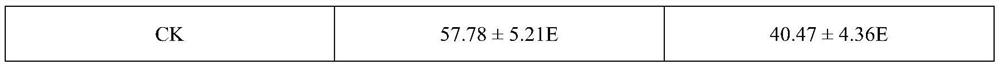Patents
Literature
84 results about "Ichneumonidae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Ichneumonidae are a parasitoid wasp family within the order Hymenoptera. Unlike other parasites, parasitoids kill their hosts. Ichneumonids are important parasitoids of other invertebrates; common hosts are larvae and pupae of Coleoptera (beetles), Hymenoptera (wasps and relatives), and Lepidoptera (moths and butterflies). About 25,000 species have been described worldwide. Estimates of the total species range from 60,000 to over 100,000 – more than any other hymenopteran family.
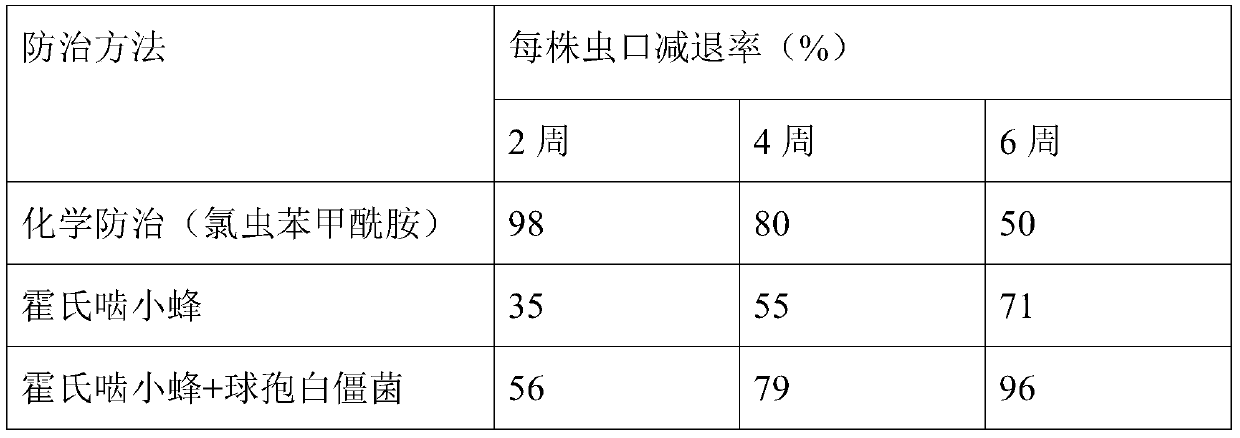
Large-scale raising method of dominant parasitoid wasps of liriomyza sativae
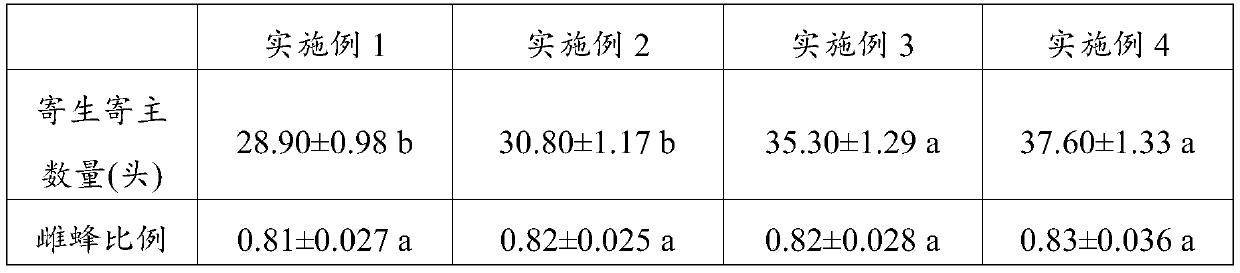
InactiveCN102524193AThe method of artificial feeding is simple and easyLow costAnimal husbandryParasitoid waspHost plants
The invention discloses a large-scale raising method of dominant parasitoid wasps of liriomyza sativae. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) cultivating host plants; (2) reproducing liriomyza sativae; and (3) raising parasitoid wasps. The method has the following beneficial effects that: the method is simple and practical; the cost is lower; the dominant parasitoid wasps of liriomyza sativae can be raised on a large scale; and huge economic, social and ecological benefits can be brought by releasing the dominant parasitoid wasps in the areas seriously harmed by liriomyza sativae.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
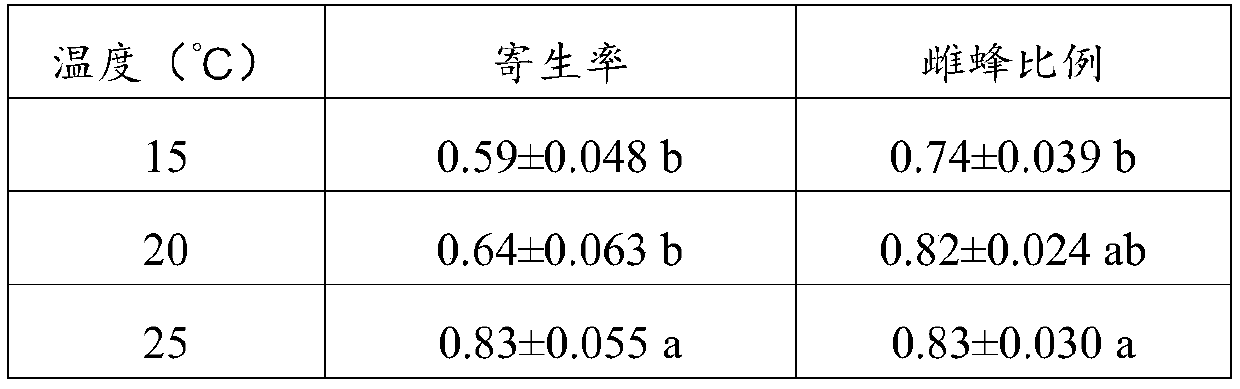
Method for improving female ratio of trichogramma progeny and application of method
ActiveCN111011313AWith preventive functionIncrease female ratioPlant protectionAnimal husbandryBiotechnologyCorcyra cephalonica
The invention discloses a method for preventing and controlling heortia vitessoides by using trichogramma pintoi and an application of the method. The method comprises the specific process of feedingthe trichogramma in eggs of alternative host corcyra cephalonica. By setting an appropriate feeding environment, host and parasitoid wasp factors, the method improves the female ratio of the trichogramma progeny on the basis of without affecting bee reproduction quality and application effects, thereby improving the biological prevention and control effect on the heortia vitessoides, and facilitating the large-scale promotion and application of the trichogramma in the aquilaria sinensis pest heortia vitessoides; and the method can greatly reduce the use of chemical pesticides, and has important significance for non-target biological safety, human health and ecological environmental protection.
Owner:中国医学科学院药用植物研究所云南分所 +1
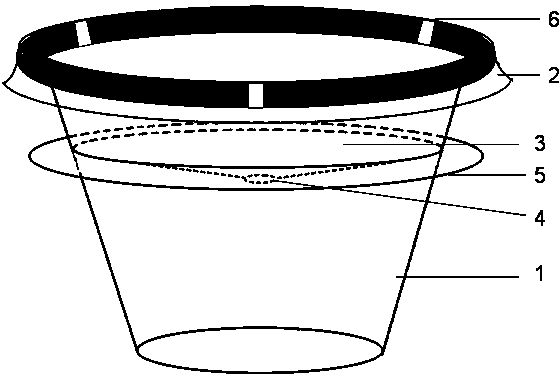
Method suitable for controlling pests by releasing parasitic wasps in paddy field and release devices
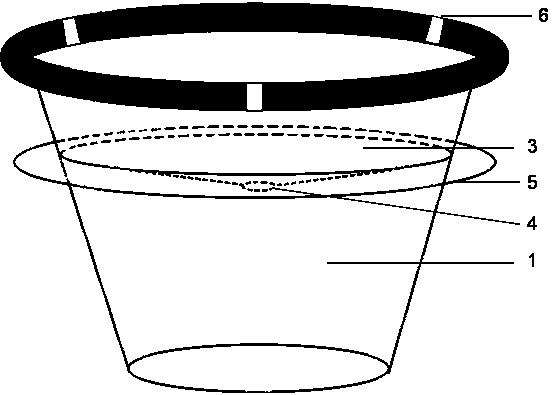
The invention discloses a method suitable for controlling pests by releasing parasitic wasps in a paddy field. A counter-weight is injected into a bearing space of a releasing device, and ova used for breeding the parasitic wasps are put into a host ovum space; then a cover is buckled onto each cup to form a whole body; the release devices containing the parasitic wasps are uniformly thrown into the paddy field and float on the water surface automatically, the parasitic wasps climb out from outgoing holes actively after eclosion of the ova of the parasitic wasps and search pest host ova; when the parasitic wasps are released in the field, operators can throw the release devices with certain weights into the paddy field on ridges of the paddy field instead of going into the paddy field, under the action of gravity, the bottom of each release device falls into the water first, and under the action of buoyancy force of the outer edge of each cup, each release device can not sink underwater, each upper space holding trichogramma can float on the water surface, even a little amount of water enters from the outgoing holes, and the water flows into a lower space containing sand through a funnel-shaped clapboard in each release device; the method can be used for preventing a predatism natural enemy from eating the host ova, can prevent rain and water accumulation, and realizing the mechanized production. The release devices are all made from a corn starch biodegradable material which can be degraded within about six months under natural conditions, and can not pollute the environment.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Artificial propagation method for parasitic wasps of bactrocera tau larvae
The invention relates to an artificial propagation method for parasitic wasps of bactrocera tau larvae. The method comprises the steps of collection of bactrocera tau and adult parasitic wasps of bactrocera tau larvae, feeding and domestication of the parasitic wasps of the bactrocera tau larvae, feeding of the adult bactrocera tau, expanding propagation and spawning domestication of bactrocera tau, egg collection of the bactrocera tau, expanding propagation of the bactrocera tau larvae, parasitism of the parasitic wasps of the bactrocera tau larvae on the bactrocera tau larvae, larva feedingand pupation after parasitism, parasitic pupae collection and parasitic wasp eclosion separation, and rejuvenation of the bactrocera tau and larva parasitic wasps. By adopting the method disclosed bythe invention, the growth and development of the bactrocera tau and the parasitic wasps are not influenced by residual pesticides, and the host searching capability of the parasitic wasps in the fieldis kept stable; after being collected, the bactrocera tau pupae where the parasitic wasps are parasitic do not need freezing treatment, damage to the bactrocera tau pupae where the parasitic wasps are parasitic is little, the separation effect of the bactrocera tau and the parasitic wasps is good, and the method has the advantages of being easy to operate, capable of saving time, little in humaninterference, high in parasitic rate, easy to breed on a large scale and particularly suitable for application and popularization.
Owner:ANSHUN UNIV
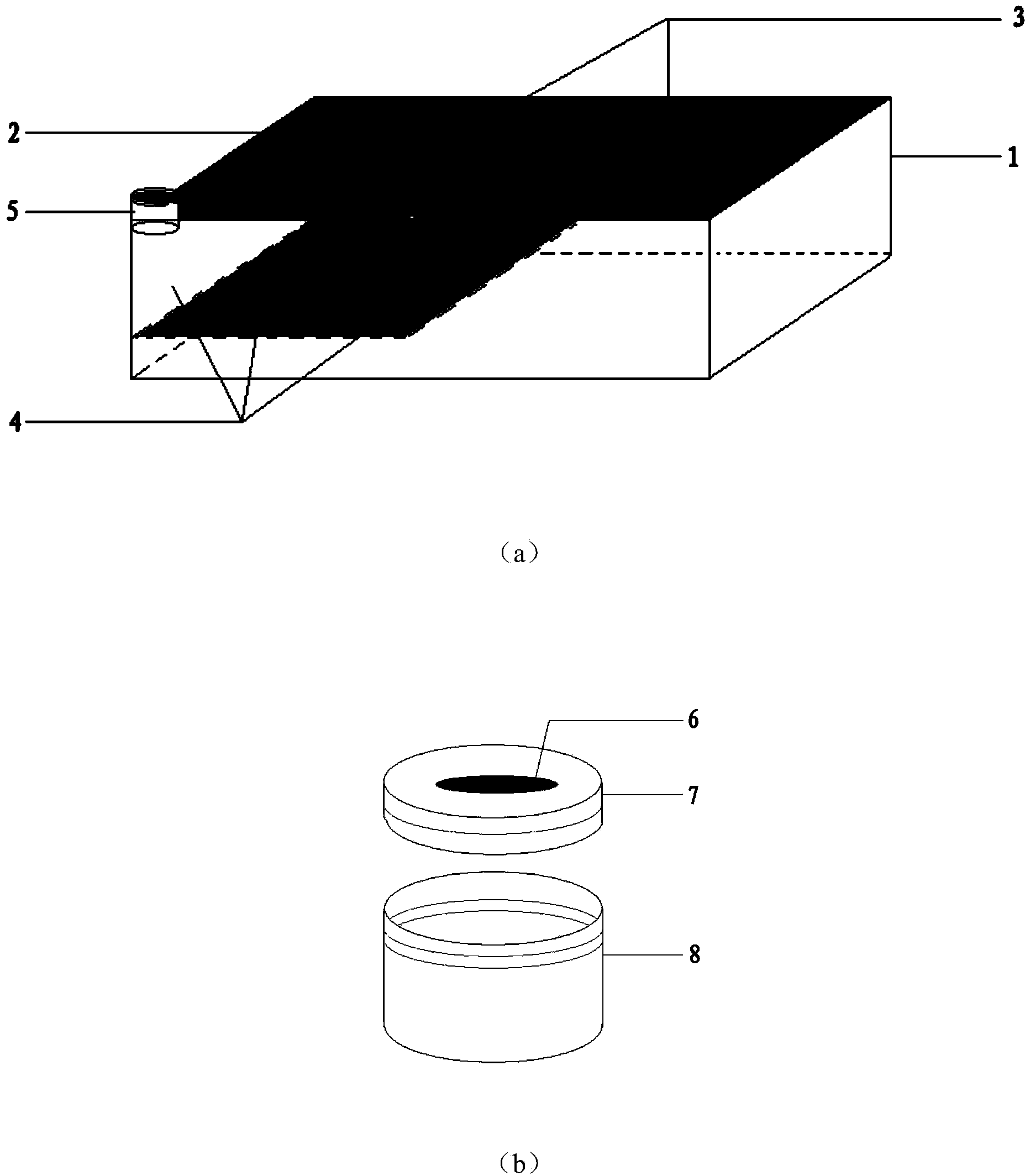
Incubation and feeding device suitable for whitefly or parasitic wasp insects and application method of device
PendingCN109315356AExtension of timeSolve the problem that air drying cannot achieve moisturizing effectAnimal husbandryEngineeringFilter paper
The invention relates to an incubation and feeding device suitable for whitefly or parasitic wasp insects and a method. The device comprises a feeding layer and a liquid storage layer, and the feedinglayer is laminated on the liquid storage layer and cooperatively connected with the liquid storage layer; the feeding layer and the liquid storage layer are of hollow cylinders with open upper bottoms; a clamping lamination circle with the diameter slightly larger than the diameter of the side wall of the feeding layer is arranged at the top of the feeding layer; multiple openings are formed in the side wall of the feeding layer; multiple holes are formed in the bottom of the feeding layer, cotton columns penetrate through the holes and are wrapped by gauze, water retention cotton covers theupper portions of the holes, and filter paper covers the upper faces of water retention cotton. The incubation and feeding device is convenient to use and easy to manufacture, the whitefly or parasitic wasp insects can be subjected to different incubation and breeding, the interval period of feed addition during feeding is effectively prolonged, the aim of increasing the eclosion rate and survivalrate of two kinds of insects is improved, breeding and propagation expansion become quick and simple, and the working efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for propagating telenomus remus by using fresh-keeping spodoptera frugiperda egg masses
The invention discloses a method for propagating telenomus remus by using fresh-keeping spodoptera frugiperda egg masses. Kraft paper is mainly used as a bearing medium for the spodoptera frugiperda egg masses, the egg masses are stored under the limiting conditions such as airtightness, light shielding and constant low temperature, hatching of the spodoptera frugiperda eggs is inhibited, meanwhile, the method ensures that the telenomus remus can parasitize on the egg masses within a long time, the purpose of intensively propagating a large number of telenomus remus populations is achieved, and the method conveniently releases parasitic wasps in the field at the right time so as to achieve the biological control effect of preventing and controlling the spodoptera frugiperda. The method issimple in operation process, safe and reliable, and provides a large number of parasitic wasp sources are provided for conveniently and rapidly utilizing the spodoptera frugiperda eggs to massively propagate the telenomus remus and applying the biological prevention and control technology for preventing and controlling the spodoptera frugiperda eggs.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Pupal-stage parasitic wasp artificial-propagation method, wasp-keeping box and manufacturing method of wasp-keeping box
The invention relates to a pupal-stage parasitic wasp artificial-propagation method, a wasp-keeping box and the manufacturing method of the wasp-keeping box. The pupal-stage parasitic wasp artificial-propagation method comprises the steps of (1) placing the parasitic wasp keeping box into a phytotron or a man-made climate box and placing parasitic wasps and hosts into the wasp-keeping box, (2) feeding the parasitic wasps periodically and guaranteeing the availability of food and water for the parasitic wasps in the box, (3) collecting and replacing the hosts, (4) supplementing parasitic wasps in the wasp-keeping box periodically and feeding the collected parasitized hosts, and (5) storing the parasitized hosts when the parasitic wasps grow to the pupal stage. By the adoption of the novel method that artificial propagation is conducted in a self-made wasp-keeping box device, people only need to open a spiral cover at the position of an inlet and use a blower to blow cold air to achieve parasitic wasp adding or host replacement, host replacement can be conducted fast in batches, and wasp propagation efficiency is improved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Propagation expanding method for parasitic wasps of Spodoptera frugiperda
InactiveCN111345188AImprove field parasitism rateIncrease productionPlant protectionAnimal husbandryEcological environmentVermin
The invention discloses a propagation expanding method for parasitic wasps of Spodoptera frugiperda. The propagation expanding method comprises the following steps: S1, cultivating the Spodoptera frugiperda; S2, inoculating the Spodoptera frugiperda for bee inoculation; S3, rejuvenating bee species; S4, releasing bee cocoons; S5, breeding the Spodoptera frugiperda; and S6, rejuvenating the Spodoptera frugiperda. The Spodoptera frugiperda are fed indoors to serve as propagation expanding hosts of Taiwan abdominal cocoon bees, the temperature, the humidity and the like are artificially regulatedto enable adult periods of the Spodoptera frugiperda and the Taiwan abdominal cocoon bees to be consistent, and adult Taiwan abdominal cocoon bees are parasitized by using egg mass of the Spodopterafrugiperda to breed the Taiwan abdominal cocoon bees, wherein a rejuvenation technology, a breed conservation technology and the like of seed bees and host populations exist. The final purpose is to artificially produce a large number of parasitic natural enemies, namely the Taiwan abdominal cocoon bees, then field release is performed in the spawning period of target pests, the field parasitism rate of the target pests is improved, the population number of the target pests is controlled, the degree of harmful crops is alleviated, the use amount of chemical pesticides is reduced, the yield andquality of agricultural products are improved, and the life safety of people and the ecological environment safety are protected.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HAINAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for increasing population quantity of wild adoxophyes braconidae by suspending rice moth larva container
The invention discloses a method for increasing the population quantity of wild adoxophyes braconidae by suspending a rice moth larva container. The method comprises the following steps of (1) singlysuspending the rice moth larva container; (2) artificially releasing the adoxophyes braconidae, and suspending the rice moth larva container; and (3) inspecting a population of the adoxophyes braconidae. According to the method for increasing the population number of the wild adoxophyes braconidae by suspending the rice moth larva container, the adoxophyes braconidae in the field natural environment is trapped or the adoxophyes braconidae is trapped and artificially released by artificially suspending the rice moth larva container in the field, so that field parasitic hosts, propagation conditions and shelters are provided for survival of the adoxophyes braconidae, establishment of the field population of the adoxophyes braconidae is ensured, the number of individuals of the population isincreased, and the effect of biological pest control of parasitic wasps is achieved.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Aphidius gifuensis Ashmaed and Encarsia formosa simultaneous breeding method
InactiveCN104756955AIncreased breeding utilizationImprove the breeding effectAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
Disclosed is an Aphidius gifuensis Ashmaed and Encarsia formosa simultaneous breeding method. Tobaccos or eggplants which is or are poor in insect resistance is or are utilized as host plants of myzus persicae and bemisia tabaci, the myzus persicae and the bemisia tabaci are bred together in a simultaneous breeding chamber after corresponding pest species and bee species are obtained through classified breeding on the myzus persicae, Aphidius gifuensis Ashmaed, the bemisia tabaci and Encarsia Formosa, the Aphidius gifuensis Ashmaed and the Encarsia Formosa are inoculated on simultaneous breeding chamber plants, and accordingly the simultaneous breeding of the Aphidius gifuensis Ashmaed and the Encarsia Formosa is implemented. The breeding utilization rate of the host plants is greatly improved, more than 10000 Aphidius gifuensis Ashmaed and more than 12000 Encarsia Formosa can be simultaneously bred on every host plant in the simultaneous breeding chamber, and the breeding efficiency is improved by 40 to 60% under the same facility condition in comparison with the common method. The two types of natural parasitic wasps can be bred simultaneously and accordingly the problem of the simultaneous harm of the two types of pests of the myzus persicae and the bemisia tabaci to the actual production can be effectively solved, the control effect is good, the efficiency is high, and the technology of prevention and control on multiple pests is improved due to the biological diversity.
Owner:SICHUAN BRANCH OF CHINA TOBACCO +2
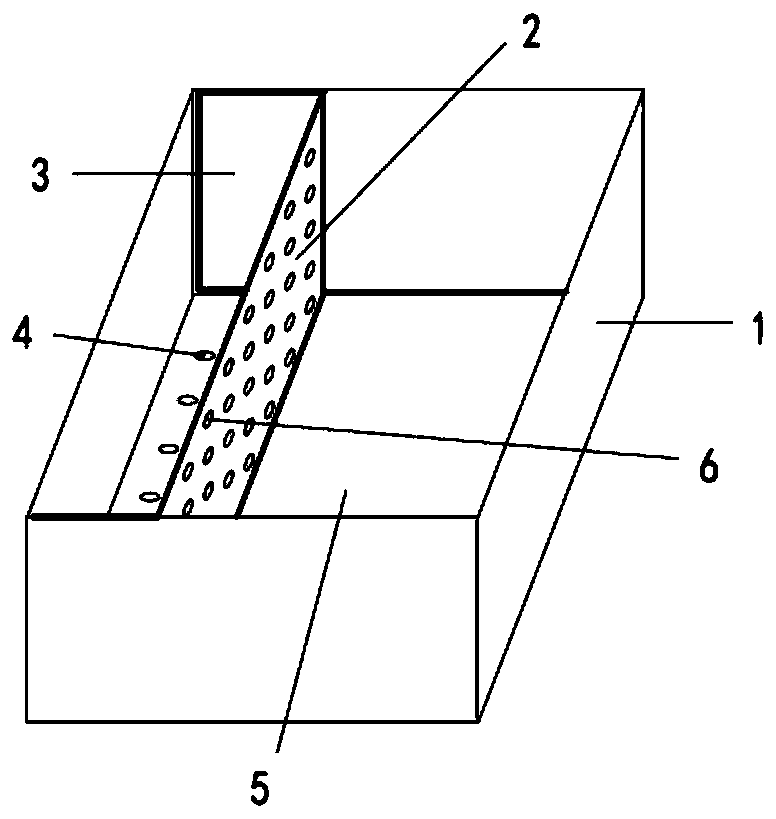
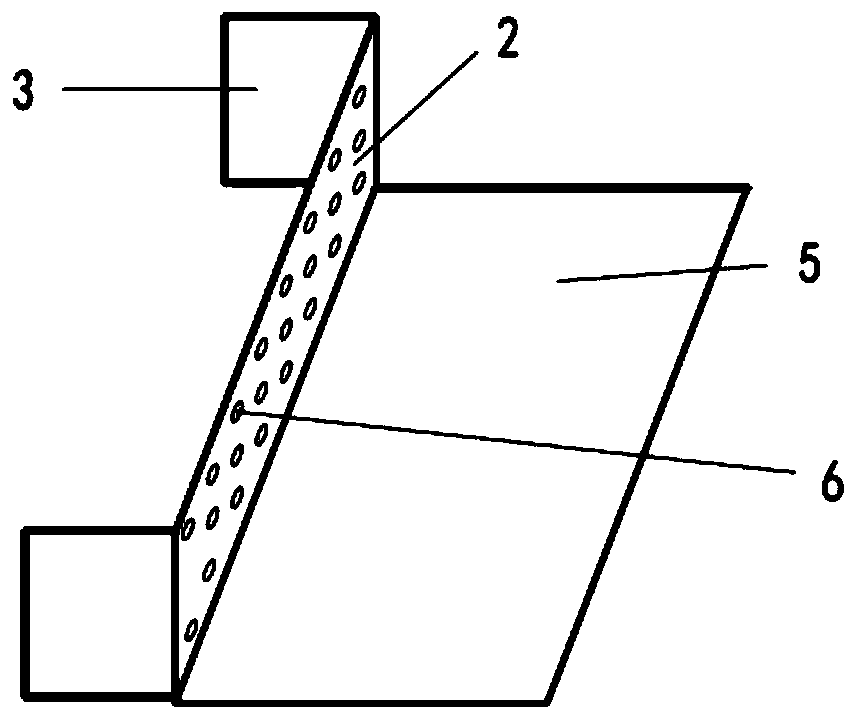
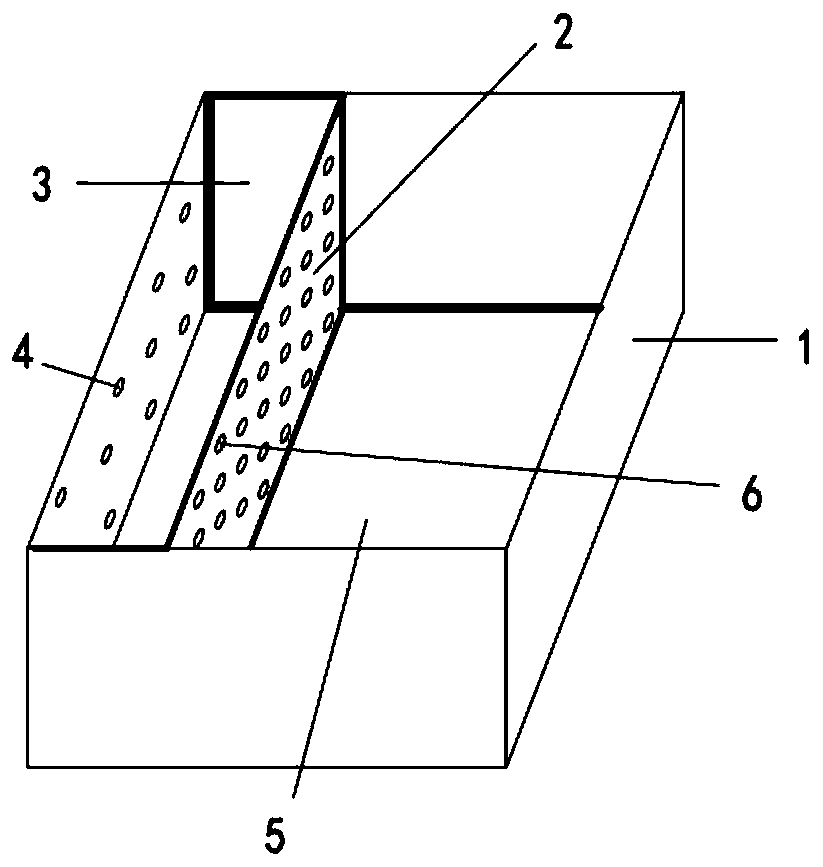
Multifunctional tephritidae natural enemy sanctuary, and preparation method and use method thereof
PendingCN110999868ASimplify the manufacturing processEasy to disassembleAnimal husbandryTephritidaeEngineering
The invention discloses a multifunctional tephritidae natural enemy sanctuary, which comprises a main body structure and a frame, wherein the main body structure comprises a rain blocking surface, parasitic wasp entering and leaving surfaces, transition surfaces and pressing edges; the frame comprises three-way pipes, metal pipes and pipe covers; the rain blocking surface is arranged on the top ofthe main body structure; the side surfaces of the rain blocking surface are independently provided with the parasitic wasp entering and leaving surface; the lower part of each parasitic wasp enteringand leaving surface is provided with the transition surface; and the lower part of each transition surface is provided with the pressing edge. By use of the multifunctional tephritidae natural enemysanctuary, the field population establishment capability and the utilization efficiency of the tephritidae parasitic wasp can be improved, the multifunctional tephritidae natural enemy sanctuary can be used for the field trapping and protection of the parasitic wasp by aiming at varied requirement functions in different types of tephritidae prevention and treatment, the field population establishment capability of the parasitic wasp can be improved, and the multifunctional tephritidae natural enemy sanctuary can be auxiliarily used for trapping and killing tephritidae adults.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
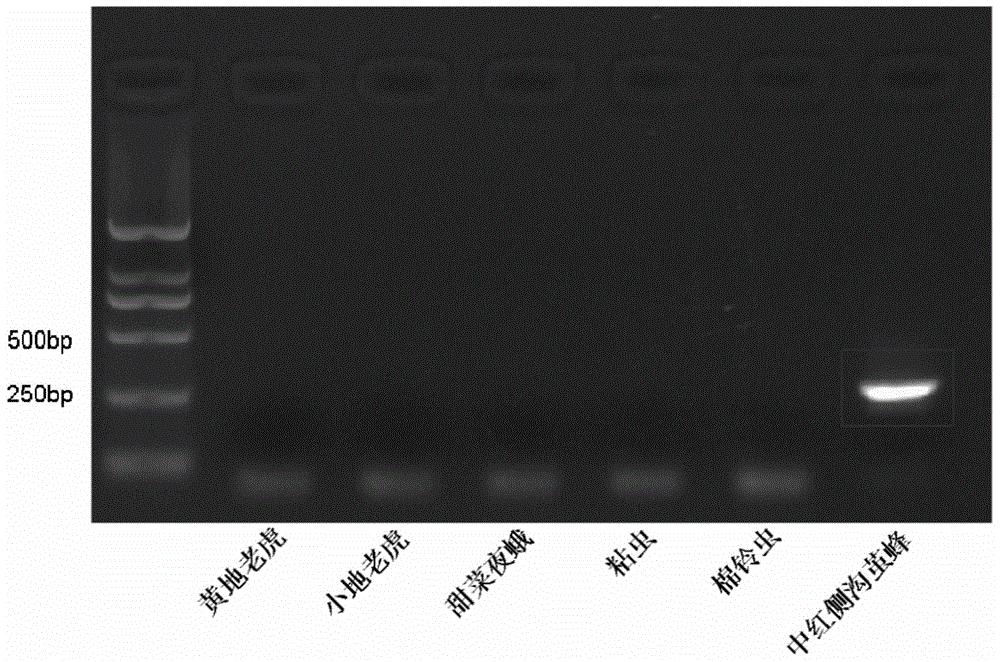
Microplitis mediator MmedCO I gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105861512AAvoid statistical errorsStatistically accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCotton bollwormMolecular level
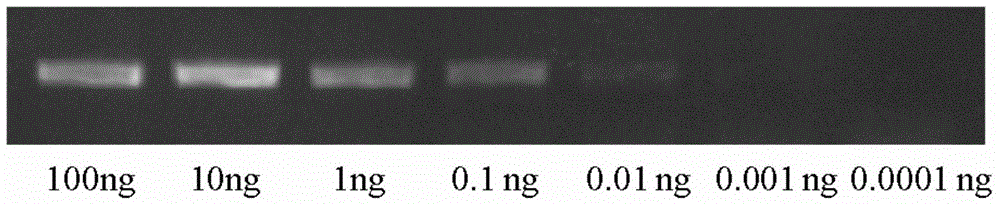
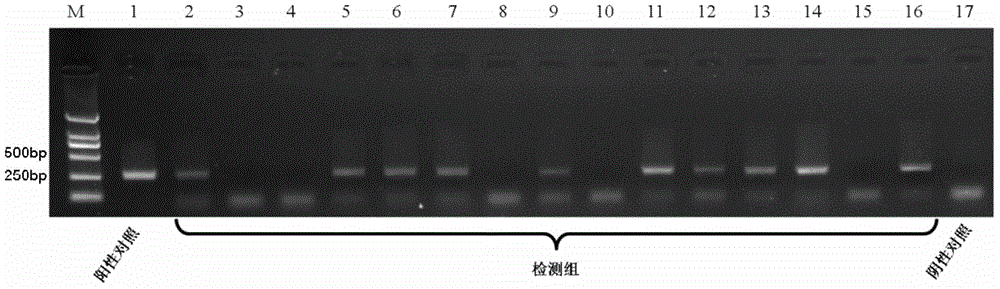
The invention relates to the field of parasitoid detection, and specifically provides a Microplitis mediator MmedCO I gene sequence (as shown in SEQ ID No.1), and specific amplification primers, which are designed based on the sequence, and provides a molecular level method for rapid detection of parasitic cotton bollworm larvae of the Microplitis mediator. The invention facilitates quick and accurate calculation of the egg laying amount of parasitic wasps or parasitism rate of host larvae. The invention can effectively detect the parasitized state of host larvae 24 hours after parasitism of the host larvae, reduce detection time, avoid statistical error due to abnormal death of host larvae and improve the accuracy of statistics.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Wax insect parasitic wasp trapping method
InactiveCN102499204AHarm reductionDoes not affect normal worm productionInsect catchers and killersAdhesiveEconomic benefits
The invention provides a wax insect parasitic wasp trapping method. Yellow adhesive paper is hung on a branch of a host plant cultivated with wax insects; volatile matters with volume concentration ranging from 0.01% to 1.0% are applied on the yellow adhesive paper; and wax insect parasitic wasps approach the yellow adhesive paper, and the yellow adhesive paper is taken down after being fully adhered with the parasitic wasps and is replaced by new yellow adhesive paper, so that trapping of the wax insect parasitic wasps is completed. A piece of flavourous yellow adhesive paper with the size of 15cmX20cm can trap 40 to 130 wax insect parasitic wasps within two to four days, a trapping effect is quite obvious, simultaneously, environments are not polluted, normal insect production and wax production of the wax insects are not affected, the quality of insect and wax products is not affected, the wax insect parasitic wasp trapping method is simple in technology, easy in popularization, low in cost and remarkable in economic benefit, and greatly reduces damage to the wax insects due to the parasitic wasps, parasitic rate of the parasitic wasps is reduced to be lower than 10%, and ecological control of the wax insect parasitic wasps is realized.
Owner:THE RES INST OF RESOURCES INSECTS RIRI OF THE CHINESE ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
Large-scale nasonia artificial-feeding method
The invention provides a large-scale nasonia artificial-feeding method. Compared with the prior art, the method has advantages that by 300Gry irradiation of 2-day-old musca domestica pupae, the Muscadomestica pupae unavailable for emergence are provided under the condition that pupa structures are undamaged, so that a step of adult musca domestica treatment is saved; by adoption of CO2 for anesthesia of nasonia, host musca domestica pupae and parasitic nasonia are separated after parasitism, escape in host replacement and parasitic wasp transferring processes is avoided, and efficiency improvement and cost saving are realized; after 10-day development, the host irradiated pupae are transferred to a refrigerating chamber at the temperature of 8-10 DEG C and in humidity of 75%-85%, development of nasonia is retarded under the condition of low-temperature constant-humidity storage, and centralized storage and release of parasitic nasonia are benefited. In addition, compared with frozen musca domestica pupae, the irradiated musca domestica pupae have the advantage that natural energy parasitic nasonia bred with the irradiated musca domestica pupae serving as hosts are high in female descendant yield, and high ecological benefits are achieved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
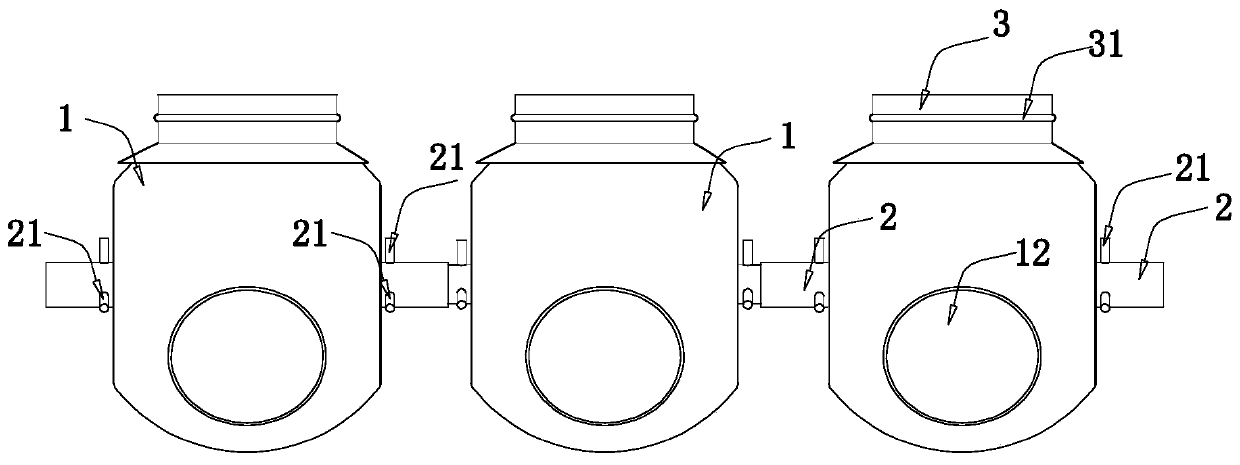
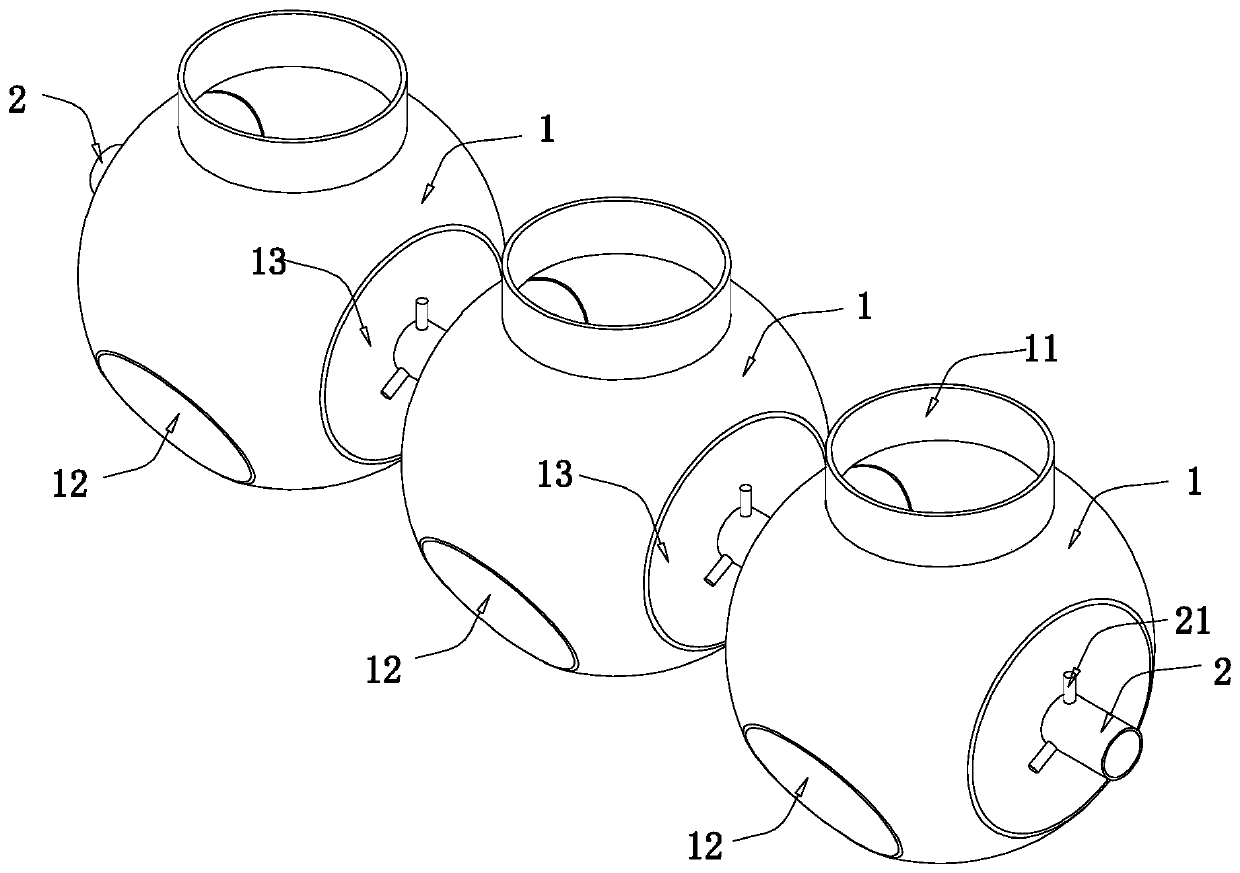
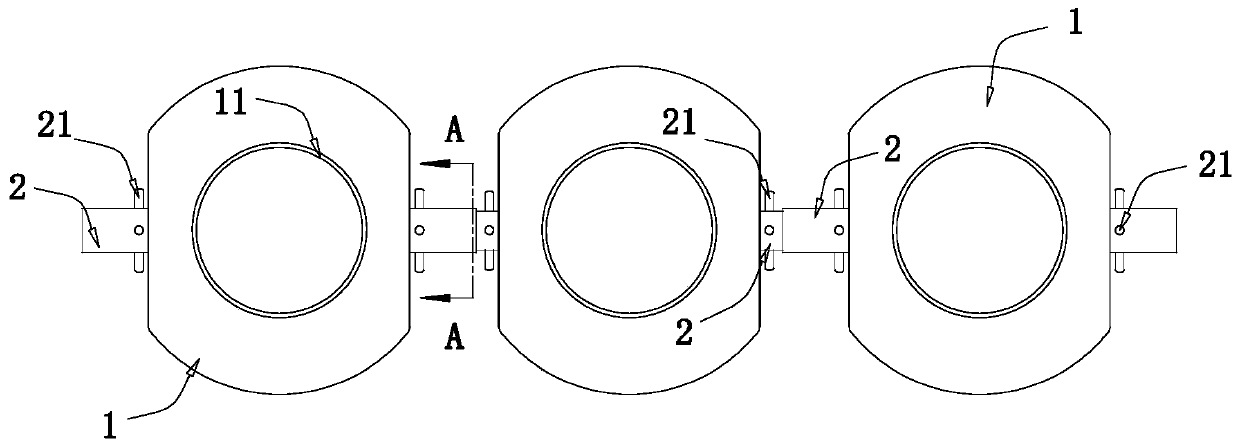
Convenient-to-operate feeding bottle for fruit-fly-pupa parasitic wasps and operation method of convenient-to-operate feeding bottle
The invention relates to a convenient-to-operate feeding bottle for fruit-fly-pupa parasitic wasps. The convenient-to-operate feeding bottle used for facilitating the breeding of the fruit-fly-pupa parasitic wasps comprises three parallel single bottles, guide pipes, opening and closing units and wasp blocking unit, wherein the guide pipes are arranged at the left end and the right end of each single bottle, and every two adjacent single bottles are connected through the guide pipe; the opening and closing units are arranged on the guide pipes and used for opening and closing the guide pipes;the wasp blocking units are arranged at the openings of the single bottles and used for preventing the parasitic wasps from flying out of the single bottles and do not affect the air exchanging insideand outside the single bottles. The convenient-to-operate feeding bottle and the operation method thereof have the advantages that parasitic wasp breeding can be achieved, the parasitic wasps can betransferred among the single bottles without opening the openings of the single bottles, and operation convenience and simpleness are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG ACAD OF GRAPE
Large-scale production method of tamarixia radiate
The invention discloses a large-scale production method of tamarixia radiate. The method comprises the steps that s1, carrier plants are managed, tender shoots are cultivated, and the carrier plants are calamondin; s2, diaphorina citri is inoculated to the carrier plants in a diaphorina citri breeding cage, and nymphs are bred; s3, the carrier plants with the 4-5-age diaphorina citri nymphs are moved into a parasitic wasp breeding cage, tamarixia radiate adults are put into the parasitic wasp breeding cage, the inoculation quantity ratio of tamarixia radiate to the diaphorina citri nymphs is 1: 10-20, and the tamarixia radiate adults are bred and collected; and s4, the carrier plants are cleaned and recovered. The carrier plants developed by the method are calamondin, the carrier plants shorten the growth cycle, the breeding capacity of the diaphorina citri and the production capacity of parasitic wasps are greatly improved, and the net yield and the female ratio of the tamarixia radiate are effectively improved according to the inoculation proportion of calamondin+tamarixia radiate to the diaphorina citri nymphs.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Method for preventing and treating spodoptera frugiperda through tetrastichus howardi
InactiveCN111280130AReduce multiplication costsIncrease parasitic rateAnimal husbandryVerminTetrastichus
The invention relates to a parasitic natural enemy tetrastichus howardi of an invasive pest spodoptera frugiperda. The parasitic natural enemy tetrastichus howardi can effectively prevent and treat spodoptera frugiperda. A method comprises the following steps of performing propagation expanding on the parasitic natural enemy tetrastichus howardi, wherein initial pupae of yellow mealworms are usedas substitute hosts; performing spraying treatment on the initial pupae of the yellow mealworms for propagation expanding with an ethanol diluent (1000 times) of trans-beta-farnesene; and before release of adult tetrastichus howardi; and performing powder spraying with beauveria bassiana (D-1) powder (beauveria bassiana spore powder, dextrin, defatted corn flour and soybean lecithin), wherein theparasitic natural enemy tetrastichus howardi can carry beauveria bassiana to be accurately parasitic on the target pest spodoptera frugiperda in a directional manner, and a biocontrol substance can becolonized and can continuously control the pests. According to the technology, the propagation expanding cost is effectively reduced, and the parasitic efficacy, the stability and the persistence areimproved.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
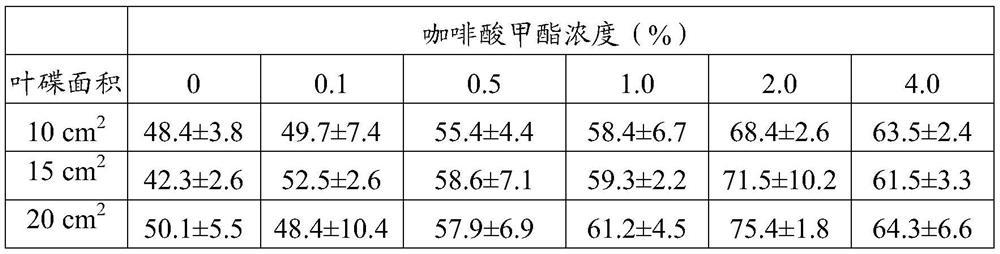
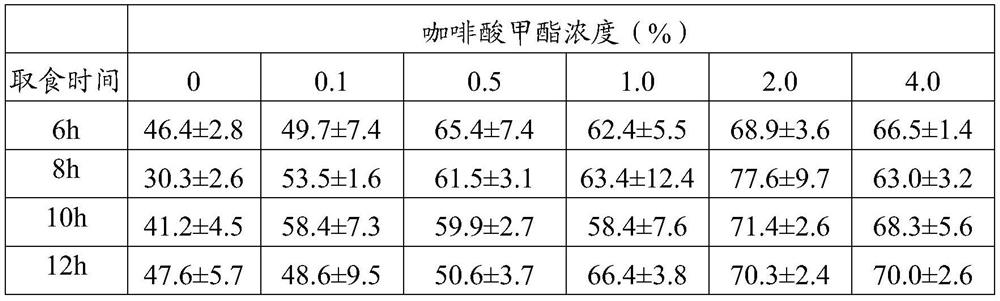
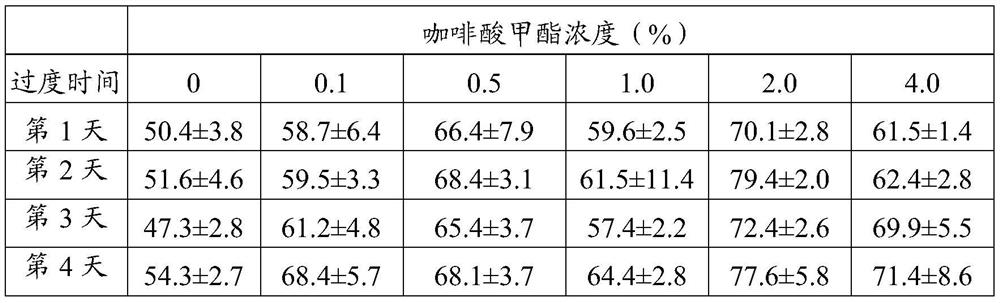
Method for increasing parasitic rate of glyphodes pyloalis parasitic wasps by using methyl caffeate
PendingCN113180010AIncrease parasitic rateIncrease production capacityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsGlyphodes pyloalisParasitism
The invention discloses a method for increasing the parasitic rate of glyphodes pyloalis parasitic wasps by using methyl caffeate. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a methyl caffeate solution; providing mulberry leaves containing the methyl caffeate for glyphodes pyloalis larvae to eat; and providing the glyphodes pyloalis larvae which eat the mulberry leaves containing the methyl caffeate for the mixed chamber to parasiticus. When the method is used for breeding the mixed-chamber cotesia, the parasitism efficiency is high, the loss is small, the operation is simple and convenient, the cost is low, the problem that leaf rolling of larvae of the stem borer family is not beneficial to parasitism of the parasitic wasps is solved, large-scale indoor production of mulberry pest mixed-chamber cotesia parasitic wasps is facilitated, and an important foundation is laid for field biological control work of the glyphodes pyloalis.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device for determining growth and development indexes of whitefly parasitic wasps by using living plants and use method
The invention relates to a device for determining growth and development indexes of whitefly parasitic wasps by using living plants and a use method. The device comprises a parasitizing device and a culture device. The parasitizing device disclosed by the invention comprises an upper parasitizing dish and a lower parasitizing dish, wherein opening faces of the upper and lower parasitizing dishes are formed oppositely, spongy cushions are separately arranged at joints, and thus, a space for parasitizing of the parasitic wasps is enclosed; 3 ventilation openings are separately formed in two sidefaces of the upper and lower parasitizing dishes, and an insect receiving port is formed in one end, close to a snapping opening, of the top of the upper parasitizing dish and is connected with an insect receiving pipe; and the culture device is a disc with a cover, a circular opening is formed in the center of the cover, and a piece of gauze is laid in the circular opening. According to the device and the use method, growth and development conditions of the whitefly parasitic wasps are observed by using the living plants, the device is relatively close to a natural environment, and determination data are more accurate.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Biological control method for hyphantria cunea
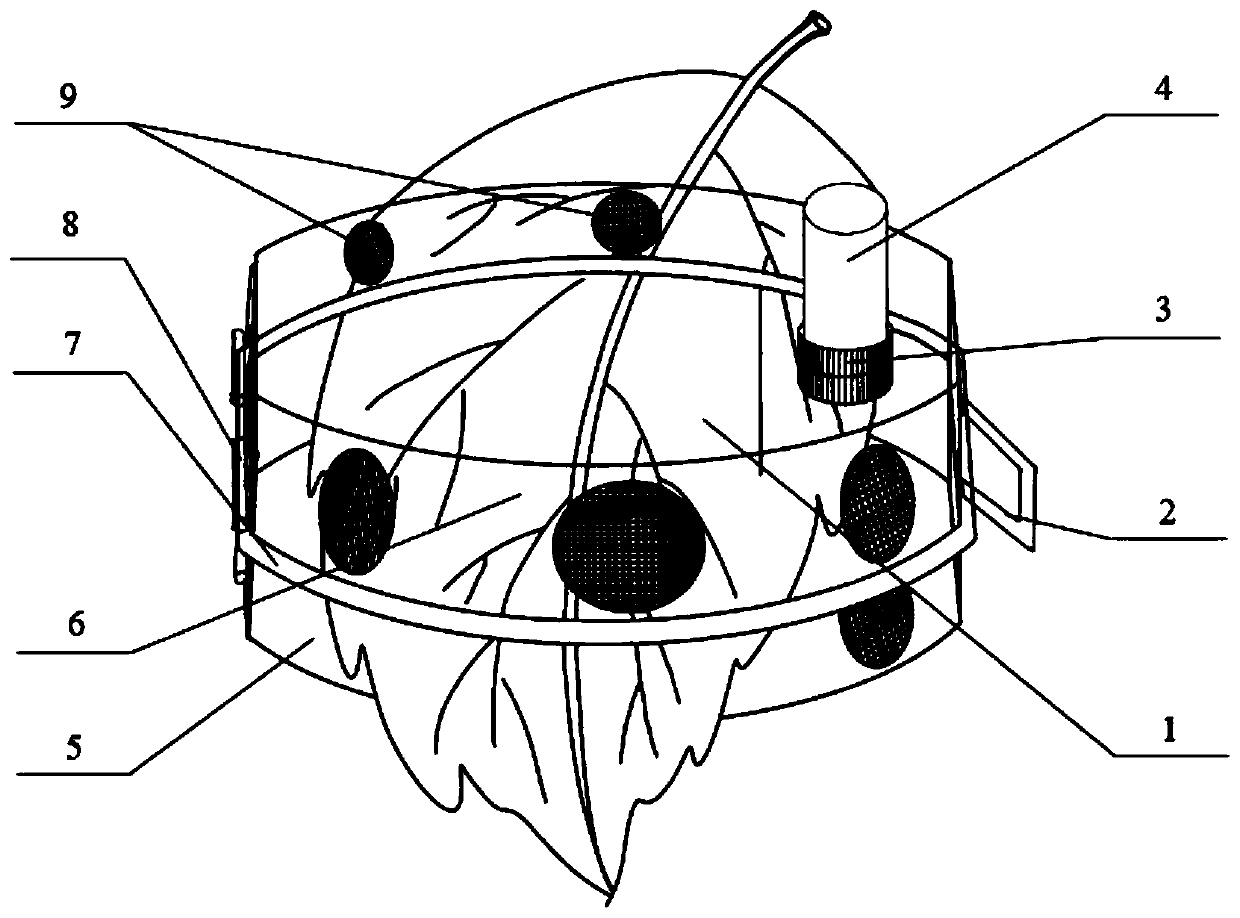
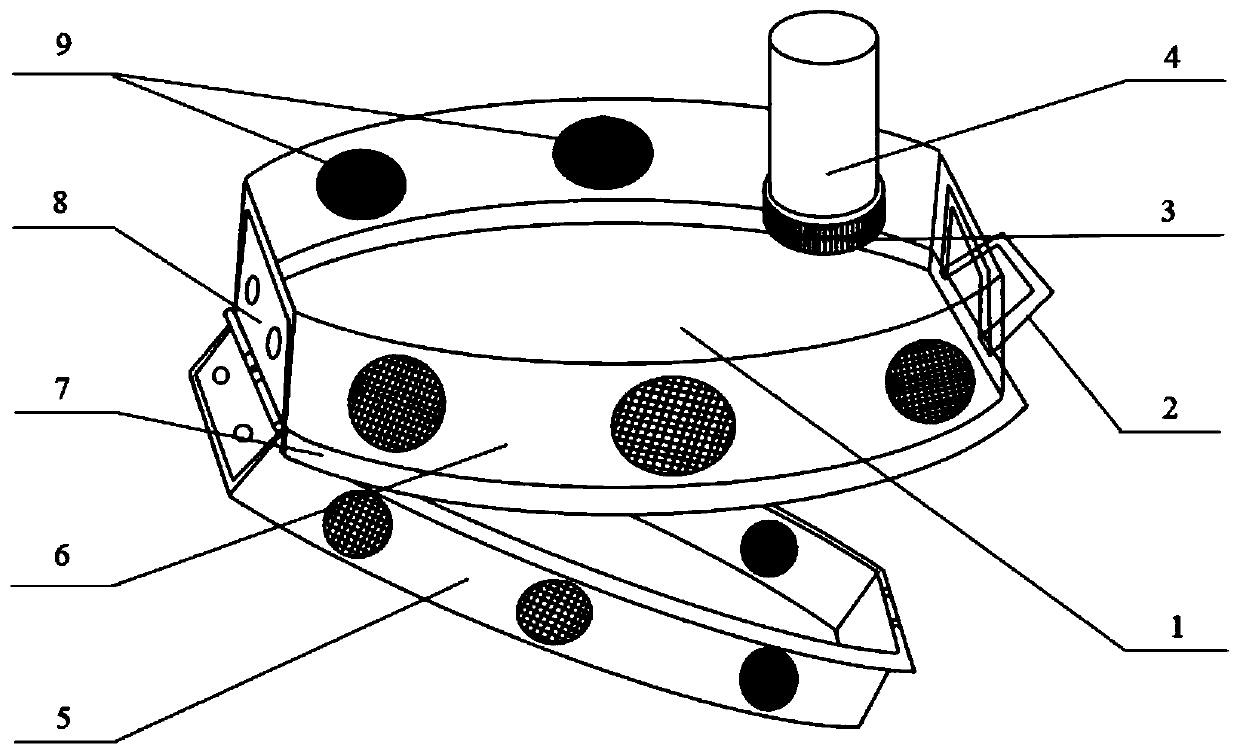
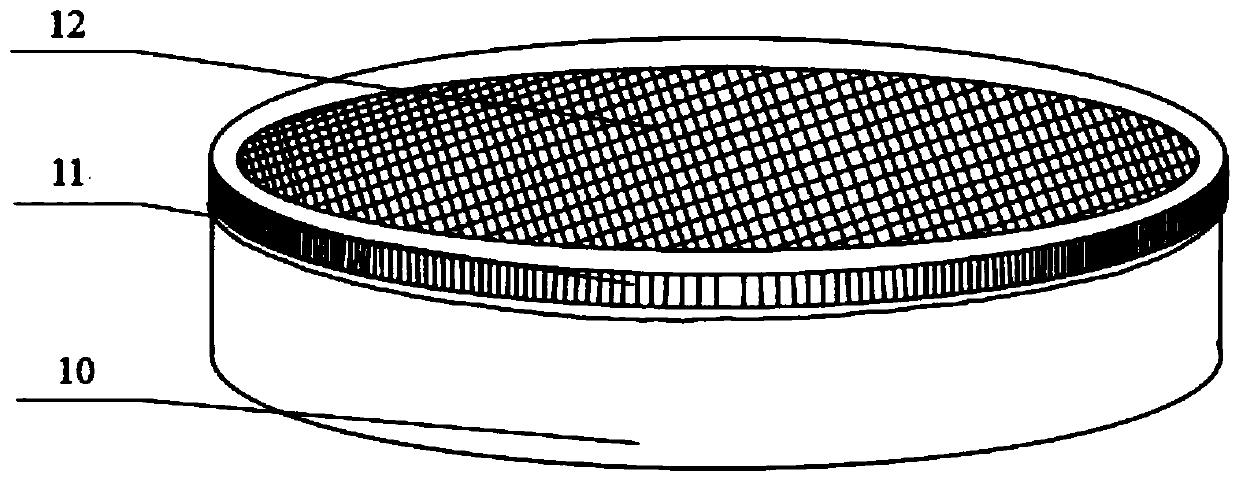
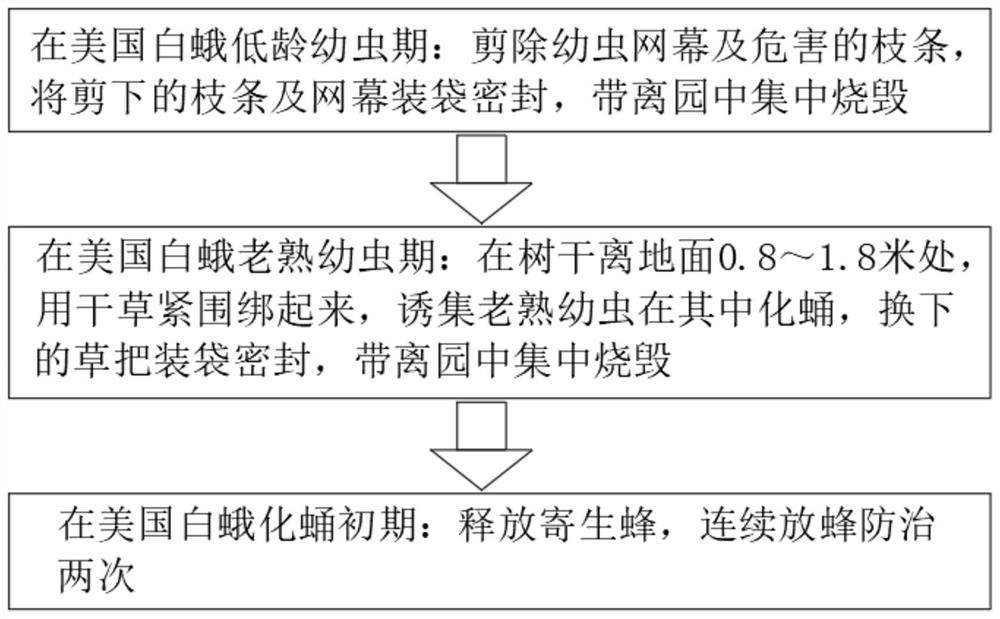
PendingCN113287456AControl happensControl spreadPlant protectionAnimal husbandryZoologyPesticide use
The invention discloses a biological control method for hyphantria cunea. The method comprises the following steps: in a low-age larva stage of the hyphantria cunea, cutting off a larva net curtain and harmful branches, bagging and sealing the cut branches and the net curtain, and taking the branches and the net curtain away from a garden for centralized burning; in a hyphantria cunea mature larva stage, before hyphantria cunea mature larvas begin to get out of a tree and pupate, tightly binding the trunk with hay at a position 0.8-1.8 m away from the ground for a circle, trapping the hyphantria cunea mature larvas to pupate in the hay, replacing hay bundles every 5-7 days during pupation, bagging and sealing the replaced hay bundles, and taking the replaced hay bundles away from the garden for centralized burning; and in the initial stage of hyphantria cunea pupation, releasing parasitic wasps, and continuously releasing the parasitic wasps for control twice. The biological control method for the hyphantria cunea is simple, the means of combining artificial physical control and biological control is adopted, occurrence and propagation of the hyphantria cunea are controlled, the population base number and propagation and diffusion of the hyphantria cunea are thoroughly controlled, the use amount of chemical pesticide is reduced, and the yield and quality of agricultural products are improved.
Owner:安徽省友林林业技术发展有限公司
Device and method for collecting parasitic wasps of lepidoptera insect larvae in field
PendingCN112471080ALong-term collectionSimple structureAnimal husbandryAnimal scienceOrder Lepidoptera
The invention discloses a device and method for collecting parasitic wasps of lepidoptera insect larvae in field, and belongs to the technical field of field artificial collection of natural enemy insects. The device comprises a box body, a box cover, support columns and support legs; the bottom of the box body is closed, the side faces are open, the side faces of the box body are surrounded and covered by gauze and provided with side doors, and multiple boxes are placed in the box body; the box cover is fixed at the top of the box body; the support columns support the bottom of the box body;and the support legs are hollow-cup-shaped, openings are upward, and the bottom ends of the support columns are fixed in the support legs. The invention also discloses a method for collecting the parasitic wasps of the lepidoptera insect larvae by using the device. The device is simple in structure, the method is simple, the cost is low, the usability is high, the collecting efficiency is high, and collection of a large number of parasitic wasps of the lepidoptera insect larvae for a long time can be achieved.
Owner:LIUYANG BRANCH OF CHANGSHA COMPANY OF HUNAN TOBACCO +2
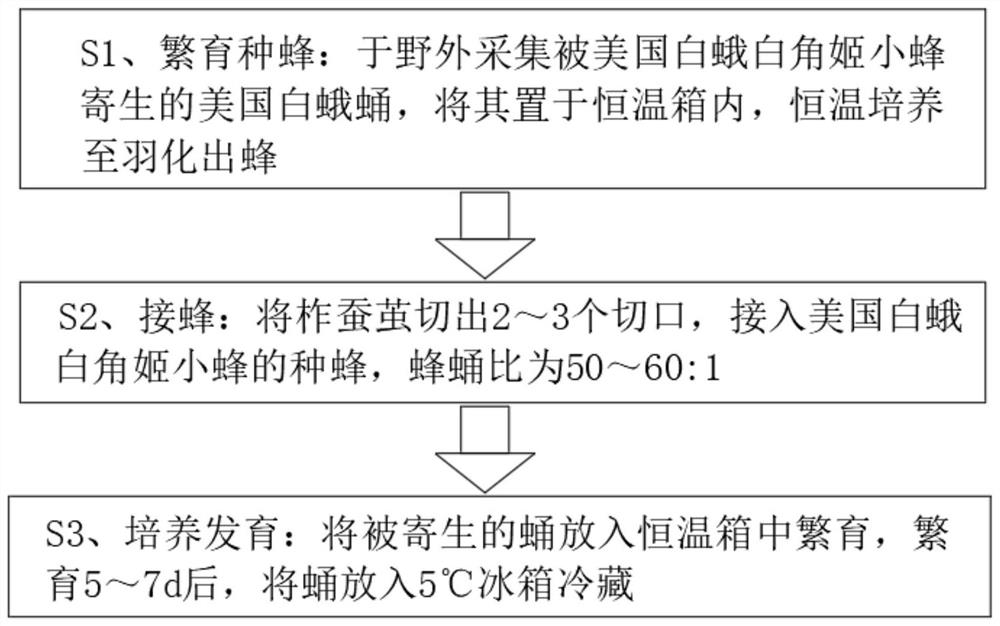
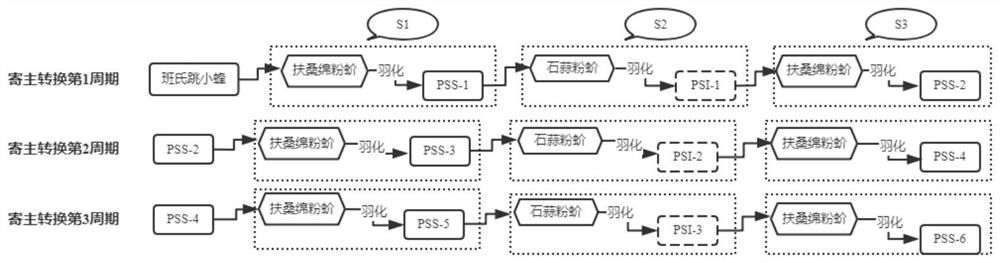
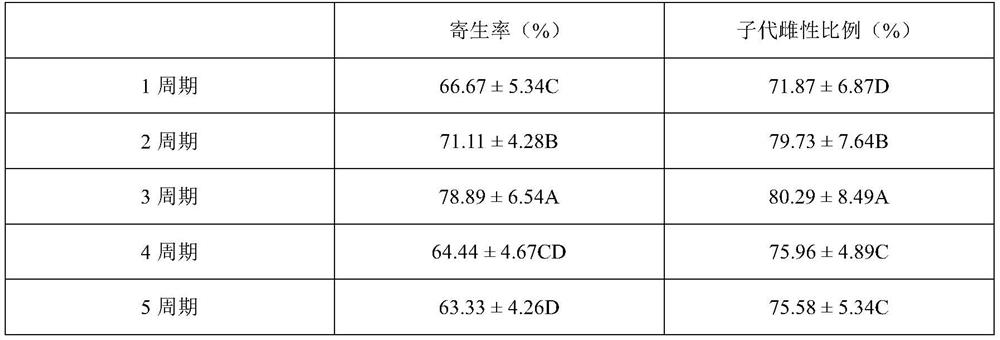
Method for optimizing population structure of Aenasius bambawalei through host conversion mode
ActiveCN113678790AHigh rate of parasitismIncrease the rate of being parasitizedAnimal husbandryAenasius bambawaleiFishery
The invention relates to the technical field of indoor breeding of insects, in particular to a method for optimizing the population structure of Aenasius bambawalei through a host conversion mode. The host conversion period specifically comprises the following steps of S1, selecting Aenasius bambawalei PSS-1 breeding multiple generations by taking Phenacococcus solenopsis as a host; S2, providing a conversion host of Phenacoccus solani for the Aenasius bambawalei PSS-1, and after offspring parasitic wasps of the PSS-1 are subjected to eclosion, obtaining the Aenasius bambawalei PSI-1 subjected to primary host conversion; and S3, providing phenacoccus solenopsis for the Aenasius bambawalei PSI-1 after host conversion for parasitism so as to obtain Aenasius bambawalei PSS-2 after secondary host conversion. According to the method, the Aenasius bambawalei carry out parasitism twice on the phenacoccus solenopsis to generate PSS-1 and the PSS-2 and once on the Phenacoccus solani to generate PSI-1, so that one host conversion period is completed; host conversion for a second period (generating PSS-3, PSI-2 and PSS-4) and a third period (generating PSS-5, PSI-3 and PSS-6) continues so as to realize the population optimization of the Aenasius bambawalei. By means of the method, the parasitism rate of the female bees of the Aenasius bambawalei can be remarkably increased, the service life of the female bees and the male bees is prolonged, the proportion of offspring female bees in a population is increased, and the population structure of the Aenasius bambawalei is greatly optimized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Artificial breeding method for dominant parasitic wasps of mulberry borers
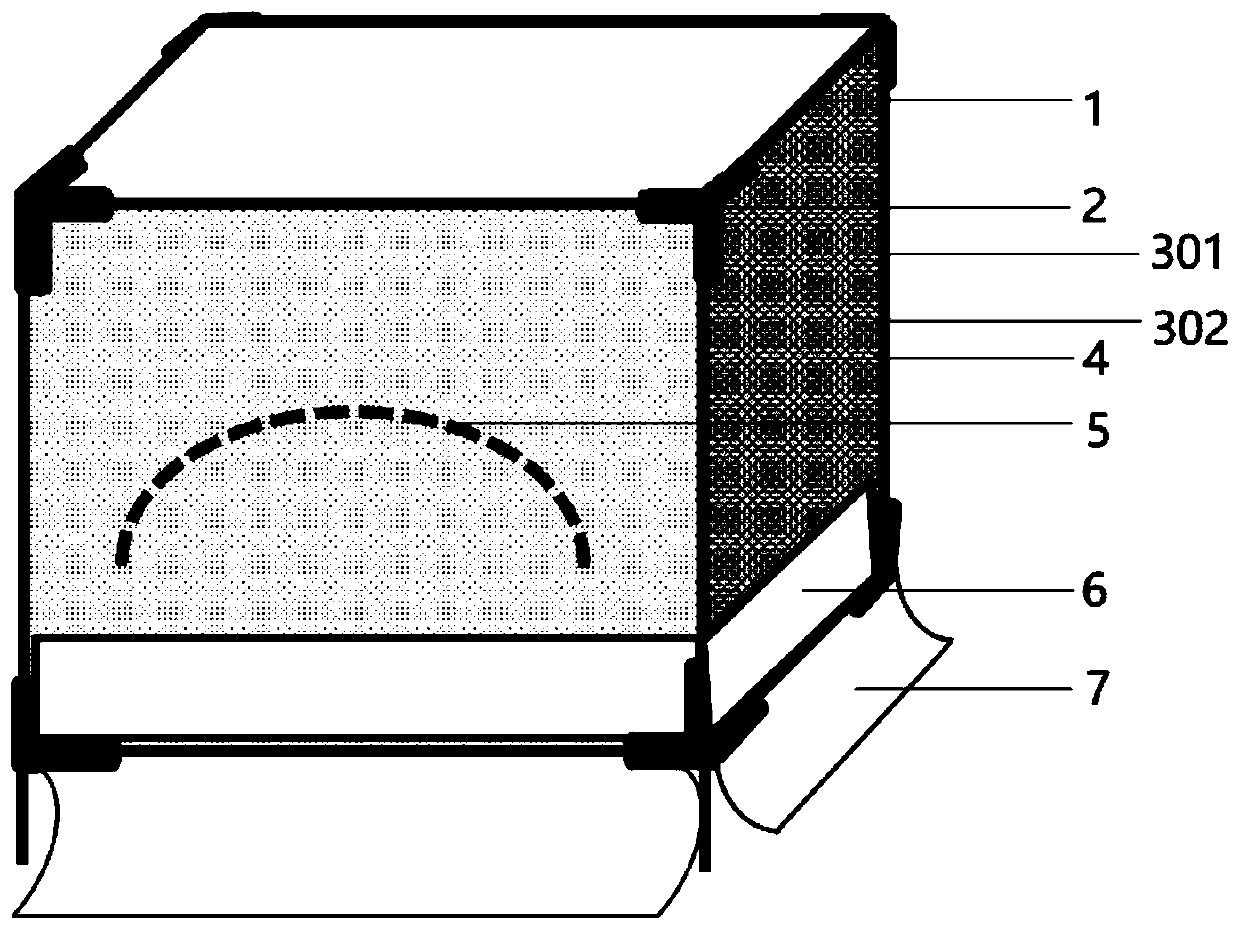
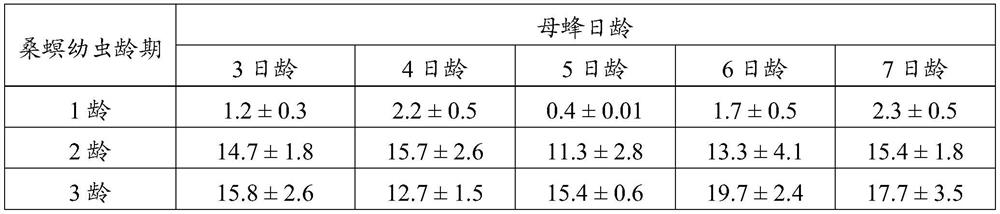
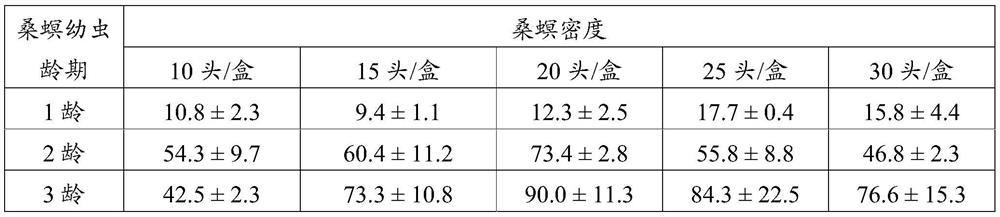
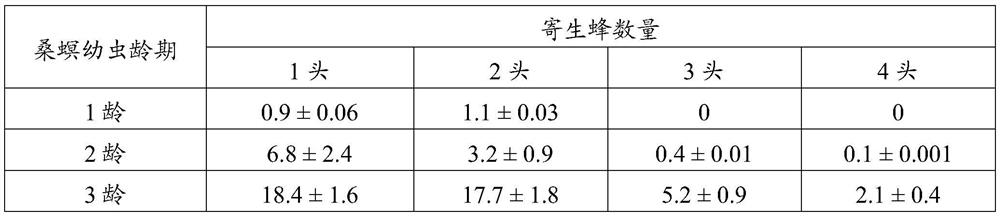
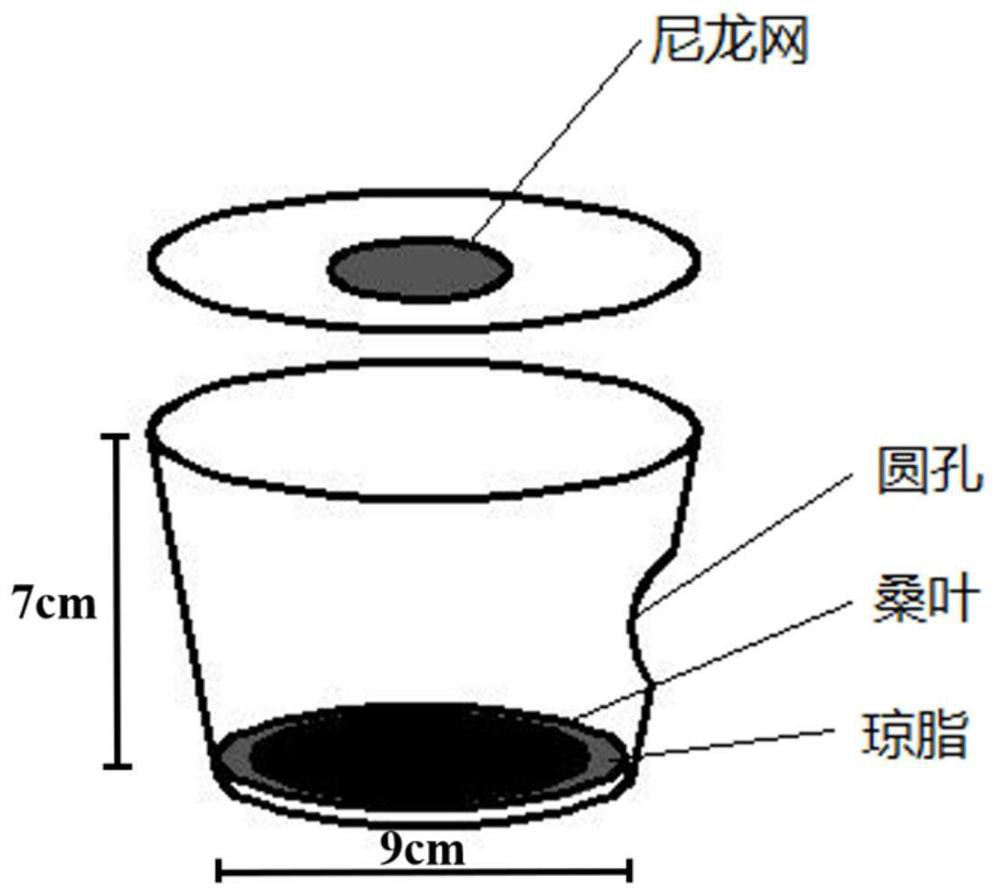
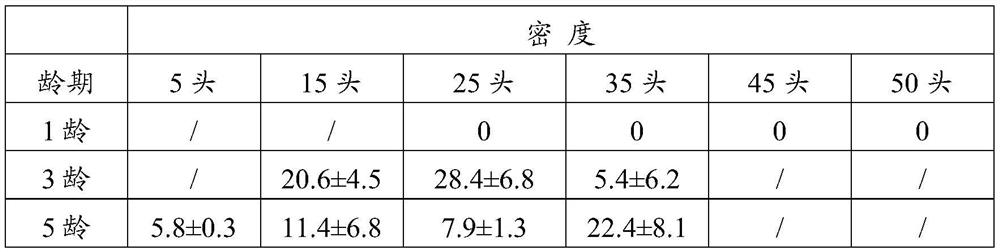
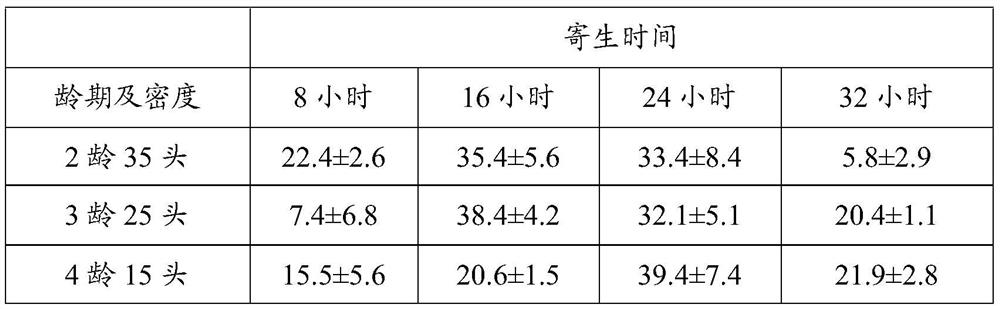
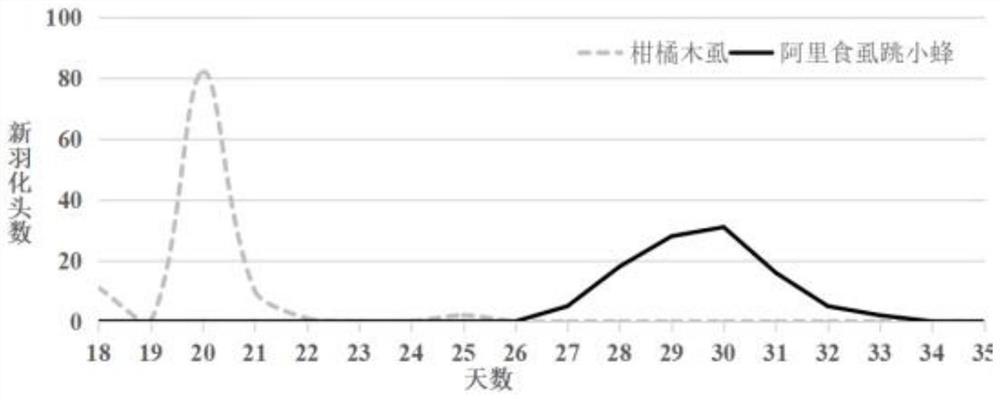
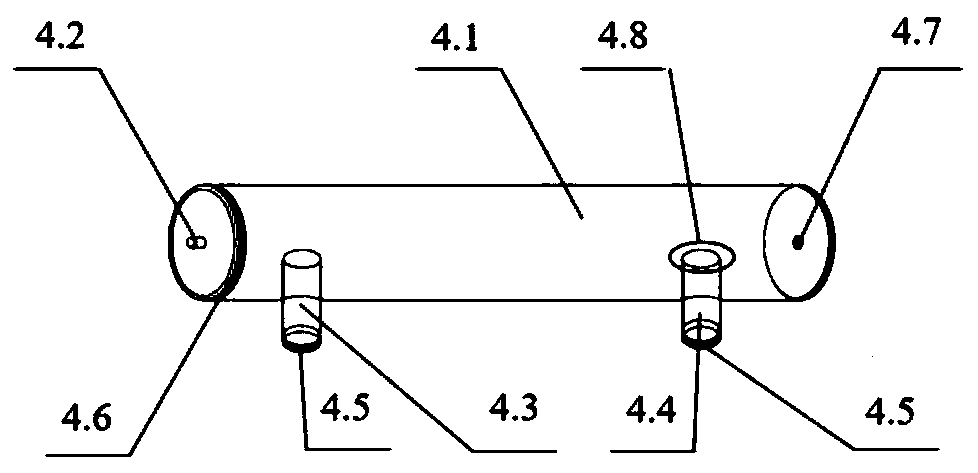
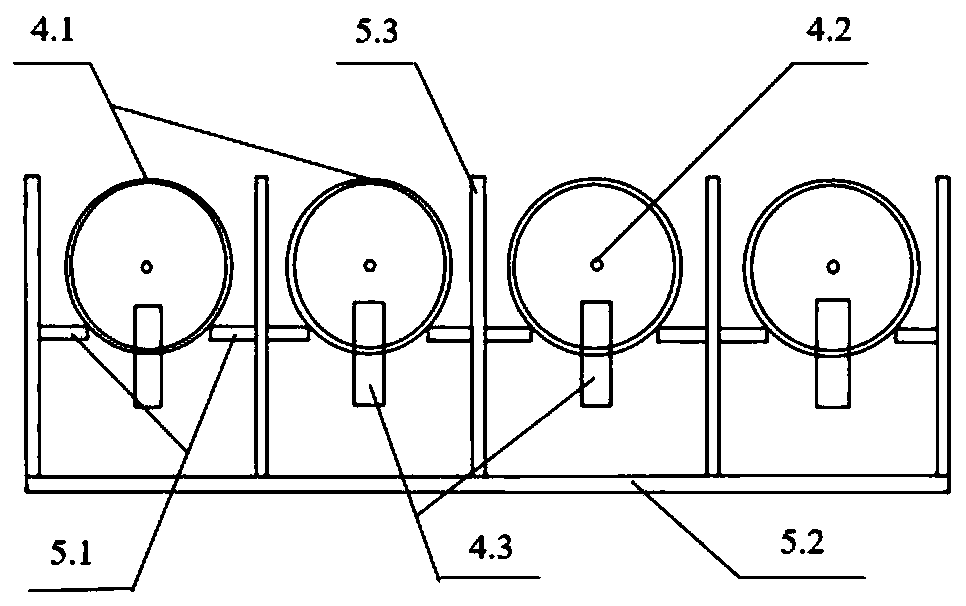
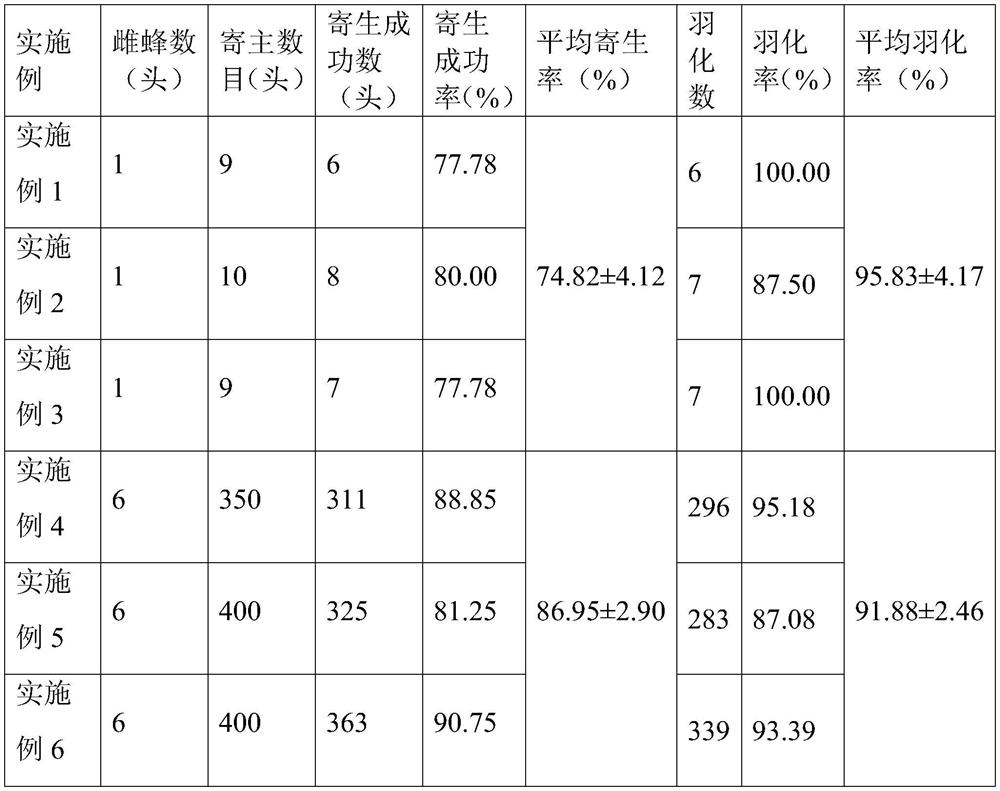
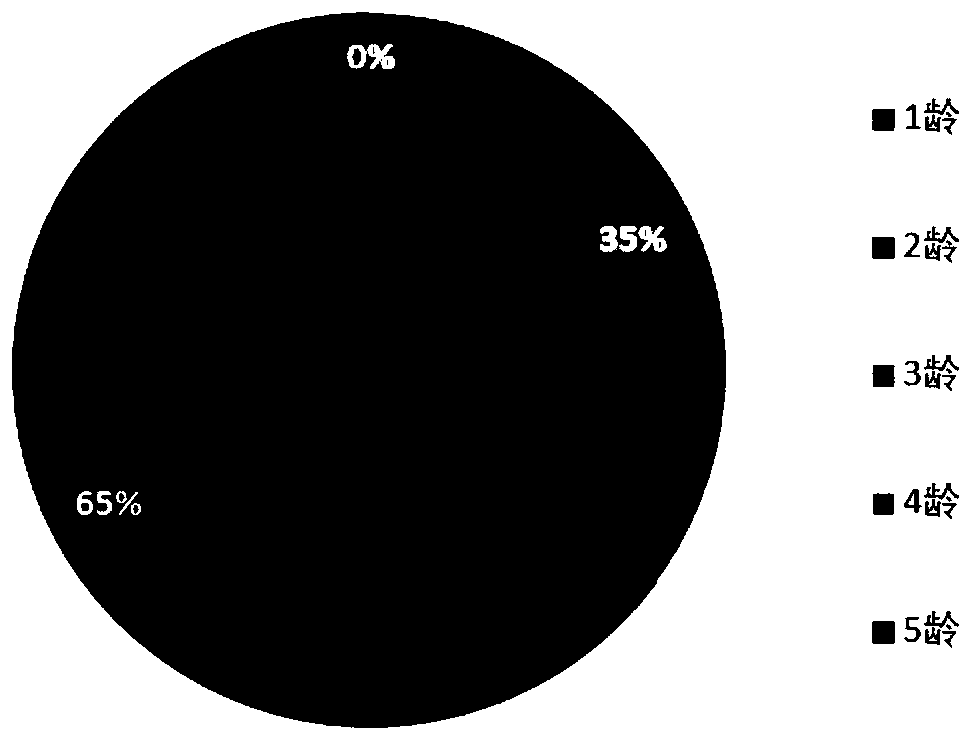
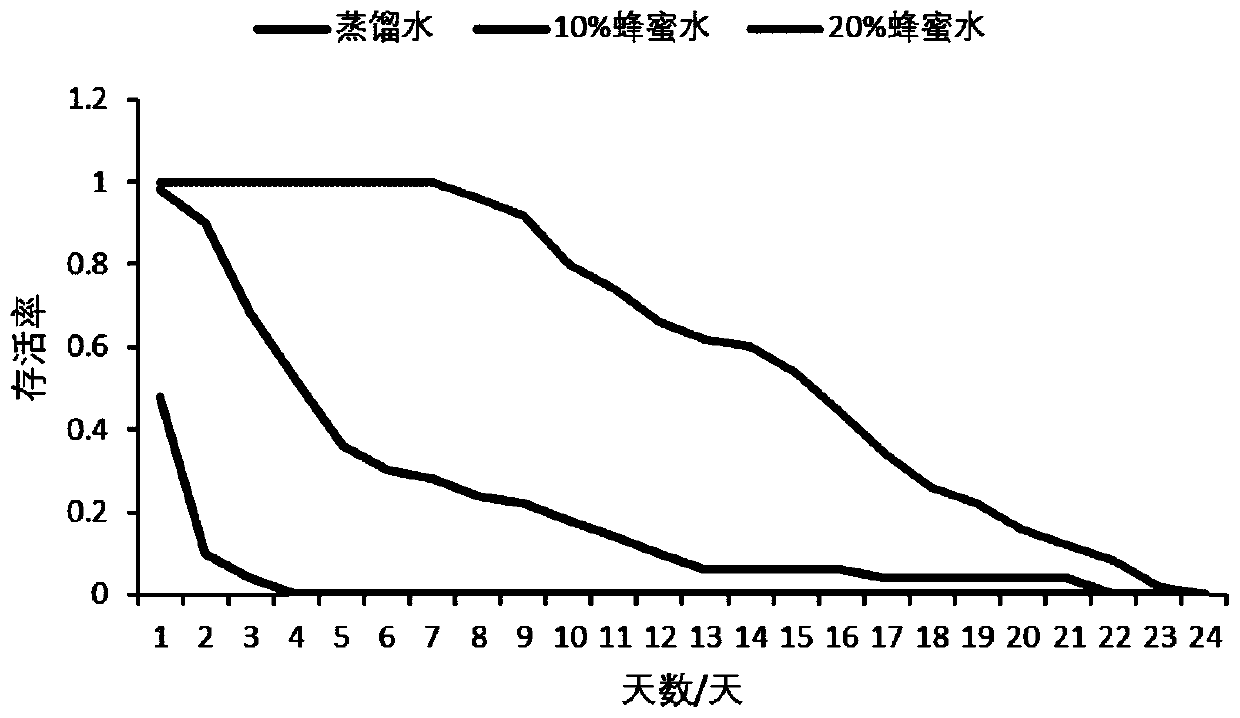
InactiveCN113826589AImprove survival rateGreen Governance GuaranteeAnimal husbandryParasitismIchneumonidae
The invention relates to an artificial breeding method for dominant parasitic wasps of mulberry borers. The artificial breeding method comprises the following steps that aiming at the biological characteristics of the mixed-chamber cotesia, larvae of the mulberry borers are taken as hosts; and the age of the mulberry borer larvae suitable for parasitism of the mixed chamber cotesia, the day age of the parasitism female bees, the density of the mulberry borer larvae during parasitism, the density of the parasitism female bees, the parasitism duration, the cocoon harvesting time after parasitism and the concentration of honey water for feeding parasitic adult cotesia are determined, so that stable mixed chamber cotesia are obtained. When the artificial breeding method is used for breeding the mixed-chamber cotesia, the parasitic efficiency is high, the operation is simple and convenient, the cost is low, the indoor artificial breeding of the dominant parasitic wasps of the mulberry borers is realized, the large-scale production of parasitic wasp products for preventing and controlling the mulberry borers in the field is facilitated, and a solid foundation is laid for performing biological prevention and control work of the mulberry borers based on the parasitic wasps.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for artificially feeding parasitic wasps by taking mulberry pyralids as hosts
PendingCN113040097AImprove parasitic efficiencyExpand host sourcesAnimal husbandrySpawning siteParasitism
The invention relates to a method for artificially feeding parasitic wasps by taking mulberry pyralids as hosts. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting mulberry pyralid larvae from a field, putting the mulberry pyralid larvae into a container paved with mulberry leaves, and collecting parasitic wasp cocoons after the parasitic wasp larvae get out of the hosts to cocoon; placing the parasitic wasp cocoons in glass test tubes, and after eclosion of the parasitic wasps, feeding the parasitic wasps with hydromel; adopting raised parasitic wasp adults for parasitism, and during parasitism, utilizing a transparent container as a spawning site, and inoculating the mulberry pyralid larvae for parasitism of the parasitic wasps; after parasitism is finished, collecting the mulberry pyralid larvae and the parasitic wasps respectively, feeding the mulberry pyralid larvae until the offspring wasps of the parasitic wasps get out of the hosts, and allowing the parasitic wasps to be used for subsequent parasitism again. When the method is used for breeding meteorus pulchricornis, the parasitism efficiency is high, the loss is small, the operation is simple and convenient, the cost is low, the host source of the meteorus pulchricornis is expanded, the indoor large-scale production of mulberry pest parasitic wasp meteorus pulchricornis is facilitated, and a good foundation is laid for the field biological control work of mulberry pyralids.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Large-scale production method of diaphorina aliensis
The invention relates to the field of biological prevention and control of agricultural pests, and discloses a large-scale production method of diaphorina algida. The large-scale production method of the diaphorina algida mainly comprises the following four steps of (1) establishing a diaphorina algida population; (2) preparing a diaphorina citri population to be parasitized; (3) inoculating a parasitic wasp of diaphorina citri, namely the diaphorina algida, into the diaphorina citri population to be parasitized; and (4) collecting the parasitic wasps. The large-scale production method of the diaphorina algida is simple in process and controllable in breeding scale, and propagation expanding work can be carried out all year round and is not limited by seasons; meanwhile, eclosion time of the parasitic wasps is concentrated, population quantity is controllable, interference of phylloxera does not need to be considered during wasp collection, and operation is simple; meanwhile, the method has no special rigid requirements on the types and sizes of host plants and is suitable for all the host plants of the diaphorina citri, and the utilization rate of the host plants is high.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Field release method of glyphodes pyloalis parasitic wasps
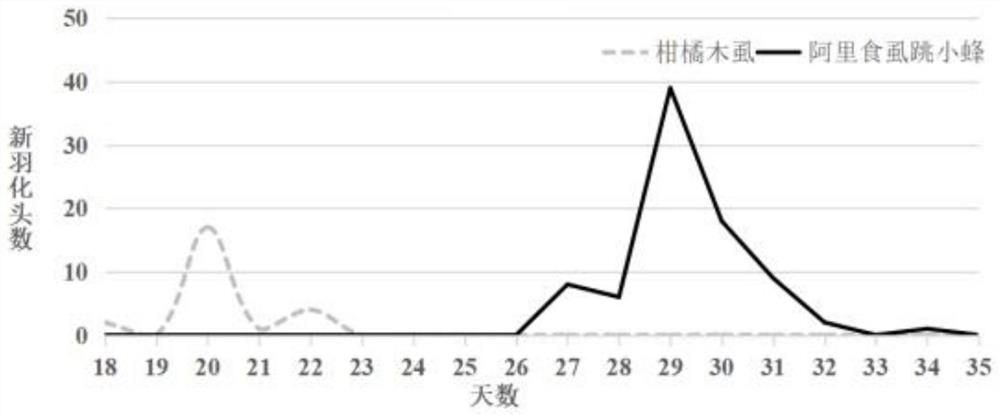
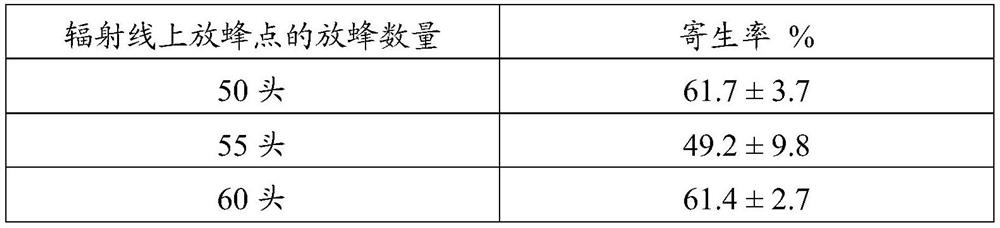
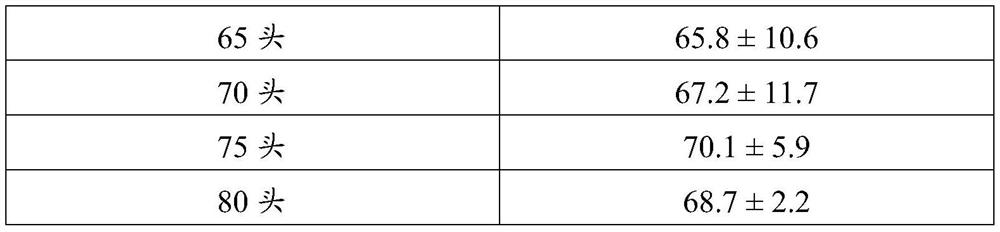
PendingCN113273548AEfficient releaseAchieve biological controlPlant protectionAnimal husbandryAulacocentrumPest control
The invention discloses a field release method of glyphodes pyloalis parasitic wasps. The method comprises the following steps: collecting aulacocentrum confusum adults, taking every 667m<2> of a mulberry field as a release unit, setting a release point in the center of each mu of the mulberry field, outwards extending 3-5 radiation lines from the release point to the boundary of the mulberry field, and setting a group of release points on the radiation lines, wherein the release number of the parasitic wasps at the central release point is 50-100, and the release number of the parasitic wasps at each position of the release points on the radiation lines is 50-75. When the method is used for releasing the aulacocentrum confusum in the field, the parasitic efficiency of the aulacocentrum confusum on the glyphodes pyloalis is high, the pest control effect is remarkable, the natural and continuous pest control capacity of the aulacocentrum confusum is high, and population growth of the third generation and the fourth generation of the glyphodes pyloalis can be stressed. The method is simple and convenient to operate and low in release cost, solves the problem of field release of the glyphodes pyloalis parasitic natural enemies, is beneficial to fully exerting the natural pest control effect of the glyphodes pyloalis parasitic natural enemies, improves the control effect on the glyphodes pyloalis, reduces the application quantity of chemical pesticides in the mulberry field, and ensures the growth safety of silkworms and the environmental safety of the mulberry field.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device for determining influence of insecticide on host positioning capability of aleyrodid pest parasitic wasps and use method
PendingCN111257547AAvoid Mutual Learning BehaviorsAvoid affecting test resultsBiological testingActivated carbonZoology
The invention relates to a device for determining the influence of an insecticide on the host positioning capability of aleyrodid pest parasitic wasps and a use method. The device comprises an activated carbon gas washing chamber, a gas flowmeter, a liquid gas washing bottle, determination pipes and a sucking pump. A parasitic wasp access port to be measured is formed in the right side of the bottom of a measuring tube body, and a volatile matter access port related to parasitic wasp host positioning is formed in the left side. There are four determination pipes which can be used for observingfour parasitic wasps at the same time. The determination pipes are placed on the pipe rack, and the isolation baffles are arranged among the determination pipes so that learning behaviors between theparasitic wasps can be effectively avoided. A long glass tube is used as a main measuring instrument, a general device for measuring the olfactory response of insects is mainly used for measuring theselectivity of insects to different substances, and the change of parasitic wasps to the host positioning time under the influence of insecticides is emphatically measured.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Indoor propagation method for steep cocoon manilensis
The invention relates to an indoor propagation method of steep cocoon manilensis. The indoor propagation method comprises the following steps: firstly, indoor breeding is conducted on pupae of the steep cocoon manilensis to obtain first-generation breeding bees, then the first-generation breeding bees are inoculated into an insect breeding cage, and then a turnover box inoculated with host beet armyworm larvae is put into the insect breeding cage to perform co-breeding of parasitic bees and hosts; after a period of time, the turnover box is taken out and placed in a new insect breeding cage, the original insect breeding cage is replaced with a new host for continuous parasitism, and the steps are repeated until all female parasitic wasps die; and parasitic wasp cocoons which are cocooned and developed to the pupal stage after parasitism are collected, and the parasitic wasp cocoons are cultured to eclosion to serve as breeding wasps to be used for breeding next-generation parasitic wasps. According to the method, beet armyworm larvae serve as the hosts, the steep cocoon manilensis can parasitize and generate a large number of offspring and can be stored in a pupa form at low temperature and normal temperature, indoor large-scale breeding of the steep cocoon manilensis is achieved, an insect source is provided for field release application of the steep cocoon manilensis, and technical support is provided for biological control of noctuid pests.
Owner:HUBEI BIOPESTICIDE ENG RES CENT
Artificial propagation method and application of psylla chinensis parasitic wasps
InactiveCN110959581AAvoid pesticide residuesSimple and fast operationCultivating equipmentsAnimal husbandryNymphMating
The invention provides an artificial propagation method and application of psylla chinensis parasitic wasps, and the method comprises the following steps: collecting psylla chinensis nymphs which havebeen spawned and parasitized by psylla chinensis parasitic wasps in a pear orchard together with pear leaves, artificially culturing the psylla chinensis nymphs until the psylla chinensis nymphs emergence; mixing newly emerged male and female adult psylla chinensis parasitic wasps, inoculating the mixture into an insect breeding cage containing pear seedlings with fourth-instar psylla chinensis nymphs and fifth-instar psylla chinensis nymphs, feeding with honey water, mating to lay eggs, taking out the pear seedlings after 3 days, transferring to another insect breeding room, continuously breeding, and observing the development state of psylla chinensis nymphs day by day; picking a single psylla chinensis nymph which has been spawned and parasitized by parasitic wasps into a centrifuge tube, artificially culturing, after eclosion of the psylla chinensis nymph, mixing newly eclosion psylla chinensis male and female adults, inoculating into a new insect breeding cage with pear seedlingsof fourth-instar and fifth-instar psylla chinensis nymph, feeding with honey water, mating and spawning. Reciprocating as such, the continuous and stable number of psylla chinensis parasitic wasps are obtained.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for preventing and controlling hyphantria cunea by using trichomalopsis genalis
ActiveCN113317282AGuaranteed source of supplyImprove labor productivityInvasive species monitoringAnimal husbandryAnimal scienceZoology
The invention relates to a method for preventing and controlling hyphantria cunea by using trichomalopsis genalis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) feeding trichomalopsis genalis adults; (2) cultivating tenebrio molitor pupae: transferring tenebrio molitor larvae into an insect breeding box with vent holes, carrying out gradient cooling treatment, and storing the treated tenebrio molitor pupae in a constant temperature box at 4 DEG C in a dark place to obtain the tenebrio molitor pupae for bee inoculation; (3) bee inoculation: heating the tenebrio molitor pupae obtained in step (2) in a reverse manner for bee inoculation, wherein a ratio of the tenebrio molitor pupae to the trichomalopsis genalis female adult is 1:3; (4) managing development of parasitic wasps; and (5) releasing parasitic wasps. In the method, the replacement host tenebrio molitor pupae are adopted to breed the trichomalopsis genalis indoors on a large scale, problems that a success rate of noculation of the replacement host bee is low and the number of bred bees is unstable are solved, meanwhile, a variety of dominant parasitic wasps for preventing and controlling hyphantria cunea is enriched, and a new means and a new method are added for biological prevention and control of the hyphantria cunea.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com