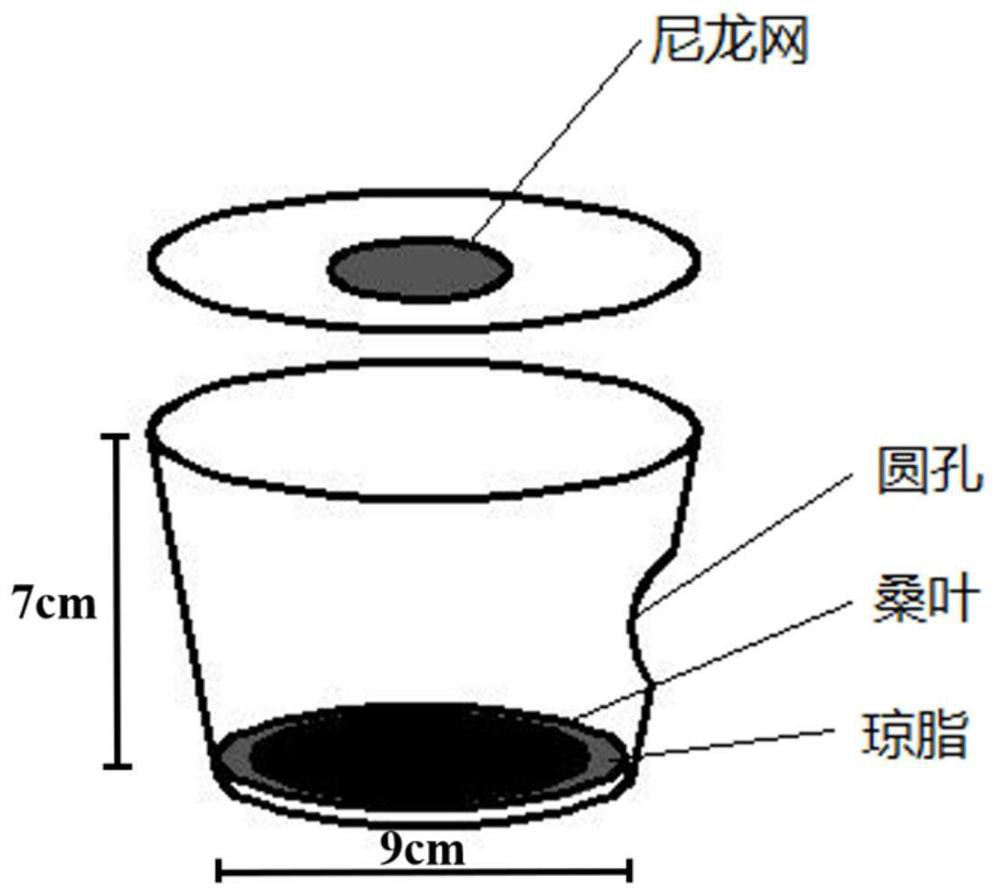
Method for artificially feeding parasitic wasps by taking mulberry pyralids as hosts
A technology for parasitic wasps and mulberry borers, which is applied in the field of biological control of agricultural pests, can solve the problems of undiscovered artificial large-scale breeding methods of S. Low, easy to make effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Example 1 Artificial Breeding of Sapphire spp. with Mulberry Borer as Host
[0016] The mulberry borer larvae were collected from the field during the blooming period of the mulberry borer. The collection object is the mulberry borer larvae in the middle and lower leaves of each mulberry tree. The collected mulberry borer larvae ranged from 1 to 5 instars. 100 mulberry borers were collected at each stage, and the collection was repeated 3 times. The collected mulberry borer larvae were brought back to the laboratory for rearing. The mulberry borer larvae of each age were raised separately in small plastic cups and fed fresh mulberry borer every day. When the parasitic wasp larvae crawled out of the mulberry borer and cocooned, the parasitic bee cocoons were collected. The parasitism rate of mulberry borer in each stage is shown in Table 1, and the parasitism rate of 2-4 instar mulberry borer larvae was the highest with no significant difference. There was no signifi...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Example 2 Artificial Breeding of Sapphire spp. with Mulberry Borer as Host
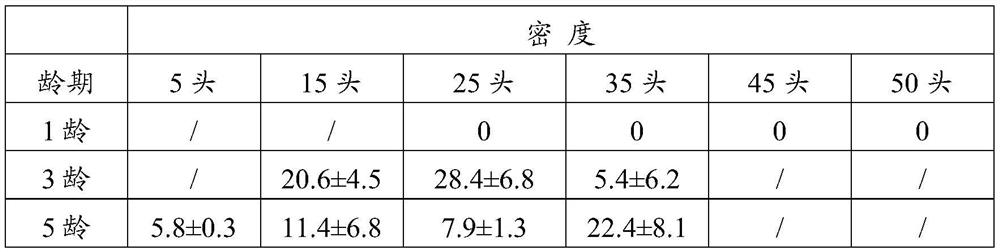
[0020] The artificial propagation experiment was carried out indoors with the mulberry moth crawled out from the mulberry borer collected in the field as the mother bee. The 6-8-day-old female bee was used as the selected wasp. Set two variables, the age of the host and the density of the mulberry borer in the parasitic box, and set the combination of different ages and host densities according to the pairwise combination. The density of borer is 5 heads, 25 heads and 50 heads per box. Considering the size of the parasitic box and the size difference of the larvae of different ages of the mulberry borer, the specific combination method is shown in Table 2. The parasitic time is 24 hours. Each treatment was repeated 3 times. Table 2 shows that there are significant differences in the indoor parasitism rate of M. mori to Mulberry Borer under different host age and density combination conditio...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3 Artificial Breeding of Sapphire spp. with Mulberry Borer as Host
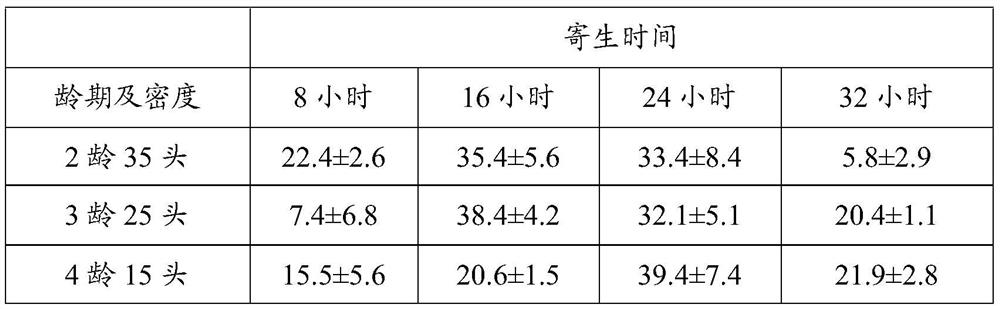
[0025] The parasitic combinations of Mulberry borer larvae of different ages and densities were set up, and the effects of different parasitic durations on the parasitic rate were investigated. The 6-8-day-old female bee was used as the selected wasp. It can be seen from Table 3 that the parasitic duration has a significant effect on the indoor parasitism rate of P. And the duration of parasitism is closely related to the age of each host and the combination of density and treatment. When the 2nd instar mulberry borer was 35 heads per box, the parasitism rate was the highest for 16 hours; 24 hours, the parasitic rate is the highest.
[0026] Table 3 Indoor parasitism rate (%) under different parasitism conditions
[0027]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com