Large-scale production method of diaphorina aliensis
A technology of lice jumping wasps and production methods, which is applied in the direction of animal husbandry, etc., can solve the problems of no public reports of artificial propagation and release, no biological experiment reports, etc. The effect of high activity and uniform age of nymphs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
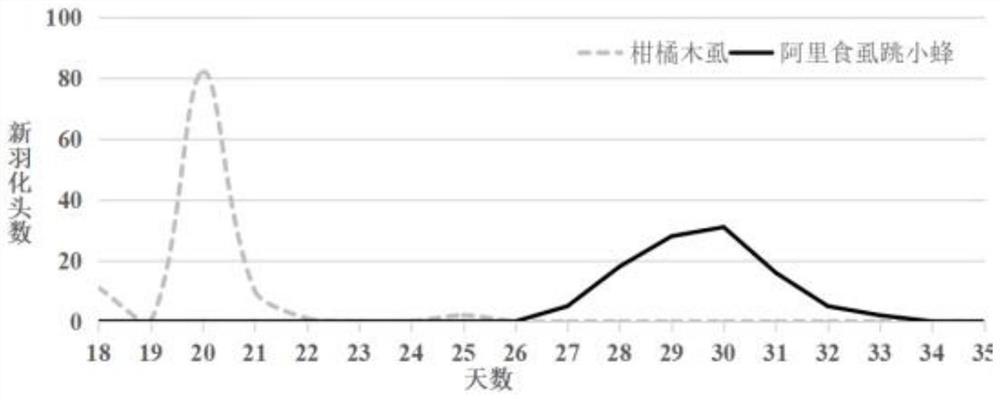
[0056] In this embodiment, 1 breeding cage is set, and 1 Siji tangerine plant is placed in the cage. The pot and soil are brought when purchased and have not been replaced. Trim a branch growing from the base of the stem to one leaf and one bud, and cut off all the leaves of the other branches, leaving about 50 buds in total. The final plant is about 30cm wide and 85cm high.
[0057] When the shoot length is about 3 cm, insert 100 citrus psyllids, 50 male and 50 male. After 72 hours (3 days) the citrus psyllids are removed leaving only freshly laid eggs on the plants. The date of inoculation of citrus psyllids was recorded as the first day, and the development of citrus psyllid nymphs on the shoots was observed every day from the seventh day.
[0058] On the 12th day, the citrus psyllid nymphs had entered the third instar, and the instars were relatively consistent. According to estimates, the number of nymphs is about 150. According to female bees: citrus psyllid nymphs = ...
Embodiment 2
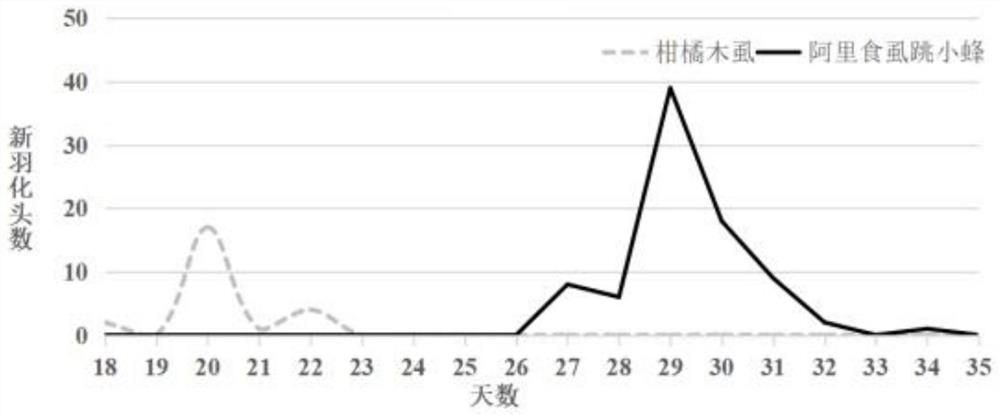
[0063] In this embodiment, 1 breeding cage is set, and 1 Siji tangerine plant is placed in the cage. The pot and soil are brought when purchased and have not been replaced. The whole plant is trimmed to one leaf and one bud, leaving about 50 buds, and the final plant is about 30cm wide and 85cm high.
[0064] When the shoot length is about 3 cm, insert 100 citrus psyllids, 50 male and 50 male. After 72 hours (3 days) the citrus psyllids are removed leaving only freshly laid eggs on the plants. The date of inoculation of citrus psyllids was recorded as the first day, and the development of citrus psyllid nymphs on the shoots was observed every day from the seventh day.
[0065] On the 11th day, most of the citrus psyllid nymphs have entered the second instar, and at this time, Ali-eating psyllid nymphs were inoculated. There are about 120 citrus psyllid nymphs, according to female bees: citrus psyllid nymphs = 1:30 (quantity ratio), 4 female psyllid bees were connected to Ali...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com