Artificial propagation method for parasitic wasps of bactrocera tau larvae
A technology for artificial reproduction and parasitic wasps, applied in the direction of animal husbandry, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the emergence rate and vitality of parasitic wasps, affecting the parasitic wasp parasitic pupae, and reducing the number of passing through gauze, etc., and achieves easy large-scale breeding, low cost, artificial less distracting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
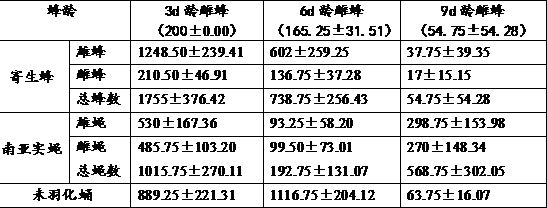
[0074] Example 1: 3d larvae parasitized by parasitic wasps of the larvae of Bactrocera cerevisiae
[0075] 1. Breeding of Bactrocera japonica adults
[0076] Weigh 100-120 g of pupae in a plastic box and put them into insect cage C. Provide 300-400 g of adult food for Bactrocera subtilis after eclosion, place a water-containing nano-sponge on the top of the cage, add water every 2 days, and cultivate at a temperature of 25±2°C. The relative humidity is (65±5)%, and the photoperiod is L:D=12:12.
[0077] 2. When the Bactrocera japonica egg-collecting insect cage C is expanded and raised to the egg-laying high bee stage, the glass culture dish (diameter φ9.0cm) is filled with artificial feed A and placed in the breeding cage to collect eggs 1 ~2h, 4~5 dishes / cage.
[0078] 3. Bactrocera larvae rearing
[0079] Add 300-500g of artificial feed C to the bottom of a 2L black rectangular plastic box, pour the eggs and feed of Bactrocera subtilis in the above-mentioned culture dish...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Embodiment 2, the parasitoid 4d larva of the parasitoid wasp of the larva of Bactrocera cerevisiae
[0094] 1. The parasitic effect of 5 parasitic wasps on the 4d larvae of Bactrocera spp.
[0095] (1) Breeding, egg collection and larval rearing of Bactrocera spp.
[0096] The larvae of Bactrocera cerevisiae were reared according to the steps 1 to 3 in Example 1, except that the larvae were reared to the 4d age.
[0097] (2), 4d South Asian fruit fly larva parasitism
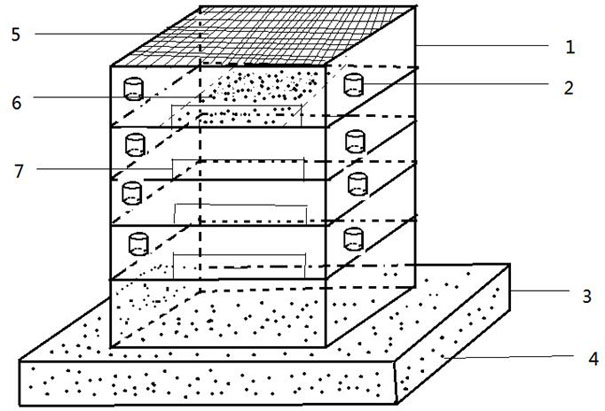
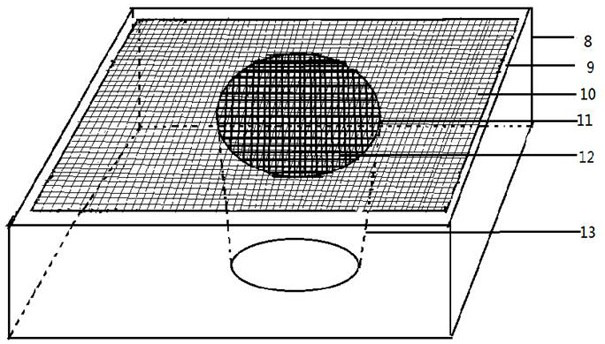
[0098] Take each 5 female and male parasitoids of eclosion in the insect cage E (the specification of the insect cage E is length * width * height is 15 * 15 * 15cm, the front of the described insect cage E is a transparent plastic film, and the back is a tube with a sleeve. white gauze, the bottom is white opaque plastic, and the rest are gauze), in the cage, use 75mL black plastic box with 10% honey water, drill a hole in the center of the box cover, cotton, until the age of female parasitoid bees to ...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Embodiment 3, indoor large-scale breeding of the parasitic wasps of the larvae of Bactrocera cerevisiae
[0114] 1. Breeding of Bactrocera japonica adults
[0115] The eclosion of Bactrocera subtilis was placed in pitcher cage A, the culture temperature was 25±2°C, the relative humidity was 65±5, the photoperiod was L:D=12:12, and adult feed and water were provided.
[0116] 2. South Asian fruit fly multiplication and large cage domestication
[0117] When raising Bactrocera subtilis to the oviposition period, fill a glass petri dish (diameter φ9.0cm) with artificial feed A, place it in insect cage A to collect eggs for 8-10 hours, take out the petri dish, and place the egg-containing feed in a Put the plastic plate on the larva culture frame in the plastic plate with artificial feed C, the culture temperature is 25±2°C, the relative humidity is 65±5, the photoperiod is L:D=12:12; Fine sand with a water content of 2-4% is used to collect larvae for pupation. The fine ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com