Artificial breeding method for dominant parasitic wasps of mulberry borers
A technology for parasitic wasps and mulberry borers, which is applied in the field of biological control of agricultural pests, can solve the problems of increased drug resistance of mulberry borers, no artificial breeding method for mixed chamber wasps, and no drugs available, and achieves simple production and low cost. , the effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] The artificial breeding of embodiment 1 mixed chamber braconid
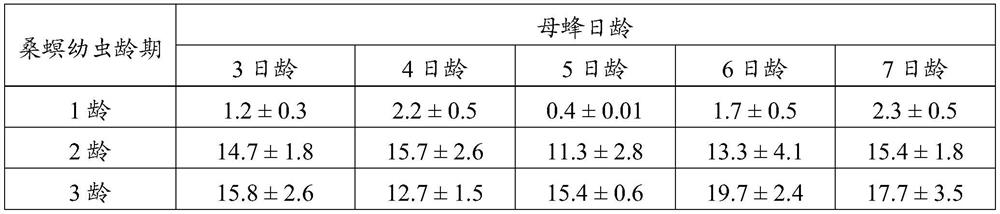
[0019] The mulberry borer is used as the host indoors, and the mixed-chamber braconid is artificially bred. The ages of the mulberry borer used are 1, 2 and 3 ages, and the parasitic female bees are 3-day-old, 4-day-old, 5-day-old, 6-day-old and 7-day-old mixed-chamber female wasps. Use a round transparent plastic box as the parasitic box. There is a small hole with a diameter of 1.5cm on the side of the parasitic box, which is convenient for introducing parasitic wasps. After the parasitic wasps are introduced, plug them into this hole with a cotton plug. Before the parasitic start, insert 20 mulberry borer larvae into the parasitic box, and half an hour later, insert the parasitic wasp mother bee. The parasitism ends after 24h. The mulberry borer larvae and female bees were recovered separately. Mulberry borer larvae were reared individually in small plastic boxes and fed with fresh mulberry leaves ev...
Embodiment 2
[0022] The artificial breeding of embodiment 2 mixed chamber braconids
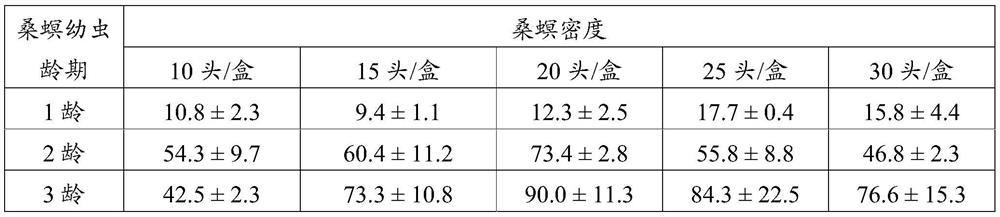
[0023] The mulberry borer is used as the host indoors, and the mixed-chamber braconid is artificially bred. The ages of the mulberry borer used are 1 age, 2 ages and 3 ages, and the parasitic female bee is the age of 6 days of mating, and the used round transparent plastic box of the parasitic place is the same as in Example 1. The density of mulberry borer larvae in each parasitic box was 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 when parasitic was set. Before the start of parasitism, the 3rd instar mulberry borer larvae were inserted into the parasitic box according to different densities, and half an hour later, a single parasitoid mother wasp was inserted. The parasitism ends after 24h. The mulberry borer larvae and female bees were recovered separately. Mulberry borer larvae were reared individually in small plastic boxes and fed with fresh mulberry leaves every day. After the cocoons of the parasitic wasps are form...
Embodiment 3
[0026] The artificial breeding of embodiment 3 mixed chamber braconids
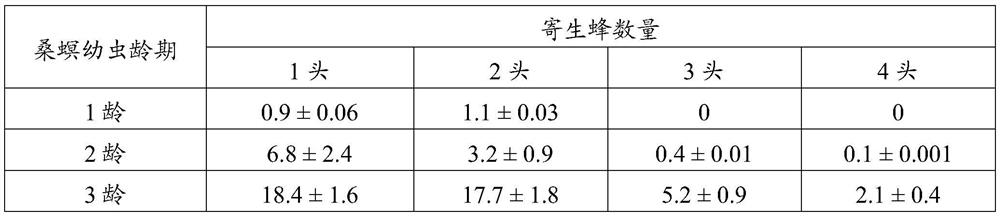
[0027] The mulberry borer is used as the host indoors, and the mixed-chamber braconid is artificially bred. The ages of the mulberry borer used are 1 age, 2 ages and 3 ages, and the host density is 20 heads / box, and the female honeybee that parasitizes is the age of 6 days of mating, and the circular transparent plastic box used in the parasitic place is the same as embodiment 1. When setting up parasitism, the number of parasitoid bees placed in each parasitic box was 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively. Before the parasitism begins, the mulberry borer larvae are first connected to the parasitic box, and half an hour later, the parasitic wasp mother wasp is connected. The parasitism ends after 24h. The mulberry borer larvae and female bees were recovered separately. Mulberry borer larvae were reared individually in small plastic boxes and fed with fresh mulberry leaves every day. After the cocoons of the par...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com